3. Equine Diagnostic Imaging
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
radiographs
What method of diagnostic imaging is often the first line in imaging in equine practice? This is often done to localize lameness to a specific region and when we suspect a boney abnormality.
A. lateromedial
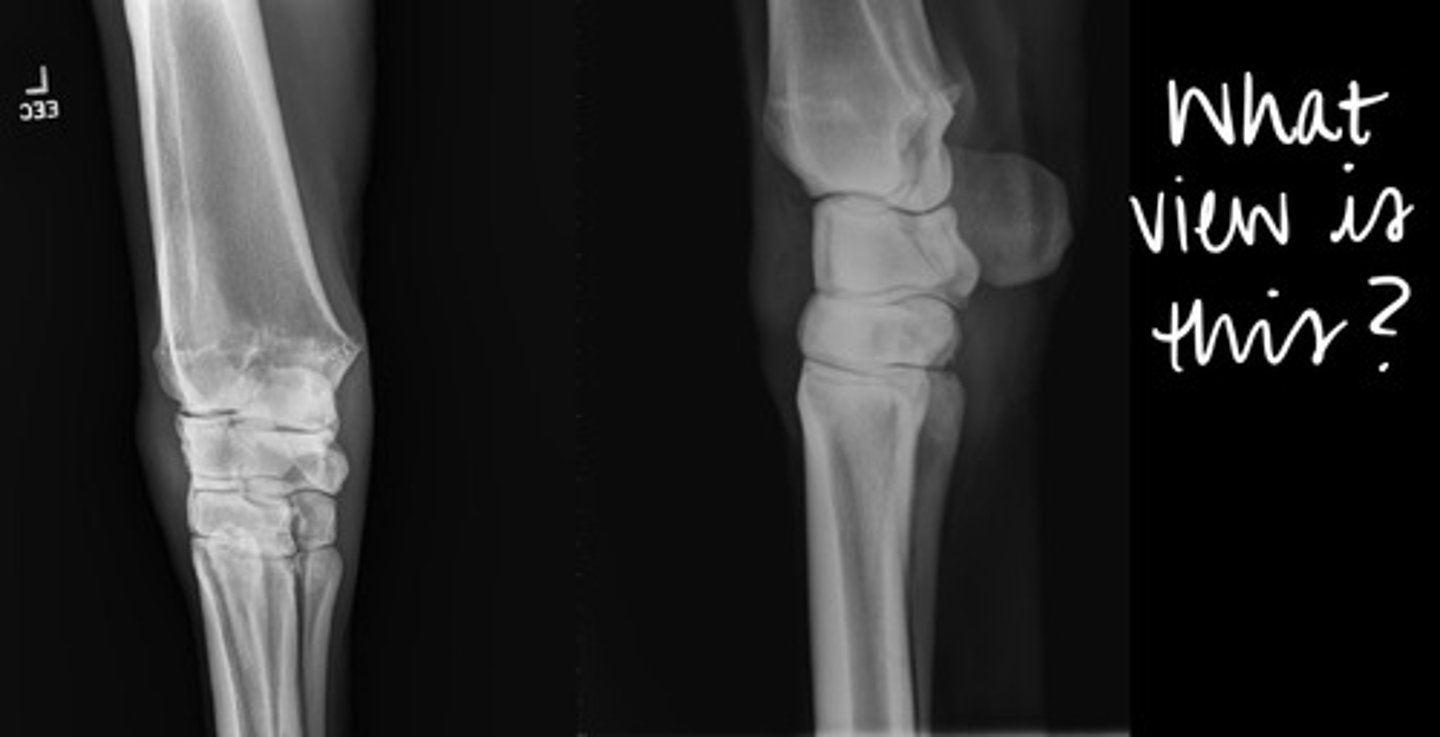
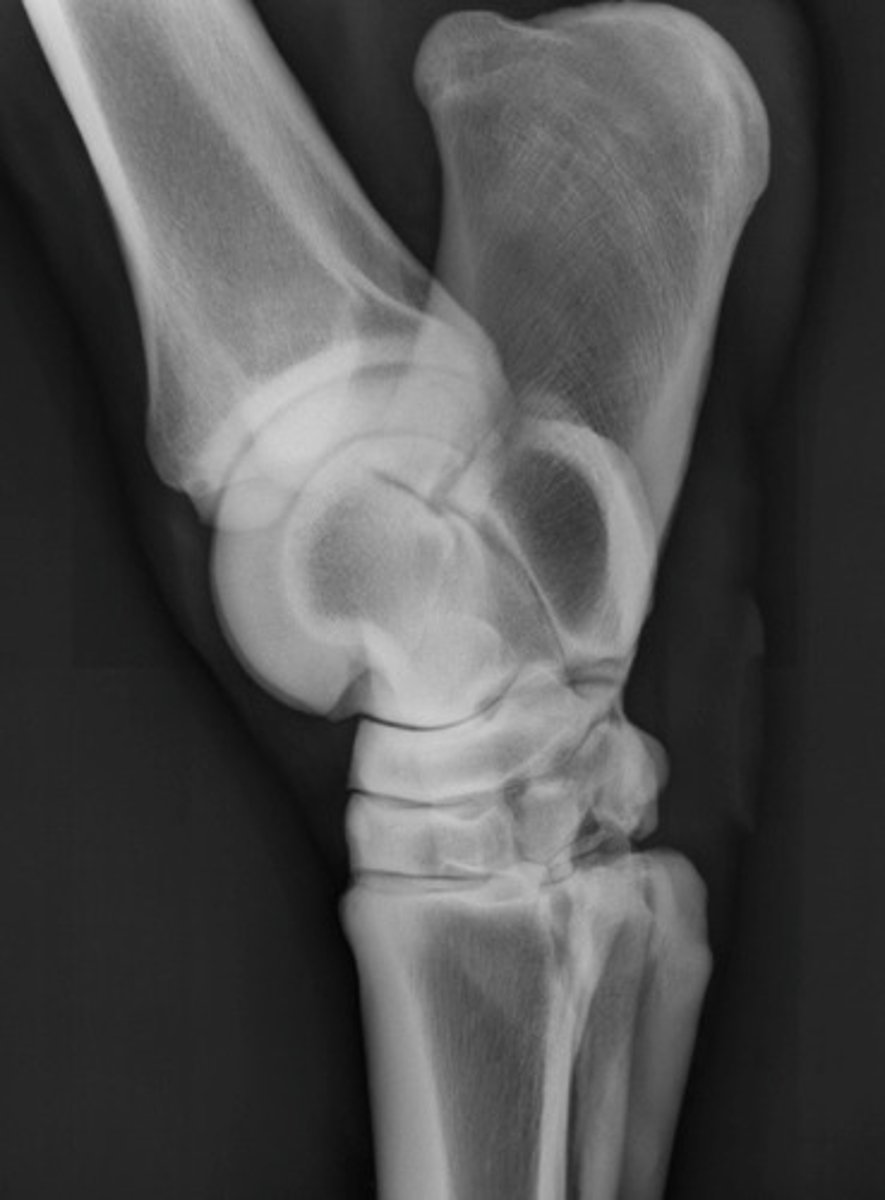
What is the name of this view of a front limb?
A. lateromedial
B. mediolateral
C. dorsopalmar
D. dorsomedial-palmarolateral oblique
if they are leaning one way or the other, it may cause compression on the joints which can look like pathology
For radiographs, the horse must stand "squarely" on the limb being radiographed. Why? Convention: Plate is always medial and almost always palmar/plantar.
lateral
When taking a radiograph, remember to always use R vs L markers. Views can be taken lateral or dorsal, but they are always [dorsal/lateral] when that's on option. Label hind vs fore if the hock/carpus are not in view.
