All definitions for OCR a A-level chemistry
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Atomic number
Number of protons or electrons in an element
Mass number
Number of protons plus neutrons
Isotopes
Atoms of the same elements that have different number of neutrons
Relative atomic mass
The average mass of an atom of an element relative to 1/12 of the mass of a carbon 12 atom
M/Z
Mass charge ratio
Acid
Releases H+ ions in solution
Alkali
Releases OH- ions into solution
Strong acid/alkali
Fully dissociated in solution
Weak acid/alkalife
Partially dissociated in solution
Neutralisation
Reaction of H+ and OH- ions to form H²O
Standard solution
A solution of accurate concentration
Oxidising agent
Electron acceptor
Reducing agent
Electron donor
Orbital
A region that can hold two electrons of opposite spins
Covalent bond
Electrostatic attraction that occurs due to the sharing of two electrons between two non-metal atoms
Ionic bond
Electrostatic attraction that occurs due to the electron transfer from a metal to a nonmetal forming positive and negative ions
Metallic bonds
Electric static attraction that occurs when a positive metal iron is surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a covalent bond
Ionisation energy
The energy required to remove one mole of electrons from gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous ions
Disproportionation
Simultaneous oxidation and reduction of a species
Activation energy
Minimum energy required for a reaction to occur
Enthalpy of combustion
And we change when one mole of a substance is completely burned in excess oxygen
Enthalpy of formation
Enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions
Enthalpy of neutralisation
Enthalpy change when one mole of water is formed in an acid-base neutralisation reaction
Standard conditions
100kPa & 298K & 1 moldm³ H+ ions
Standard states
Physical states understandard conditions
Equilibrium
The rate of the Fords and backwards reactions are equal and the concentrations of reactants and products are constant
Homologous series
Family of compounds with the same general formula, the same empirical formula, similar reactivity, and shows a trend in physical properties
Functional group
The reactive part of the molecule
Alkyl group
CnH2n+1
Aliphatic
A compound containing carbon and hydrogen in straight chains, branched compounds, or cyclic compounds (but not aromatic)
Alicyclic
A cyclic aliphatic compound (not aromatic)
Aromatic
A compound containing benzene
Saturated
Contains single C-C bonds only
Unsaturated
