Circulatory System+ Blood
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:05 PM on 12/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
1
New cards
Blood is a…
tissue, since cells are working together to carry out a function
2
New cards
What are 5 functions of blood?
1. Transports heat
2. Fights infections
3. Transports gases, enzymes, hormones and nutrients
4. Acts as a solvent
5. Blood clotting
3
New cards
What 4 parts does blood consist of?
1. Plasma
2. Red Blood Cells
3. White Blood Cells
4. Platelets
4
New cards
List 3 primary functions of plasma
1. Transports substances around the body (ex. red blood cells, CO2, proteins etc.)
2. Transports heat around the body
3. Is an excellent solvent, as it is 90% water
5
New cards
Where are red blood cells produced?
Red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow
6
New cards
What do red blood cells transport?
Transport oxygen around the body
7
New cards
Do red blood cells have a nucleus or mitochondria?
No
8
New cards
Can red blood cells repair themselves?
No, they cannot repair themselves but haemoglobin is recycled by the liver
9
New cards
List 3 ways in which red blood cells are adapted to transport oxygen:
1. Flexible Cells (don’t damage easily)
2. Biconcave (maximum surface area, 2 concaves)
3. Contains haemoglobin (a protein containing an iron pigment that has an affinity to oxygen)
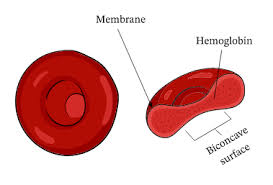
10
New cards
Where are platelets produced?
In the bone marrow
11
New cards
What is the function of platelets?
Clotting blood
12
New cards
What are the two purposes of blood clotting?
1. Preventing blood loss
2. To prevent the entry of pathogenic microorganisms
13
New cards
Haemophiliacs suffer from a….
platelet deficiency and cannot clot blood.
14
New cards
What are the two types of white blood cells?
1. Monocytes
2. Lymphocytes
15
New cards
Define monocytes
white blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens
16
New cards
Define lymphocytes
white blood cells that produce antibodies
17
New cards
Distinguish between monocytes and lymphocytes
They are both WBC
\-monocytes __engulf and destroy pathogens__, while lymphocytes __produce antibodies__
\-monocytes __engulf and destroy pathogens__, while lymphocytes __produce antibodies__
18
New cards
Define the Rhesus Factor
* a chemical found on red blood cells
* If you have the rhesus factor, your blood is positive Rh+
* If you don’t have, it your blood is negative Rh-
* ex. A+ and A-
* If you have the rhesus factor, your blood is positive Rh+
* If you don’t have, it your blood is negative Rh-
* ex. A+ and A-
19
New cards
Does a person with B- blood have the rhesus factor?
No
20
New cards
Does a person with A+ blood have the rhesus factor?
Yes
21
New cards
Blood mixing
Blood is very specific, therefore A+ cannot accept AB or A-
22
New cards
Which blood type is universal and can transfuse to any group?
O-
23
New cards
Which organ prevents the blood from a pregnant mother and baby from mixing?
The placenta, formed by the mother prevents mixing
24
New cards
What are the two types of blood systems?
1. Open Circulatory System
2. Closed Circulatory System
* They both consist of veins, arteries, heart(s), capillaries etc.
25
New cards
Describe the Open Circulatory System
* Blood flows from the heart to all the cells of the body, with the blood not always being in vessels the entire time.
* The flow comes from: body movement, pumping organ
* Ex. Insects and crabs
\
* The flow comes from: body movement, pumping organ
* Ex. Insects and crabs
\
26
New cards
Describe the Closed Circulatory System
* Blood remains within blood vessels at all times
* Materials pass in and out of blood to and from cells
* Animals have a closed system
* Materials pass in and out of blood to and from cells
* Animals have a closed system
27
New cards
Which circulatory system is more effective? open or closed
The closed circulatory system is more effective
* Allows blood to be pumped around the body __faster__
* Blood flow to different organs can be more specific
* Allows blood to be pumped around the body __faster__
* Blood flow to different organs can be more specific
28
New cards
Arteries carry blood…
away from the heart
29
New cards
Veins carry blood…
towards the heart
30
New cards
Function of capillaries
Capillaries __connect__ arteries and veins and it is where the __substances__ are __exchanged between cells__
31
New cards
How are blood vessels adapted?