![<p>When taking a radiograph, remember to always use R vs L markers. Views can be taken lateral or dorsal, but they are always [dorsal/lateral] when that's on option. Label hind vs fore if the hock/carpus are not in view.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e144df2b-523a-4f95-b58a-ee80633838e5.jpg)
DLPMO
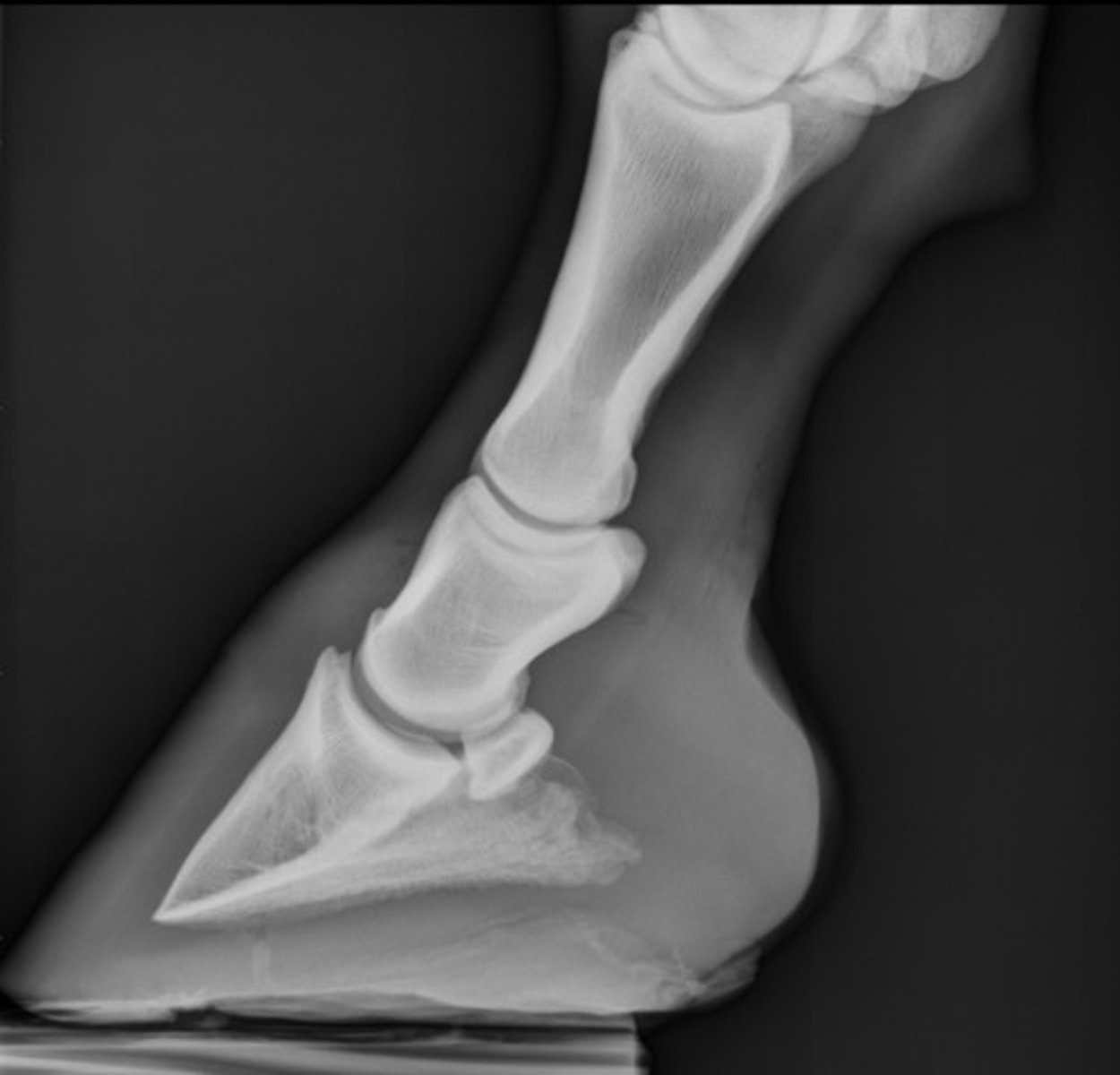
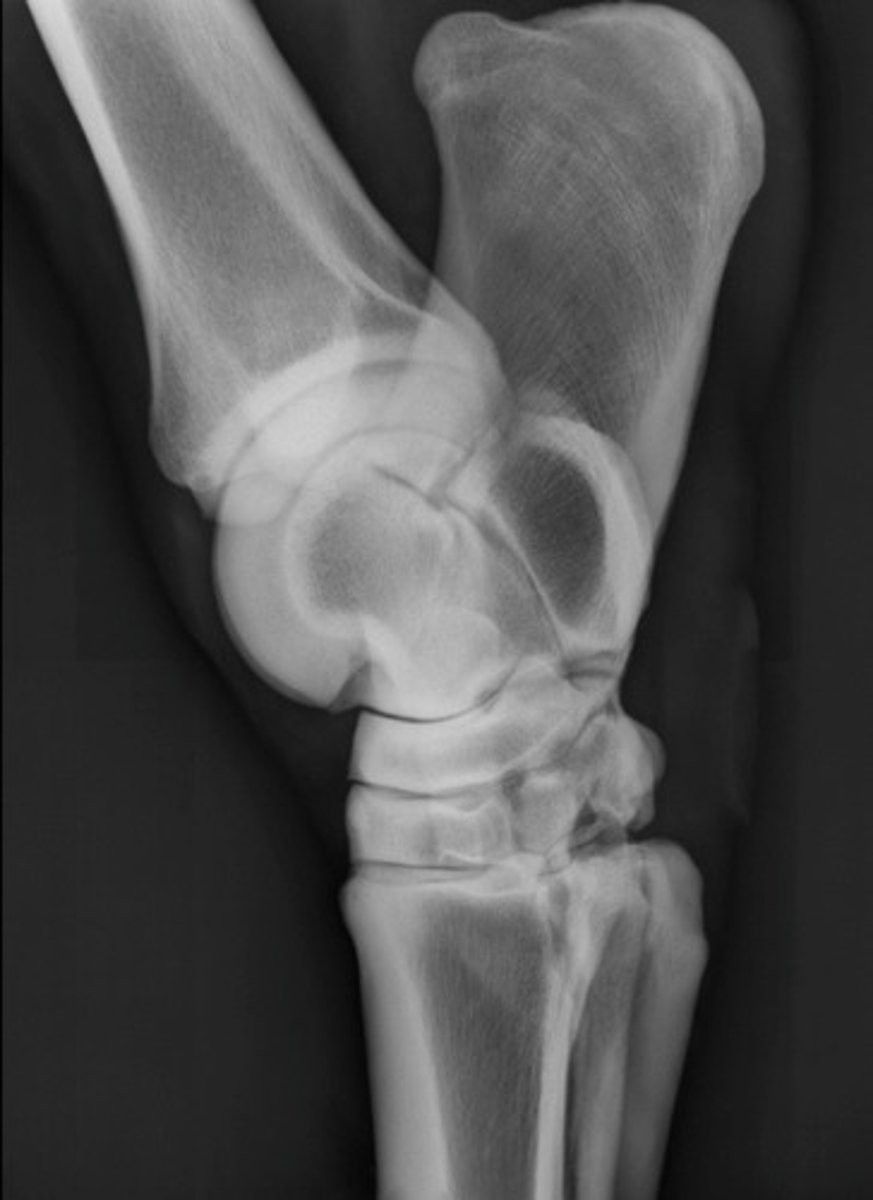
What view is being taken in this image?

A. Coffin (DIP)
Which joint is this diagnostic for? HINT: Which joint can you see better?
A. Coffin (DIP)
B. Pastern (PIP)
C. Fetlock (MCP)
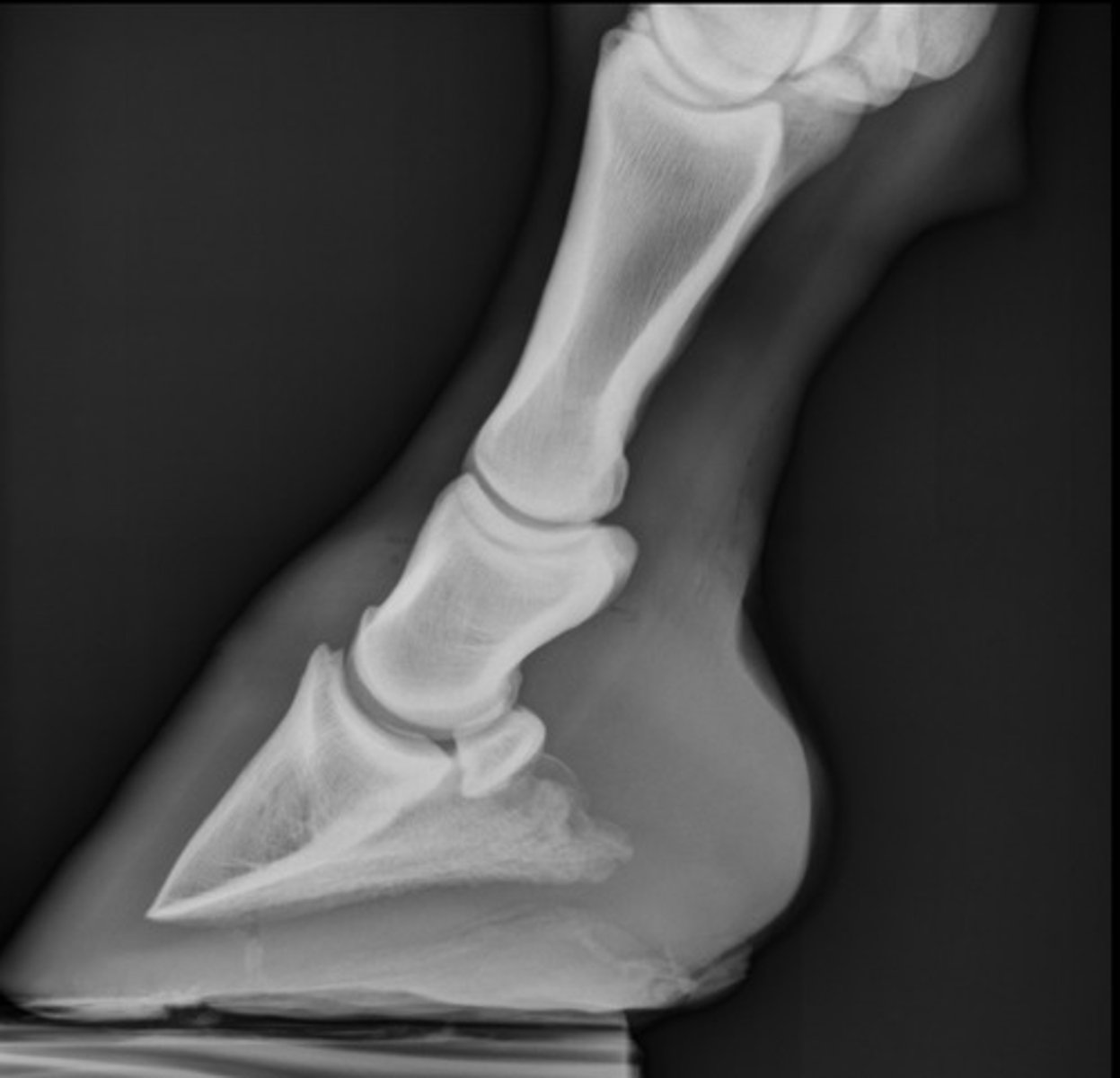
D. LM
What view is this?
A. DLPMO
B. DP
C. DMPLO
D. LM
A. Yes
Is this image diagnostic quality?
A. Yes
B. No
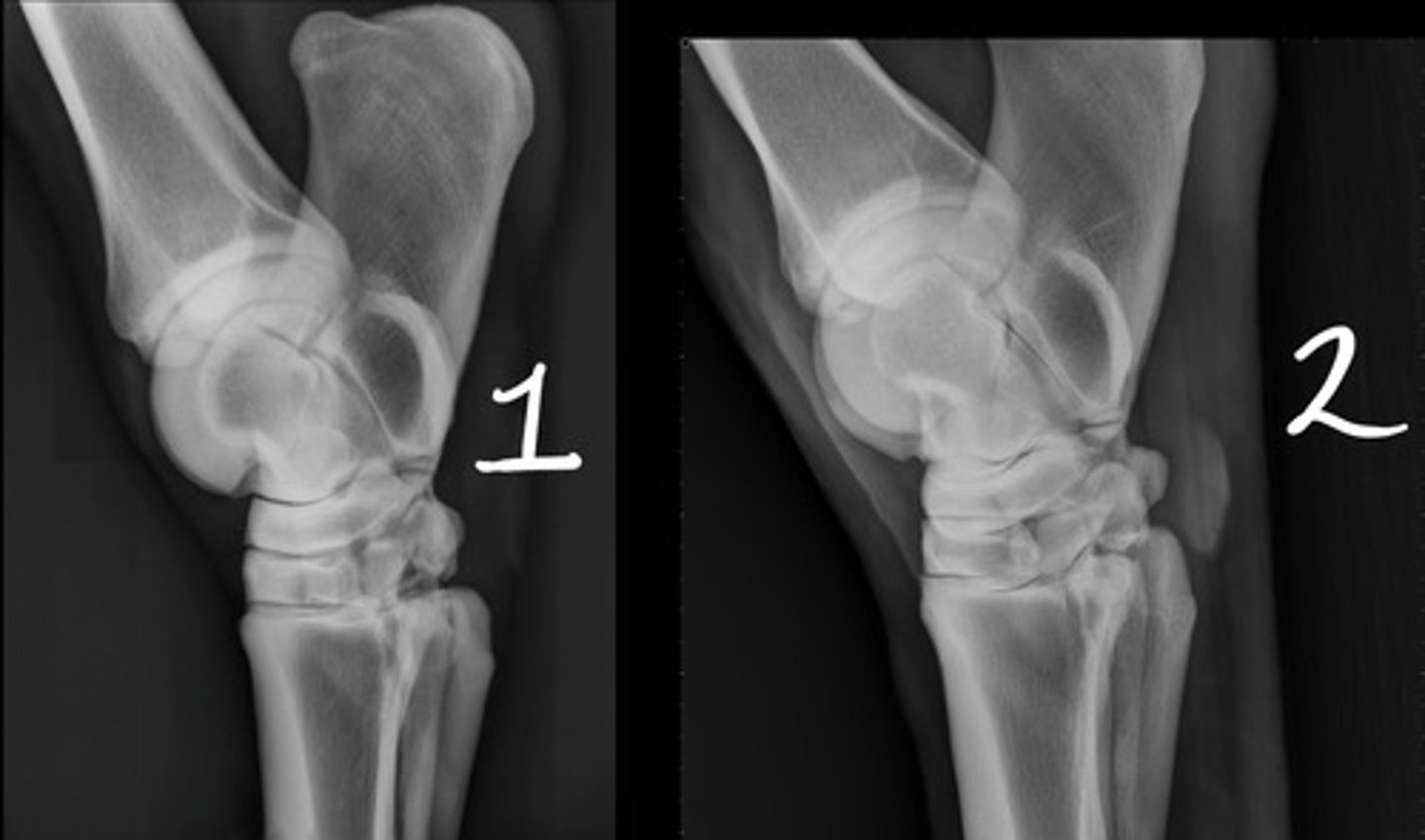
2
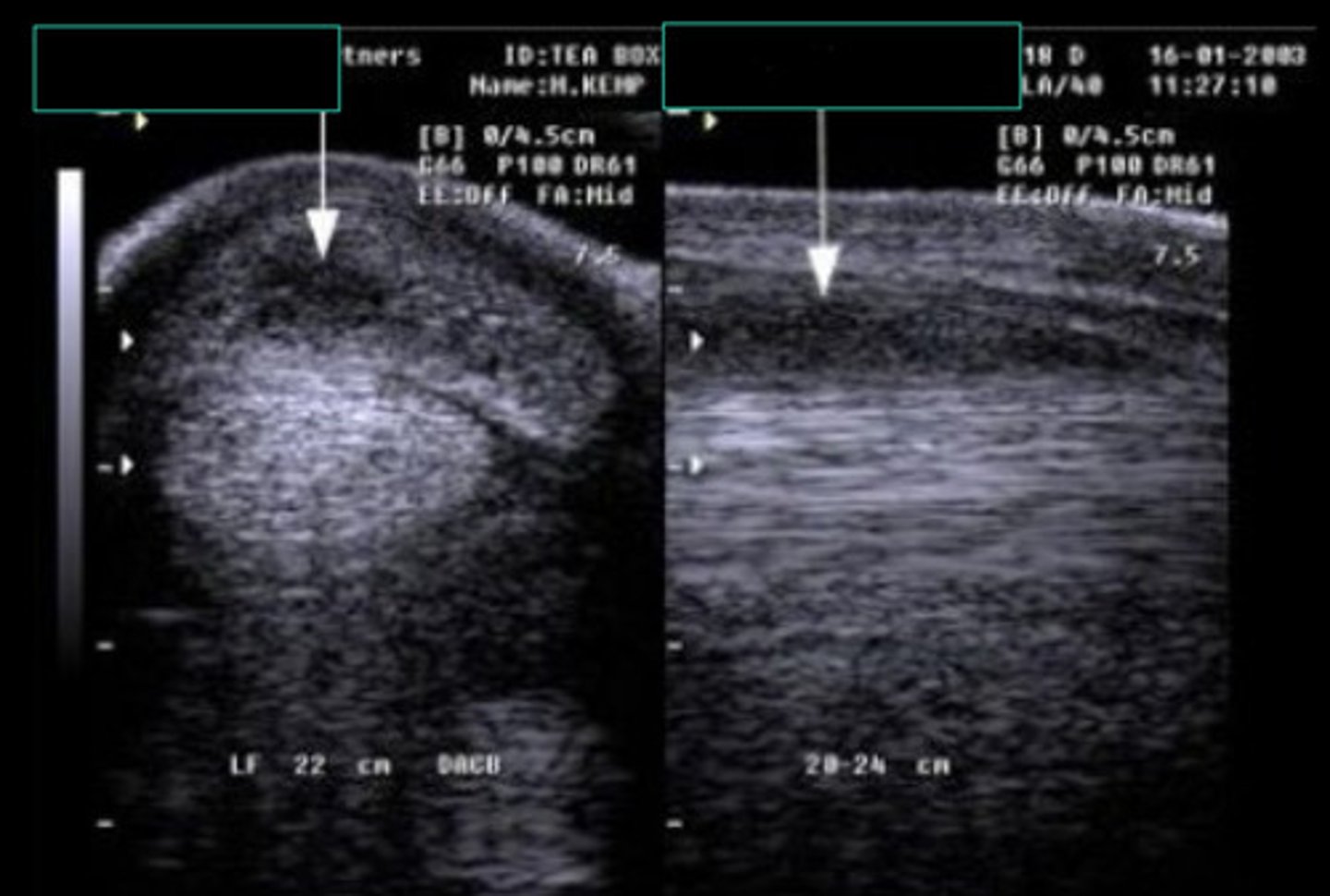
Which image is bad: 1 or 2?
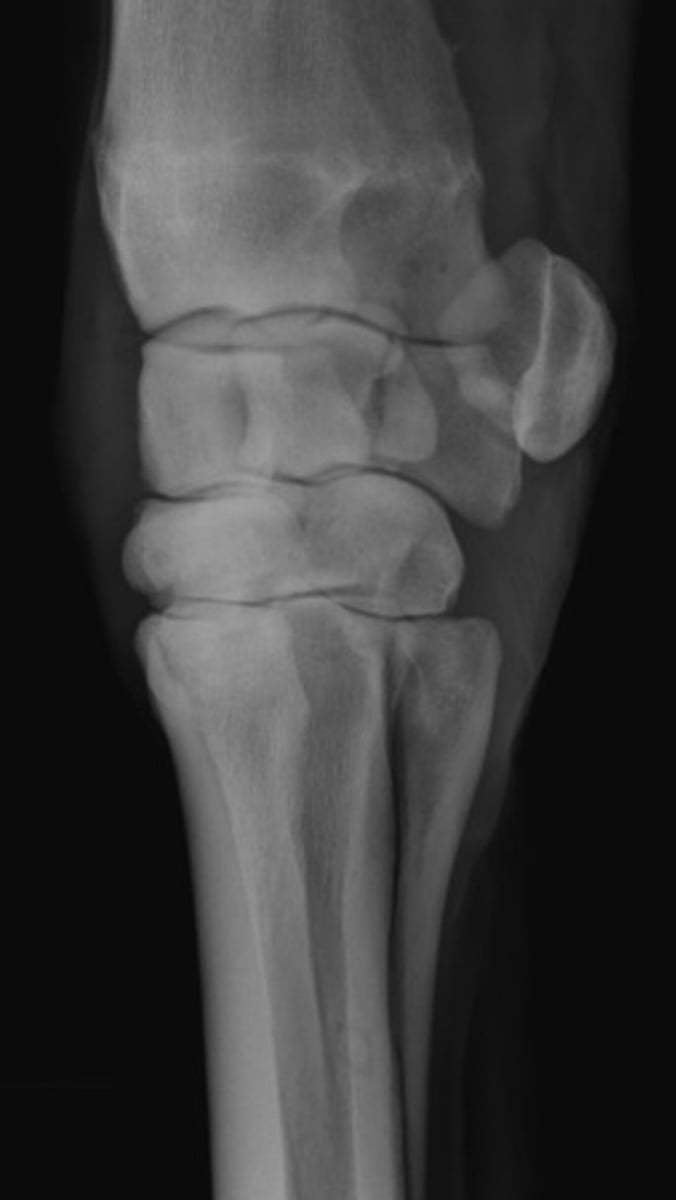
A. DLPMO
What view is this?
A. DLPMO
B. DP
C. DMPLO
D. LM
HINT: What structure is lateral on a carpus? Is it plantar or dorsal?
