MGT 180 MIDTERM 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Research & Development department
Oversees invention and redesign; develops innovations needed to keep company ahead of competition.
-Responsible for "product" portion of 4 P's
-invents new products and changes specifications for existing products
R&D Marketing decisions
-the positioning of each products inside a market segment on the Perceptual Map
-the number of products in each segment
-the age of products
-the reliability (MTBF rating) of each product
R&D Production decision
-the cost of material
-the purchase of new facilities to build new products
-automation levels (the higher the automation level, the longer it takes to complete an R&D project)
repositioning
requires a new size attribute and/or a new performance attribute
-to keep up with segment drift, a product must decrease its size and increase its performance (down & to the right of the perceptual map)
-repositioning a product can change age (if it is newer and improved, the customers cut the age in half)
Positioning costs
affects material costs - the more advanced, the more expensive
Reliability (MTBF) costs
MTBF = reliability rating for existing products; improving reliability increases material costs
Marketing department
department responsible for drumming up interest in the company's products & in charge of sales forecasting
-responsible for 3 remaining P's: price, place, and promotion
promotion
product's promotion budget determines its level of awareness
sales
product's sales budget contributes to segment accessibility
-segment's accessibility percentage indicates the number of customers who can easily interact with your company via salespeople, customer support, deliverty, etc.
sales forecasting
predicting future sales levels and sales trends
-manufacturing too many units --> higher inventory carrying costs
-manufacturing too few units --> stock out and lost sales opportunities
Production department
Puts everything together; coordinates and plans manufacturing runs
-each product has its own assembly line
-need to consider sales forecasts to determine the number of units to produce for the upcoming year
First-shift capacity
number of units that can be produced on an assembly line in a single year with a daily 8 hour shift
Second-shift capacity
Assembly line can produce up to twice its first-shift capacity (2,000,000 per year, can produce 4,000,000 units with a second shift)
-second-shift labor costs are 50% higher than the first shift
selling capacity
selling all units on assembly line/liquidating products in order to discontinue product
automation
The use of technology to ease human labor or to extend the mental or physical capabilities of humans.
-as automation levels increase, labor costs and the number of labor hours required to produce each unit falls.
TWO factors to be considered:
1. automation is expensive
2. as you raise automation, it becomes increasingly difficult for R&D to reposition products short distances on the Perceptual Map (long moves are less affected).
Finance department
monitors the company's flow of money; verify that sales forecasts and prices are realistic; make worst case (lowering forecasts) and best case (raising forecasts) proformas & compares them to next year's annual reports
-concerned with 5 issues:
1. Acquiring the capital needed to expand assets, particularly plant and equipment.
- capital can be aquired through: current debt, stock issues, bond issues (long term debt), & profits
2. Establishing a dividend policy that maximizes the return to shareholders
3. Setting accounts payable policy and accounts receivable policy
4. Driving the financial structure of the firm and its relationship between debt and equity
5. Selecting and monitoring performance measures that support your strategy
current debt
borrowed money that must be repaid within one year
-company can "roll" that debt by simply borrowing the same amount again
-as a general rule, companies fund short term assets like accounts receivable and inventory with current debt offered by banks.
-no brokerage fee
bonds
Certificates of debt that carry a promise to buy back the bonds at a higher price; all are 10-year notes
-as a general rule, bond issues are used to fund long term investments in capacity and automation
stock
A share of ownership in a corporation.
-as a general rule, stock issues are used to fund long term investments in capacity and automation
credit policy
Company determines the number of days between transaction and payments
-shortening A/R (accounts receivable) recovers a loan made to customers; reduces customer survey score
-extending the A/P (accounts payable) extract loan from your suppliers; suppliers withhold material for production as lag grows
Value Chain Analysis
strategy tool used to analyze internal firm activities. Its goal is to recognize, which activities are the most valuable (i.e. are the source of cost or differentiation advantage) to the firm and which ones could be improved to provide competitive advantage.
-operating efficiently creates value for customer, customer is willing to pay more
SWOT analysis
Strengths: business processes, team, skills, education, technology
Opportunities: markets, regulations, perception utilization
Weaknesses: improvement, assets needed, team gaps
Threats: competitors, suppliers, change in consumer behavior
KPI (Key Performance Indicators)
The quantifiable metrics a company uses to evaluate progress toward critical success factors; measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives
-companies use to determine if they are in good shape, borderline in trouble, or in trouble
TQM (Total Quality Management)
A philosophy that involves everyone in an organization in a continual effort to improve quality and achieve customer satisfaction.
