ch 11 and 12
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
origin
non movable part of muscle
the attachment of a muscles tendon to the stationary bone
insertion
The attachment of a tendon of a muscle to the movable
bone across a jointMovable part
belly
middle fleshy part of the bone
biceps brachii
Origin: Scapula
Insertion: Radius
Action: pronate and flex the arm
triceps brachii
Origin:
Scapula near shoulder joint
Upper lateral and posterior sites of humerus
Posterior surface of humerus
Insertion: Back of olecranon process of ulna
Action: Straighten (extend) the arm
lever
A rigid structure that can move around a
fixed point is called a lever
Muscles, tendons, bones, and joints can
form three different types of levers in the
body.
When producing movement, bones act as
levers, and joints function as the fixed point
of movement called the fulcrum.
In a lever, the point of movement
(fulcrum) is acted on by two different
forces: Effort (muscle) and load
(Resistance).
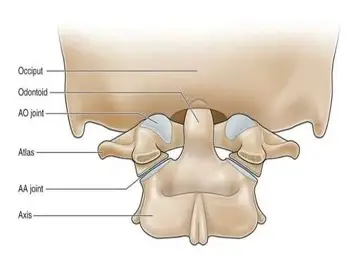
1st class lever (few examples)
fulcrum: atlanto-occipital joint
locad: facial bone
effort: muscles of the back of the neck
2nd class lever (rare)
one in human body
can compare with a wheelbarrow
metatarsophalangeal joints are the fulcrum
gastronemius and soleus muscles are the effort
whole body weight is resistance
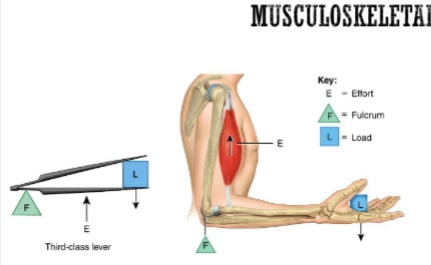
3rd class lever (most common)
The most common
Example: Elbow Joint
Load: Bones of hand, can add a weight
Effort: Biceps Brachii
Fulcrum: Elbow Joint
Can compare with a tweezer
prime mover (agonist)
Within opposing
pairs, the prime mover or agonist (“the
leader”) is the muscle primarily responsible
for causing the desired movement
ex. in flexing forearm at elbow, brachialis is prime mover or agonist
antagonist
stretches and yield to effects of the prime mover
most skeletal muscles arranged in opposing pairs at joints (antagonistic)
ex. in flexing forearm at elbow, triceps brachii is antagonist
synergists
Muscles used to aid or assist the
movement of the prime mover.The biceps acts synergistically with the brachialis
fixator
Type of synergist muscle that are used
to steady or fix the proximal joints of a prime
mover.Shoulder stabilizers for the forearm flexors
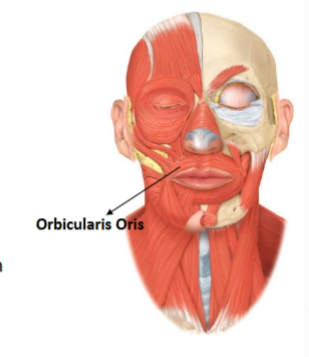
orbicularis oris
Action: Closes and protrudes lips for kissing
Origin: Surrounding the opening of the mouth
Insertion: The skin at the corner of the mouth
muscles of mastication
muscles that move the mandible (lower jaw)
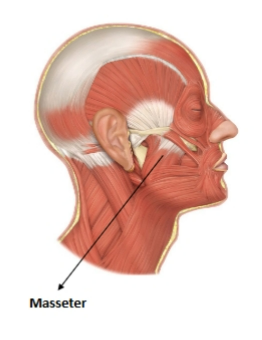
masseter
Origin: Maxilla and zygomatic arch
Insertion: Mandible
Action: Closes the mouth
muscles of mastication
Masseter
Temporalis
Medial Pterygoid