All of them contain __elastic fibres__ to ensure __flexibility__ and __prevent easy tears or breaks__
32
New cards
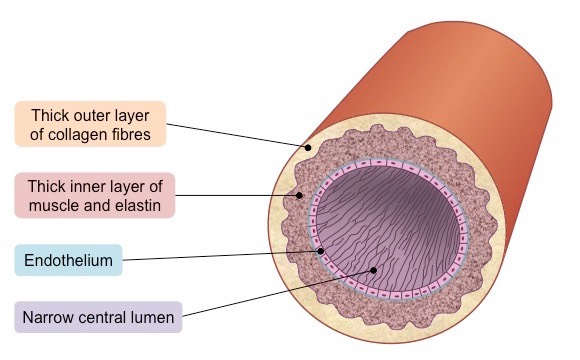
Describe the function of arteries in relation to their structure
* Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
* Arteries are under a lot more pressure than veins, hence a need for thicker walls of muscles and elastic fibres
1. Small lumen
2. Thick wall and endothelium
3. No valves (already under pressure)
* Arteries are under a lot more pressure than veins, hence a need for thicker walls of muscles and elastic fibres
1. Small lumen
2. Thick wall and endothelium
3. No valves (already under pressure)
33
New cards
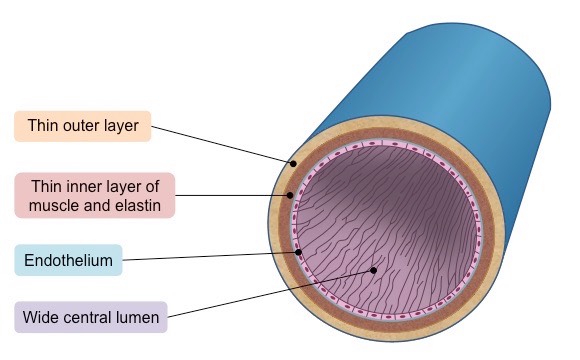
Describe the function of veins in relation to their structure
* Veins carry blood towards the heart
1. Veins are not under a lot of pressure, hence valves are needed.
2. Veins have a wide lumen
3. A thin wall and endothelium
1. Veins are not under a lot of pressure, hence valves are needed.
2. Veins have a wide lumen
3. A thin wall and endothelium
34
New cards
Describe the order of blood flow in vessels
1. Arteries→__Arteriole__→Capillaries→__Venules__→Veins
35
New cards
Describe the structure and function of capillaries
1. Very thin walls
* Capillaries are found all over the body incl. lungs, kidneys and small intestine
* The thin wall allows the capillaries to be permeable for the exchange of gases, nutrients and hormones
36
New cards
* Arteries connect to… before connecting to the capillaries, and capillaries connect to…before connecting to veins.
* …. and … are essentially… versions of arteries and veins.
* …. and … are essentially… versions of arteries and veins.