-In a TQM effort, all members of an organization participate in improving processes, products, services, and the culture in which they work.
HR (Human Resources)
the division of a company which hires employees and takes care of all employee-related matters (recruitment, training, staffing)
-train individuals so that they can be better at their work
Strategy
all about positioning for sustainable competitive advantage (having something that is difficult to copy or can not be copied)
-assets, attributes, abilities that are hard to duplicate
-well drafted strategy needs an integrated plan to win, clear source of sustainable competitive advantage, and communication at all levels
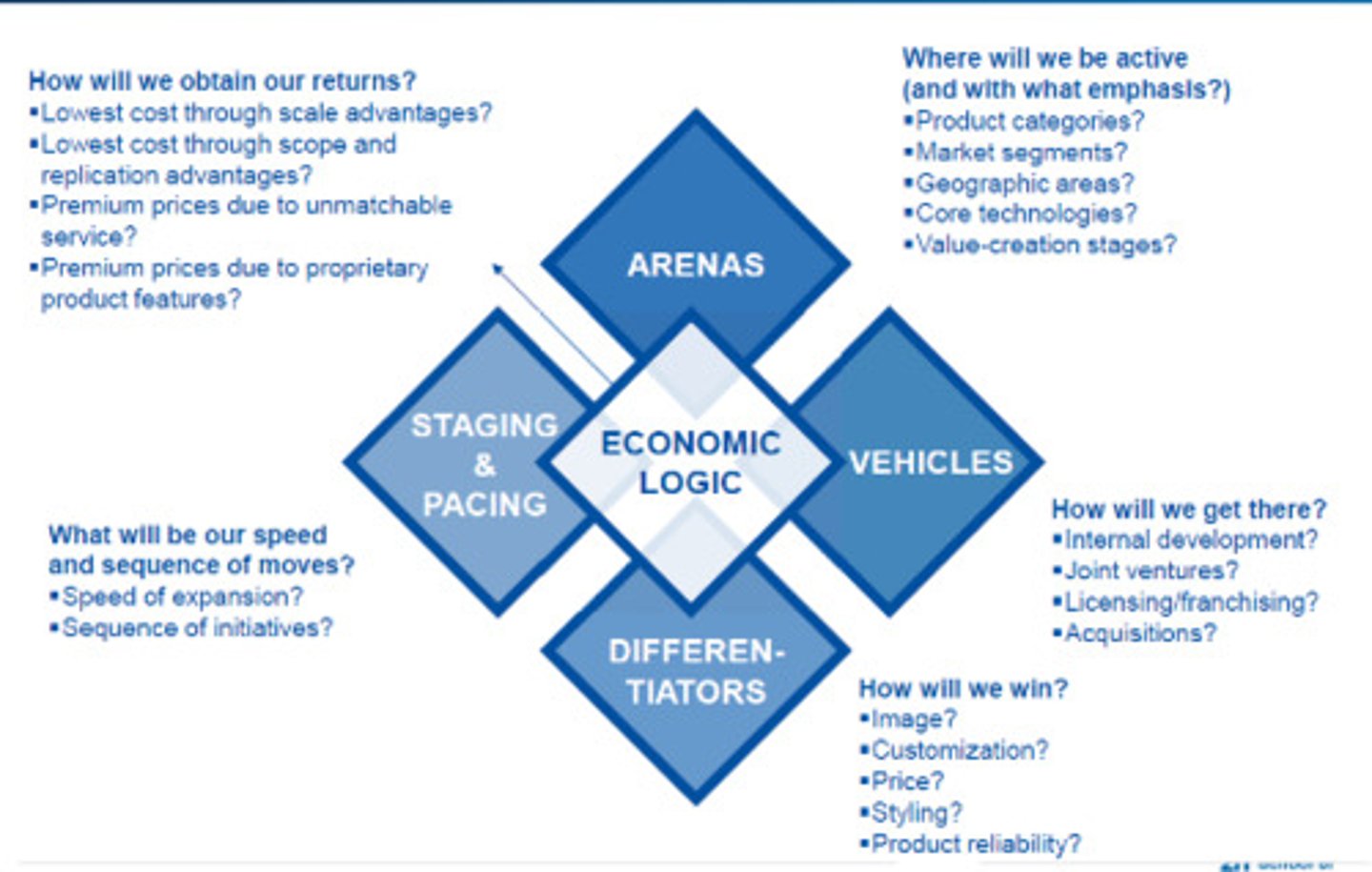
Strategy Diamond: Staging
-timing and sequence
-when to make a move
-how to allocate resources
Strategy Diamond: Arenas
-place to do business
-target market/customers
-product category
-geography
Strategy Diamond: Differentiation
-Why us? Things that make you different
-innovation, price
-quality, brand, service
Strategy Diamond: Vehicles
-how to get there
-acquisitions
-internal
-joint ventures
Strategy Diamond: Economic Logic
-how to make profit
-cost leadership or differentiator
Broad Cost Leader
-both markets; attempts to be the low-cost producer in every segment of the market
-use R&D to keep costs low
-compete on price
-high automation
i.e southwest, walmart
Broad Differentiator
-both markets; It wants to be well known as a maker of high quality/highly desirable products.
