Autonomic nervous System
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
Peripheral Nervous system
Somatic Nervous System
VS
Autonomic Nervous System
Both a part of the Peripheral Nervous system:
Somatic Nervous System:
Responsible for conscious perception and the resulting voluntary response via the skeletal system (movement).
General sensory neurons Skeletomotor neurons
Autonomic Nervous System:
Receives sensation from the visceral sense, and provides the involuntary response.
Para/sympathetic motor neurons, visceral general sensory neurons
e.g heartbeats, digestion, pupil dilation, etc.
Autonomic Nervous System function
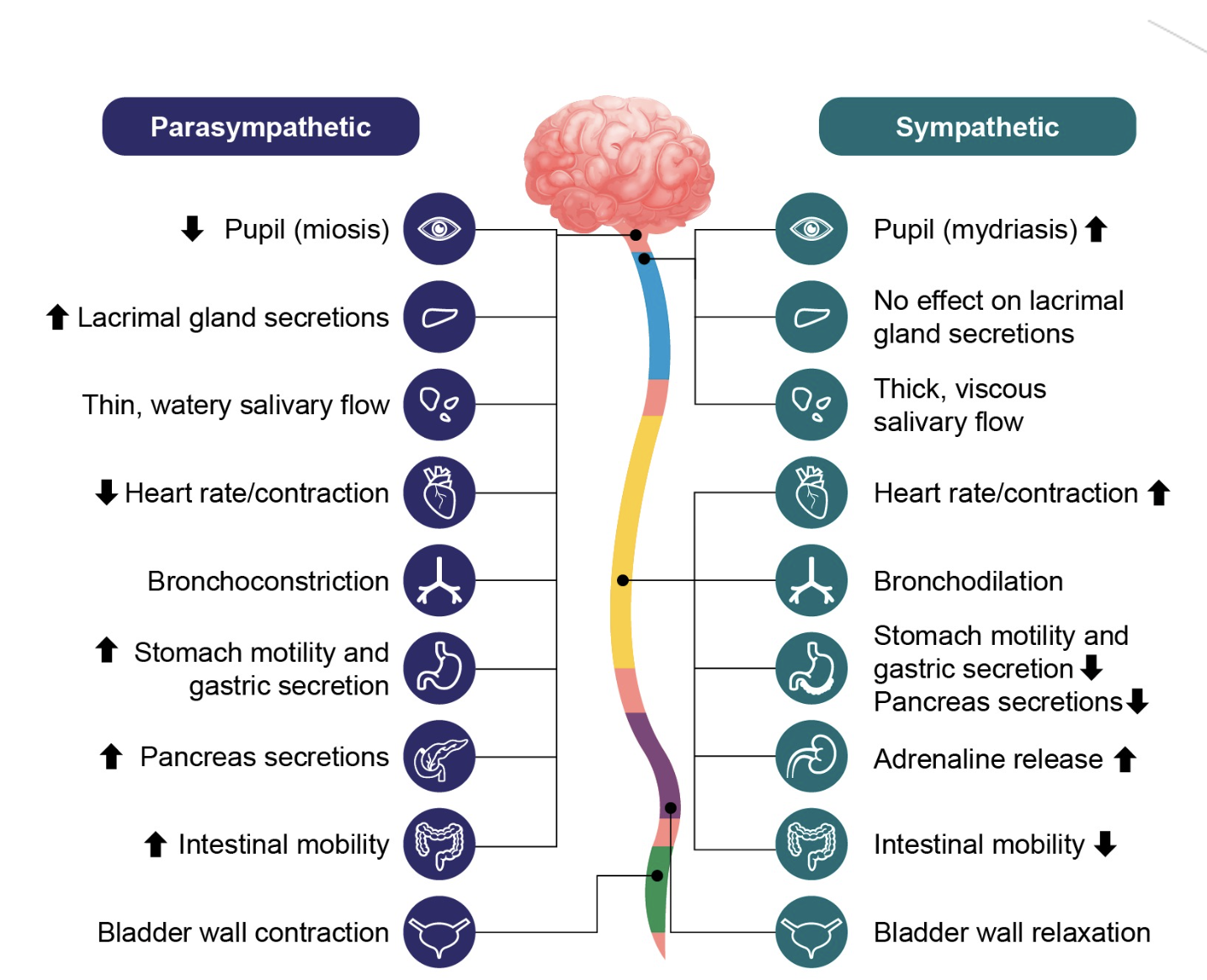
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system:
Fight, flight or freeze