arterioles, venules, narrower
37
New cards
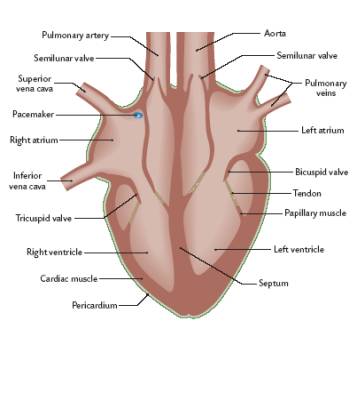
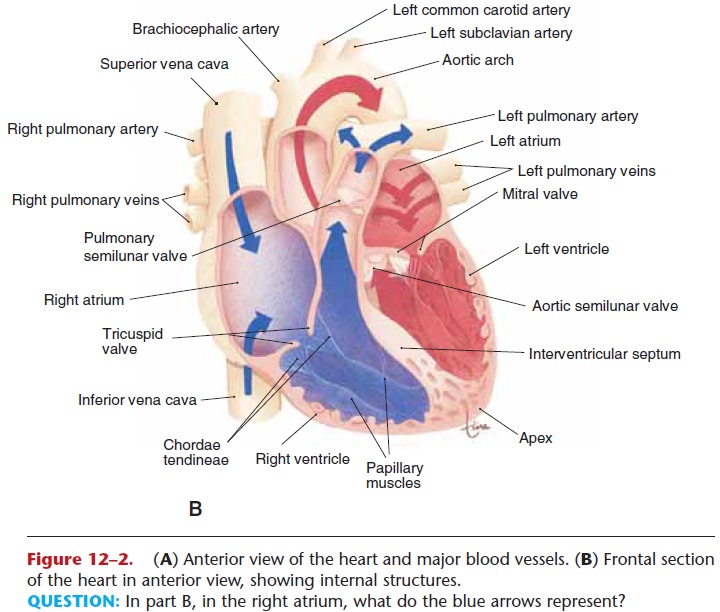
List all of the parts of the heart found on the RHS
1. Pulmonary Artery
2. Semilunar valve
3. Superior Vena Cava
4. Pacemaker
5. Right atrium
6. Inferior Vena Cava
7. Tricuspid Valve
8. Right ventricle
* extra:
\-cardiac muscle and pericardium
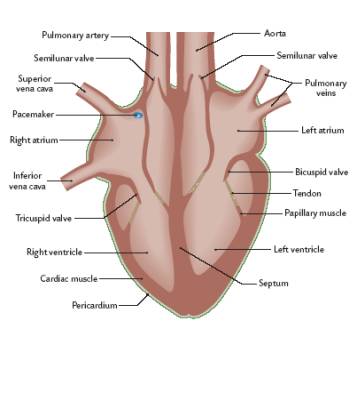
38
New cards
List all of the parts of the heart found on the LHS
1. Aorta
2. Semilunar valve
3. Pulmonary veins
4. Left atrium
5. Bicuspid Valve
6. Tendon
7. Papillary Muscle
8. Left ventricle
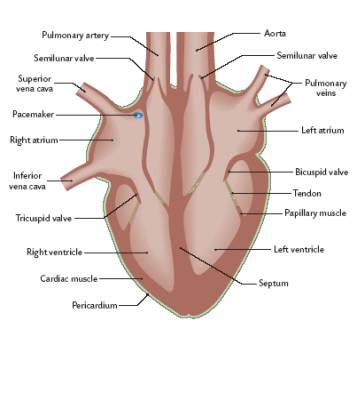
39
New cards
* The RHS of the heart pumps…. blood from… to….
