Genetics unit 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards
The central dogma of molecular biology
DNA- RNA- proteins
2
New cards
Stages of transcription
Initiation, elongation, termination
3
New cards
Function of rna polymerase
Synthesize a strand of mRNA in 5-3
4
New cards
mRNA ends
5’ g cap and a 3’ poly a tail to prevent other enzymes eating it up
5
New cards
Purpose of RNA splicing
Introns removed by spliceosomes exons are pasted together to make a mature mRNA strand
6
New cards
Large ribosomal subunit
Catalyzes peptide bond formation
7
New cards
Small ribosomal subunit
Decodes genetic message
8
New cards
Alternative splicing
More tan one stand of mRNA can be made from the same gene
9
New cards
Histones
DNA is wrapped around positively charged proteins that provide structural support to the chromosome
10
New cards
Histone acetlyation
Alters chromatin structure and allows dna binding proteins to interact with exposed sites to activate transcription
11
New cards
DNA methylation
Represses transcription
12
New cards
Operon structure
Operator promoter and structural genes
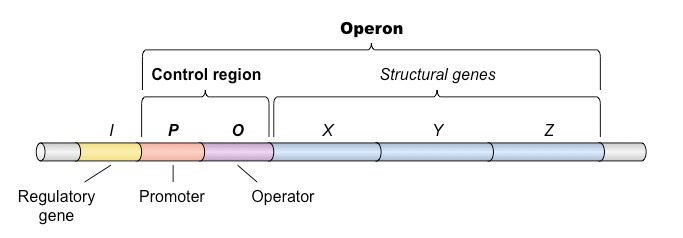
13
New cards
Repressor
Turns transcription off when turned on (TRP)
14
New cards
Inducer
Turns transcription on (LAC)
15
New cards
CRISPR
Go in an edit one specific gene
16
New cards
Gene therapy
Use viruses to deliver functional copies of genes
17
New cards
Gene switches
Alter the switches with regulate the expression of genes by binding to different proteins that affect rna polymerase
18
New cards
Exon skipping
Shortened but functional protein
19
New cards
Small molecule drugs
Interact directly with disease causing proteins block negative affect s of disease causing proteins or restore