Reproduction In Plants
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Reproduction
Process of making more of the same kind of organism
Asexual reproduction
Process resulting in the production of genetically identical offspring from one parent. Only one parent, offspring are genetically identical to parent.
Advantages and disadvantages of AR
A: 1. Faster reproduction(doesnt require mate) 2. Consistent offspring (advantageous in a stable environment ) 3. Energy efficient (doesn’t waste energy searching for mates or making gametes) 4. No need for pollination
D: 1. No genetic diversity (bad in a changing environment, poopulatio may not adapt to new conditions) 2. Vulnerable to disease (since genetically identical, disease that spreads to one organism can affect whole population)
Sexual reproduction
Process involving the fusion of the nuclei of two gametes to form a zygote and the production of offspring that are genetically different from each other
Fertilisation
the fusion of the nuclei of gametes. Sperm and ovum, or pollen nucleus and ovum
Haploid and diploid
nuclei of gametes are haploid (23 chromosomes) and the nucleus of a zygote is diploid (46 chromosomes)
Advantages and disadvantages of SR
A: 1. Increased genetic diversity (more adaptable to changing environemnt) 2. Less vulnerable to disease (can withstand disease) D: 1. Requires fusion of 2 gametes (requires time and energy for mate) 2. Slower process (reducing speed of reproduction and low production yields)
Sexual reproduction in plants
Typically contain both male (stamen) and female (carpel) reproductive parts. Male gametes are in pollen grains and female gametes are in ovum.
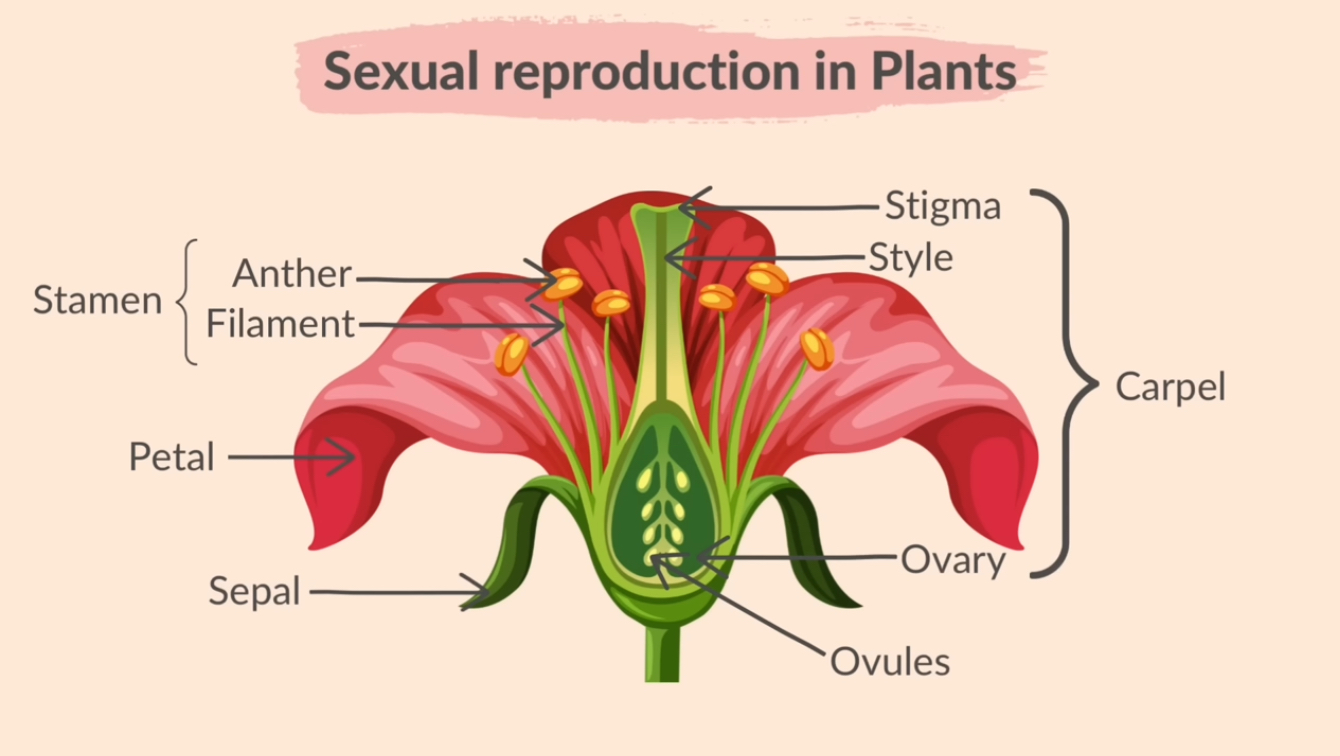
Functions of flower
Sepal: Protects the unopened flower
Petal: Brightly coloured in insect-pollinated flowers to attract insects
Anther: Contains pollen (the male sex cells)
Filament: Supports the anther
Stigma: The sticky surface that catches pollen
Style: Links stigma to ovary
Pollination
Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma. Insects or wind.
Insect-pollinated flowers
Petals: large & bright to attract insects
Pollen: Moderate in number, Large, sticky & spiky
Stigma: sticky and inside the flower
Anther: inside the flower, firmly attached
Scent & Nectar: is present to attract insects
Wind-pollinated flowers
Petals: small & dull
Stigma: feathery and outside the flower
Pollen: Large amounts, Smooth, small & light
Scent & Nectar: absent
Anther: outside the flower, swinging loose
Self-pollination
transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or a different flower on the same plant. Reduces genetic variation and limits adaptability of offspring to changing environment conditions
Cross-pollination
transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower on a different plant of the same species. Increases genetic variation but depends on pollinators. Wind pollinated plants are not affected
Fertilisaiton in flowers
Pollen nucleus fuses with an ovule nucleus. 1. Pollgen grains lands on stigma. 2. Pollen tube begins to grow down style until it enters ovule through micropyle. 3. Pollen nucleus moves down pollen tube 4. Pollen nucleus fuses with ovum nucleus. Ovule develops into seed. Ovary wall develops into fruit.
Factors affecting seed germination
The beginning pf seed growth is known as germination. 1. Water: causes seed to expand and activates enzymes within embryo to initiate growth. 2. Oxygen: For respiration to release energy for growth. 3. Suitable temperature to increase rate of germination since enzyme-catalysed reactions are temperature dependent