* Beginning through the…, then the right…, through the…valve, the right…, the… valve and out the … to the…
* Beginning through the…, then the right…, through the…valve, the right…, the… valve and out the … to the…
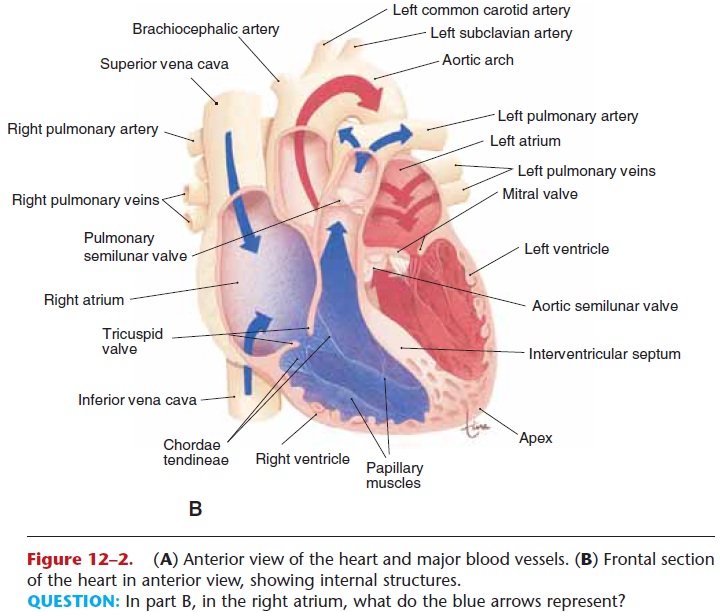
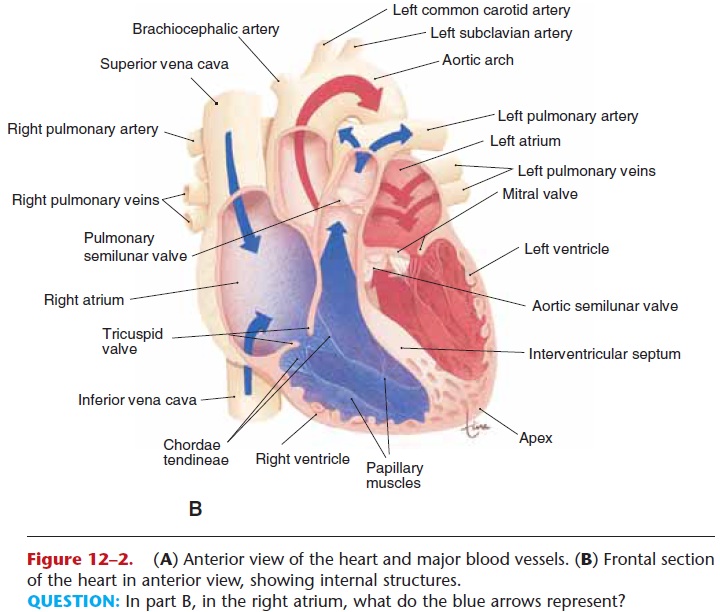
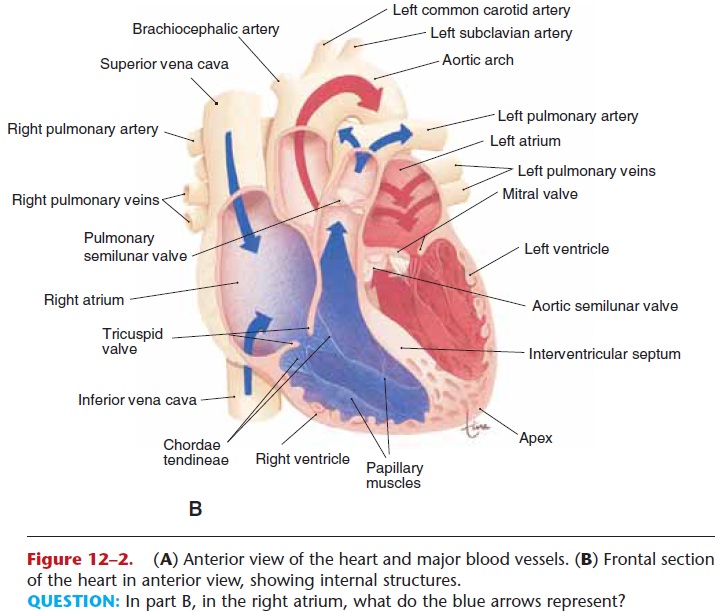
The RHS of the heart pumps __deoxygenated__ blood from __the head and body__ to __the lungs.__
\
Beginning through the __vena cava__, then the right __atrium__, through the __tricuspid__ valve, the right __ventricle__, the __semilunar__ valve, and out the __pulmonary artery__ out to the __lungs__.
