comparative anatomy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
nucleus
contains chromatin: DNA complexed with histones (nucleosomes)
site of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA synthesis
euchromatin/ heterochromatin (denser)
inside of nucleus, all sorts of nucleic acids
rough endoplasmic reticulum
membrane network covered with ribosomes
site of protein synthesis (outerface allows them to be modified)
specific sorting signals allow import into RER
smooth ER
no protein synthesis
lipid synthesis
toxin breakdown
golgi complex
carbohydrate synthesis
modification of proteins for specific targeting
involved in protein trafficking through the membrane
lysosomes
originate from golgi, can fuse with other vesicles
contains digestive enzymes to hydrolyse macromolecules
originate from ER → incorporate lipids and proteins from cytoplasm
oxidises alcohols and fatty acids
mitochondria
organelle with its own genome (15kbp and 37 genes)
mitochondria multiply by division
rich in membranes
produces ATP and reducing power
chloroplasts
made of thylakoids and found in the stroma
converts light into organic compounds via calvin cycle
own circular DNA/ translation machinery and multiply by division
flagella/ cilia
consists of a bundle of 9 pairs of microtubbules surrounding central pair (axoneme)
microtubules are connected to adjacent ones via nexin molecules
motion is driven by ATP hydrolysis, carries out by dynein molecules
microtubules slide against one another, giving a whiplike movement
made up of cytoskeleton
nucleoid
usually a singular, circular chromosome
DNA complexes with histone-like proteins (compact)
genetic material also includes plasmids
cytoplasm
some prokaryotes do contain organelles
contains several inclusion bodies
carboxysomes
storage granules (S, PO43-, N)
gas vesicles
envelope
made up of multiple layers: cytoplasmic membrane, peptidoglycan, polymers covalently bound to peptidoglycan and outer membrane
appendages
pilus: appendage dedicated to conjugation
fimbriae/pili: involved in adherence to host cells/surfaces; antigenic structures made of 1 major protein
flagella: supramolecular assembly involved in bacterial motility
ATP hydrolysis causes a conformational change causes rotation
endosymbiotic origin of eukaryotes
stable incorporation of endosymbiotic bacteria resulted in the formation of mitochondria and chloroplasts
nucleus appears before the acquisition of mitochondria and chloroplasts by endosymbiosis
origin of organelles
mitochondria: originated from engulfment of H2- producing bacterium by a H2-consuming archarea
nucleus: genes for lipid synthesis were transferred to host
chloroplasts: acquired later by endosymbiosis
protozoa ecological importance
ciliates play a role in a food web (zooplankton)
apicomplexans have a major impact on human health
dinoflagellates are key players in the carbon cycle
alveolates
contains alveoli- cytoplasm sacs of fluid surrounded by a lipid membrane
motile organisms
mostly aquatic but not exclusively
ciliates
alveoli under cytoplasmic membrane
cilia and trichocyst (protusible filaments)
contains many digestive vacuoles
2 (can vary) micronuclei and a macronuclei
the micronuclei is usually diploid and the macronuclei is haploid, allows for transcription of RNA
undergoes binary fission or conjugation
use cilia for motility and to capture prey
ampicomplexa
spore-forming protozoans
contains an apical complex involved in entry into the host cell
apicoplast: generates chloroplast (no chlorophyll) carrying out fatty acid metabolism
undergoes many morphological changes during its life cycle
predatory algae: dinoflagellates
mixotrophs: uses sources of energy that are not light or carbon (other than CO2)
responsible for algal blooms
2 flagella including 1 wrapped around the cell
cell walls can be made of cellulose plates called thecae
contains extrusome
mostly vegetative reproductions and can exist as dormant
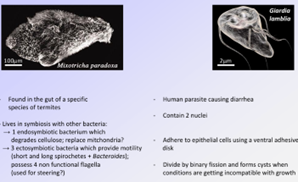
other parasitic protozoa: metamonads and trypanosomes
mobile, mostly harmful parasites
can be transmitted via a vector or direct contact
transmitted through a fly
2 successive phases of the disease: fever, headache, lymph node inflammation or if not treated; the parasite invades the central nervous system, disrupting sleep cycles
can also infect cattle
slime molds and amoebas
very common predatory organisms found in damp environments
display a complex life cycle with distinct morphology
both share developmental stages with a similar morphology
differentiate to multicellular reproductive stage when food supply is low
amoebas are responsible for human diseases
amoebas
shape is extremely variable
conferred by pseudopods created by actin polymerisation/ disassembly
the mechanism is shared with human phqgocytes
Cellular slime mold: Dictyostelium discoideum
grows as an amoeboid unicellular organism that divides by binary fission
under starvation, cells produce a metabolite (cAMP) that drives aggregation to form a slug which undergoes differentiation onto a fruiting body
spores (cysts) are released to initiates a new cycle
Plasmodial slime mold: physarum polycephalum
physarum grows and divides by binary fission as an ameboid single cell
individual cells can aggregate to form a plasmodium
the plasmodium then undergoes differentiation into a fruiting body
spores (cysts) are released to initiate a new cycle