Stimulatory (sometimes)
e.g pupil dilation: allows more light to enter & more vision
Parasympathetic nervous system
Rest & digest
Inhibitory (sometimes)
e.g pupil constriction: lets less light to enter & less vision
Pathway through nervous systemn
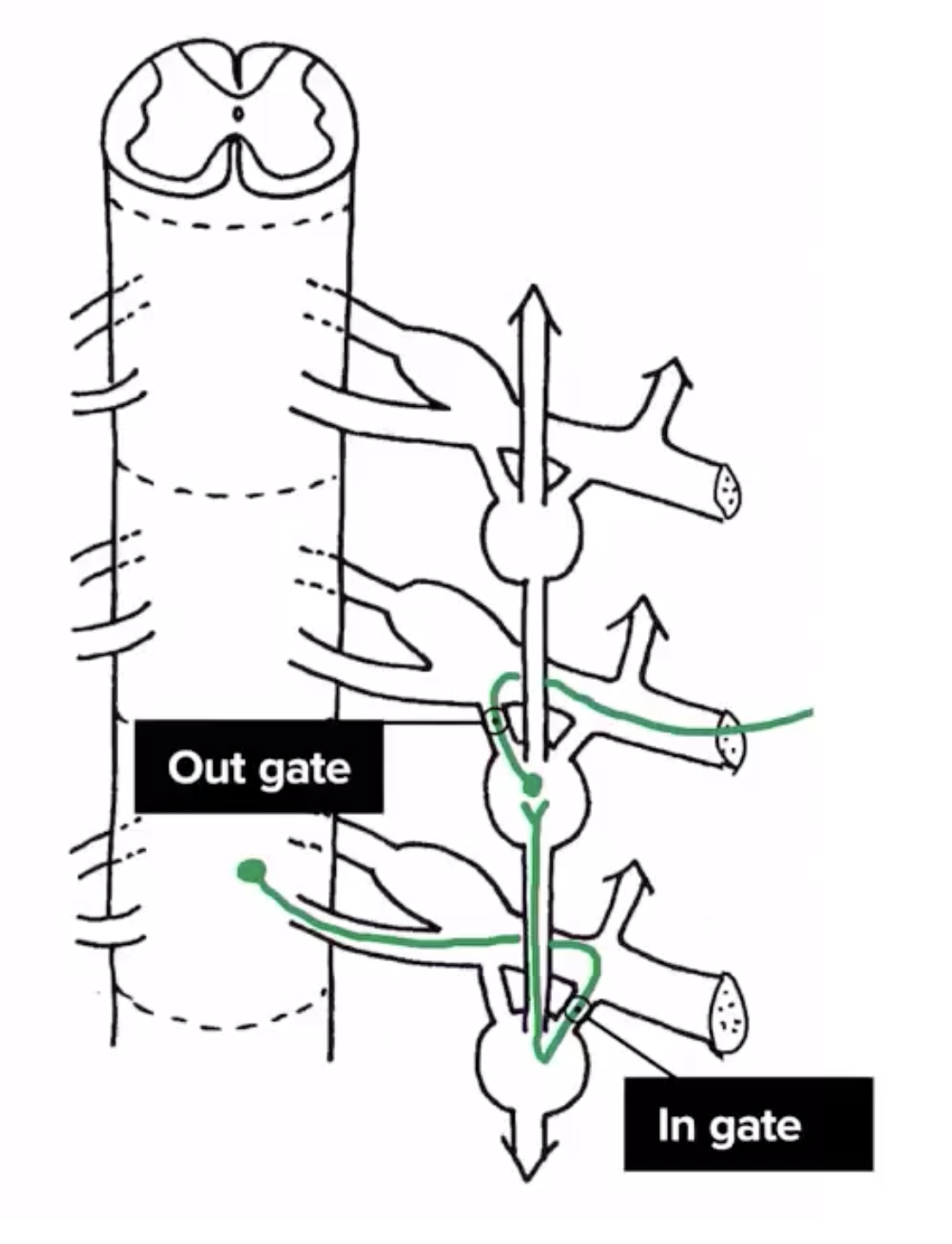
Sympathetic nervous system
Synapse at the same level
Synapse at a higher or lower level
Synapse in a distant collateral ganglion
Thoracomlumbar outflow:
Neurons only exit from the lateral horn of spinal segments
Sympathetic motor neurons originate from the lateral horns of T1-L2 spinal segments
Information travels to the sympathetic chain via the pre-ganglionic neuron
Pre-ganglionic neuron synapses with the post-ganglionic neuron in the sympathetic ganglion which makes up the sympathetic chain via the ingate