\
Beginning through the __vena cava__, then the right __atrium__, through the __tricuspid__ valve, the right __ventricle__, the __semilunar__ valve, and out the __pulmonary artery__ out to the __lungs__.
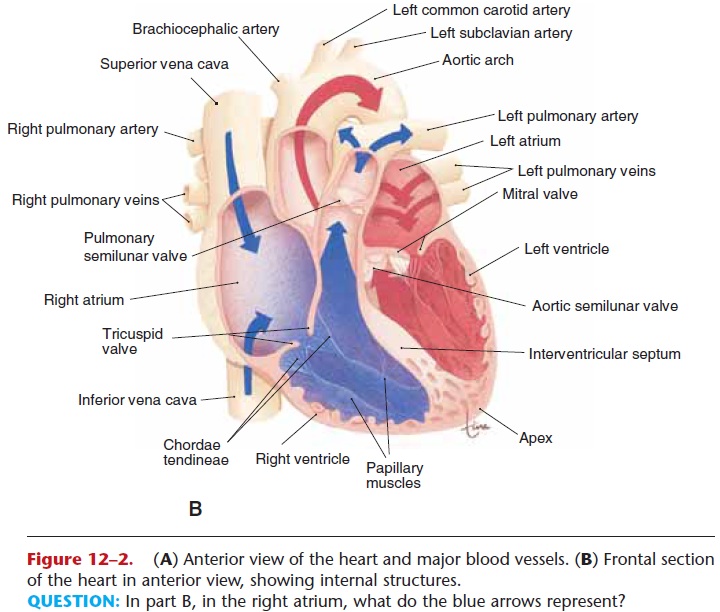
40
New cards
The only artery to carry deoxygenated blood is the…
pulmonary artery
41
New cards
The pericardium
a membrane that reduces friction while the heart is beating
42
New cards
What is the function of the bicuspid valve?
prevents the backflow of blood
43
New cards
The cardiac muscle is a … muscle
involuntary muscle. Meaning it continuously pumps blood all over the body. It is also the toughest muscle
44
New cards
On which side of the heart is cardiac muscle thicker?
* Thicker on the LHS since this side is responsible for pumping blood throughout the entire body, except for the lungs
45
New cards
What is the backside of the heart known as?
* The backside of the heart is know as the __dorsal__ side
46
New cards
What is the frontside of the heart known as?
the front side is known as the __ventral__ side
47
New cards
List 3 valves and their location in the heart
1. __Tricuspid Valve__- RHS, connects the right atrium to the right ventricle.
2. __Bicuspid Valve__- LHS, connects the left atrium to the left ventricle
3. __Semi-lunar valve__-LHS and RHS, ventricles through to the pulmonary artery (RHS) or aorta (LHS)
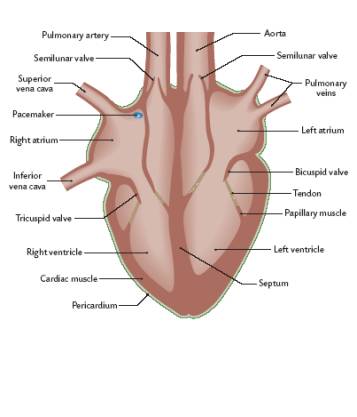
48
New cards
What is the function of the 3 valves of the heart?
1. __Tricuspid valve__-prevents back flow into the right atrium.
2. __Bicuspid valve__- prevents back flow into the left atrium.
3. __Semi-lunar valve__- prevents back flow into the heart
49
New cards
What are the four major blood vessels of the heart?
1. Vena Cava
2. Pulmonary Artery
3. Pulmonary Vein
4. Aorta
50
New cards
What is the function of the Vena Cava?
