Separation Techniques, Spectroscopy, and Analytical Methods
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
gas liquid chromatography setup
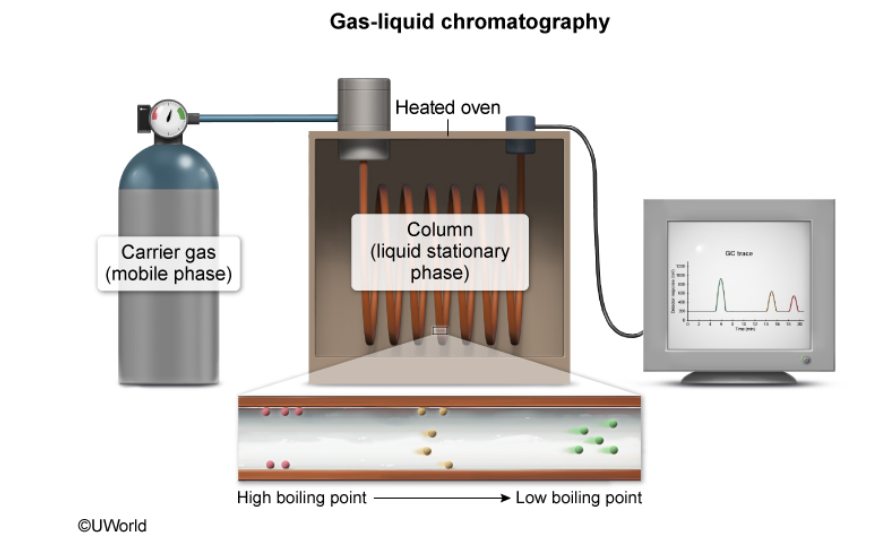
what phases are included in gas-liquid chromatography?
gas mobile phase and liquid stationary phase
what is gas-liquid chromatography?
a technique that separates molecules in a mixture based on their boiling points
what is the mobile phase in gas-liquid chromatography?
the mobile phase is an inert gas such as helium or nitrogen
what is the stationary phase in gas-liquid chromatography?
the stationary phase is a liquid that coats a solid support (a column in a heated oven)
what does a gas chromatograph consist of?
an injector, a stationary phase and a mobile phase, a column inside a heated oven, an injector, and a computer for data analysis
how does gas-liquid chromatography start?
a small amount of a liquid mixture is injected into the gas chromatogram, and the compounds in the mixture are vaporized by heating
what happens to the vapors in gas-liquid chromatography?
the vapors then travel through the column in a heated oven to the detector
what happens to molecules with low boiling points in the gas-liquid chromatography?
the most volatile molecules (i.e. low boiling points) spend more time in the gas phase than they spend interacting with the stationary phase of the column, so they rapidly migrate to the detector
what happens to molecules with high boiling points in gas-liquid chromatography?
molecules with high boiling points condense more readily and spend more time interacting with the liquid stationary phase, these molecules make their way through the column slowly as the temperature in the oven increases
in gas-liquid chromatography, how are mixture components primarily separated?
mixture components are separated primarily based on boiling point
what factors account for boiling point in gas-liquid chromatography?
boiling point is determined by several factors, e.g. polarity, intermolecular forces, molecular weight
for molecules with the same number of carbons, how does the boiling point increase?
the boiling point increases with the increasing strength of intermolecular forces and relative polarity
what is an example of a sufficiently large nonpolar molecule that can have a higher boiling point than a small polar molecule?
for example, a nonpolar 20-carbon alkane chain has a higher boiling point than a polar 4-carbon carboxylic acid (343 degrees Celsius vs 164 degrees Celsius) and would move through the column more slowly despite being relatively nonpolar
in gas-liquid chromatography, the column must be placed where?
the column must be placed in a heated environment to allow volatile molecules to remain in the gas phase, columns kept at room temperature would not separate the molecules
what is the difference between molecules with lower boiling points and molecules with higher boiling points in gas-liquid chromatography?
molecules with lower boiling points reach the detector before molecules with higher boiling points
dilution factor formula
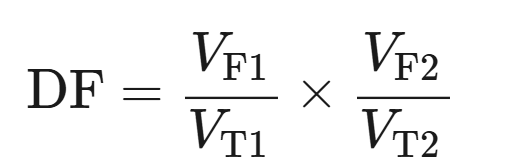
what is the identity of a precipitate in a hydrazinolysis reaction?
the least soluble component of the reaction mixture is the major component of the precipitate
what is solubility?
the solubility of a substance is a quantitative measure of the maximum mass that can be dissolved in a specific volume of solvent
what are solubility trends?
solubility trends typically adhere to the premise of “like dissolves like,” where solubility increases when the polarity of the solute is similar to the polarity of the solvent
what is solubility often directly related to?
since a compound’s polarity results from the presence and spatial arrangement of functional groups, solubility is often directly related to molecular structure and its intermolecular forces with other materials
how does the solubility of solid solutes increase?
with temperature, the heat provides additional kinetic energy to overcome the intermolecular forces between solid molecules and between solvent molecules
how can cooling a solution form a precipitate?
if the solubility of the solid solute decreases and the quantity of dissolved solute exceeds the new, lower solubility limit
how do you determine the best solvent for an organic extraction?
if a compound is polar, the second liquid needs to be an organic liquid that does not dissolve in the compound