1. Wait 10 days to see if there is callus formation or resorption at the fracture site
2. Additional imaging
What should be done if there are no radiologic abnormalities but you still suspect a bone injury? List 2 things.
CT and MRI
Which 2 additional imaging modalities should not be done under general anesthesia if you suspect a fracture? Nuclear scintigraphy can be done under general.
high
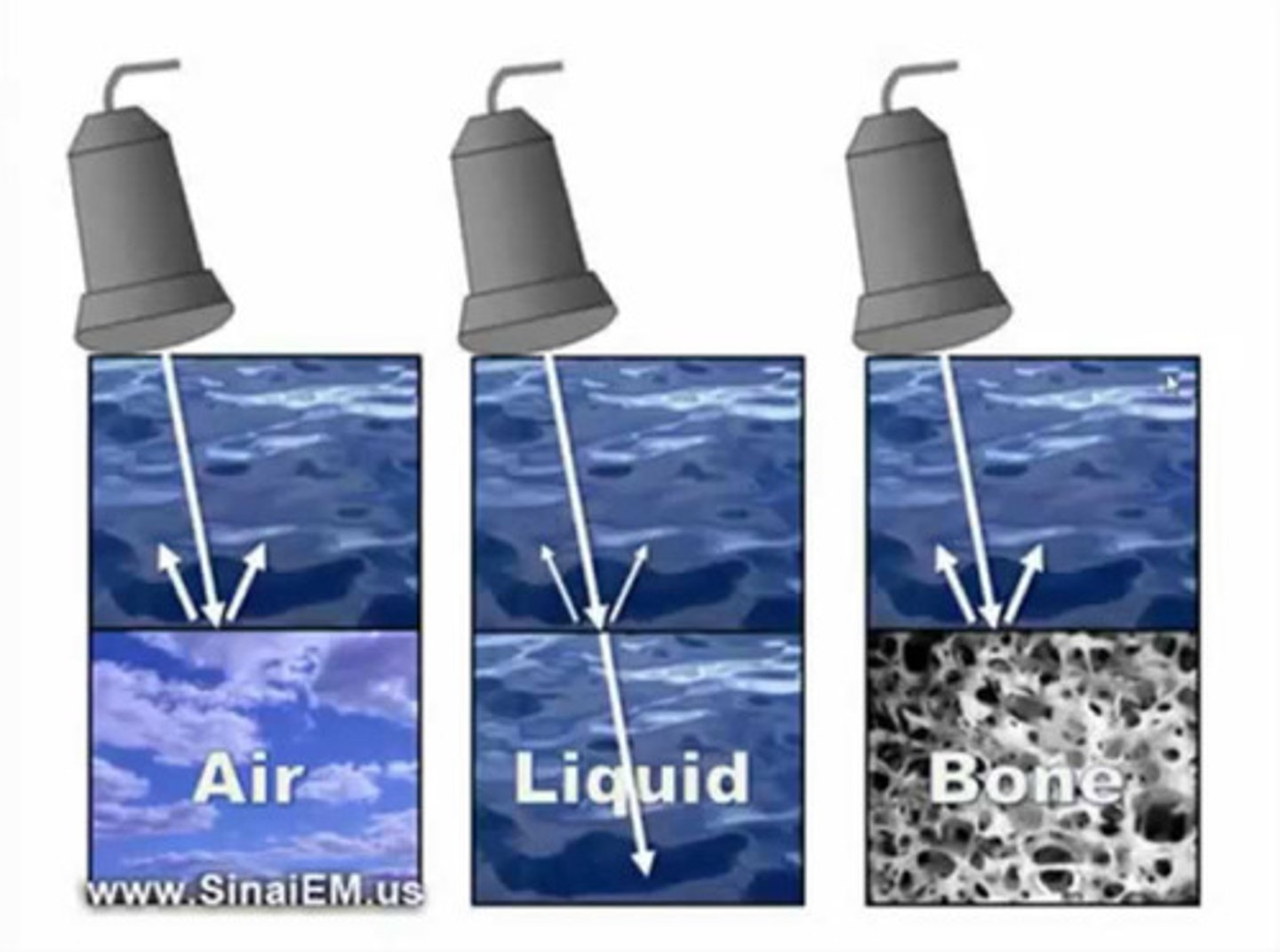
When performing an ultrasound, [high/low] frequency sound waves penetrate tissue and bounce back to the transducer.
![<p>When performing an ultrasound, [high/low] frequency sound waves penetrate tissue and bounce back to the transducer.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9ac9eef8-dc93-48f5-a54e-8ab5c78d9d84.jpg)
crystals
What structures within the ultrasound probe convert sounds waves to an electric current? The computer in the ultrasound machine converts the electric current to an image.
1. joints
2. ligaments
3. surface of bone
4. tendons
List 4 anatomic structures that can be visualized with ultrasound.
