Ch 14 - Instrumentation
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Gamma Camera: Performance Characteristics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
sharpness and detail of the images it produces, the efficiency which it detects radiation, ability to measure energy, and the counting rate it can handle without dead time losses
the performance of a gamma system is defined by the:
no
is a gamma camera capable of producing the “perfect” image of radionuclide distribution
electronic circuitry and the collimator
what are a couple inherent imperfections characteristics that arise from the performance of the detector?
image artifacts
what can also be caused by malfunctions of various camera components?
spatial resolution
this is a measure of the sharpness and detail of a gamma camera image
spatial resolution
sharp edges or small pointed objects produce blurred rather than sharply defined images
intrinsic spatial resolution
the limit of spatial resolution which is achievable by the detector and the electronics (ignoring the blurring caused by the collimator)
multiple scattering of gamma ray photons within the detector and statistical fluctuation in the distribution of light photons among PM tubes from one scintillation event to the next
two factors that affect intrinsic spatial resolution
one event can be recorded as two which leads to blurring
what can happen when multiple scattering of gamma ray photons within the detector via compton scattering occur?
6.4mm
Anger calculated that a detector thickness of ____ has less than 10% of photons misplaced by more than 2.5mm as a result of multiple scattering events
10%
Anger calculated that a detector thickness of 6.4mm has less than ___ of photons misplaced by more than 2.5mm as a result of multiple scattering events
2.5mm
Anger calculated that a detector thickness of 6.4mm has less than 10% of photons misplaced by more than ____ as a result of multiple scattering events
statistical fluctuation in the distribution of light photons among PM tubes from one scintillation event to the next
the primary cause of limited intrinsic resolution is:
a signal to be read from a very thin line of activity that may not necessarily correspond to the actual activity in the patient
with the scintillation material reacting to the radiation that is being emitted events can overlap causing:
lead mask containing 1mm slits placed in from of the camera (no collimator) and a 140 keV Tc99m point source
how can we measure and characterize intrinsic spatial resolution?
no
when measuring intrinsic spatial resolution, is the collimator on?
gamma ray energy and detector crystal thickness
intrinsic resolution also depends on:
less gamma rays are converted into light photons
what happens gamma ray energy decreases?
1 divided by the square root of the energy level
as a general rule, intrinsic resolution is proportional to
there is a greater spreading of scintillation light before it reaches the PM tubes
what happens as the detector crystal thickness increases?
efficiency of collection of scintillation photons
intrinsic resolution improves with increased:
smaller crystals
for nuc med purposes, what general size of crystal is ideal for improving intrinsic resolution?
5 cm diameter
what is the average PM tube size
2-5 cm
how thick are NaI crystals in probes?
6.4-12.7 mm
how thick are NaI crystals in gamma cameras?
thicker crystals
detection efficiency increases in what size of crystal?
thinner crystals
intrinsic spatial resolution improves in what size crystal?
higher energy
as the crystal gets thicker, it allows the _____ emission to be absorbed better
drops
as the crystal gets smaller, the detection efficiency _____ over the energy spectrum
energy resolution
determines the efficiency for discrimination against low energy scatter photons interacting with the detector via Pulse Height Analyzer
Pulse Height Analyzer
the energy resolution determines the efficiency for discrimination against low energy scatter photons interacting with the detector via the ________
light collection efficiency
what is required for good energy resolution?
statistical fluctuations in the number of light photons collected from a scintillation event
energy resolution, like intrinsic resolution, depends largely on:
linearly
the number of light photons released in a scintillation event increase _____ with gamma ray
1 divided by the square root of the energy
energy resolution improves approximately in proportion to:
9-11%
energy resolution for gamma cameras is typically in the ____ range for Tc99m
130-150 keV
Tc99m is typically imaged with a window set for:
15%
the 130-150 keV window setting for Tc99m corresponds to approx. a ___ range
more efficiency detection of unscattered photons
what is the result in the photopeak becoming narrower
photopeak becoming more narrow
what can increase the number of valid events recorded and improve the statistical quality of the image?
