Honors Bio Cellular Structure and Function Unit 4.5
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/39
Last updated 3:22 AM on 1/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
endocytosis
when a cell takes in an external substance through the cell membrane by creating vesicles (sacks) to “hug” it in
2
New cards
exocytosis
to get rid of macromolecules that are too big for the cell, it releases macromolecules by fusing the vesicle with the plasma membrane
3
New cards
large cell size makes it…
hard to move nutrients into the cell
4
New cards
cells function best when
there is a larger surface area to volume ratio
5
New cards
small cell size makes it…
easy to absorb nutrients and excrete waste
6
New cards
unicellular organisms…
reproduce/clone asexually via cell division
7
New cards
multicellular organisms…
use cell division to grow and develop, and repair and renew cells once fully grown
8
New cards
interphase
when a cell grows and copies its DNA in prep for mitosis--90% of the cell cycle happens here
9
New cards
G1 phase “first gap”
cell growth and protein synthesis
10
New cards
S phase (synthesis)
dna replicated
11
New cards
G1/S Checkpoint
if cell does not pass, cycle stops completely, goes into senescence
12
New cards
G2 phase“second gap”
growth, protein synthesis, and organelle development
13
New cards
mitosis
division of nucleus, then division of cytoplasm (cytokinesis)
14
New cards
G2/M checkpoint
if cell does not pass, cycle stops to prepare DNA
15
New cards
G0 (senescence)
cell retirement home, waiting to die
16
New cards
apoptosis
cellular suicide…cell is damaged/gets signal proteins, shrinks, proteins help break down cell components, enzymes break down nucleus, cell parts removed from the body
17
New cards
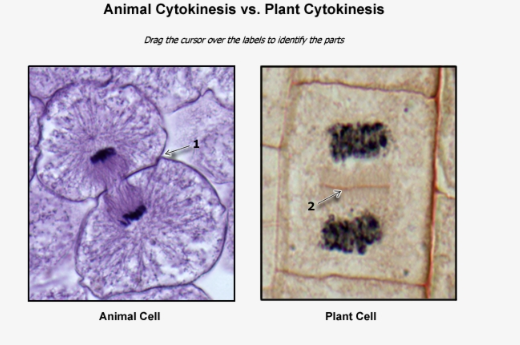
in plant cells, vesicles form…
a cell plate
18
New cards
in plant cells, the cell plate…
forms a cell wall, causing the cell to split into two daughter cells
19
New cards
metastasis
the spread of cancer cells
20
New cards
in animals, cells are separated by…
the cleavage furrow drawing the plasma membrane towards the center, until the cell is eventually split into two daughter cells
21
New cards
the stages of mitosis in order are…
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
22
New cards
prophase
chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and mitotic spindle starts forming
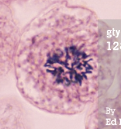
23
New cards
chromaTIN
substance from cell’s nucleus made of proteins and dna…
24
New cards
chromaTID
two sister chromatids make up a chromosome
25
New cards
chromosome
humans have 46, half from each parent chromatin condenses into chromosomes as the cell enters the mitotic phase
26
New cards
metaphase
nuclear membrane/envelope disintegrates, sis chromatids line up along metaphase plate with help from spindle fibers
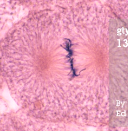
27
New cards
metaphase plate:
invisible line that separates the two poles in a cell
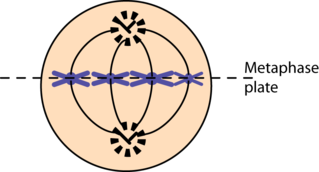
28
New cards
anaphase
spindle fibers pull the sis chromatids apart, towards opposite poles. centromeres of the chromatids break apart

29
New cards
telophase
genetic material is completely separated, two new nuclear membranes/envelopes are formed around the chromosomes
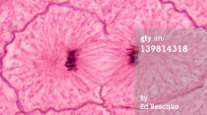
30
New cards
cytokinesis
completion of mitosis, cytoplasm and cell organelles are separated
31
New cards
cancer cell abnormalities:
* too many dividing cells,
* large, dif shaped nuclei
* large nucleas to cytoplasm ratio
* dif shapes and sizes of cells
* loss of norm cell features
* disorganized, jumbled
* poorly defined tumor boundary
* large, dif shaped nuclei
* large nucleas to cytoplasm ratio
* dif shapes and sizes of cells
* loss of norm cell features
* disorganized, jumbled
* poorly defined tumor boundary
32
New cards
when mitosis and apoptosis are not in homeostasis…
tumor can form
33
New cards
prophase
34
New cards

anaphase
35
New cards
metaphase
36
New cards

\
telophase/cytokinesis
37
New cards
\
prophase
38
New cards
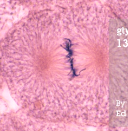
metaphase
39
New cards
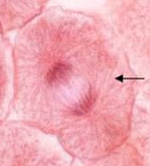
anaphase
40
New cards
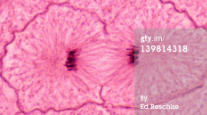
telophase/cytokinesis