True
When performing an ultrasound:
- remove grease with alcohol
- lots of gel
- 8-15 mHz transducer
- standoff provides better detail in areas with less soft tissue (ex: tendons)
T/F: You must clip hair when performing ultrasonography of the equine limb.
F. B & C
With increasing mHz of the transducer, how does the image change?
A. increase depth
B. decrease depth
C. increase resoltuion
D. decrease resolution
E. A & D
F. B & C
image the "normal" limb for comparison
If you are performing ultrasound and are unsure of your findings, what should your next step be?
core lesion
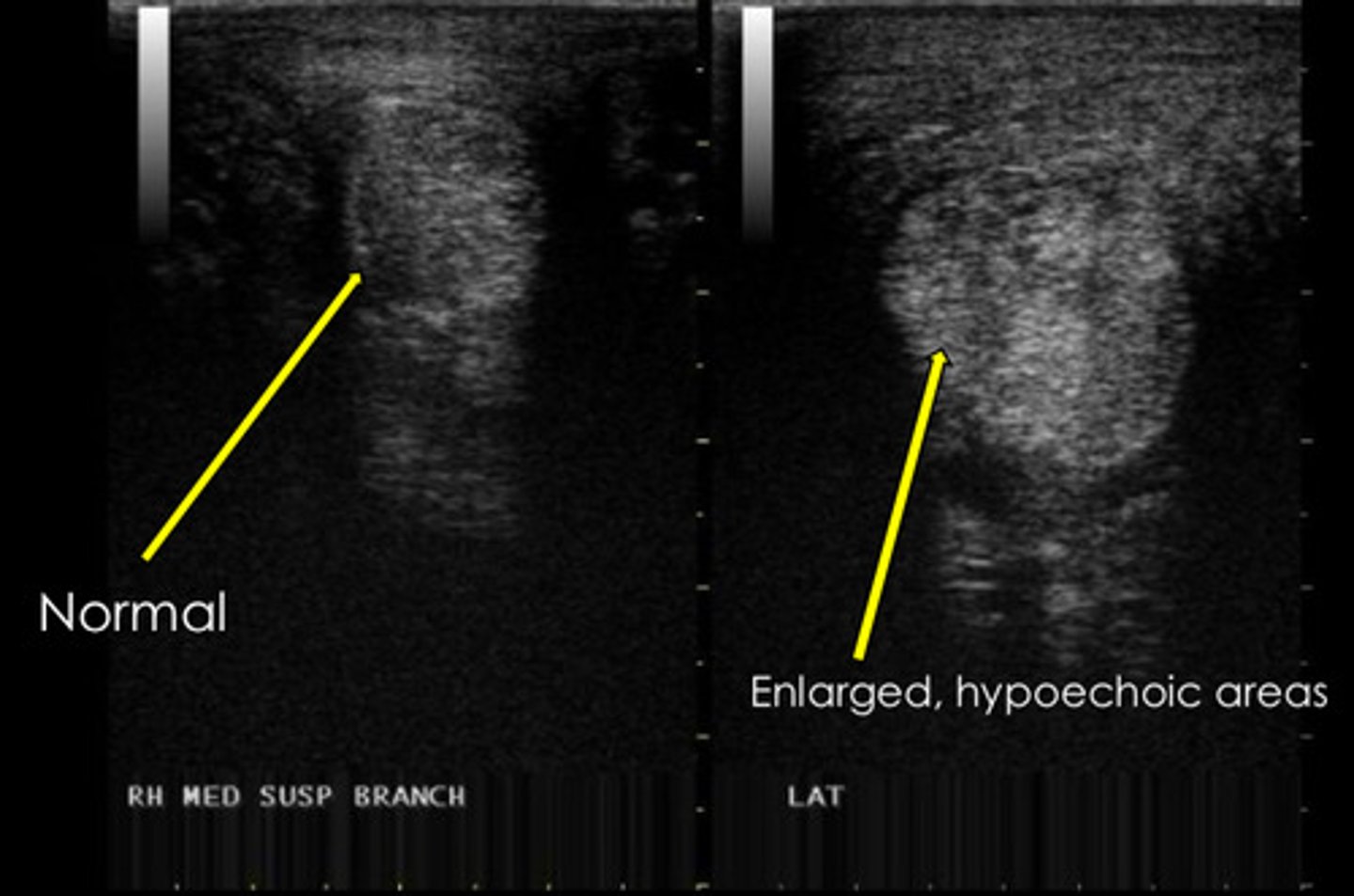
What common lesion is shown? Fluid = edema = inflammation.
longitudinal and transverse
When ultrasounding the equine limb, you need to see the lesion in 2 views. What are those 2 views? It is also true that 2 imaging modalities may be better than 1.
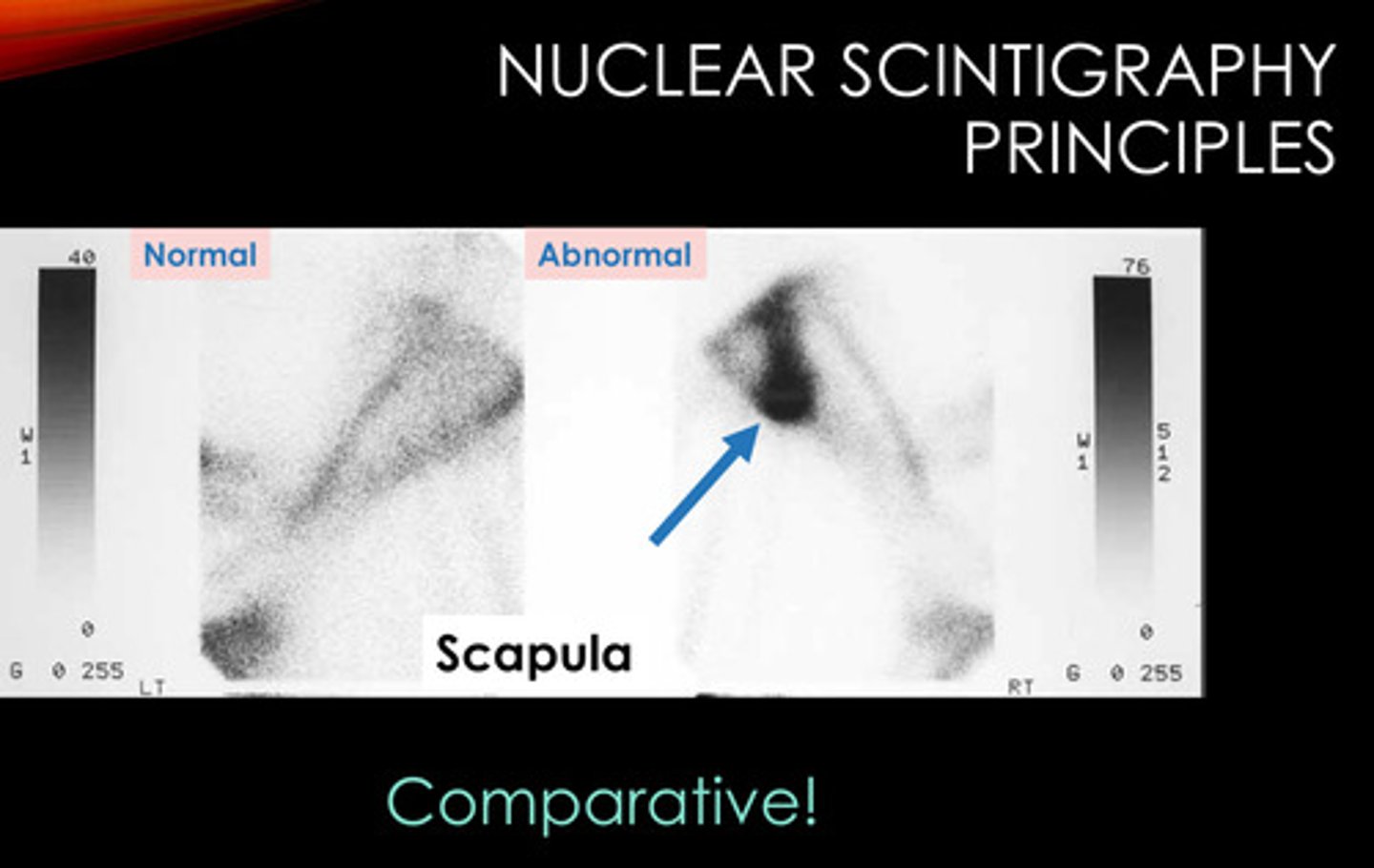
nuclear scintigraphy
The following are all indications for what imaging modality?
- fail to localize lameness with blocks
- localize lameness but no lesions seen on other modalities
- multiple limb lameness
- upper limb or axial MSK issue (not easily accessible for rads and hard to block)
- suspect fracture not imaged on rads
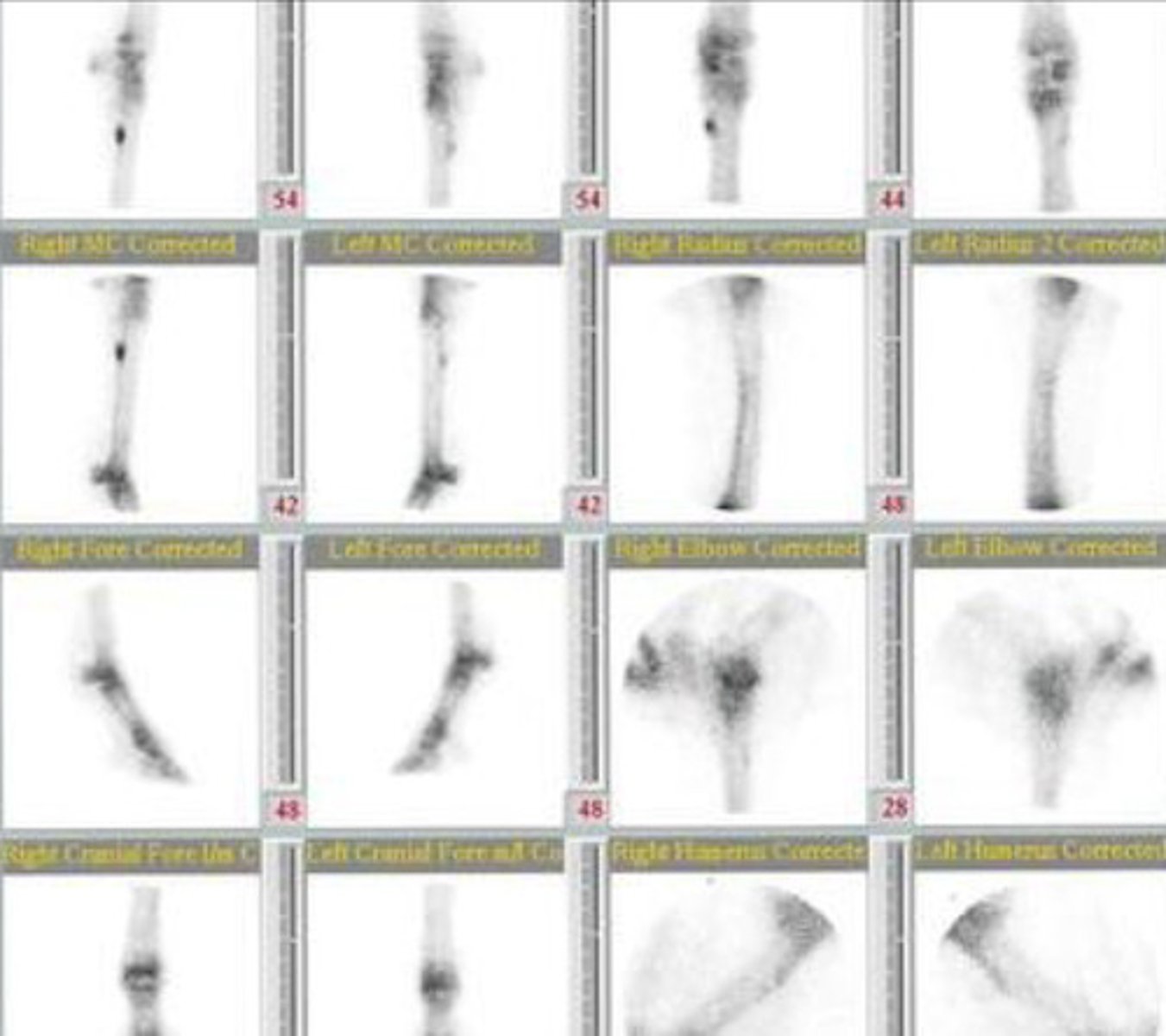
Technutium-99m
When performing nuclear scintigraphy, you inject a drug that is bound to a rapidly decaying radioactive atom. What is the most common drug?
