Cardiopulmonary Rehab Vitals Skill Test
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
MI
Blockage of coronary artery(s) leading to ischemia/necrosis of heart muscle. Chest pain (fullness, tightness, pressure, squeezing), SOB, and possibly radiating pain to the arms, neck, or jaw.
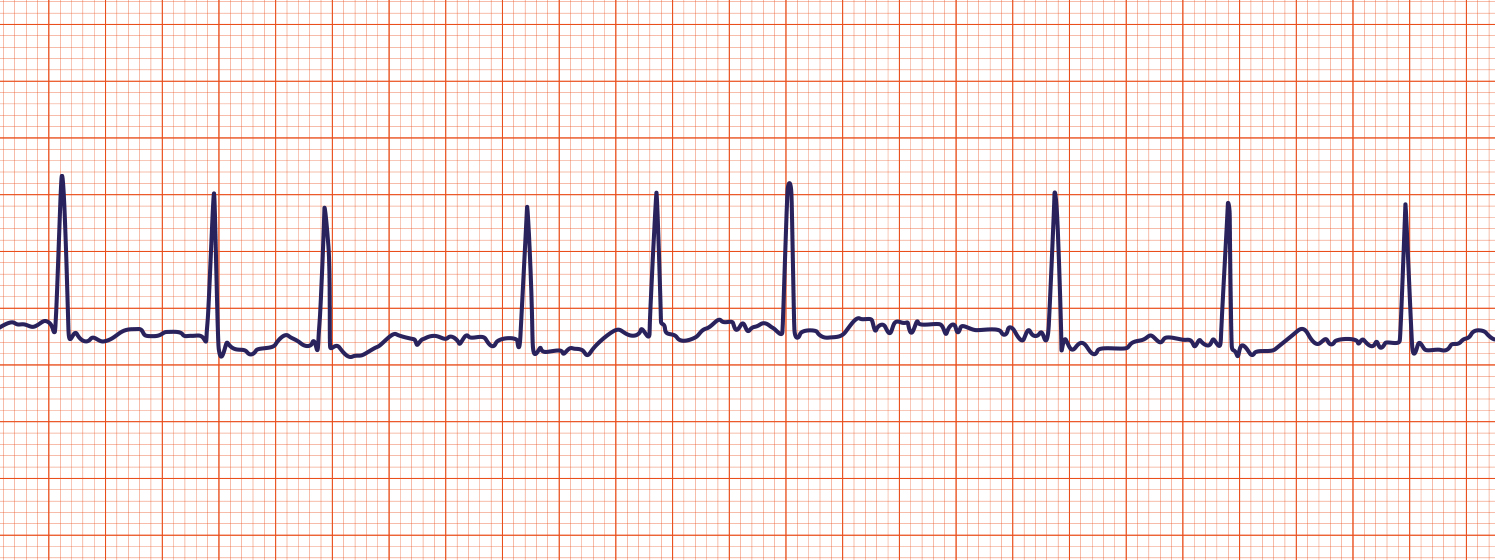
Atrial Fibrillation
Chaotic electrical impulses in atria; fast irregular rhythm (100-175+ bpm). Little or absent p-wave and normal QRS.
Left-sided Heart Failure
Left ventricle can’t pump effectively. Blood backs up into left atrium into the pulmonary veins and lungs. Pulmonary effects.
Right-sided Heart Failure
Right ventricle fails to pump blood effectively, causing fluid to back up into the right atrium and the body's veins, leading to symptoms such as edema and ascites.
HTN
May experience headache, vision problems, chest pain, nosebleed, and fatigue or confusion that may lead to serious health complications if untreated.
High blood pressure, stage 1: 130-139 or 80-89
High blood pressure, stage 2: 140 or higher or 90 or higher
Hypertensive crisis: higher than 180 and/or higher than 120
CAD
Coronary artery diseaseis the narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries due to plaque buildup, leading to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Angina and SOB are common symptoms.
CHF
Congestive heart failure; caused by chronic HTN, CAD/MI, diabetes, chronic alcohol use, chemotherapy, lung disease, and family history/genetics.
CABG
Coronary artery bypass grafting, a surgical procedure to improve blood flow to the heart by bypassing blocked coronary arteries. Requires sternotomy (think of sternal precautions).
PAD
Caused primarily by atherosclerosis of the peripheral arteries, particularly in LE. Pain in calf and/or thigh during exercise is a hallmark symptom, known as claudication.
Lopressor
Beta blocker; blocks the effects of epinephrine on beta receptors. Causes the heart to beat more slowly and with less force, reducing blood pressure and heart workload.
Can prevent HR/BP from increasing in response to exercise
Zocor, Crestor and Lipitor
Statins; reduce cholesterol levels in the blood by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme involved in cholesterol production.
Coumadin and Warfarin
Anticoagulants; blocks fibrin formation to prevent clots. Used for DVT and PE treatment.
Digoxin
Increases calcium uptake to improve heart contractions. Used often with CHF.
Lisinopril
ACE inhibitor; blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Lowers blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels. It is commonly prescribed for hypertension and heart failure.
Lasix
Diuretic; increases excretion of sodium and urine to reduce plasma volume and blood pressure. Used to treat HTN and edema associated with heart failure.
Aspirin and Clopidogrel
Antiplatelet; used to prevent platelets from sticking together to form clots in arteries to prevent MI and CVA.
Procardia
Calcium channel blocker; reduced calcium entering the myocardial cells and arteries. Decreases HR and BP by relaxing blood vessels. Used for arrythmias, HTN, angina, and CHF.
Can prevent HR/BP from increasing in response to exercise.