-design, awareness, accessible
-R&D will pace with market
-prices above average
i.e starbucks
Niche Cost Leader
-seeks to dominate the price- sensitive low tech market; Its aim is to set prices below all competitors — and still be profitable.
-use R&D to keep costs down
-compete on price
-high automation
Niche Differentiator
-concentrates on the high tech segment and gains a competitive advantage by distinguishing its product with an excellent design, high awareness, and easy accessibility
-R&D will pace with market
-prices above average
Cost Leader: Product Lifecycle Focus
-seek to minimize costs through efficiency and expertise. Products will be allowed to age and change in appeal from High End, to Traditional, and eventually Low End buyers
-keep costs at a minimum
-compete on price
-use mature high-tech product in low-tech segment
i.e toyota
Differentiator: Product Lifecycle Focus
-seeks to be known far and wide as the top producer of the best performing state-of-the-art products.
-design, awareness, accessible
-high tech to low tech segment; multiple product lines in targeted segments (High End, Traditional, and Low End)
-R&D pace with market; continually reposition product lines and keep products fresh
-price above average
i.e apple
What makes a strategy a good strategy?
The elements of the strategy are congruent --> have to complement each other
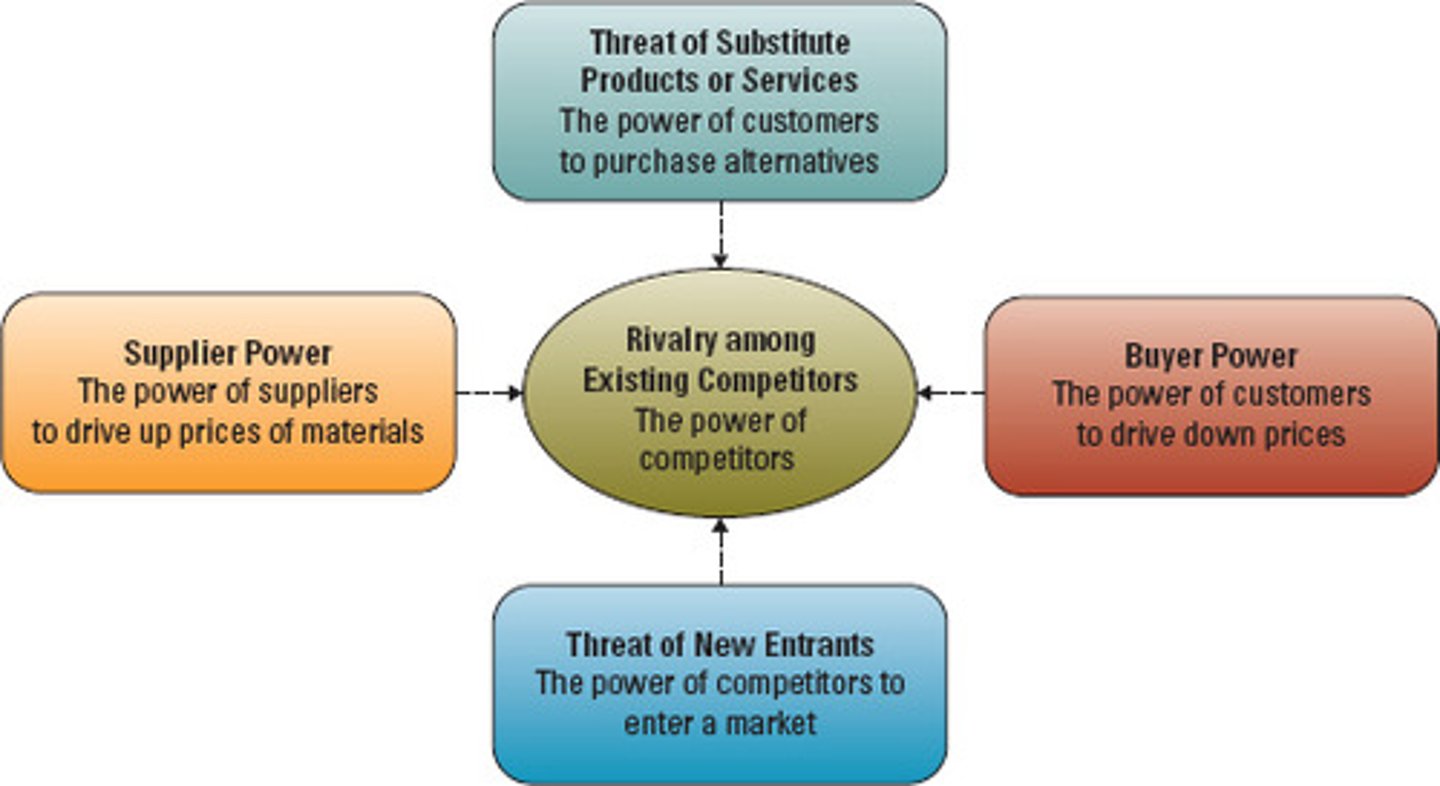
Five Forces that Shape Strategy
1. Bargaining power of suppliers
-cost management
-more suppliers drive cost down, less suppliers drive cost up
2. Threat of substitutes
-cross product substitution
-cost of change
3. Bargaining power of buyers