Lateral Pterygoid
muscles of facial expression
orbicularis oris
orbicularis oculi
occipitofrontalis
zygomaticus major
zygomaticus minor
buccinator
muscles are originated in fascia or bones of the skull and inserted into the skin of the face
bells palsy
facial paralysis
paralysis of muscles of the facial expression
due to damage to VIII cranial nerve
entire side of face droops in severe cases
sign and symptoms: unable to wrinkle forehead, close eye, or pucker lip on affected side
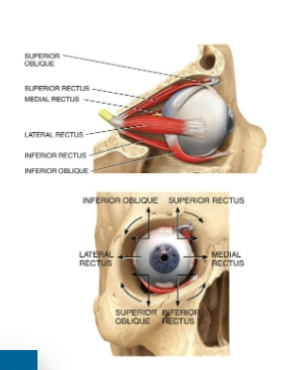
extraocular muscle
3 pair give each eye very precise movement
Origin: Back of the orbit
Insertion: Different parts of the eyeball
Action: Precise and rapid movement of the eyes
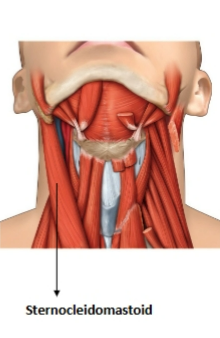
sternocleidomastoid
origin: clavicle and sternum
insertion (moveable): mastoid process of temporal bone
action: flex and rotate head
pectoralis major and pectoralis minor are muscles that move the pectoral girdle (shoulder)
pectoralis major:
origin: clavicle and sternum
insertion: proximal humerus
action: adducts and medially rotates the arm at the shoulder joint
pectoralis minor:
origin: ribs 3-5
insertion: coracoid process of the scapula
action: internally rotates the shoulder
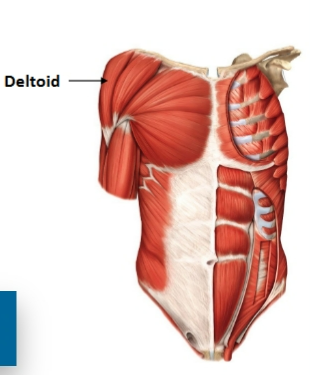
deltoid muscle
muscle that moves pectoral girdle (shoulder)
origin: lateral clavicle and upper scapula
insertion: deltoid tuberosity on humerus shaft
action: abducts, flexes, and medially rotates upper arm at the shoulder joint
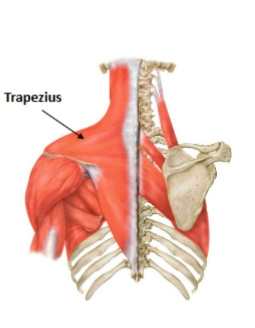
trapezius muscle
muscle that moves the pectoral girdle (shoulder)
origin: occipital bone and cervical spine
insertion: clavicle, scapula and lower thoracic vertebrae
action: supports the arm and moves the scapula up, down, in, and out
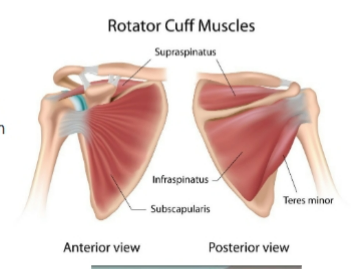
rotator cuff
Rotator cuff is made up of muscles and
tendons that keep the ball (head) of the
upper-arm bone (humerus) in the shoulder
socket. It also helps raise and rotate the arm
Muscles are:
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
fixed by reconstruction surgery
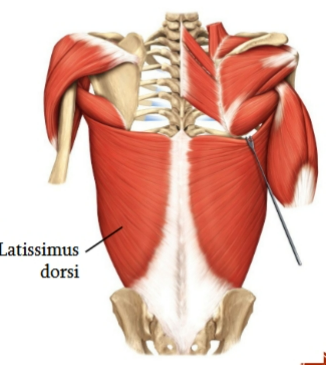
latissimus dorsi
muscle that moves pectoral girdle (shoulder)
lower back
origin: thoracic and lumbar vertebrae and the iliac bone
insertion: mid-humerus
action: drives arm inferiorly and posteriorly (swimmer’s muscle)
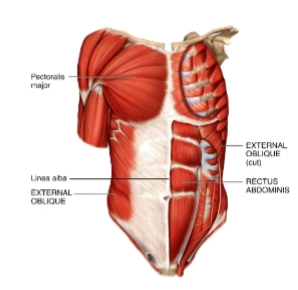
rectus abdominis
anterior abdominal wall
origin: pubic bone
insertion: ribs and sternum
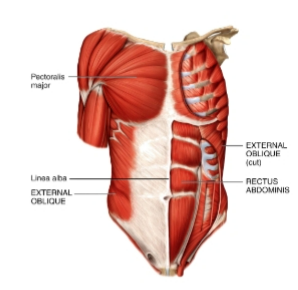
external oblique
anterior abdominal wall
origin: ribs 5-12
insertion: iliac crest and linea alba
actions: flexes vertebral column and compresses abdomen
diaphragm
The main muscle of inspiration