hydroxyapatite
_____ is formed by osteoblasts in areas of active bone formation.
- proportional to bone resorption
gamma
With nuclear scintigraphy, the _____ camera detects decay of a radioactive atom. This takes a few minutes.
increased
[decreased/increased] bone activity -> increased uptake -> increase in atoms decaying -> increase in signal
![<p>[decreased/increased] bone activity -> increased uptake -> increase in atoms decaying -> increase in signal</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9e6dd5b5-2091-4c87-9875-c6a32e938850.jpg)
computed tomography
Which imaging modality is being described?
- detailed evaluation of bone
- limited soft tissue detail
- requires injection of contrast
- fracture repair planning
- image navicular apparatus
- image the head
- x-ray tube in a circle
- intensity of x-ray allows for differentiation of structures
- "slice" image
- software can reconstruct slices into 3D image
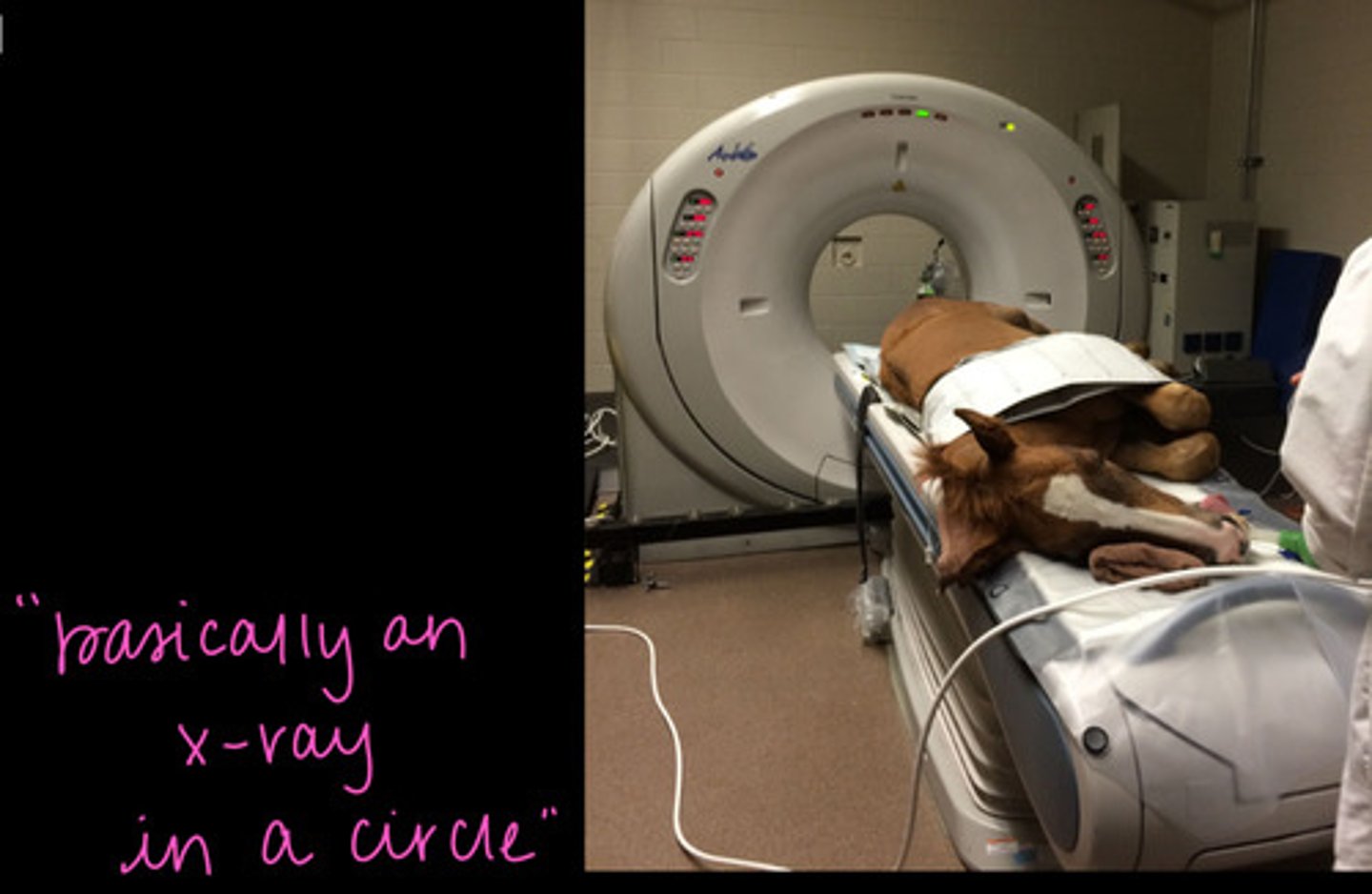
True
T/F: With CT, the horse is generally anesthetized.
Imaging is limited to carpus/tarsus and distal limb and head.
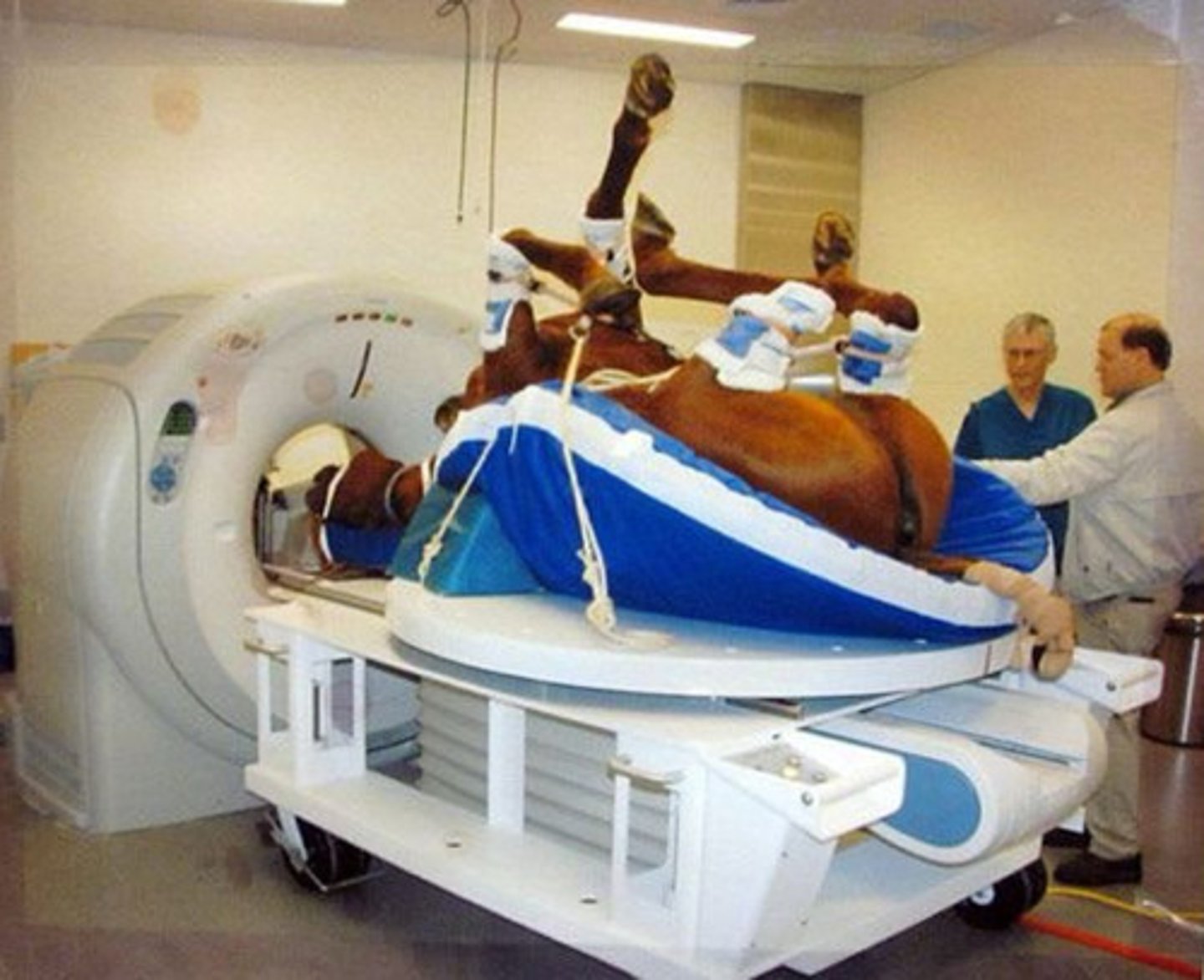
magnetic resonance imaging
Which imaging modality is being described?
- imaging soft tissue and bone lesions
- where ultrasound is not possible (the foot)
- similar limitations in structures that may be imaged as CT
- horse has to fit in

radiofrequency
MRI Principles:
All tissues have lots of hydrogen protons because they are made of H2O. The magnet is applied and protons are excited by a _____ pulse.
Pulse removed -> protons relax -> emits signal
Protons in different tissues relax differently (superior contrast in tissues).
