genetic diversity and chromosome mutation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what are 2 way of increasing genetic variation
crossing over and independent assortment
what is crossing over
This happens at prophase 1 of meiosis where the bivalents first form. whilst the 2 homologous chromosomes are joined in a bivalent bits from one chromosomes are swapped with corresponding part of the other chromosomes
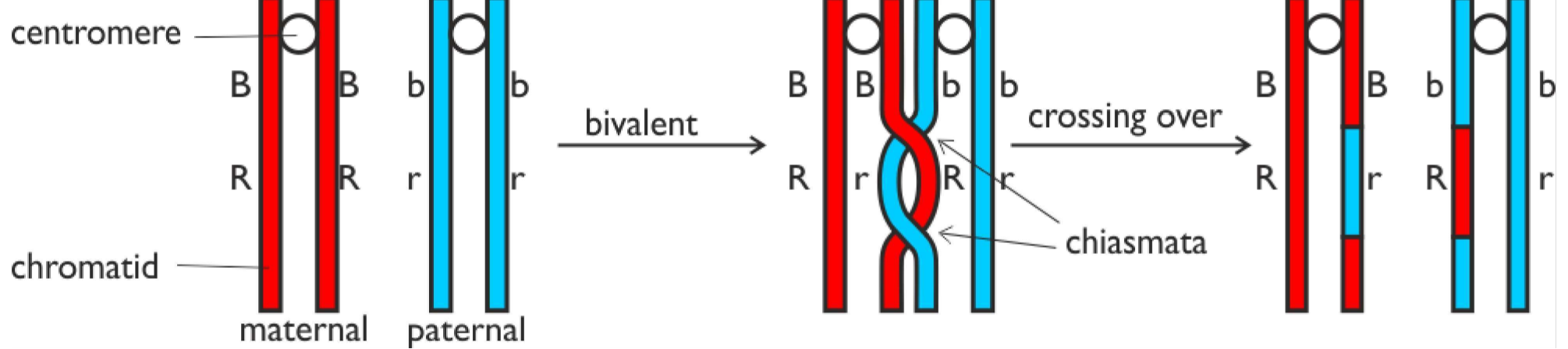
when does crossing over occur
This happens at prophase 1 of meiosis where the bivalents first form
what is the point at which chromosomes cross over
chiasmas
what are specific rules about crossing over
they have to be the same length and same genes that get crossed
how does crossing over diversify genetics
crossing over means that maternal and paternal alleles can be combined even though there on physically different chromosomes. This means gametes can have a new phenotype
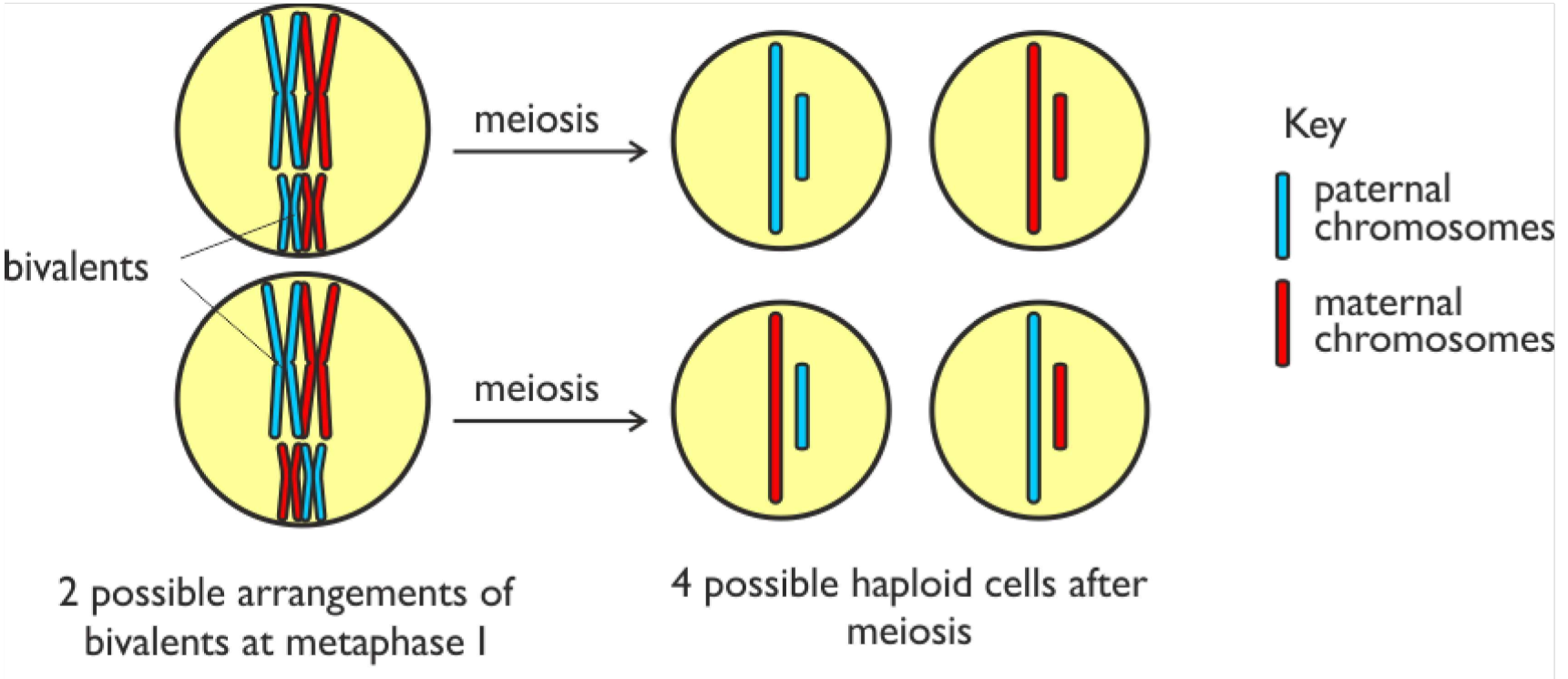
independent assortment
