HG Unit 2 Test (continued)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
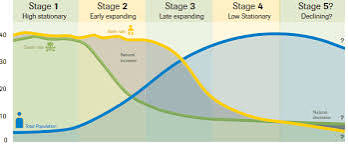
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
based on historical population trends of two demographic characteristics – birth rate and death rate
Demographic Momentum
the tendency for growing populations to continue growing after a fertility decline because of their young age distribution
Epidemiological Transition Model
describes changing patterns of population distributions in relation to changing patterns of mortality, fertility, life expectancy, and leading causes of death
Boserup Theory
population growth is a postive force in agricultural innovation, that it drives technology foward
Pronatalist Policy
For birth
Birth bonuses, both cash and goods
Lower tax rates with increasing numbers of children (Japan,Italy)
Anti natalist policy
Against birth
Prevention of births and termination of births
Bangladesh, India, China
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration
counter migration
most migration throughout history has been from rural to urban areas
woman are most likely to move internally while men are more likely to move internationally
Counter migration
migration flows produce movemnets in the opposite direction
Gravity model
migration will be higher in countries with a high population
people move to the places closest nearby and places that have large urban centers
Aging Population
the dependency ratio is growing as fewer and fewer people are supporting more and more retirees
Migration
permanant move to a new loction
Net Migration
diffrence between immigrants and emigrants
Intervening Obstacles
barriers that make reaching their desired destination more difficult
Intervening Opportunities
a feature (usually economic) that causes a migrant to choose a destination other than his original one
Voluntary Migration
a movemnet undertaken by choice that is often permanant
Involuntary/ Forced Migration
movement where people do not have a choice
International Migration
movement outside the country you are leaving
Internal migration
movement within international borders
Interregional Migration
historically rural to urban for jobs
across a region
Intraregional Migration
usually within urban areas from older cities to newer suburbs
within a region
Refugee
a person being forced to leave their country, cannot return
Asylum seekers
a person who has left their country and is seeking protection from persecution and serious human rights violations in another country, but who hasn't yet been legally recognized as a refugee
Internal Displaced Persons
has been forced to migrate for similar political reasons as a refugee but has not migrated across an international border
Tranhumance
nomadic herding; seasonal migration
Transnational Migration
across international borders
Chain Migration
follow previous relatives
Step Migration
series of small, less extreme moves
Rural to Urban Migration
movement from a rural place to an urban place
Guest Workers
people who migrate to the more developed countries of Northern and Western Europe, usually from Southern and Eastern Europe or from North Africa, in search of higher-paying jobs
Remittances
money earned in their new country mailed back home
nearly 40% of the income of countries like Tajikistan and Kyrgyzation
Zelinsky Migration Transition Model
because of high population growth in stage 2 and 3 countries, people will migrate to countries in stage 4 or 5
Xenophobia
an aversion or hostility to, disdain for, or fear of foreigners, people from different cultures, or strangers
Ethic Enclaves
a geographical area where a particular ethnic group is spatially clustered and socially and economically distinct from the majority group