First Macro Test
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Foundations of Economics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
An economy is operating at a point inside its
production possibilities curve (PPC). Which of
the following will most likely cause the economy
to move toward the current PPC in the short run?
(A) A decrease in government spending
(B) A decrease in inflation
(C) An increase in human capital
(D) An increase in employment
(E) An increase in imports
(D) An increase in employment
An increase in which of the following will most
likely promote economic growth?
(A) Taxes on investment
(B) The price level
(C) Human capital
(D) Consumption of nondurable goods
(E) Interest rates
(C) Human capital
Which of the following will cause aggregate
supply to increase in Country X?
(A) An increase in personal income taxes
(B) The discovery of low-cost alternative sources of energy
(C) A decrease in labor productivity with no change in nominal wages
(D) Depreciation of country X’s currency on the foreign exchange market
(E) An increase in the price level
(B) The discovery of low-cost alternative sources of energy
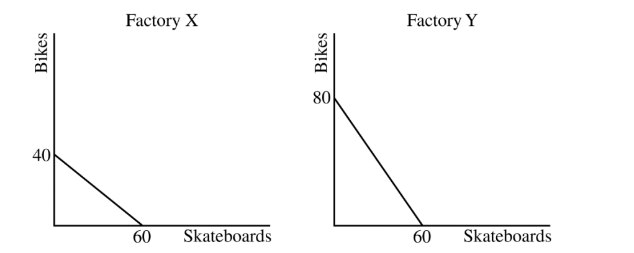
The graph above shows the production possibilities curve for Factory X and Factory Y. If Factory X uses the same amount of resources to produce skateboards and bikes as Factory Y uses, which of the following is true?
(A) Factory X has an absolute advantage in producing bikes.
(B) Factory X has an absolute advantage in producing skateboards.
(C) Factory X has a comparative advantage in producing skateboards.
(D) Factory Y has a comparative advantage in producing skateboards.
(E) Factory Y has an absolute advantage in producing skateboards.
(C) Factory X has a comparative advantage in producing skateboards.
An increase in the price of oil, an important
input to production, will result in which of the
following in the short run?
(A) A decrease in the price level
(B) A decrease in short-run aggregate supply
(C) A decrease in unemployment
(D) An increase in real wages
(E) An increase in aggregate demand
(B) A decrease in short-run aggregate supply
An economy is currently operating at the
full-employment level of output. Which of the
following would result in a recessionary gap in
the short run?
(A) An increase in the costs of production
(B) An improvement in the productivity of labor
(C) An increase in money supply
(D) A positive supply shock
(E) A decrease in income tax rates
(A) An increase in the costs of production
Thailand and Malaysia are trading partners. If
the price level in Thailand decreases relative to
the price level in Malaysia, what will happen to
Thailand’s exports to Malaysia and Thailand’s
aggregate demand?
Thailand’s Exports Thailand’s Aggregate Demand
(A) Increase Decrease
(B) Increase Increase
(C) Increase Indeterminate
(D) Decrease Decrease
(E) Decrease Increase
(B) Increase Increase
Which of the following is a fiscal policy action
aimed at reducing unemployment?
(A) Decreasing government expenditures
(B) Decreasing income taxes
(C) Decreasing tax credits
(D) Increasing nominal interest rates
(E) Increasing required reserves
(B) Decreasing income taxes
Increases in human capital can be achieved by
which of the following?
(A) Building more factories
(B) Reducing immigration of skilled workers
(C) Improving the quality of job-training programs
(D) Increasing the physical capital per worker
(E) Increasing government spending on infrastructure
(C) Improving the quality of job-training programs
Assume the economy is currently in long-run
equilibrium. An increase in the money supply
will affect unemployment in the short run and
in the long run in which of the following ways?
Short Run Long Run
(A) Falls Falls
(B) Rises Rises
(C) No change Remains at the natural rate
(D) Rises above the natural rate Falls back to the natural rate
(E) Falls below the natural rate Rises back to the natural rate
(E) Falls below the natural rate Rises back to the natural rate
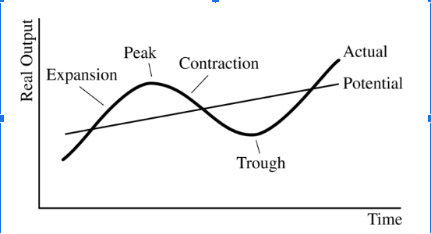
According to the business cycle represented in the diagram above, the actual rate of unemployment equals the natural rate of unemployment when the economy is
(A) in expansion
(B) in contraction
(C) at the peak
(D) at the trough
(E) on the potential line
(E) on the potential line
A fiscal policy action to reduce inflationary
pressure would be to increase which of the
following?