-switching cost can be low
-bargain shoppers
-force industry to lower price
4. Threat of new entrants
-barriers to entry (capital, strong players, government)
5. Rivalry among existing competitors
-focal industry
core competencies
those functions that the organization can do as well as or better than any other organization in the world
-competencies = "what they are good at" i.e materials engineering
-core products = "applications" i.e adhesives, films/substrates
-business = "stuff they make" i.e post it notes, surgical tape
When is a sustainable competitive advantage obtained?
1. needs to be VALUABLE (customers find value in it)
2. needs to be RARE
3. can't be COPIED (no one can easily create something similar)
4. ducks in order: ORGANIZED management systems, processes, policies, organization structure and culture
-needs to meet ALL 4 criteria for there to be advantage
Resource vs. Capability
-Resources = things we have
-Capabilities = things we can do (aka "competencies"); the ability to do something productive with resources, organize and perform complicated tasks using many resources
Capabilities can turn into liabilities
-capabilities are hard to adapt
-tightly integrated and congruent activities create efficiency, but when environment changes or competitors render them obsolete, they're hard to change
-companies have to change with the times in order to not fall behind
Data and forecasting
prediction - take old data and create a trend to show what future will look like
-as you go further into the future, the prediction is going to lose more confidence; need to update forecast often
What happens when forecasts are off?
