YEAR 10 BUSINESS
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
WHAT IS AN ENTREPENEUR?
A person who sets up a business or businesses, taking on financial risks in the hope of profit.
BEING SELD EMPLOYED (ADV)
ADVANTAGES
Sense of independence
own profit, reward and satisfaction
develop own ideas
employ family members
BEING SELF EMPLOYED (DISADV)
hard work and longer hours
income may fluctuate
risk of failure
stress
high levels of responsibility
SOLE TRADE → LEGAL STRUCTURE
OWNER HAS AND OPERATED BY ONE PERSON
HAS UNLIMITED LIABILITY AND UNINCORPORATED
Adv:
Low entry cost/operation cost
Complete control
Less government regulation
Dis:
Unlimited liability/unincorporated
Difficult to operate when sick
End of business when owner dies
PARTNERSHIP → LEGAL STRUCTURES
OWNER AND OPERATED BY 2-20 PEOPLE
CAN BE FORMED VERBALLY, IN WRITING OR WITHOUT ANY LEGAL BNDING AGREEMENT
HAS UNLIMITED LIABILITY AND UNINCORPORATED
Adv:
Low entry/operation cost
Shared responsibility and workload
Business continues if parter dies
Dis:
Unlimited liability/unincorporated
Possibility of disputes
Difficulty finding suitable partners
PRIVATE COMPANIES → LEGAL STRUCTURES
2-50 PRIVATE SHAREHOLDERS, USUALLY HAS ‘PTY LTD’ AT THE END OF ITS NAME
INCORPORATED, LIMITED LIABILITY
SHARES ONLY SOLD IF THE DIRECTOR APPROVES
ADVANTAGES OF OWNING A COMPOANT
EASIER TO ATTRACT FINANCE
LIMITED LIABILITY/INCORPORATED
EXPERIENCED MANAGEMENT
DISADVANTAGES OF OWNING A COMPANY
COST OF FORMATION
DOUBT TAXATION
MUST MAKE A YEARLY ANNUAL REPORT OF ACCOUNTS
WHAT IS PROMOTION
MAKING PEOPLE AWARE OF YOUR BUSINESS
ADVERTISING → PROMOTION MIX
messages communicated through mass media
ADVANTAGES
Attracts attention
Shares in about business to wider audience
DISADVANTAGES
Costly for advertisements
Risk of low response rates
PERSONAL SELLING→ PROMOTION MIX
the activities of a sales representative directed to a customer to make a sale
ADVANTAGES
Personalised approach → assuming their needs
DISADVANTAGES
Hiring and training a sales force can be expensive
RELATIONSHIP MARKETING →PROMOTION MIX
making long-term, cost effective and strong relationships with individuals customers
ADVNTAGES
Increased customer lifetime value
Improved customer retention
DISADVANTAGES
Difficult to manage time
The expectations of returning customers
SALES PROMOTION → PROMOTION MIX
the use of activities or materials as direct inducements to customers
ADVANTAGES
Enhances the attraction to new customers
Increases productivity and performance of employees
DISADVANTAGES
Short-term impact
Cannibilisation: sales promotion reduces to regular products/services or shift the demand from one period to another
PUBLICITY → SALES PROMOTION MIX
any free news story about business product (not under business control)
ADVANTAGES
Credibility
Cost effective
Broad reach
DISADVANTAGES
Lack of control
Negative publicity
Unreliable timing
PUBLIC RELATIONS → PROMOTION MIX
activities aimed at creating and maintaining favourable relations between the business and its customers
ADVANTAGES:
enhanced brand credibility
Cost-effective
DISADVANTAGED:
increased competition
Unpredictable
PLACE STRATEGIES → DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS
DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS REFERS TO THE CHANNELS CHOSEN TO GET THE PRODUCTS TO THE CUSTOMER. THERE ARE THREE TYPES OF DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS. THESE INCLUDE:
PRODUCER TO CUSTOMER
PRODUCER TO RETAILER TO CUSTOME
RPRODUCER TO WHOLESALER TO RETAILER TO CUSTOMER
CHANNEL CHOICES → PLACE STRATEGIES
CHANNEL CHOICES REFERS TO HOW AVAILABLE THE BUSINESS CHOOSES TO MAKE THE PRODUCT ACROSS A MARKET. THERE ARE THREE CHANNEL CHOICES, THESE INCLUDE:
INTENSIVE
SELECTIVE
EXCLUSIVE
INTENSIVE → CHANNEL CHOICE
Business is available in all stores
ADV:
increased market coverage,
higher sales volume
DIS:
lower profit margins,
increased distribution costs
SELECTIVE → CHANNEL CHOICE
Business is open in certain stores
ADV
greater control over brand image
Better retailer relationships
DIS
Limited market reach
Increased pressure on brand loyalty
EXCLUSIVE → CHANNEL CHOICE
Business is open only in the actual store itself
ADV
strong brand image and prestige
Increased customer loyalty
DIS
Limited market reach
High dependency on the chosen retailer
WHAT IS HUMAN RESOURCES
The management of the relationship between employee and employers
TYPES OF TRAINING METHODS
off the job training → ex, taking courses
On the job training → ex, being taught how to make meals at a restaurant
Mentoring → ex. A mentor is not a dictator, simply a help and guide
BENEFIT OF TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT → NEW WORKERS
Opportunities for promotion and self improvement
Improved job satisfaction through better job performance
A challenge (chance to learn new things)
INTERNAL SOURCE OF FINANCE
funds generate from inside the business
Main type of finance is; retained profits
Retained profits = profits that are kept in the business for investments in future business activities
In Australia, approx 50% off profits retained to be reinvested.
