5.6 Production planning
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Supply chain management
The management of the sequence of activities from the production of a good or service, to it being delivered.
What are the key functions of scm
-Stock control
-Quality control
-Supplier networks
-Transportation
What are advantages of SCM?
-it helps to achieve lean production
-Prevents mistakes from occuring
-Manages stock to prevent delays or high costs, increasing efficiency
What are drawbacks of SCM?
-Time/language/cultural differences can cause delays
-interdependance can cause major disruptions
What is Just-in-case?
It is maintaining large amounts of stock in case of supply or demand fluctuations (the opposite of Just-in-time). It is reserve stock for emergencies.
What are advantages of Just-in-case?
-Increased flexibility
-businesses can meet sudden changes in demand
-no need to wait for delivery of stock (it is time saving)
-Purchasing economies of scale - discounts when buying in bulk
What are disadvantages of Just-in-case?
-higher costs of storage (insurance, room costs)
-the business has more materials than they need, so many go to waste
-there are changing tastes and fashions
-food products may expire
What is stockpiling?
Holding excess stock, more than the business needs (Just-in-case)
What are stock-outs?
When a firm ran out of stock, so the product is unavailable for purchase
What are disadvantages of stockpiling?
-high storage costs
-if food is being stored, it may go bad
-there are changing fashions and tastes
What are disadvantages of stock-outs?
-lost sales and customers due to rivals (if someone goes to the store and what they’re looking for isn’t there, they go to another store)
-damaged corporate imagery
-decreased customer loyalty
What is a stock control chart?
It is a chart which graphically illustrates a simplistic system of stock control
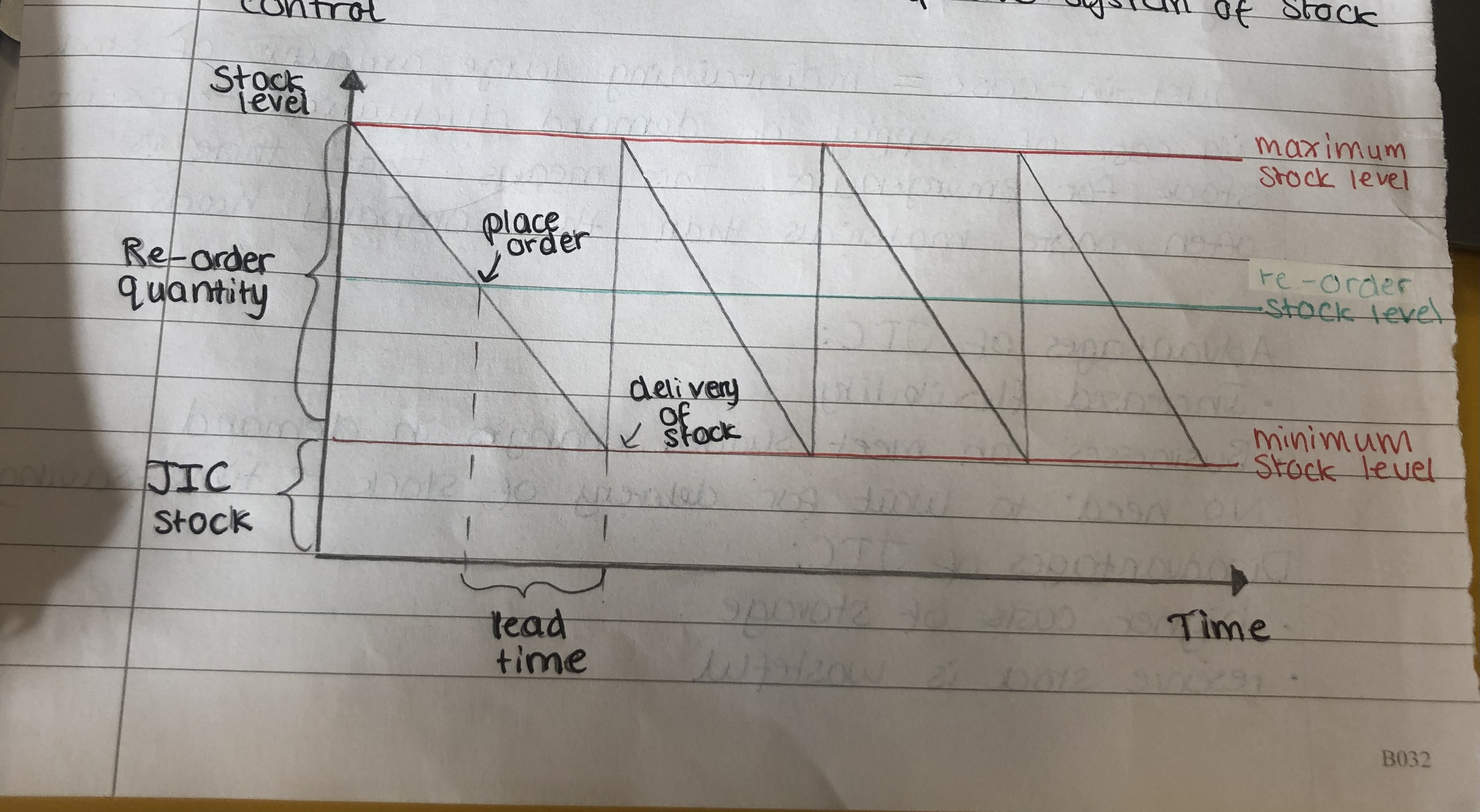
What factors influence the amount of stock held
-Short lead times → if the stock gets delivered quickly, the amount of stock held is lower
-Long lead times → if the stock takes long to be delivered, the amount of stock held is higher, to ensure that they will never run out
What is capacity utilization?
It measures the firm’s output level as a percentage of its potential output → how efficient they are being

How do you calculate capacity utilization rate?
(current output/productive capacity) x 100
What are defects?
Defects occur when the quality of a particular product is unacceptable
How do you calculate defect rate?
(defective output/total output) x 100
How do you calculate labour productivity?
(total output/number of workers) x 100
How do you calculate capital productivity?
(total output/number of capital hours) x 100
How do you calculate productivity rate?
(total output/ total input) x 100
The input can be number of capital hours, number of workers, amount of money invested etc.
What are some factors that determine productivity rate?
skills and experience of labour
technology → efficiency of machinery
the amount of competition
working conditions of labour
What is cost to buy?
How much a business would have to pay if they ordered products/materials for their own use
How do you calculate cost to buy?
price x quanitity
What is cost to make?
How much a business would have to pay if they were to make their own products/resources
How do you calculate cost to make?
fixed costs + (variable costs x quantity)
What are factors that play a role in make or buy decisions?
speed of delivery
time taken for production
costs
reliability of suppliers
skills and knowledge