Ap psychology unit 4
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Learning
a relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience
Ecological Perspective on learning
Focuses on how learning is influenced by the environment and interactions with it.
Stimulus
any event or situation that evokes a response
response
a reaction to a stimulus
Reflex
a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus
Ivan Pavlov
discovered classical conditioning; trained dogs to salivate at the ringing of a bell
unconditioned stimulus (US)
A stimulus that naturally triggers a response
unconditioned response (UR)
A natural reaction to the unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
A once-neutral stimulus that now triggers a response after being paired with the US.
Conditioned Response (CR)
A learned reaction to the conditioned stimulus.
Nuetral Stimulus
a stimulus that elicits no response before conditioning
acquisition
The process of learning the association between two stimuli.
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
Extinction
When the conditioned response fades because the CS is no longer paired with the US.
Spontaneous recovery
the reappearance, after a pause, of an extinguished conditioned response
Generalization
responding similarly to a range of similar stimuli
Discrimination
Learning to respond differently to similar but distinct stimuli.
second-order conditioning
When a new neutral stimulus becomes conditioned by being paired with an already conditioned stimulus.
stimulus discrimination
a differentiation between two similar stimuli when only one of them is consistently associated with the unconditioned stimulus
Stimulus generalization
When a conditioned response happens to stimuli similar to the original conditioned stimulus.
John Watson and Little Albert
Demonstrated that fear can be conditioned in humans (Albert learned to fear a white rat).
Tolerance and drug addiction
The body learns to expect drugs in certain settings, causing tolerance and withdrawal effects.
Food/taste aversion
Classically conditioned avoidance of a food or taste, usually occurs after only one pairing
John Garcia
Researched taste aversion. Showed that when rats ate a novel substance before being nauseated by a drug or radiation, they developed a conditioned taste aversion for the substance.
One-trial conditioning
Learning with only one pairing of stimulus and response.
counter conditioning
Replacing a negative response with a positive one (e.g., pairing a feared object with relaxation).
Edward Thorndike
Pioneer in operant conditioning who discovered concepts in intstrumental learning such as the law of effect. Known for his work with cats in puzzle boxes.
law of effect
Thorndike's principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and that behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely
B.F. Skinner
Behaviorist who developed the theory of operant conditioning by training pigeons and rats using reinforcement and punishment
Reinforcer
Anything that increases the likelihood of a behavior.
punishment
Anything that decreases the likelihood of a behavior.
positive reinforcement
Adding something good to increase behavior (e.g., giving candy).
negative reinforcement
Removing something bad to increase behavior (e.g., stopping a loud noise).
positive punishment
Adding something unpleasant to decrease behavior (e.g., scolding).
negative punishment
Taking away something good to decrease behavior (e.g., losing privileges).
Discriminative stimulus
A cue that signals when a certain response will be reinforced.
Secondary reinforcers
Learned rewards (e.g., money, grades) that get value from primary reinforcers.
