Aural Rehab Exam 1
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
what's included in the PAS
outer, middle, and inner ear
what is the mode of operation and function for the outer ear
vibration in air ; protection, amplification, amplification
what is the model of operation and function of the middle ear
mechanical energy based on ossicle movement; impedance matching, selective oval window stimulation, pressure equalization
what is the mode of operation and function of the inner ear
hydro-dynamics and hydraulic energy ; filtering, distribution, transduction
what is the mode of operation and function of the central auditory system
electrochemical signals ; information processing
what structures are included in the middle ear
ear drum, ossicles, Eustachian tube, oval and round windows
what's the purpose of the tensor tympani and stapedius muscles
protects middle and inner ear for extreme level of input sound
what is an acoustic impedance
more pressure is needed for a stimulus to be propagated in the inner ear than middle and outer ear
what is the solution for the acoustic impedance problem
33 db
what is the cochlea responsible for
hearing
what is the vestibular system responsible for
maintaining balance
cochlea provides the central auditory system with information about what
frequency, intensity, phase, time
what are characteristics of the cochlea
has 2.5 turns around modiolus, is about 30-35 mm long, has 3 fluid filled scalea
what scalea contain perilymph
scala vestibuli and scala tympani
what is the function of inner hair cells
sends auditory signals to the center brain ; afferent
how many rows are inner and outer hair cells arranged in
IHC = 1 row, OHC=3-5 rows
what is the function of outer hair cells
receive neural signals from the brain ; efferent
what is the stria vascularis
produces endolymph and provides oxygen required for basic metabolic control of the cochlea
what is the tonotopic organization of the cochlea
amplitude of higher simple frequencies are at the basal end, and amplitude of lower simple frequencies are at the apical end
in tonotopic organization, high frequency needs what
higher stiffness and smaller mass
in tonotopic organization, low frequency needs what
lower stiffness and larger mass
what is resting potential in the cochlea
when a neuron is not sending a signal due to insufficient input at rest and no input sound is going into cochlea
what is the difference between polarization and depolarization
polar: separate ; depolarize: bring together
what is hyper polarization in hair cells
when cilia bend away from kinocilium which closes leaking ion channels
what are the 2 functions of central auditory system
preserving information and processing information
what is the pathway for hearing from talker to auditory cortex
sound source, sound propagation in air, peripheral auditory system, cochlear nucleus complex, superior olivary complex, lateral lemniscus, inferior colliculus, medial geniculate body, primary auditory cortex
anterior
rostral
posterior
caudal
superior
dorsal
inferior
ventral
what is the main function of the cochlear nucleus complex
frequency processing
what is the superior olivary complex composed of
lateral superior olive, medial superior olive, and medial nucleus of the medial trapezoid body
SOC is the first structure to receive auditory inputs from both ______ and _____ cochlear nuclei
ipsilateral and contralateral
what is the lateral lemnsicus function
it is unknown! but it does have good temporal resolution compared to others
what is the main function of the inferior colliculus
spectral processing and sound localization
what does the medial geniculate body influence
direction and maintenance of attention
the primary auditory cortex receives input form ipsilateral and contralateral fibers to...
maintain tonotopic representation and retain functional plasticity
amplitude information is neurally coded by what
discharge rates if nerve fibers, number of nerve fibers, and number of related nerve cells
what is phase/time coding
discharge rate of nerve fibers in synchrony to the phase of sound
what is the place theory in frequency coding
that the auditory nerve is also organized topographically
what is the equation for the temporal theory
f=1/t
in the spring and mass system mass causes _____ while spring causes ____
inertia and elasticity
what kind of waves are sound waves?