This happens in metaphase meiosis 1 when homologous chromosomes join together to form bivalents that line up at the equator. Each bivalent is made up of a maternal and a paternal chromosome . Since they can line up in any orientation the maternal and paternal version of chromosomes get mixed up in the final gametes
what is a chromosomal mutation
A chromosomal mutation is a change in the number or structure of chromosomes, leading to alterations in the arrangement of many genes.
what are the 2 types of chromosomal mutations
non disjunction and translocation
nondisjunction
this types of mutation changes the number of chromosomes in the cell its cause by a fault in anaphase either one or 2 where either the chromosomes or the chromatids move to opposite poles of the cell. In non disjunction either chromosomes or chromatids get stuck together this result in one cell with an extra chromosome or chromatid and another cell with one less chromosome or chromatid
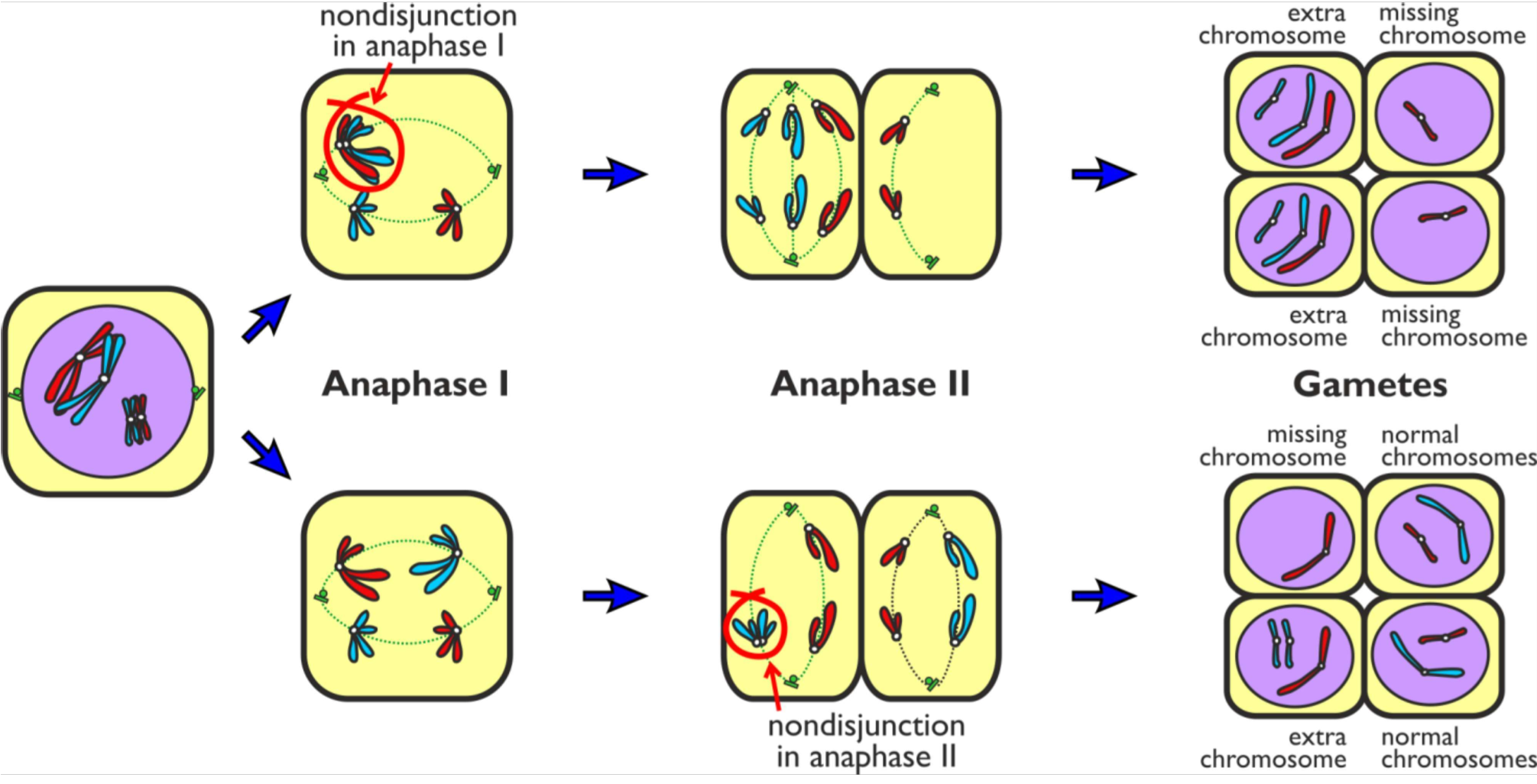
what is monosomy
Monosomy = loss of one chromosome (missing copy).