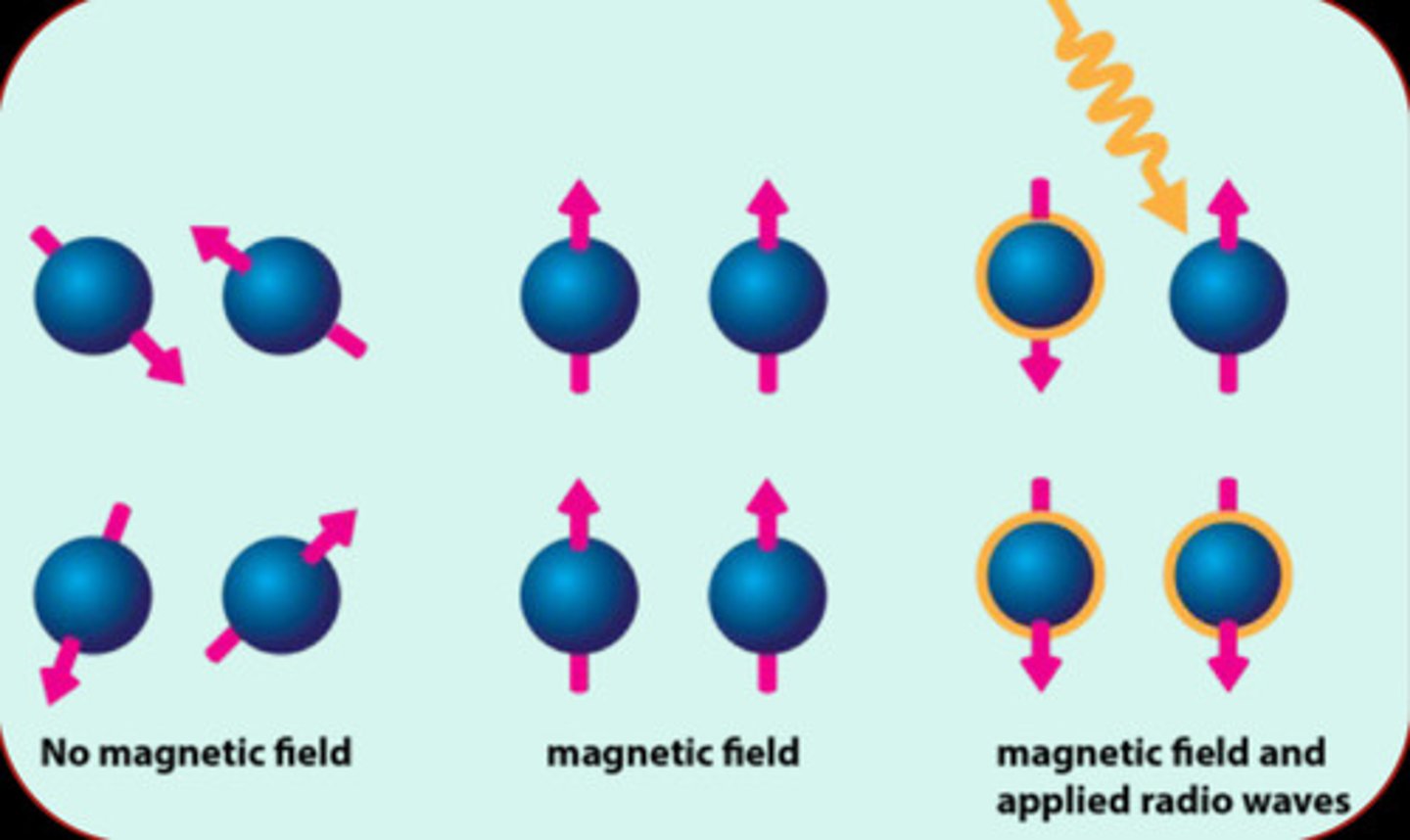
contrast
With MRI, we can use different types of pulses and measure different types of relaxation to allow for greater _____ and focus on different types of structures (bone vs. soft tissue).
core lesion
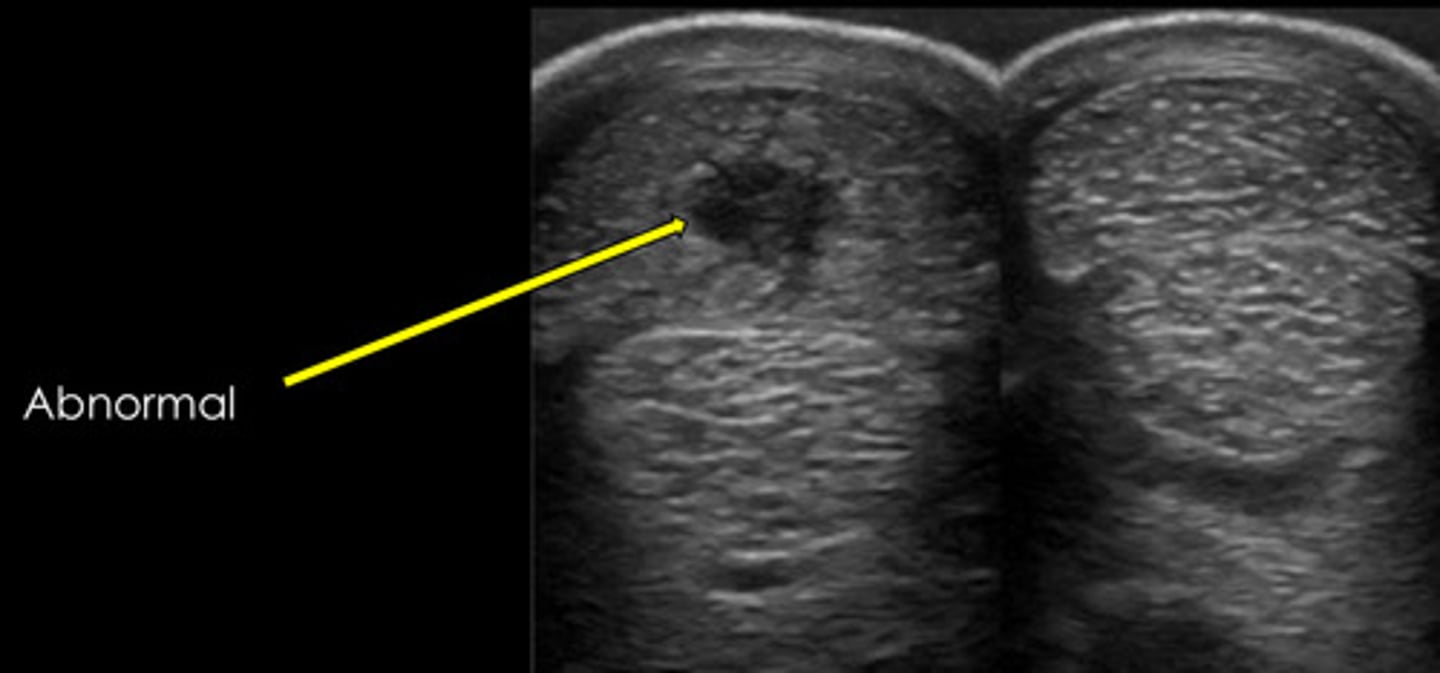
DDF
What type of lesion is pictured? What structure is it present in?
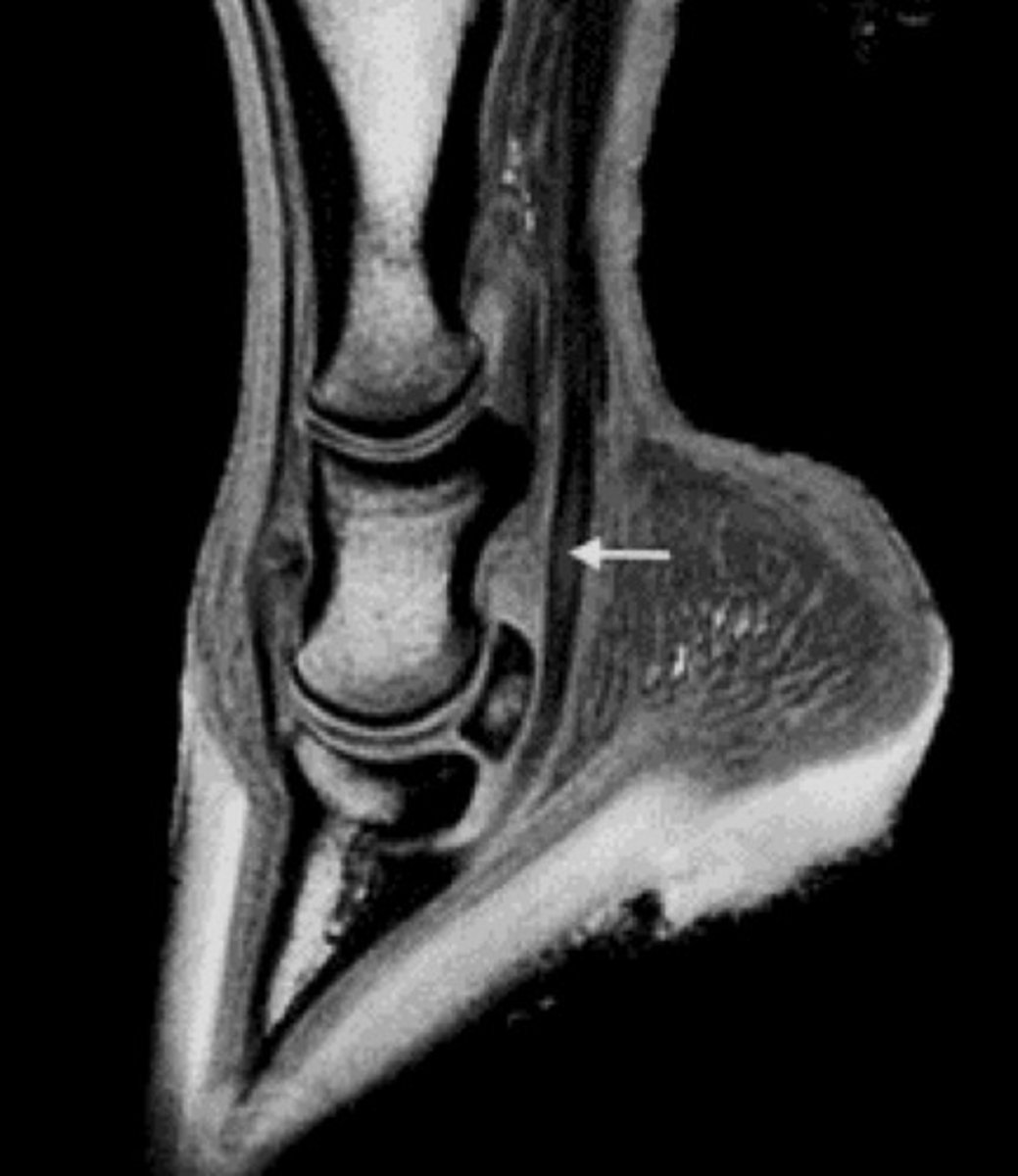
2
Which image is bad: 1 or 2?