Carries deoxygenated blood from the head and body to the right atrium
51
New cards
What is the function of the Pulmonary Artery?
Carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
52
New cards
What is the function of the pulmonary vein?
Brings oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left artia
53
New cards
What is the function of the Aorta?
Takes blood from the heart and carries it to the rest of the body
54
New cards
How many blood circuits are there in the body?
2
55
New cards
Name the two blood circuits and their course
1. __Pulmonary Circuit__- heart→lungs→heart
2. __Systemic Circuit__- heart→rest of body→heart
56
New cards
What are the two benefits of having two blood circuits?
1. Allows for O2 rich and poor circuits to be separate
2. Ensures that blood pressure remains high enough to reach all parts of the body.
57
New cards
Which side of the heart is O2 rich and poor?
“LORD”
\-left oxygenated
\-right deoxygenated
\
note:your left and your right.
\-left oxygenated
\-right deoxygenated
\
note:your left and your right.
58
New cards
Draw a diagram of the pulmonary and systemic circuit
1. __Pulmonary Circuit__- heart→lungs→heart
2. __Systemic Circuit__- heart→rest of body→heart

59
New cards
Describe the course of the blood as it enters, travels and exits the heart.

60
New cards
What is the difference between plasma and serum?
* blood plasma contains blood cells and clotting factors, whereas blood serum does not.
* serum is plasma, but without clotting proteins
* serum is plasma, but without clotting proteins
61
New cards
Where are red blood cells broken down?
Dead red blood cells are broken down in the liver and spleen.
62
New cards
When red blood cells are broken down, haemoglobin is broken down to form…
Haemoglobin is broken down to form __bile__.
63
New cards
Haemoglobin gains oxygen from the lungs, forming…
Haemoglobin gains oxygen from the lungs, forming __oxyhaemoglobin__.
64
New cards
Oxyhaemoglobin loses oxygen to body cells, forming …
Oxyhaemoglobin loses oxygen to body cells, forming __haemoglobin__
65
New cards
Erythrocytes
red blood cells
66
New cards
Leucocytes
white blood cells
67
New cards
Describe the structure of leucocytes
* These have no definite shape but do have a nucleus.
* They are bigger than red blood cells but are less numerous
* They are bigger than red blood cells but are less numerous
68
New cards
Bone marrow is part of the… system
lymphatic system
69
New cards
Thrombocytes
platelets
70
New cards
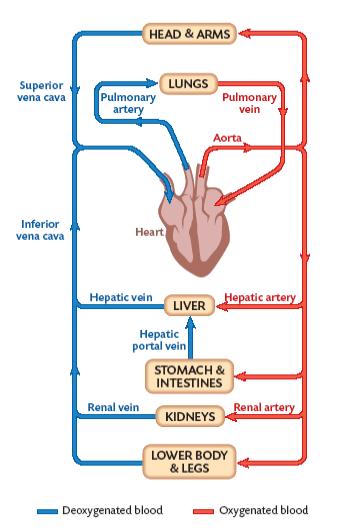
What is a portal system? Name an example
A portal system is a blood pathway that begins and ends in capillaries
\-eg. Hepatic Portal system (mentioned in the digestive system chapter)
\-eg. Hepatic Portal system (mentioned in the digestive system chapter)
71
New cards
The hepatic portal vein is part of a portal system. What is its function?
* The hepatic portal vein connects the small intestine to the liver.
* This allows nutrients from the small intestine to move directly to the liver for storage or metabolic processes (ex. detoxifying)
* This allows nutrients from the small intestine to move directly to the liver for storage or metabolic processes (ex. detoxifying)
72
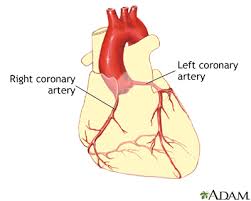
New cards
Which vessel supplies oxygenated blood to the heart?
