E155 Homeostasis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
set-point
The physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates
What are the components of a negative feedback loop and what is the function of each one?
sensor/receptor, control center, effector
sensor/receptor
monitors a physio value and alerts the control center of changes
control center
compares changes identified by the sensor to the normal values
effector
causes change to revert back to normal values
What are some examples of physiological variables that are regulated by a negative feedback loop?
homeostasis, body temperature, blood sugar concentration
negative feedback loop
a mechanism that reverses a deviation from the set point… maintains body parameters within their normal range
positive feedback loop
intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition rather than reversing it.
Example = childbirth
positive vs negative feedback
Positive feedback increases the response, while negative feedback takes measures to decrease it.
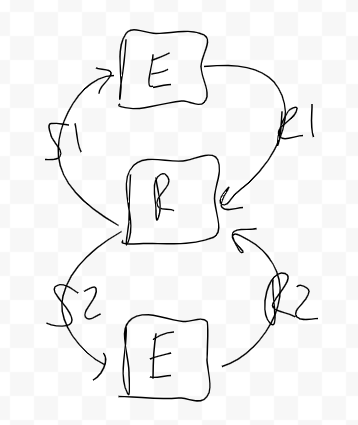
Draw and describe a simple feedback loop that includes a(n) effector, receptor, response and stimulus.
Example = seeing a speed limit sign
Receptor (R): human eye
Effector (E): foot to step on the gas
Stimulus 1 (S1): going 40 mph
Response 1 (R1): slowing down
Stimulus 2 (S2): going 20 mph
Response 2 (R2): speeding up
Explain why Type I diabetes is an example of a disrupted feedback loop
T1D: when the pancreas is unable to produce insulin, which is responsible for bringing glucose into the cell from the bloodstream
Without insulin, the negative feedback loop is disrupted, therefore, to ensure proper function, DM1 patients use insulin injections.
homeostasis
regulation of various values
physio variable: pH, osmosis, ions, glucose, BP, blood gases, body temp
some deviation along the set point
you have a pt with an elevated body temp. make a diagram that shows how the body temperature will be returned to normal
increase body temp → sensor (central hypothalamus; peripheral skin receptors) → integrating center (hypothalamus) → effector (different sites like sweat glands) → response (blood vessels constriction or dilation, metablism, sweating, muscles
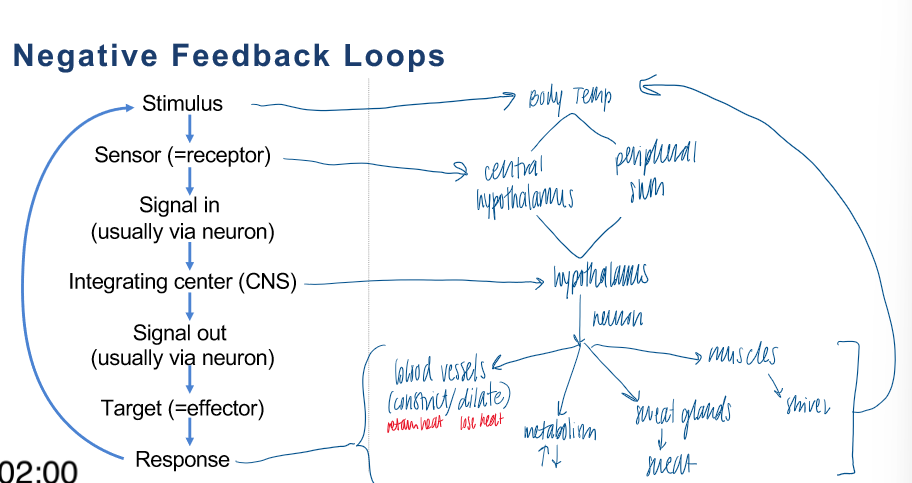
what happens if the blood vessels cannot constrict efficiently
hypothermia
losing heat because the body cannot retain it via constriction
stays in a dilated position, losing heat
blood vessels and heat
constriction = retaining heat
dilation = losing heat
simple positive feedback loops
ex - someone yells “pop quiz” → panic level increases → number of people running away increases → also increases panic level
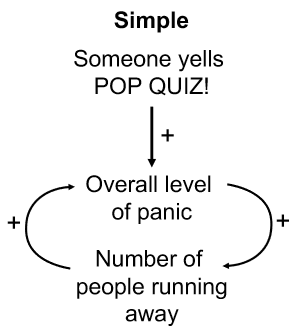
examples of positive feedback loops
blood clotting after a wound
iniation = a cut that damages blood vessels
variable sensed = chemicals being released
variable amplified = platelet count
receptor = skin receptors
effector = immune system
ex - immune activation, sepsis, ovulation
why is this false? homeostasis is the same thing as an equilibrium
homeostasis revolves around a set point that moves forward and backward rate of the reaction
homeostasis is maintaining around the set point, not necessarily equilibrium
why is this false? negative feedback always means that a variable (ex - heart rate) is decreasing
negative feedback always means a variable is maintained with homeostasis (ex - glucose concentration can go up or down)
why is this false? heart rate can change, therefore, it is a regulated variable
HR = no receptor specific to HR (HR is not regulated; it changes due to regulation of something else)
regulated variable: narrow range (ex = BPM could have a wide range)