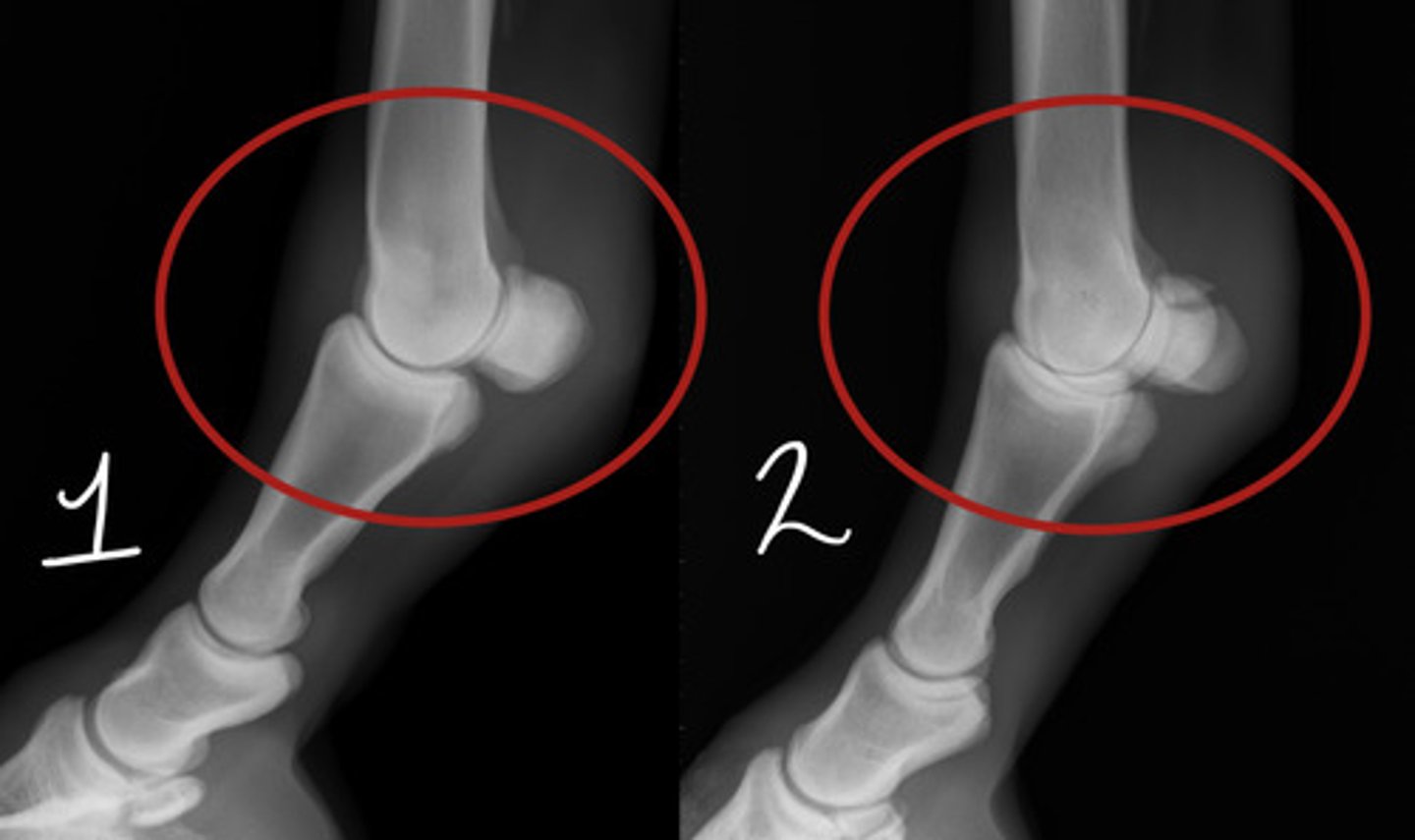
2
Which image is bad: 1 or 2?
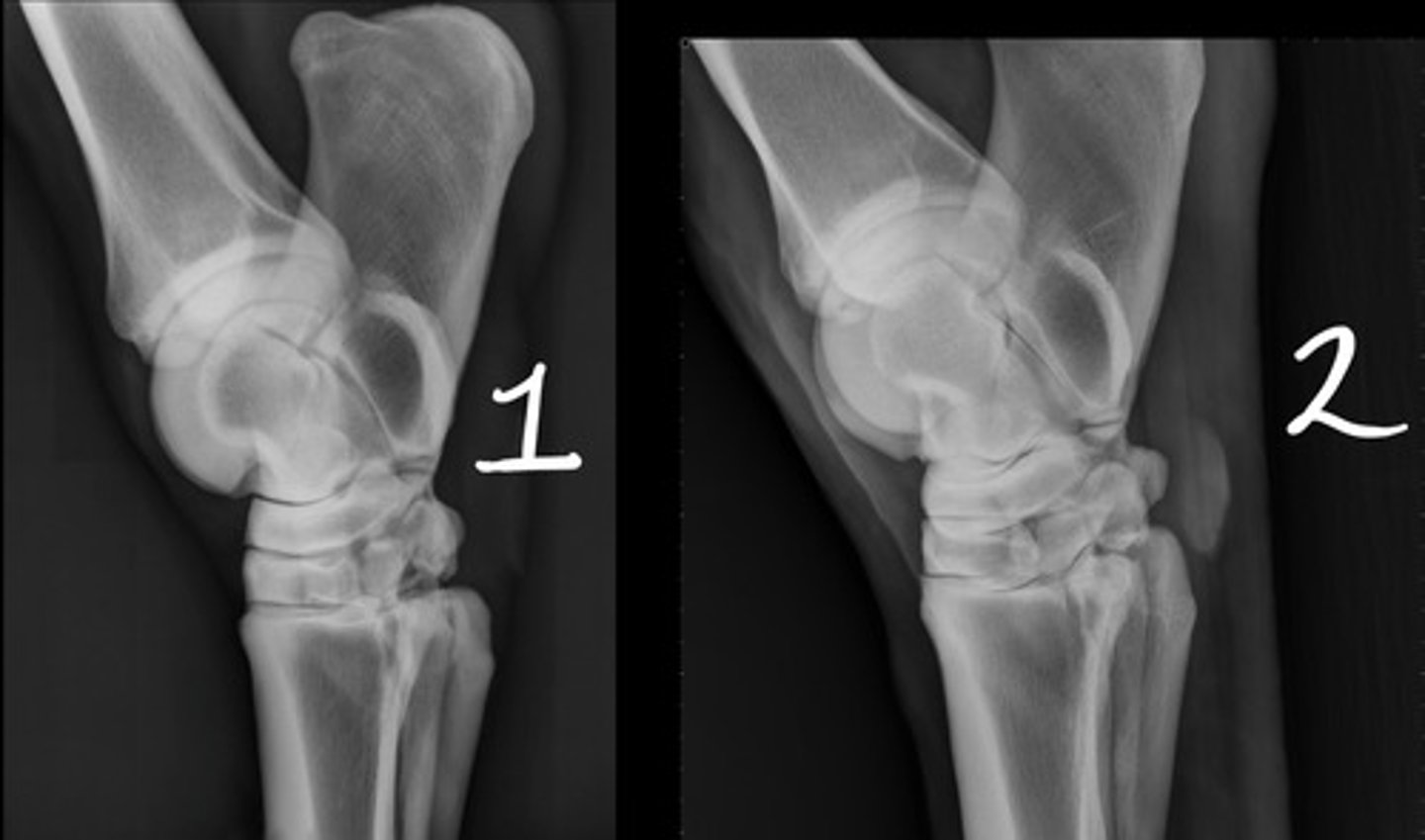
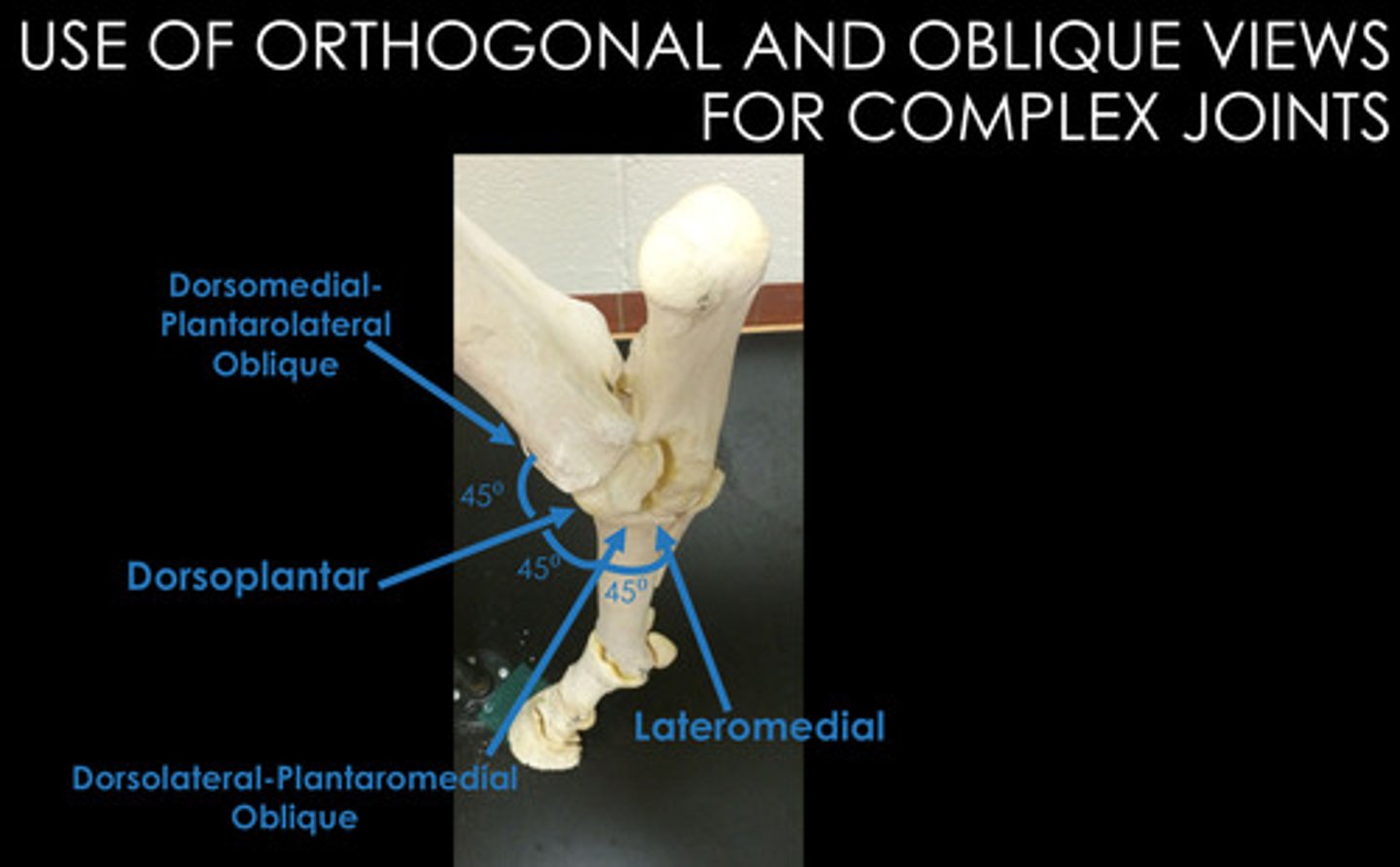
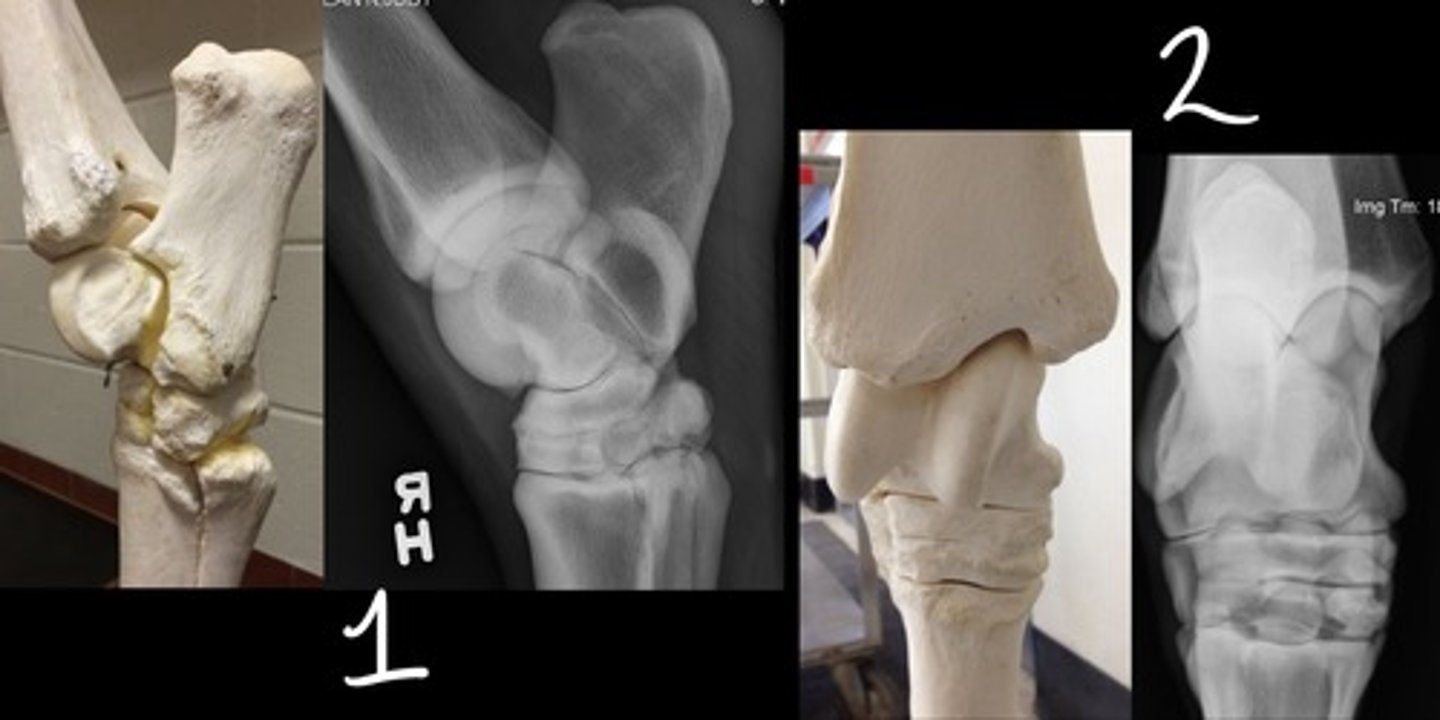
Lateromedial
Which radiographic view is represented by #1?