(A) The required reserve ratio
(B) The discount rate
(C) Transfer payments
(D) Government spending
(E) Income tax rates
(E) Income tax rates
Economic growth is shown by a rightward shift in
(A) the aggregate demand curve
(B) the long-run Phillips curve
(C) the production possibilities curve
(D) the short-run aggregate supply curve
(E) the money supply curve
(C) the production possibilities curve
If businesses become optimistic about the profitability of investments in an economy, which
of the following will happen in the loanable funds market in the short run?
(A) The supply and demand for loanable funds
will increase.
(B) The supply and demand for loanable funds
will decrease.
(C) The demand for loanable funds by the private
sector will decrease.
(D) The real interest rate will increase.
(E) The real interest rate will decrease.
(D) The real interest rate will increase.
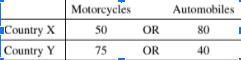
The table above shows the quantity of motorcycles and automobiles produced by two countries that use the same amount of resources. Which of the following is true?
(A) Country X has an absolute and comparative advantage in the production of motorcycles.
(B) Country X has an absolute and comparative advantage in the production of both goods.
(C) Neither country has a comparative advantage in the production of motorcycles.
(D) Country Y has an absolute and comparative advantage in the production of automobiles.
(E) Country Y has an absolute and comparative advantage in the production of motorcycles.
(E) Country Y has an absolute and comparative advantage in the production of motorcycles.
Assume a country’s government increases taxes and its central bank decreases the money supply. The actions will result in an increase in which of the following in the short run?
(A) Aggregate demand
(B) Aggregate supply
(C) Investment spending
(D) Unemployment
(E) Inflation
(D) Unemployment
When there is excess demand in the loanable funds market, which of the following will occur?
(A) National savings will exceed investment
spending.
(B) The economy will remain at full
employment.
(C) Real interest rates will increase.
(D) An inflationary gap will exist.
(E) The money supply will increase.
(C) Real interest rates will increase.
The measured unemployment rate is often
criticized for understating the level of joblessness
because
(A) individuals working in the underground
economy are counted as employed
(B) individuals working more than one job
are counted more than once
(C) discouraged workers are counted as
unemployed
(D) discouraged workers are not counted in the
labor force
(E) part-time workers are counted as unemployed
(D) discouraged workers are not counted in the
labor force
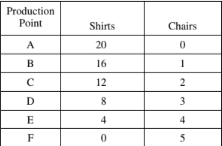
The table shows the production possibilities for
Country X in producing shirts and chairs when it
uses all its available resources. The opportunity
cost of producing one additional chair is
(A) zero
(B) constant
(C) increasing
(D) decreasing
(E) indeterminate
(B) constant
An increase in which of the following will most
likely cause an increase in aggregate demand and
inflation in the short run?
(A) Income tax rates
(B) Input prices
(C) Government spending
(D) Real interest rates
(E) Savings
(C) Government spending
Country X’s government increases its spending
without raising taxes. Which of the following is
true about the effect on Country X’s real interest
rates and its subsequent effect on Country X’s net
exports?
(A) Real interest rates increase and net exports
increase.
(B) Real interest rates increase and net exports
decrease.
(C) Real interest rates increase with no change in
net exports.
(D) Real interest rates decrease and net exports
increase.
(E) Real interest rates decrease and net exports
decrease.
(B) Real interest rates increase and net exports
decrease.
Which of the following shifts the money demand
curve to the right?
(A) An increase in the price level
(B) A decrease in the price level
(C) An increase in interest rates
(D) A decrease in interest rates
(E) A decrease in the nominal gross domestic
product
(A) An increase in the price level
Which of the following is an example of frictional
unemployment?
(A) A former mayor doing volunteer work
(B) A factory worker who loses her job because
of recession
(C) A college student working part-time at the
campus bookstore
(D) A college graduate interviewing for two
available positions
(E) An architect whose job is replaced by
computer software that designs buildings
(D) A college graduate interviewing for two
available positions
Assuming no government policies, which of the
following will occur in the long run if the actual
unemployment rate exceeds the natural rate of
unemployment?
(A) Prices will increase.
(B) Unemployment will increase.
(C) Wages will fall.
(D) Aggregate demand will increase.
(E) Long-run aggregate supply will decrease.
(C) Wages will fall.
Assume that the market for bottled water is in
equilibrium. If both the supply of and the demand
for bottled water decrease, what will be the effect
on equilibrium price and quantity?
Price Quantity
(A) Decrease Decrease
(B) Decrease Increase
(C) Increase Decrease
(D) Increase Indeterminate
(E) Indeterminate Decrease
(E) Indeterminate Decrease
An increase in government spending that is
financed by an equal increase in taxes results
in which of the following changes in aggregate
demand (AD) and short-run aggregate supply
(SRAS) curves?
AD Curve SRAS Curve
(A) Shifts to the right Shifts to the right
(B) Shifts to the left Shifts to the left
(C) Shifts to the right No change
(D) Shifts to the left No change
(C) Shifts to the right No change