their energy spread within the pulse height spectrum is also smaller
why are gamma rays that are scattered through large angles rejected more efficiently
improves image contrast
what happens to the image with scattered gamma rays are rejected
image quality
improved energy resolution results in better _____
high counting rates
what increases the likelihood of recording two events at the same time?
pulse pile up
recording two events at the same time is known as
counting losses and image distortion
two undesireable effects from pulse pile up are
counting losses
cause inaccurate counting rates to be recorded at high counting rates
analog buffers
derandomizers aka
analog buffers
electronic circuits that can hold onto the pulse and release it instead of having a backup occur during uptake
paralyzable systems
gamma cameras behave as
window fraction
what does the apparent dead time for a selected energy window depends on?
window fraction
the ratio of the time the system is actively detecting events to the total time, which includes both the detection time and the dead time.
window fraction
fraction of total spectrum counting rate occuring within that window
larger the apparent dead time
the smaller the window fraction the:
image distortion
causes the image to record activity in areas where there isnt any due to pulse pile up distortion of the counts
in the circuitry via the incorporation of a pulse tail extrapolation
how can image distortion be fixed?
both counts to be counted and contribute to the exam
an estimator and subtractor off of known decay schemes for the photon pulses allows for what?
image nonlinearity
straight lines appear with inward or outward bowing
inward
pincushion distortion direction
outward
barrel distortion direction
nonlinearities
result when the X and Y position signals do not change linearly with displacement distance of a radiation source across the face of the detector
image nonuniformity
exposing the detector crystal to a uniform flux of radiation produces a flood field image with a small but noticeable nonuniformities in intensity, even with a properly functioning camera
intrinsic flood images
what kind of images are acquired with the collimator removed, using a point source placed far enough from the surface of the gamma camera to give uniform irradiation of the surface (Tc99m-pertecnatate)
extrinsic flood field images
what kind of images are acquired with the collimator in place using a disk or thin flood phantom that covers the area of the detector, typically pertechnetate Tc99m-O42 or a Co57 sheet source are used
nonuniform detection efficiency and image nonlinearities
the two primary causes of gamma camera nonuniformities
nonuniform detection efficiency
what arises from small differences in the pulse-height spectrum for different PM tubes
monthly tuning for Tc99m on the camera
how can the position dependent collection efficiency of scintillation light, particularly for events located over the gaps and dead areas between the PM tubes compared with events located directly over the center of the PM tube be fixed?
edge packing
this can occur when there is a bright ring around the edge of the image
edge packing
this occurs from internal reflection in the scintillator material to be picked up at the outer edge of the camera
higher photon energies