Habituation
Getting used to a stimulus so you no longer react to it.
Blocking Effect
When a previously learned cue prevents learning a new cue.
hefferline experiment
One group was told that they had to make a certain movement to make a static noise stop while listening to music, and another group was told nothing. Both groups involuntarily made the thumb twitch needed to stop the static because they had been operantly conditioned unknowingly
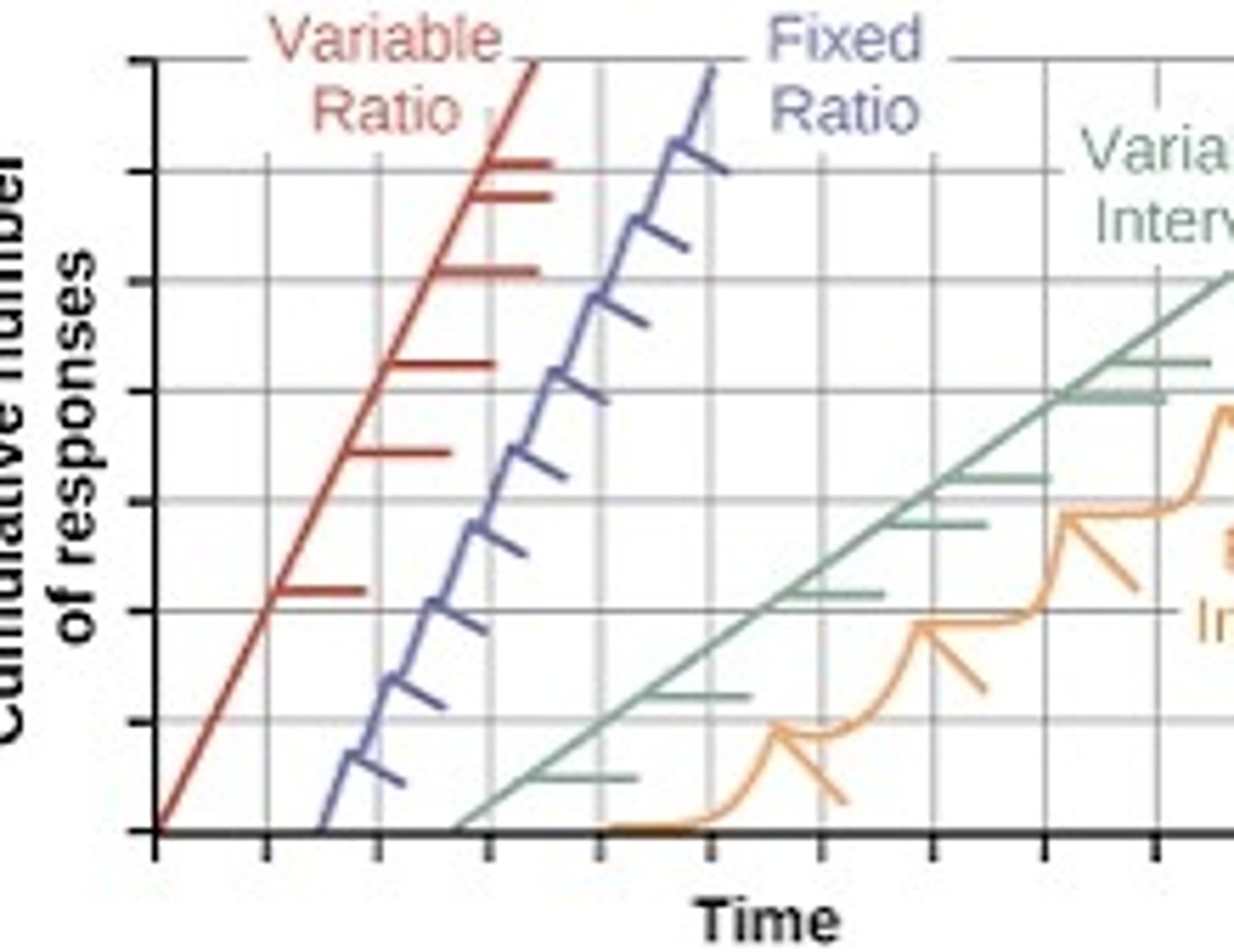
Schedules of reinforcement
Rules about how and when behaviors are reinforced.
fixed ratio
Reinforcement after a set number of predictable responses. (5th time)
variable ratio
Reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses (slot machine)
fixed interval
reinforces a predicted response only after a specified time has elapsed (every 10 min)
variable interval
reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals (pop quizzes)
Scalloped graph
A pattern seen in fixed-interval schedules where responses increase as the reward time approaches.
S-S theory
Learning is about forming a mental link between two stimuli.
S-R theory
Learning is about forming a direct link between a stimulus and a response.
Difference in S-S and S-R theory
S-R theory posits that a stimulus directly causes a response, whereas S-S theory suggests that the first stimulus leads to a mental representation of the second stimulus
Expectancy Theory
The theory that motivation will be high when workers believe that high levels of effort lead to high performance and high performance leads to the attainment of desired outcomes.
Reward Contrast effects
A sudden shift in the attractiveness of a reward
Negative Contrast Effects
When a smaller reward than expected decreases motivation.
Positive contrast effect
When a bigger reward than expected increases motivation.
Means-end knowledge
Understanding that one action leads to a specific outcome.
Tolman's cognitive maps
Mental representations of physical spaces, showing learning without reinforcement (latent learning).
David Bandura
Psychologist who studied learning through observation. (bobo doll)
observational learning
learning by observing others
Modeling
the process of observing and imitating a specific behavior
Bobo Doll Experiment
Bandura's study showing children imitate aggressive behavior they observe.
Social Learning Theory
the theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished
vicarious conditioning
Learning by seeing others being rewarded or punished.
Delayed Gratification
Resisting an immediate reward for a better one later.
Overjustification Effect
The effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now see the reward, rather than intrinsic interest, as the motivation for performing the task.
Latent Learning
learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it - not obvious signs until after
insight learning
Sudden realization of a solution ("aha!" moment).
Priming Effect
exposure to a stimulus influences a response to a later stimulus
mirror neurons
Brain cells that fire when you do or observe an action.
Behaviorism
the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes. Most research psychologists today agree with (1) but not with (2).
Shaping
Gradually training a behavior by reinforcing closer and closer approximations to the desired action.
Chaining
Teaching a complex behavior by linking smaller learned behaviors together in sequence
Instinctive Drift
When learned behavior slowly returns to natural instincts, even after conditioning.
Learned Helplessness
When someone stops trying to escape or improve a bad situation because past efforts failed.