-if demand underestimated, lost sales and drop in stock value
-if demand overestimated, there is overstock --> inventory write and down and drop in stock value
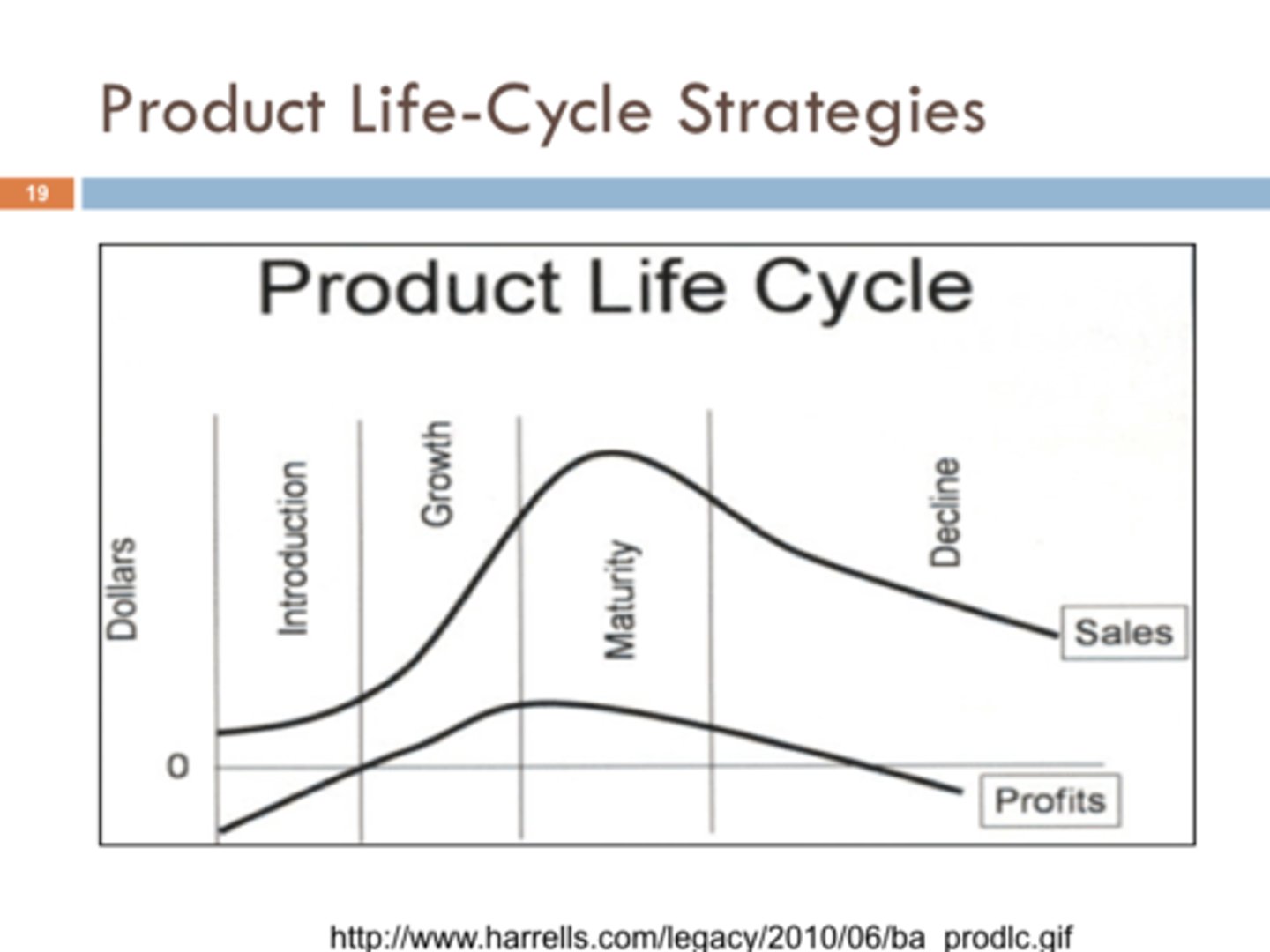
Life Cycle of a New Product Concept
1: Introduction
-low sales
-negligible profits
-innovative customers
-few competitors
2. Growth
-fast sales
-peak level profits
-mass market
-growing competitors
3. Maturity
-slow sales
-declining profits
-mass market
-many competitors
4. Decline
-declining sales
-low/zero profits
-laggard customers
-declining competitors
Changes in marketing across product life cycle: Introduction
-product: one or few
-place: build channels, maybe selective distribution
-promotion: pioneering, informing
-price: skimming or penetration
-competitive situation: monopoly or monopolistic competition
Changes in marketing across product life cycle: Growth
-product: variety, build brand familiarity
-place: build channels, maybe selective distribution
-promotion: inform and persuade
-price: meet competition or price dealing
-competitive situation: monopolistic competition or oligopoly
Changes in marketing across product life cycle: Maturity
-product: battle of the brands
-place: move toward more intensive distribution
-promotion: persuading and then reminding
-price: meeting competition or price cuts and deals
-competitive situation: monopolistic competition or oligopoly --> heading toward pure competition
Changes in marketing across product life cycle: Decline
-product: some drop out
-place: move toward more intensive distribution
-promotion: persuading and then reminding
-price: meeting competition or price cuts and deals
-competitive situation: monopolistic competition or oligopoly --> heading toward pure competition
Products are invented and revised by which department?
R&D
Prices are established by which department?
marketing