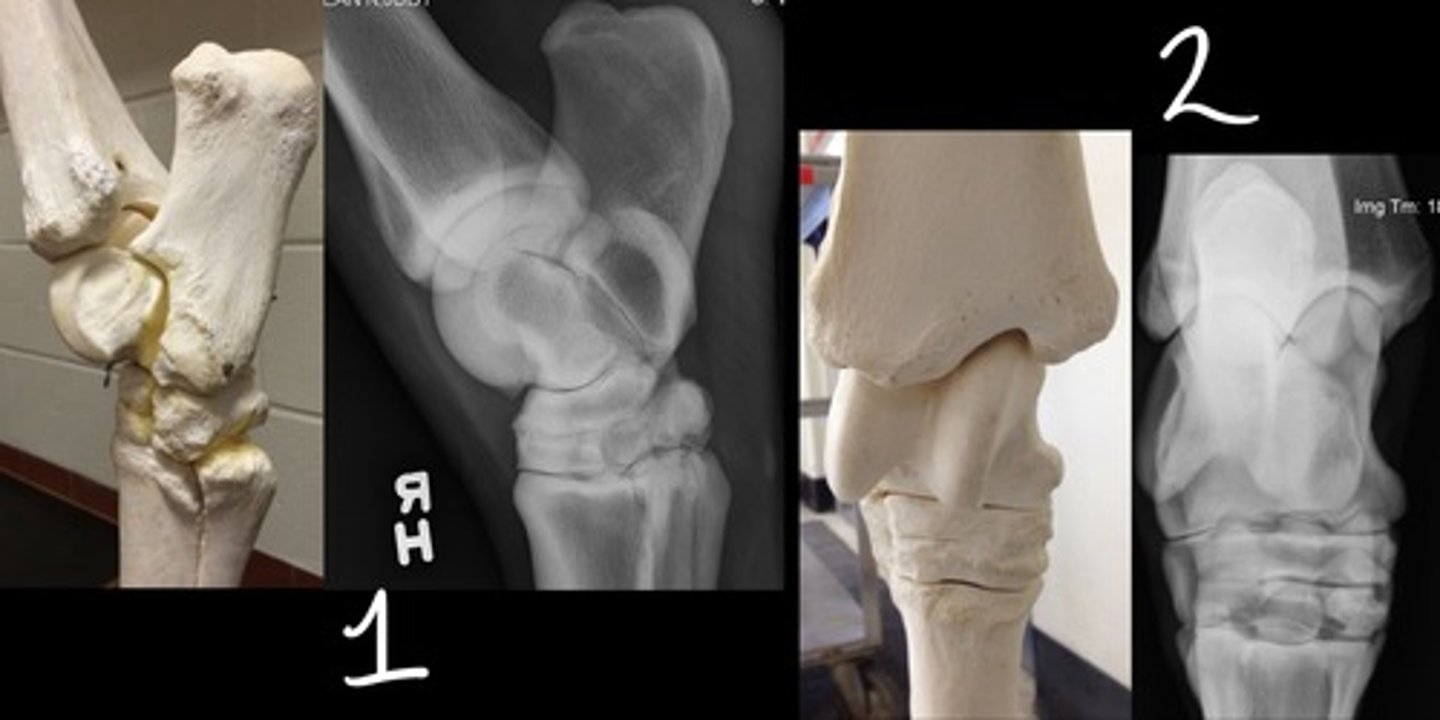
Dorsoplantar
Which radiographic view is represented by #2?
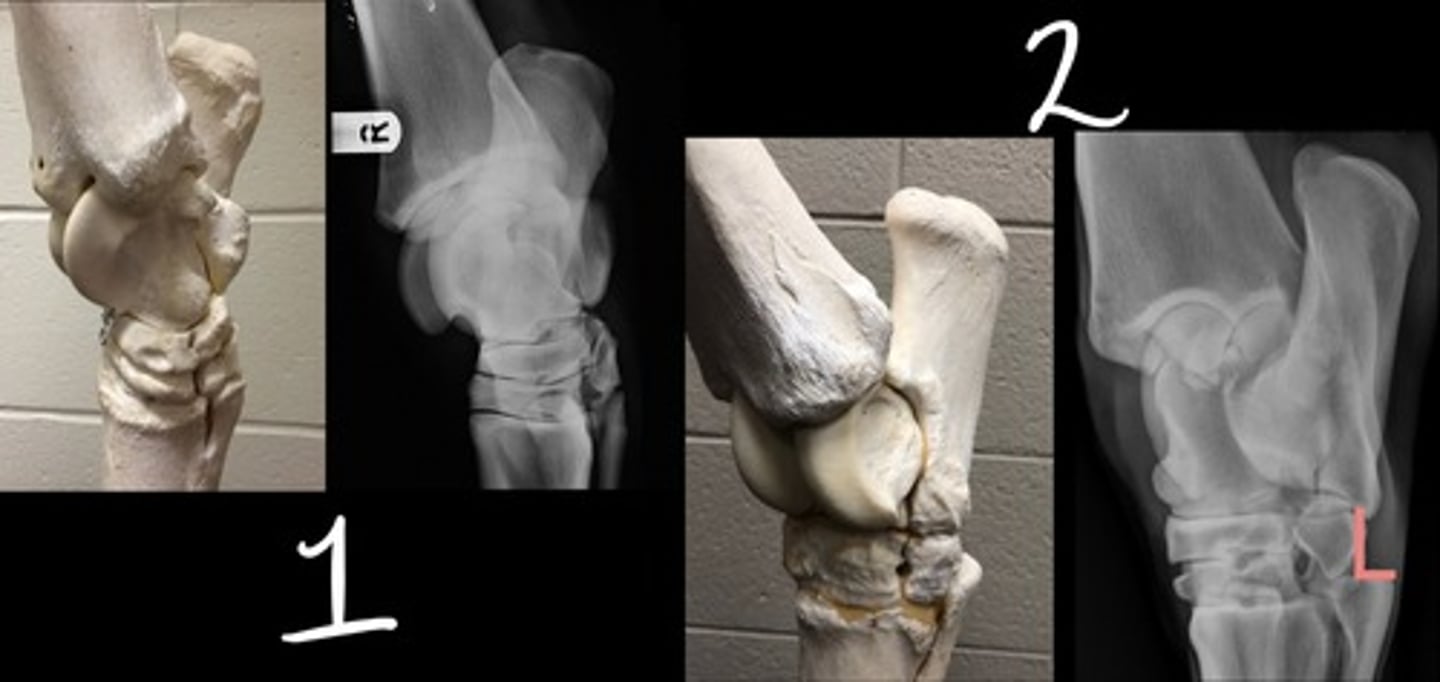
DMPLO
Which radiographic view is represented by #1?
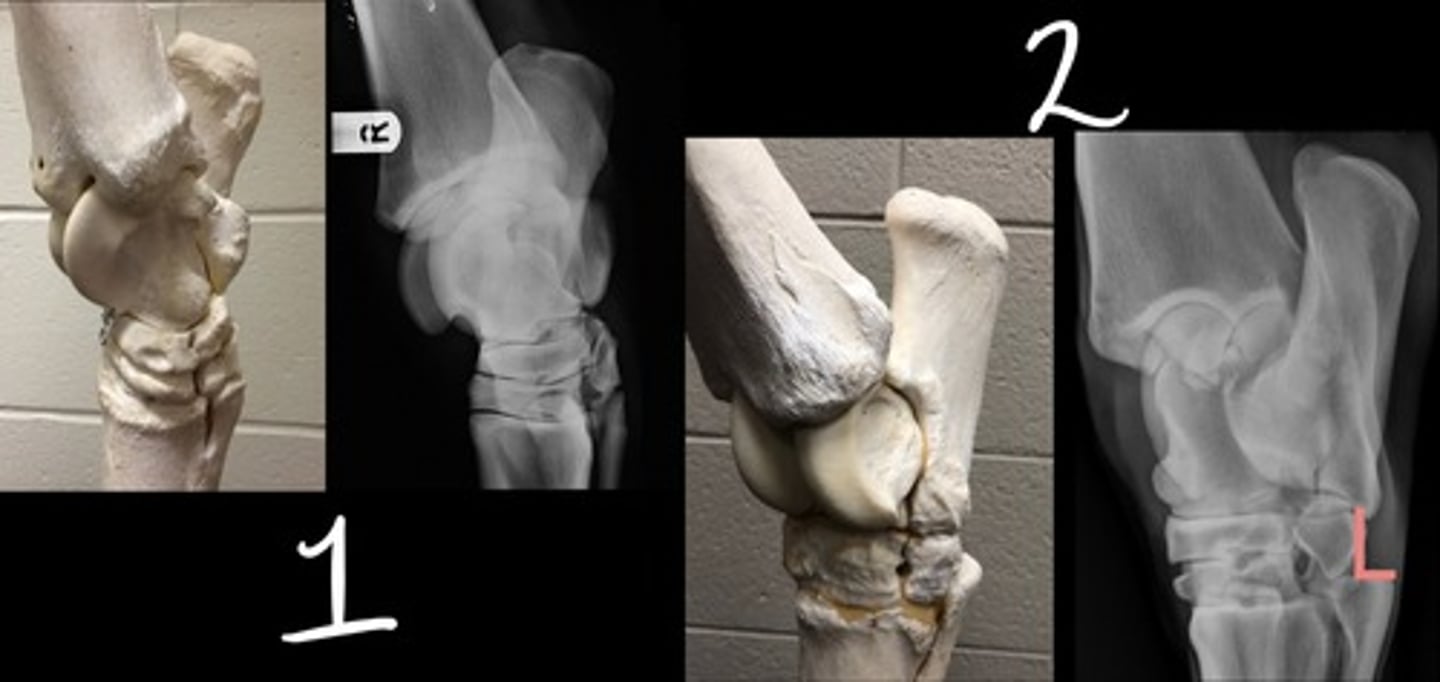
DLPMO
Which radiographic view is represented by #2?
DMPLO