Origin: Inferior 6 ribs (anteriorly) and lumbar
vertebrae (posteriorly)
Insertion: Central tendon
upper extremity muscles
Upper Extremity Muscles:
Biceps Brachii
Triceps brachii
Brachialis
Brachioradialis
Palmaris longus
Flexor Digitorum longus
Thenar muscles
Hypothenar muscles
lower extremity muscles
Lower Extremity Muscles:
Gluteus maximus
Biceps femoris
Quadriceps group:
Rectus femoris, vastus lateralis
vastus intermedius
vastus medialis
Tibialis anterior
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
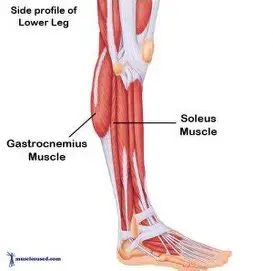
gastrocnemius and soleus
Muscles that plantar flex the foot at the ankle
joint (standing on “tip toes”)
Gastrocnemius and soleus muscles function as
one – often called the calf muscle
Origin: Femur, capsule of knee, and head of
fibula
Insertion: Calcaneus by way of calcaneal
(Achilles) tendon
spasm
A sudden involuntary contraction of a single muscle within a large group of muscles
Cause unknown
Usually, painless
cramp
Cramp
Involuntary
Often painful muscle contractions
Causes:
Abnormal blood electrolyte levels
Inadequate blood flow to muscles (such as in dehydration)
Overuse and injury of the muscles
fibrosis (myofibrosis)
replacement of muscle fibers by excessive amounts of connective tissue (fibrous scar tissue)
myosclerosis
Hardening of the muscle caused by calcification
Both myosclerosis and muscle fibrosis occur as a result of trauma
and various metabolic disorders
ch .12
nervous system functions
regulate body activities by responding rapidly using nerve impulses (action potentials)
initiates all voluntary movement
responsible for perceptions, behaviors, memories, thought, intellectual etc
accomplishable by excitable characteristics of nervous tissue
organization of nervous system
work with endocrine system
central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
neurology: study of functions and disorders of nervous system
3 fundamental steps of nervous system
sensory function
integrative function
motor function
sensory function
Sensory receptors
detect internal and external stimuli. Then
sensory information carried to the brain
and spinal cord through cranial and spinal
nerves
integrative function
The brain or spinal
cord processes the sensory by analyzing it
and making decisions for appropriate
responses...Known as integration
motor function
After integration, the
nervous system elicit an appropriate
motor response by activating effectors
(Muscles for contraction and glands for
secretion)
peripheral nervous system is further divided into
somatic ns
automatic ns
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
all nervous tissue outside the CNS
ex. nerves, ganglia, enteric plexus, sensory receptors