what is polysomy
Polysomy = gain of extra chromosome(gains a copy).
what is trisomy
This is when there are 3 of the same chromosomes its a form a polysomy
give an example of monosomy
turners and polyploidy
turners
they only have one sex chromosome X hey are sterile
polyploidy
all chromosomes remain together the genome is triploid its very common in the plant kingdom
give an example of polysomy
down syndrome. If a gamete is fertilised by another gamete with an extra chromosome the zygote will have an extra chromosome. down syndrome is caused by trisomy of the 21st chromosome. They have distinct faces and short height heart defects poor vision sever learning difficulties and shorter life expectancy
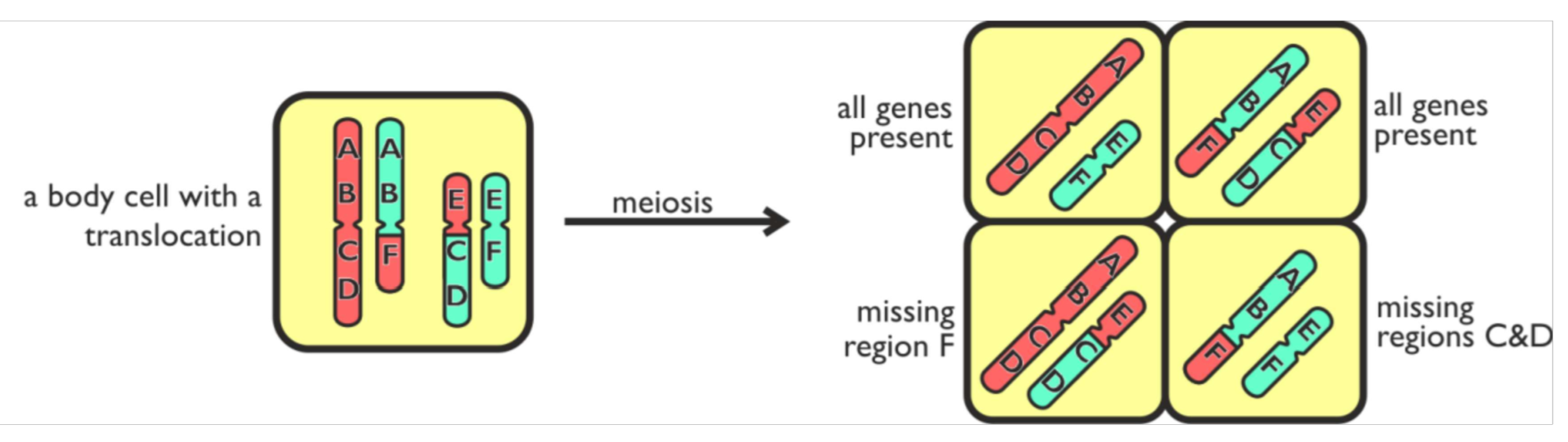
Translocation
A translocation is a chromosome mutation where one part of a chromosome is swapped with part of a different chromosome. This sounds like crossing over. However it doesn’t have to be equal and doesn’t swapping so you end up with different sized chromosomes . The swapping isn’t between homologous chromosomes

why can lots of translocation mutations be harmless
the exact same genes and alleles are still present. Even though some are on different chromosomes
How can translocation mutations cause harm
cell with translocation can undergo mitosis without any problems but meiosis doesn’t work properly since some of the chromosomes are no longer homologous so cant form bivalents properly. Even if meiosis is completed some cells wont have certain genes
also when regions are cut out and swapped into there own locations it may disrupted other genes leading to cancer
fusion gene may be formed this is when 2 parts of genes are fused together the effects are unpredictable