* The coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart, the aorta is its origin
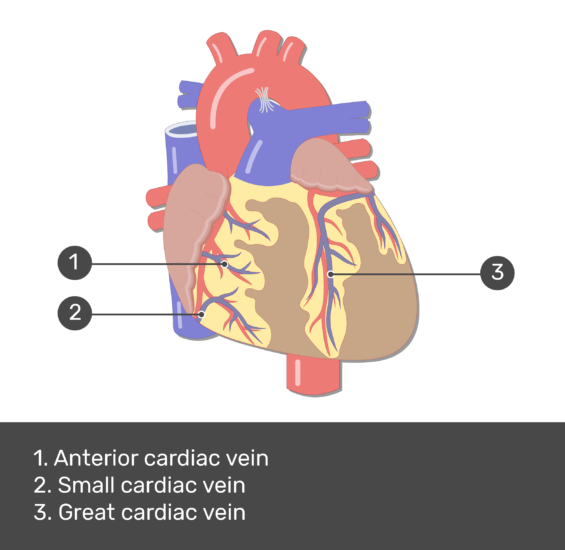
73
New cards
What is the function of the coronary vein?
The coronary vein __carries deoxygenated blood out__ of the muscles of the heart.
74
New cards
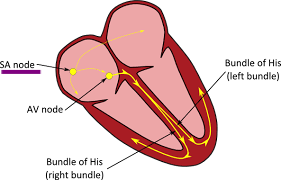
What causes both atria to contract?
* The __SA node__ located at the top wall of the right atria is __stimulated by electrical impulses from the brain__ and causes both atria to contract.
75
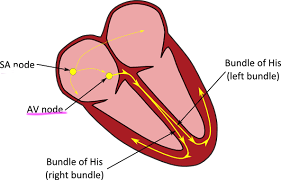
New cards
What causes the ventricles to contract?
* The SA node located at the top wall of the right atria is stimulated by electrical impulses from the brain and causes both atria to contract.
* The __electrical impulse__ that caused this __moves to the AV__ __node__ in the __septum__, and this now causes the ventricles to contract.
* The __electrical impulse__ that caused this __moves to the AV__ __node__ in the __septum__, and this now causes the ventricles to contract.
76
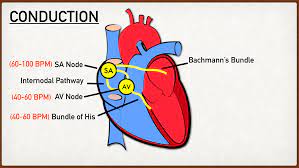
New cards
What moves the blood through the heart?
* Electrical impulses sent by the brain stimulate the SA node (atria contractions) and then move to the AV node (ventricle contractions)
* These contractions make the blood move
* These contractions make the blood move
77
New cards
What controls the rate of the heartbeat?
* Pacemaker (SA node and AV node)
* Emotions, exercise and temp have an effect too.
* Emotions, exercise and temp have an effect too.
78
New cards
State the precise location and describe the role of the sinoatrial (SA) node
* *Location:* In the wall of the right atrium.
* *Role:* Sends impulses to the atria, causing them to contract. Also stimulates the AV node.
* *Role:* Sends impulses to the atria, causing them to contract. Also stimulates the AV node.
79
New cards
State the precise location and describe the role of the atriovenular (AV) node
*Location:* In the wall of the heart, between the __right atrium and the right ventricle__.
*Role:* Sends impulses down the septum to the ventricles, causing the ventricles to contract.
*Role:* Sends impulses down the septum to the ventricles, causing the ventricles to contract.
80
New cards
What exactly is being measured when a person’s blood pressure is taken?
The __force of the blood on the arteries__ when the heart is in systole (contracted) and diastole (relaxed)
81
New cards
Name two substances, other than food molecules and water, that are transported in the blood. Also state the location at which they enter the blood.
