circulatory system
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
circulatory system
-Brings air into respiratory system
-Provides gas exchange for circulatory system
-These two systems supply cells throughout the body, with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive
-basically a pump (heart), network of tubing (blood vessels) and fluid (blood)
-moves oxygen, carbon dioxide, glucose, hormones, waste products, and lipids around the body
the heart
-almost entirely muscle
-hollow organ, about the size of your fist
-enclosed by a protective sac called the pericardium
-contracts on avg 72X /min
-pumping about 70mL's per beat
septum
-divides the left and right sides of the heart
-prevents mixing of blood between chambers under high pressure
atria
-top chambers
-smaller
-less muscular
ventricles
-bottom chambers
-larger
-more muscular
blood fllow
-pulmonary circuit: blood travels through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, then to the lungs for gas exchange
-systemic circuit: blood travels through the aortic valve into the aorta to the rest of the body
atrioventricular valves
-atria from ventricles
-tricuspid (right side)
-mitral (left side)
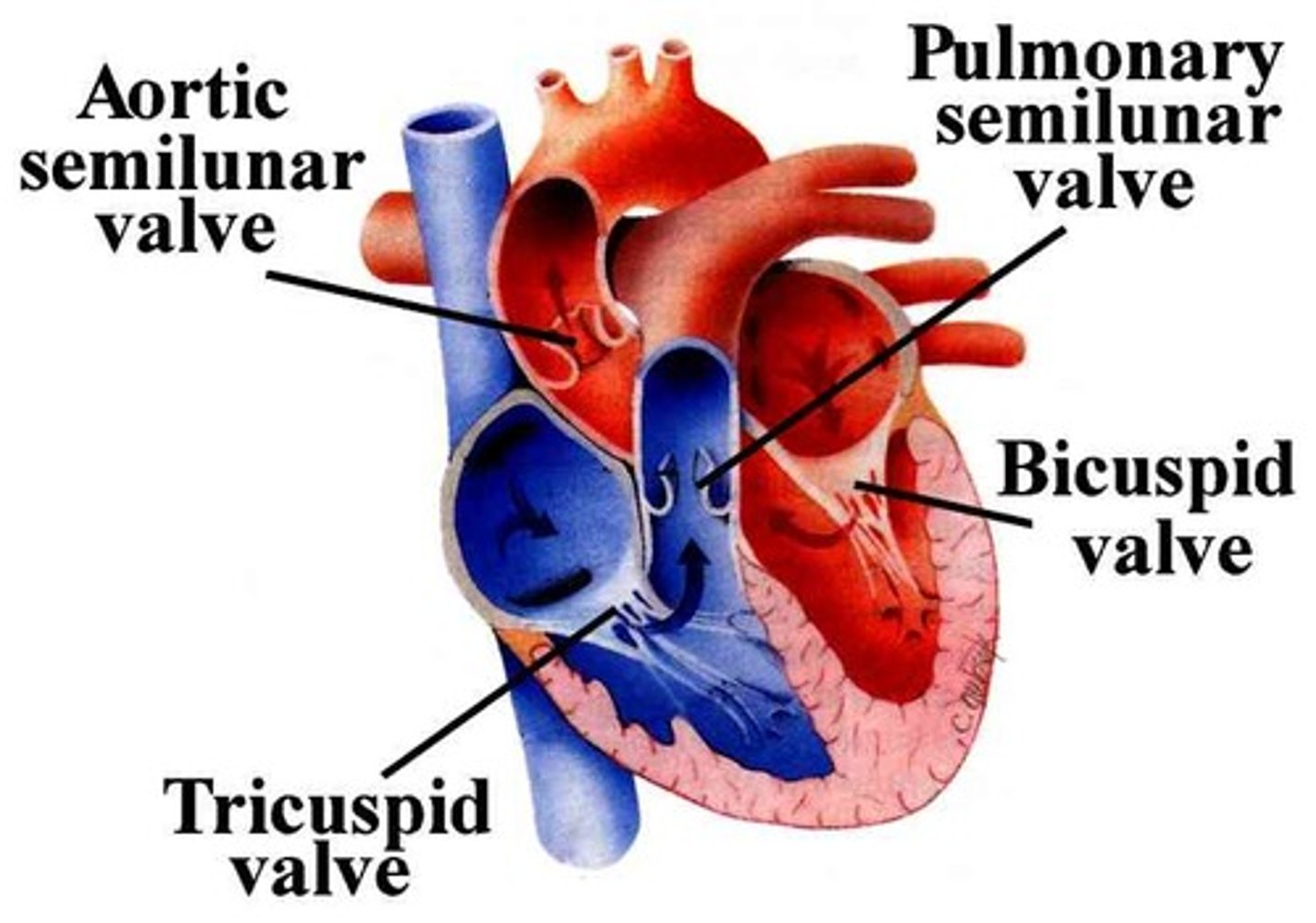
semilunar
-ventricles and blood vessels
-pulmonary - on the way to the lungs
-aortic - on the way to the aorta
heartbeat
-two networks of muscle fibers, one in the atria and one in the ventricles, coordinate the heart's pumping action
-Varies depending on body's need for oxygen or need to release carbon dioxide
-Autonomic system of the nervous system controls heart rate
-Sympathetic system increases heart rate ("fight or flee")
-Parasympathetic system decreases heart rate ("rest and digest")
-Contraction in the Atria forces blood to the ventricles
-Contractions of the ventricles forces blood out of the heart
sinoatrial (SA) node
-Group of cardiac fibers in the right atrium starts the contraction
-When SA node fires, electrical impulse spreads through the muscle fibers in the atria and contract
-Also called the "pacemaker" because it sets the pace for the heart
atrial fibrillation
-heart's upper chambers (atria) contract randomly and sometimes so fast that the heart muscle cannot relax properly between contractions
-Reduces the heart's efficiency and performance
-Happens when abnormal electrical impulses suddenly start firing in the atria
blood vessels
-Blood leaving left side of the heart is loaded with oxygen from lungs
-Passes through the Aorta, throughout the body
-moves through 3 types of vessels (arteries, capillaries, veins)
artery
-carries blood away from the heart
-Blood is under pressure, have thick, muscular walls that regulate their diameters to regulate blood flow
-Get smaller as they move from the heart and branch into arterioles and, ultimately, capillaries
capillaries
-smallest blood vessels
-Site of exchange between blood and tissues
-Oxygen and nutrients (glucose) leave blood
-CO2 and wastes leave tissues and enter blood
veins
-carries blood toward the heart