longitudinal
what is condensation
as the object vibrates away from vibrating object, air pressure increases above static air pressure at any one location
what is rarefaction
as the object vibrates toward the vibrating object, air pressure decreases below the static air pressure at any one location
what is instantaneous amplitude
The amplitude of a waveform at some specific instant of time
which is RMS
2
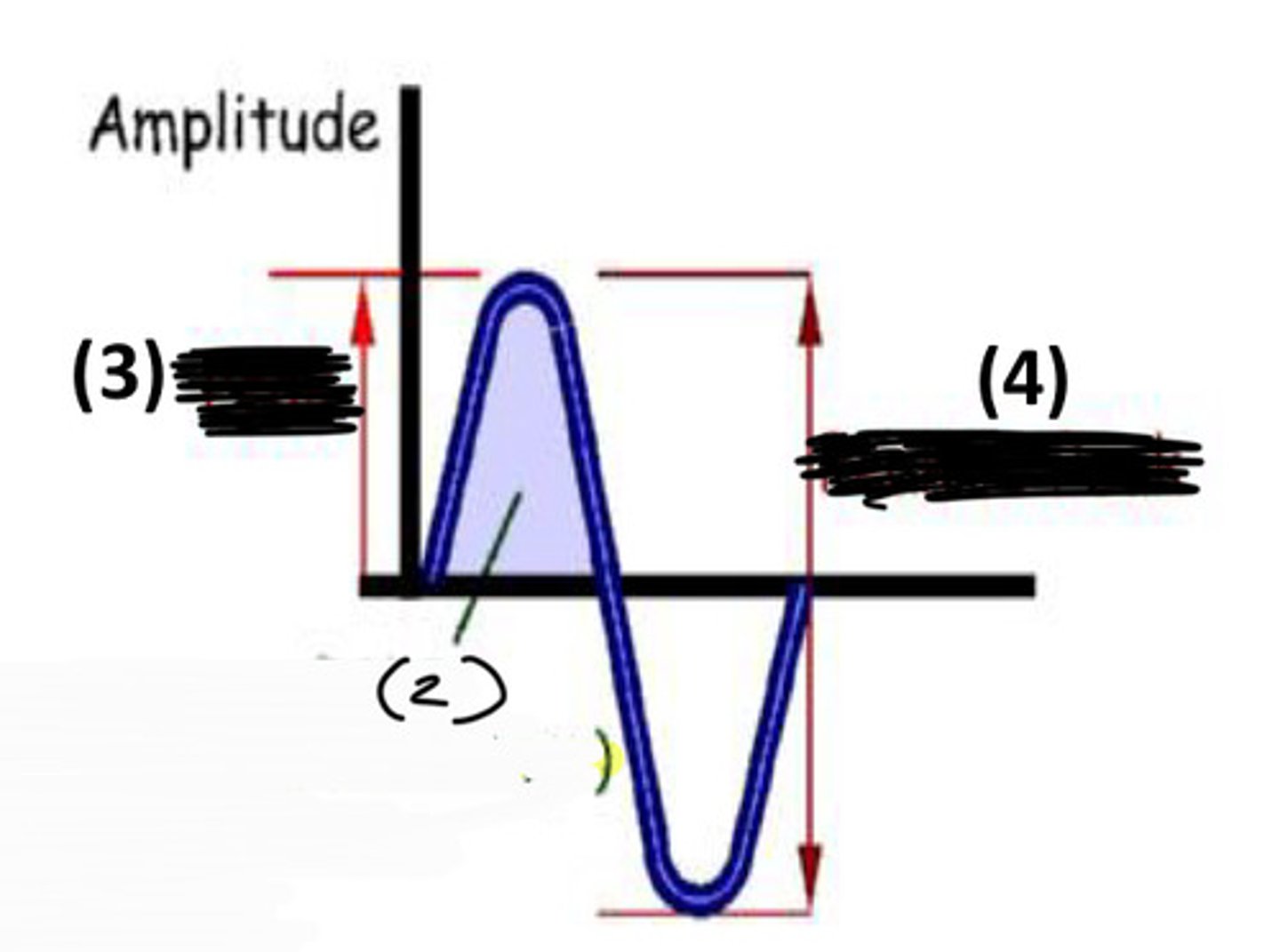
which is peak amplitude
3
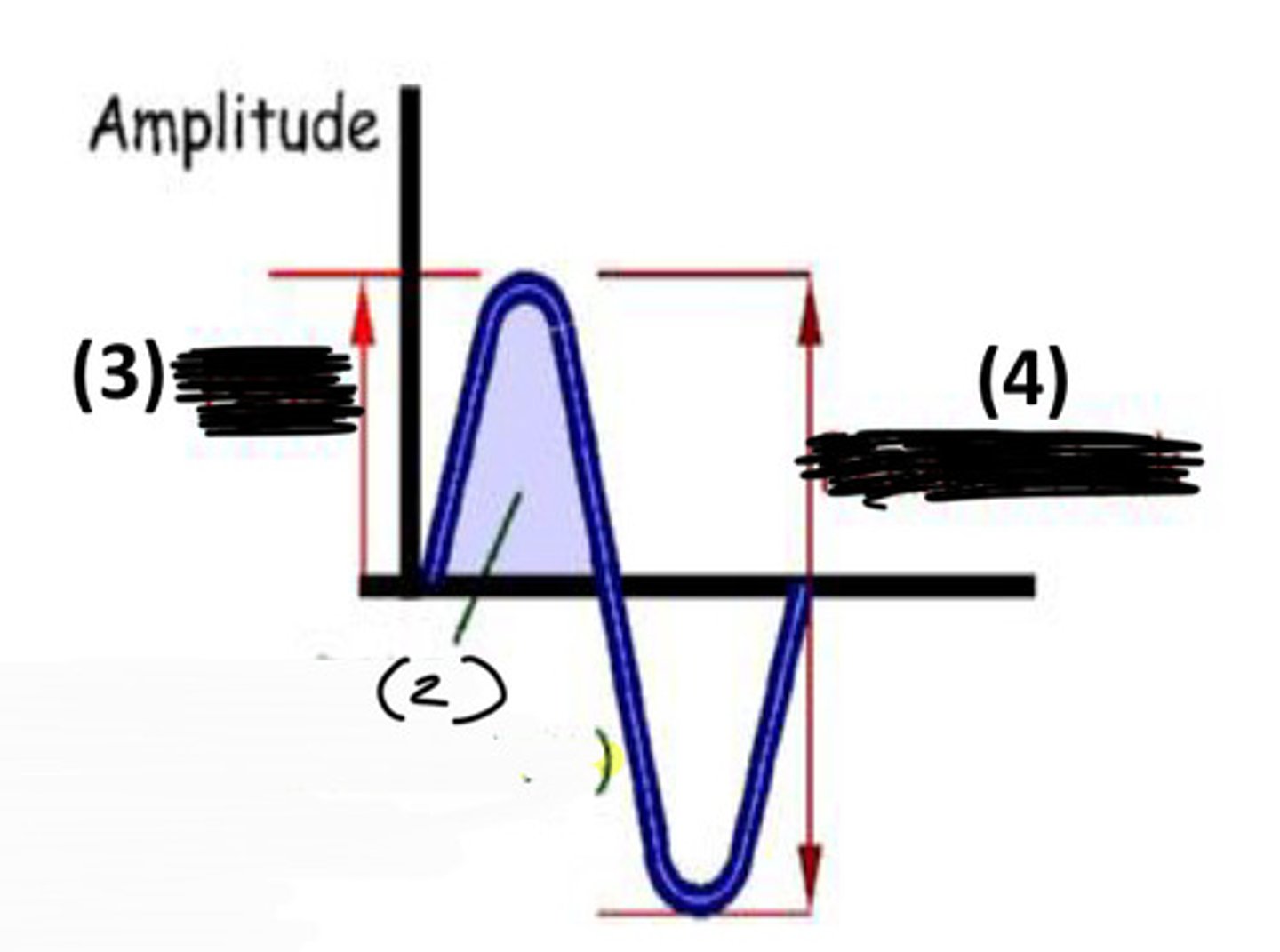
which is peak to peak amplitude
4
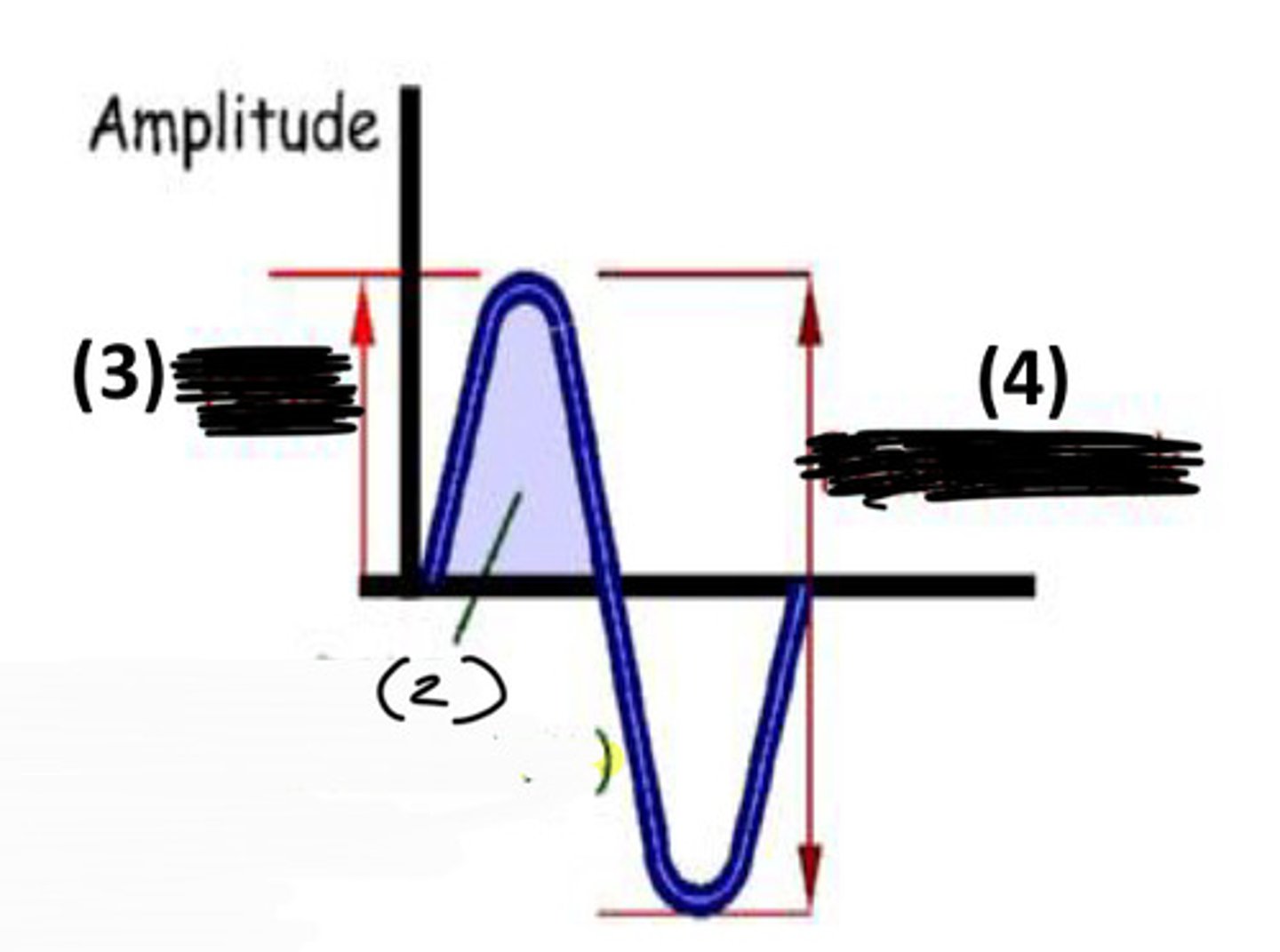
what does RMS apply to and what is the equation
applies to only pure tones; .707 x peak amplitude
what does 180 degrees out of phase look like
both waveforms are mirroring each other
what are transverse waves
air molecules are moved up or down through condensation and rarefaction
what are simple waves
a single sine wave with repeated patterns of vibration
what are complex waves
any vibration consisting of more than one sine waves, can have repeated patterns
who are ideal candidates for hearing aids
people with moderate to severe sensorineural loss
what are the 4 components of a hearing aid
microphone, amplifier, receiver, and battery
what is the purpose of a microphone on a hearing aid
picks up input acoustic sound and converts it to electrical signals