EXTERNAL SOURCE OF FINANCE
funds provided from sources outside the business
Debt and equity
ADVANTAGES OF DEBT
owner does not have to sell any ownership in the business
Easy to access
Tax deductions
DISADVANTAGES OF DEBT
Needs to be repaid
Has interest
Makes company less attractive to investors
May need to offer ‘collateral’
ADVANTAGES OF EQUITY
No repayments need to be made
Low risk
No additional financial burden
Cheaper source of finance
Investors with expertise and connections
DISADVANTAGES OF EQUITY
loss of ownership and control
Dividends must be paid
Reduced profits for owners
Can’t be acquired at short notice
3 TYPES OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
CASH FLOW STATEMENT
INCOME STATENMENT
BALANCE SHEET
CASH FLOW STATEMENT
indicate the movement of cash receipts and cash payments resulting from transactions over a droid of time.
Measures liquidity → the ability to meet short-term financial obligations
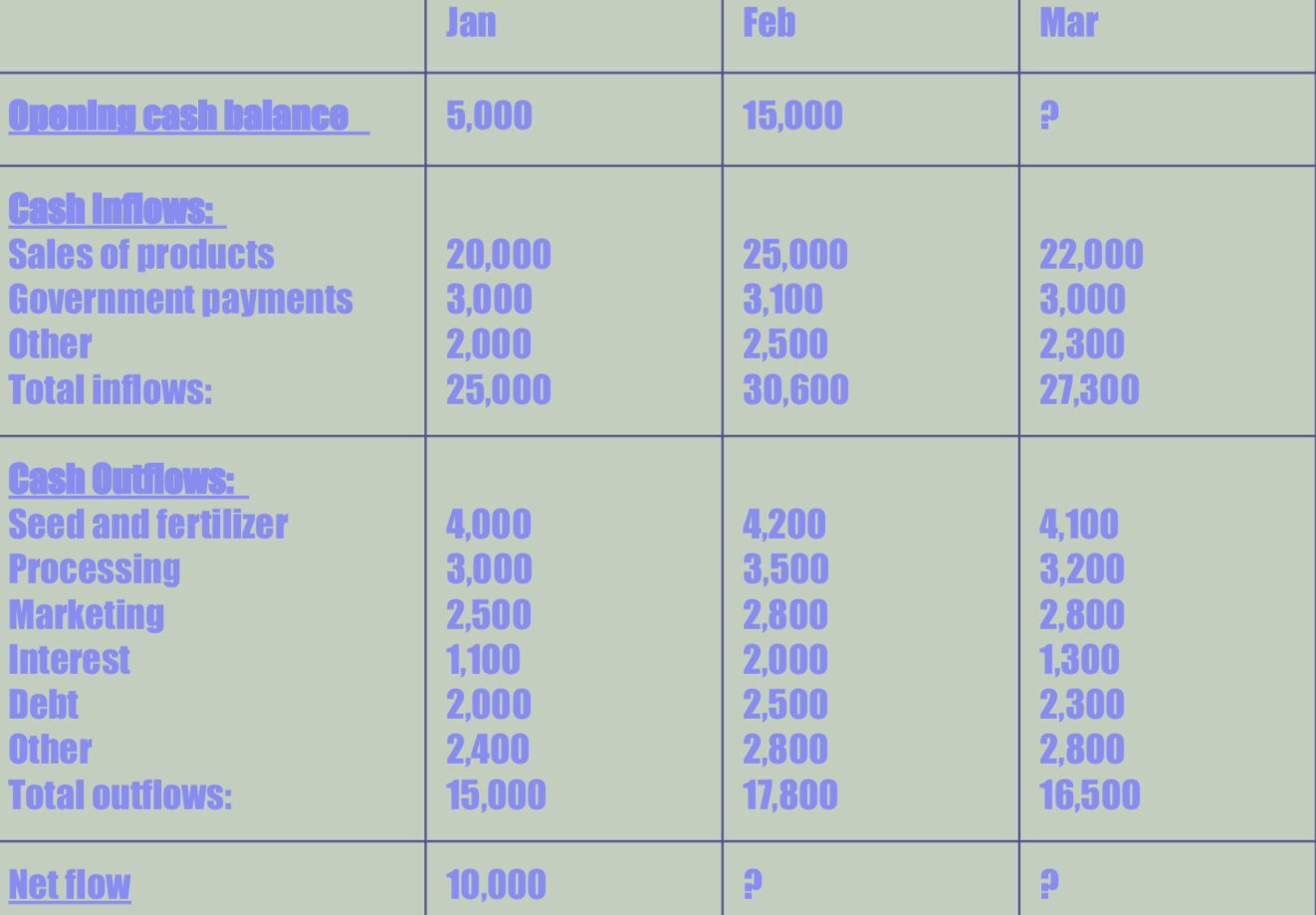
CASH INFLOW → MONEY COMING IN
Sales
Loan
Investment (equity)
CASH OUTFLOW → MONEY COMING OUT
Debt
Wages
Bills
Marketing
WHAT IS LIQUIDITY
means to see if you accomodate for financial obligation
FORMULA:
INFLOW - OUTFLOW → OPENING BALANCE + NETFLOW = CLOSING BALANCE
MARKET SHARE
IS THE AMOUNT OF SALES A BUSINESS HAS IN A INDUSTRY
SHARE MARKET
SHARE MARKET IS WHERE YOU GO TO BUY SHARES (ASX)