Contains double or triple bonds
Structural isomers
Two molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
Homolytic fission
Splitting of a bond to form two radicals, each gets one electron
Heterolytic fission
Splitting of a bond to form two opposently charged ions, one gets both electrons
Sigma Bond
Overlap of two s-orbitals
Pi Bond
Overlap of two p-orbitals
Stereoisomers/geometric isomers
Same molecular formula but different spatial arrangement
Nucleophile
Electron pair donor
Electrophile
Electron pear exceptor
Radical
The species with an unpaired or lone electron
pH
=-log10^H+
Kw
=[H+][OH-]
Buffer solution
A solution that minimizes changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added
Enthalpy of atomisation
Enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed from an element in its standard state
Electron affinity
Enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous ions is formed from one mole of gaseous atoms
Lattice enthalpy
The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of an ionic solid is formed from its gaseous ions
Enthalpy of solution
The anthropy change that occurs when one mole of an ionic compound dissolves in water
Enthalpy of hydration
The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of gaseous ions forms aqueous/hydrated ions
Entropy
The measure of dispersal of energy in a system
Transition metal
A metal that can form one or more ions that have partially filled d-orbitals
Ligand
A molecule that has at least one lone pair of electrons
Complex ion
A central metal ion surrounded by ligands
Coordination number
How many bonds there are to the metal ion
Monodentate ligand
A ligand with only one lone pair of electrons
Bidentate ligand
A legend with only two lone pair of electrons
Multi or polydentate ligand
A legend with more than two lone pair of electrons
Chiral center
A carbon atom surrounded by four different groups
Optical isomer
Two non superimposable mirror images
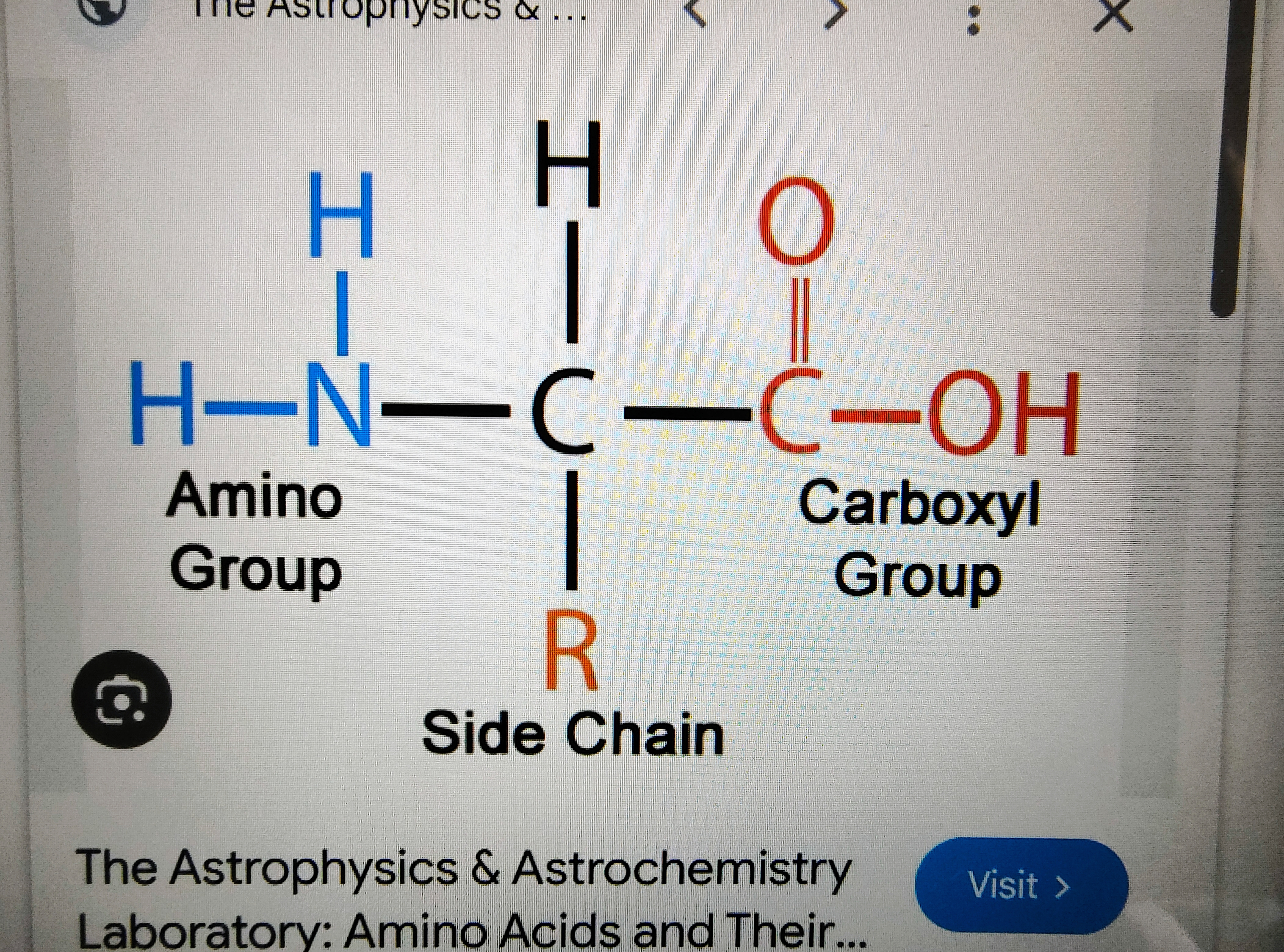
A-Amino acid
The NH² and the COOH are attached to the same carbon
Condensation polymerisation
Where by a polymer is produced by repeated condensation reactions between monomers with the removal of a small molecule usually water or HCl
Hydrolysis
The breaking of a bond usually by adding water
TLC
Thin layer chromatography
GC
Gas chromatography
Retention time (chromatography)
How long it takes for a compound to come off the column or to be detected
What does TMS do
TMS also known as tetramethylsilane act as a reference standard in NMR= sharp peak at 0