this result in a worsening detector nonuniformity
data
___ is stored in a matrix of offset counts for each PM tube and pixel location that can correct for image nonuniformity
tuning map
every single isotope must complete its own ____ for the camera to be properly calibrated for the scanner
tuning map
what are these?
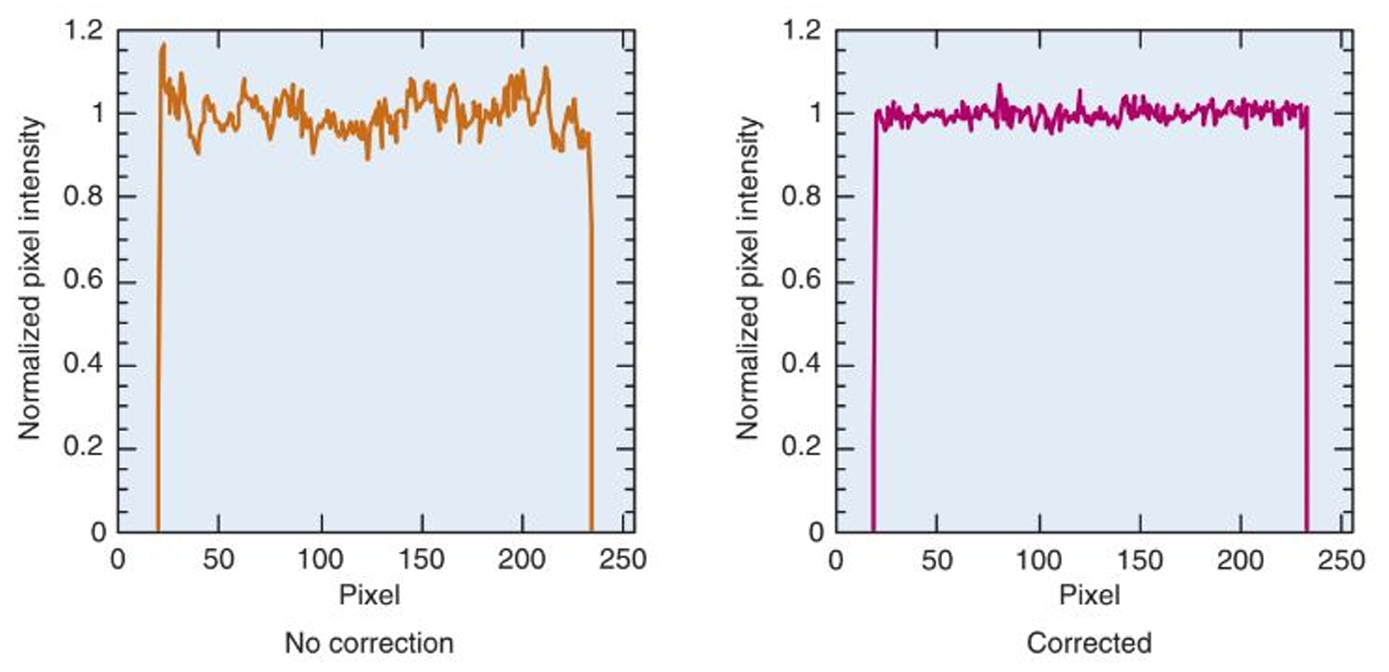
intrinsic resolution
improvements in camera uniformity also contribute to improvements in what?
counting statistics
older cameras needed to have thicker light guides to ensure that all of the photons were absorbed for good _______
thinner or no light guides at all
how thick are the light guides on newer scanners
image acquisistion
because of constant use and wear on PM tubes, it is important to manually tune the PM tubes for proper ______
due to Earth’s rotating magnetic field influencing changes in the PM tube gain
why is continuous tuning important in SPECT?
the collimator
what is the weak link for the performance of a gamma camera system
absorptive collimation
general collimators emply the principles of:
collimator efficiency
the fraction of gamma rays striking the collimator that actually pass through it to project the gamma ray image onto the detector
small
the collimator efficiency is usually a very ____ percentage
collimator resolution
refers to the sharpness or the detail of the gamma ray image projected onto the detector
collimator design
A primary consideration in ________ is to ensure that septal penetration by gamma rays crossing from one collimator hole into another is negligibly small.
septal penetration
A primary consideration in collimator design is to ensure that _______ by gamma rays crossing from one collimator hole into another is negligibly small.
negligibly small
A primary consideration in collimator design is to ensure that septal penetration by gamma rays crossing from one collimator hole into another is ______.
high atomic number and density
what characteristic of collimator material should minimize gamma ray interference.
lead
what is the preferred material for collimators
150 keV
low energy collimator have an upper limit of approximately
400 keV
medium-energy collimators have an upper limit of approximately
511 keV
high energy collimators have an upper limit of approximately
collimator efficiency
tc99m can be scanned with a medium energy collimator, but what is sacrificed in the mean time?
septa
if collimator ____ are too thin, they may be virtually transparent to high energy photons
geometry of the collimator holes
collimator performance is affected by the ____
shape, length, and diameter
what features of collimaotr holes affect performance
hexagonal, or circular made up of tightly packed square array on the camera
the ideal shape of collimator holes
collimator resolution and efficiency
what does collimator hole length affect?
collimator resolution
the FWHM of the radiation profile from a point or line source of radiation projected by the collimator onto the detector
point spread function or line spread function
the radiation profile from a point or line source of radiation projected by the collimator onto the detector is also called the:
intrinsic resolution, collimator resolution, scattered radiation, and septal penetration
the sharpness of images recorded with a gamma camera is limited by: