operant conditioning
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is operant conditioning?
Involves associating stimuli with responses (behaviours) which are in turn influenced by consequences
who was burrhus frederic skinner?
a psychologist that believed organism would repeat behaviours with desirable consequences and not repeat behaviours with undesirable consequences.
what is phase 1: antecedent
a stimuli that occurs before a behaviour is initiated
what is phase 2: behaviour
the action you voluntarily complete after the presence of the antecedent stimulus
what is phase 3: consequences
the environmental event that follows behaviour also affecting he occurrence of the behaviour.
the behaviour is followed by a reward or a punishment.
example of operant conditioning process
antecedent - the word male on a bathroom door - behaviour - enter if your a male - consequence - release your full bladder - positive reinforcement - will continue to go bathroom when bladder is full.
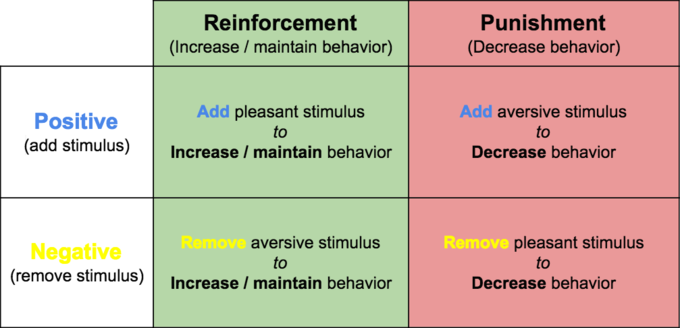
what is positive reinforcement?
a stimulus that increases the likelihood of the behaviour being recreated for the satisfying consequence.
what is negative reinforcement?
the removal of a aversive stimulus that when removed increases the likelihood of the behaviour being recreated for the satisfying consequence.
example of positive reinforcement
help your brother you get money from parents more likely to do it again
example of negative reinforcement
feel sick take a panadol removes headache more likely to take a panadol in the future
positive
adding something pleasant
negative
removing something unpleasant
what is reinforcement?
to occur when a stimulus strengthen or increase the frequency of likelihood of a response that it follows.
what is punishment?
the delivery of an unpleasant consequence following a response, or removal of a pleasant consequence following a respons
what is negative punishment?
involves the removal of a stimulus so that the behaviour will not be completed again.
example of negative punishment?
never being able to play sports with your friends again because you were late to class
what is positive punishment?
involves the presentation of a stimulus that decreases the likelihood that the behaviour will be repeated.
example of positive punishment?
having to run extra laps in gym class for being late
reinforcement….
increases the likelihood of a behaviour reoccurring
punishment…
decreases the likelihood of a behaviour reoccurring
what are some factors that influence the effectiveness of reinforcement and punishment?
- timing must be given immediately after response
- appropriateness
reinforcer = pleasing
punishment = unpleasing
what is stimulus generalisation?
the correct response can be made even if the stimulus isn't exactly the same
what is stimulus discrimination?
the correct response will only be made to ONE stimulus.
what is extinction?
the gradual decrease of the learned response
what is spontaneous recovery?
shows response again after extinction has occurred.