post-ganglionic neuron goes out to innervate viscera via the out gate
Pathway through nervous systemn
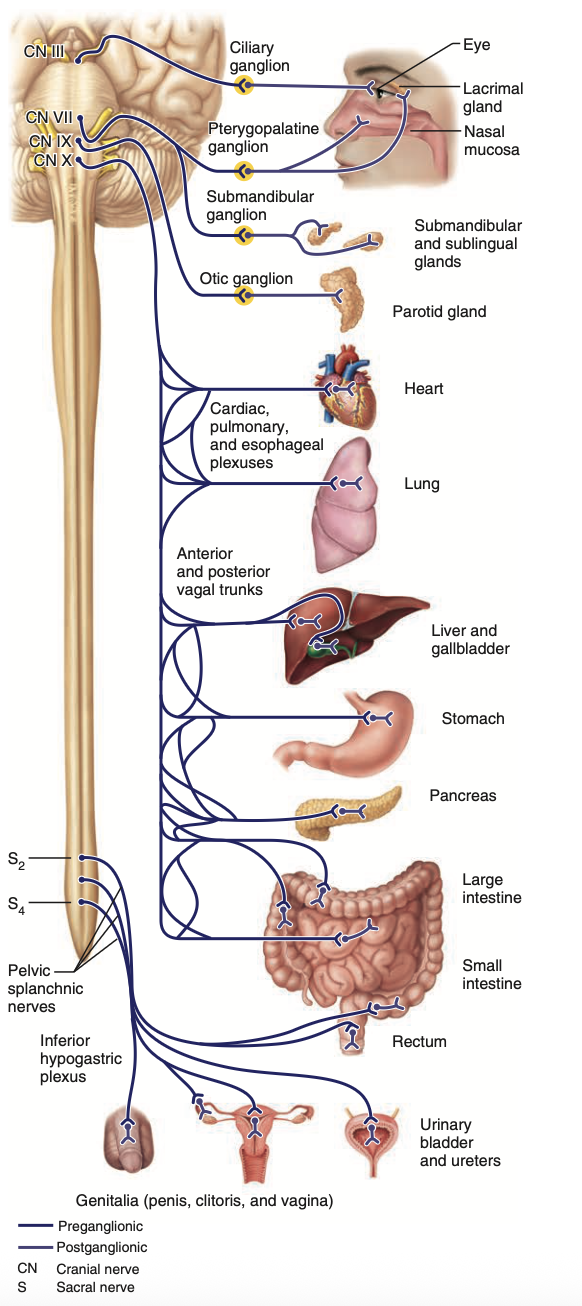
Parasympathetic nervous system
Cranial & sacral divisions/outflow:
Neurons only exit from the grey matter of spinal segments
Sympathetic motor neurons originate from the grey matter of T1-L2 spinal segments (not enough grey matter in sacral spine segments to form lateral horns)
Synapsing of pre-ganglionic neuron and post-ganglionic neuron occurs CLOSE to the visceral structures
Innervates visceral organs
Cranial divisions have synapsing occur close to the organs
Sacral divisions have preganglionic neurons exit from grey matter, synapsing close to true pelvic organs