what is the purpose of an amplifier on a hearing aid
increases the amplitude of the electrical signal from the microphone
what is the purpose of a receiver on a hearing aid
converts amplified electrical signal back to acoustic sound
what is the purpose of the battery on a hearing aid
provides power to drive the amplifier
what is the function of a telecoil
uses electromagnetic to help enhance telephone communication
how are directional and omnidirectional microphones different
omnidirectional is equally sensitive in all directions, while directional is designed to respond to sounds from a specific direction
what is dynamic range
the range of intensities from softest sounds we hear to. the loudest sounds
what is the dynamic range for normal hearing
5-105 dbhl
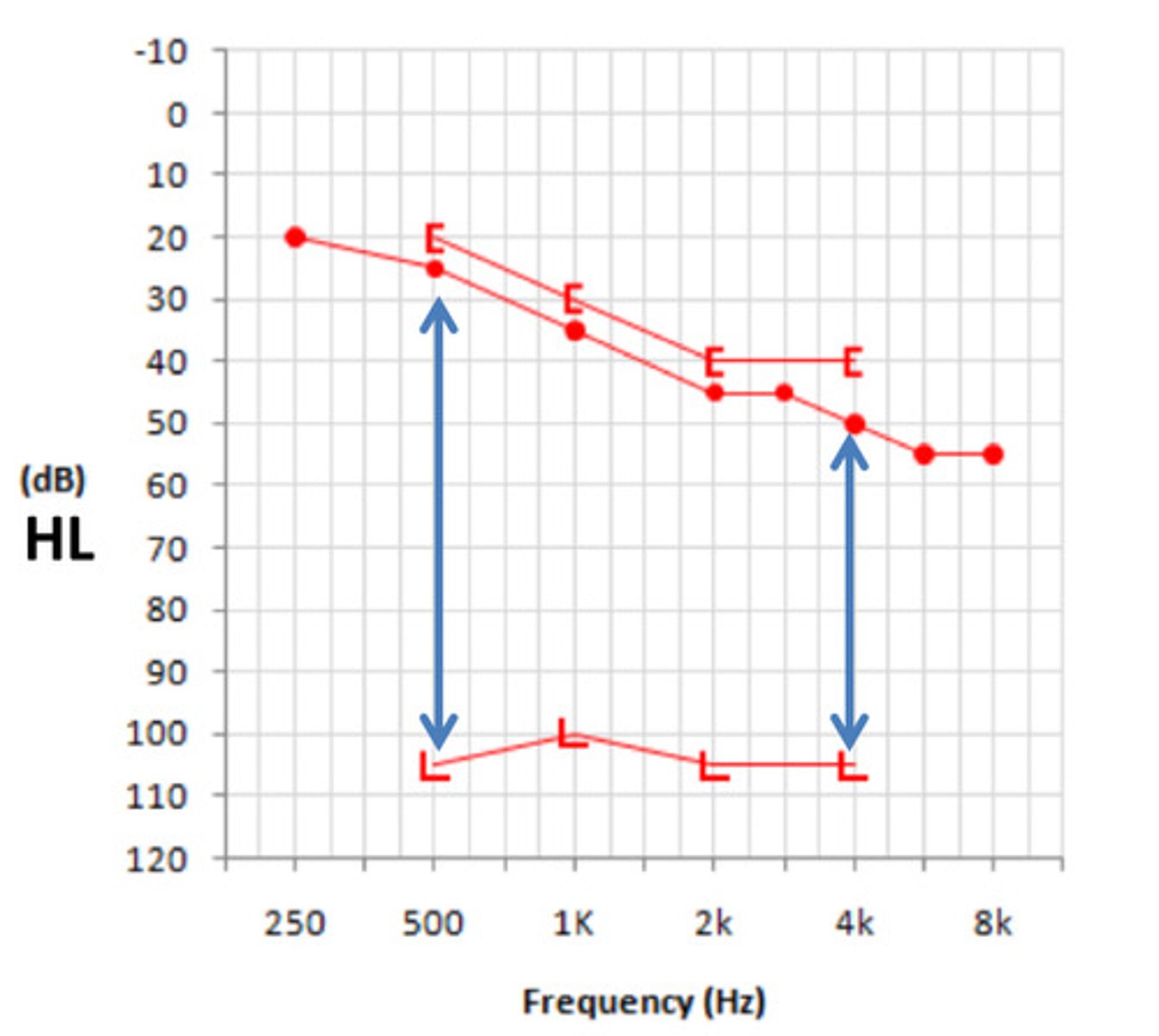
the discomfort level of the hearing impaired listeners is about _______ across frequencies
110 dbhl
gain of a hearing aid can be defined in what 3 ways
difference between aided and unaided, difference between input and output, and difference between input level to hA and output level to HA
what style of hearing aids is more common in adults and teens
teens use more in the canal aids, and adults use more behind the ear aids
what is the most common style of hearing aid
behind the ear