-Less pressure, skeletal muscles provide movement
-Contain valves to prevent backflow
-Less muscular than arteries, and often found in skeletal muscle
blood pressure
-Like any pump, the heart produces pressure
-Heart contracts 🡪 a wave of fluid pressure on the arteries 🡪 known as blood pressure (BP)
-BP decreases when the heart relaxes
-Without pressure the blood would stop flowing
sensory receptors
-maintain blood pressure
-at several places in the body, measures blood pressure
-If pressure is unsafe, messages are sent to the medulla oblongata and the brain stem
-if too high, the autonomic nervous system Neurotransmitters are released to relax smooth muscle walls of arteries
kidneys
-maintain blood pressure
-Hormone produced by the heart and other organs cause kidneys to remove water from blood when pressure is too high, this reduces the pressure (diuretics)
how is blood pressure measured?
-using a sphygmomanometer
-Measures two numbers (systolic and diastolic)
-Typical reading 120/80
systolic
-Top number
-The force felt in arteries when ventricles contract
diastolic
-Bottom number
-Force felt when ventricles relax
Atherosclerosis
-one of the leading causes of heart disabilities in the U.S.
-a result of plaque build up in the arteries
-In coronary arteries (blood to heart muscle), part of heart muscle can die (heart muscle also requires oxygen)
-Can cause heart attack after time
-Stroke can occur if a clot is formed from fatty build up, it breaks loose, can cause lack of oxygen to brain
-heart must work harder
Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs)
-Conditions present at birth
-can affect the structure of a baby's heart and the way it works
-the most common
type of birth defect
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
-ASD is a hole between atrial (upper) chambers, a fairly common heart defect present at birth
-Oxygenated blood escapes from the left to the right atrium
-Too much blood is pumped to the lungs, lungs can't convert enough oxygen
-Small ASDs may close on their own
-Larger holes make the right pumping chamber work harder
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
-VSD is a hole between ventricles (lower) chambers, a fairly common heart defect present at birth
-Oxygenated blood escapes from the left ventricle into the right ventricle and into the lungs
-This forces the heart and lungs to work harder
Pulmonary Artery Stenosis
-Narrowing of the pulmonary artery, the large blood vessel that takes blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs
-This narrowing may force the heart to pump harder, leading to an enlarged heart and high blood pressure in the right side of the heart
heart rate
-gives you a measurement of beats per minute (BPM)
EKG (or electrocardiogram)
-measures the electrical activity (of heart rate)
-more dimensions to the rhythm
-provides a more indepth picture of the heartbeat and potential defects
-If the test is normal, it should show that your heart is beating at an even rate of 60 to 100 bpm