\-Carbon dioxide
\-Oxygen
*Carbon dioxide:* all body cells where respiration occurs
*Oxygen:* at the alveoli
\-Oxygen
*Carbon dioxide:* all body cells where respiration occurs
*Oxygen:* at the alveoli
82
New cards
Give one way in which lymph differs from blood
Lymph has no RBC
83
New cards
Name a major blood vessel that returns blood to the heart
Vena Cava
84
New cards
What is the function of the coronary artery?
Supplies oxygenated blood to heart __muscle__.
85
New cards
Each heartbeat causes two audible sounds. What causes these sounds?
The __rhythmic closing and opening of the heart valves__ as blood is pumped in and out of the chambers.
86
New cards
There is a two circuit circulatory system in humans. Name the circuit which
1. the right ventricle pumps blood
2. the left ventricle pumps blood
1. the right ventricle pumps blood
2. the left ventricle pumps blood
1. pulmonary circuit
2. systemic circuit
87
New cards
Human RBC live for about 120 days. Give a reason for this
They have no nucleus nor mitochondria
88
New cards
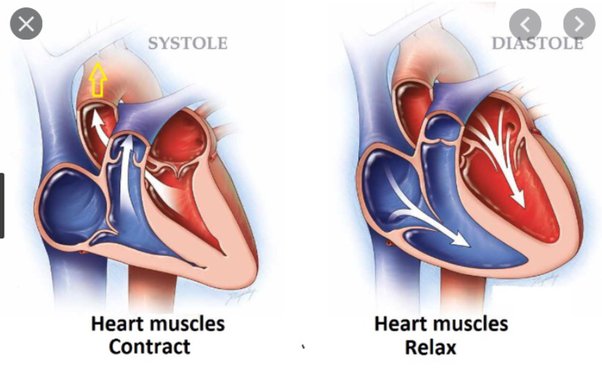
By looking at the diagram, explain how you know the heart has contracted
1. Ventricles have elongated and have reduced in volume
2. The semilunar valves have opened to allow blood flow out
3. Tricuspid and dicuspid valves closed to prevent backflow
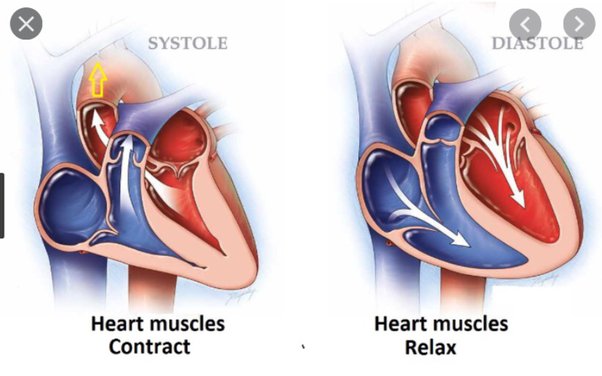
89
New cards
State two ways other than colour in which RBCs differ from WBCs
1. RBC do not contain a nucleus nor mitochondria, while WBC do.
2. RBCs are biconcave, WBCs have
no definite shape.
90
New cards
Where are red blood cells made?
In the bone marrow
91
New cards
Explain the term plasma
The clear, yellowish, fluid part of the blood that carries the blood cells.
92
New cards
What is the key component of RBCs?
haemoglobin
93
New cards
What shape are RBCs and why?
Biconcave- to be able to maximise the oxygen concentration, increase surface area
94
New cards
RBCs are elastic. Why?
To be able to get through arteries and veins without breaking
95
New cards
Name the 4 primary blood types
A, B, O and AB
96
New cards
What is the name of the factor that is sometimes present in blood?
The rhesus factor- have it, positive blood type
97
New cards
What part of the cell produces carbon dioxide that is then transported by the blood?
mitochondria- respiration byproduct
98
New cards
Is blood classified as a tissue or an organ?
Tissue- made up of a ton of cells working together
99
New cards
What exactly is being measured when persons blood pressure is taken?
The force of blood against the artery wall.
100
New cards
Name a vein that transports blood __out__ of the muscle of the heart
Coronary vein