why does a traditional BTE hearing aid need an earmold
it will help deliver amplified sound from hearing aid to the ear, couple the hearing aid to the wearer, and prevent acoustic feedback
what are pros and cons of BTE
pros: high gain, flexibility for most people; cons: stigma compared to customs, wind noise
what are factors to consider when choosing the right hearing aid for your client
gain and hearing aids output needs for HL, audiogram configuration, need for various features, compression characteristics based on dynamic range
what are pros and cons of ITE/ITC
pros: cosmetic appeal, high gain even though small, reduction in wind noise; cons: expensive, problems with acoustic feedback, battery size
what are pros and cons of CIC
pros: invisible and elimination of wind noise; cons: occlusion effect, lower gain, short battery, expensive
what are the guidelines for HA fitting suggested by American Academy of Audiology
selection, quality controls, fitting, verification
what are 3 common approaches to verify HA fitting
electroacoustic outcome measures using devices, audiological measures using behavioral assessment, and self report outcome measures using questionnaire
what is electroacoustic outcome measures using devices
how the hearing aid is performing by real ear measurement
what is audiological measures using behavioral assessment
how patient is performing with HA in terms of speech perception
what is self report outcome measures using questionnaires
how hearing aid users are doing in real world
what are the basic test parameters for an electroacoustic check according to ANSI
gain, frequency, response, OSPL90, HA compression features, distortion limits, directional microphone positioning, and telecoil response
what is OSPL90
90db presented to see how hearing aid reacts and confirm its quality
what is compression attack time
time a hearing aid takes to put less gain when input level is high
what is compression release time
time a hearing aid takes to put prescribed gain when input level is soft
what is the fundamental idea for 2 prescriptive hearing aid measures
NAL-NL1 and 2 and DSL
what does DSL and NAL NL1 and 2 do
DSL makes sounds comfortably loud, and NALNL1 and 2 maximizes speech intelligibility
on an audiogram, what are the units/labels for x and y axis
x - frequency hertz, y - amplitude db
which structure in the cochlea is responsible for sending the signal out to the brain
spiral ganglion; inner hair cells responsible for sending signals
on an audiogram, how do you tell which ear's hair cells are more damaged
whichever loss is considered worse
how do you tell which hemisphere receives better frequency information from an audiogram and what role does the cochlear nucleus complex play in this
on the audiogram, you look at which ear has less loss to determine which hemisphere. the CNC sends signals contralaterally so if the left ear is better, the right hemisphere is receiving better information
what is the difference between 100 hz and 1000 hz
100 hz has 100 complete cycles per second, while 1000 has 1000 complete cycles
frequency is directly related to both _______ and _____
intelligibility and loudness
what is the human audible range
20 to 20000 hz
does amplitude decay over time
yes, the closer to the sound the louder and the further away, the quieter
how do we utilize phase information
binaural hearing and sound localization
what kind of waveforms are speech and music
complex
when does the cochlea completely develop
at birth
how many IHC are in the cochlea compared to OHC
there are about 3500 IHC and 12000 OHC
do both IHC and OHC send auditory neural information to the CNS
yes, even though IHC are afferent and OHC are efferent they both are relaying auditory information
what is the main function of superior olivary complex
sound localization
what is the first structure to send neural signal to contralateral sites
cochlear nucleus
what does the processor do in a hearing aid
controls a whole hearing aid system