menstrual cycle and secondary sexual characteristics 17
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the menstrual cycle?
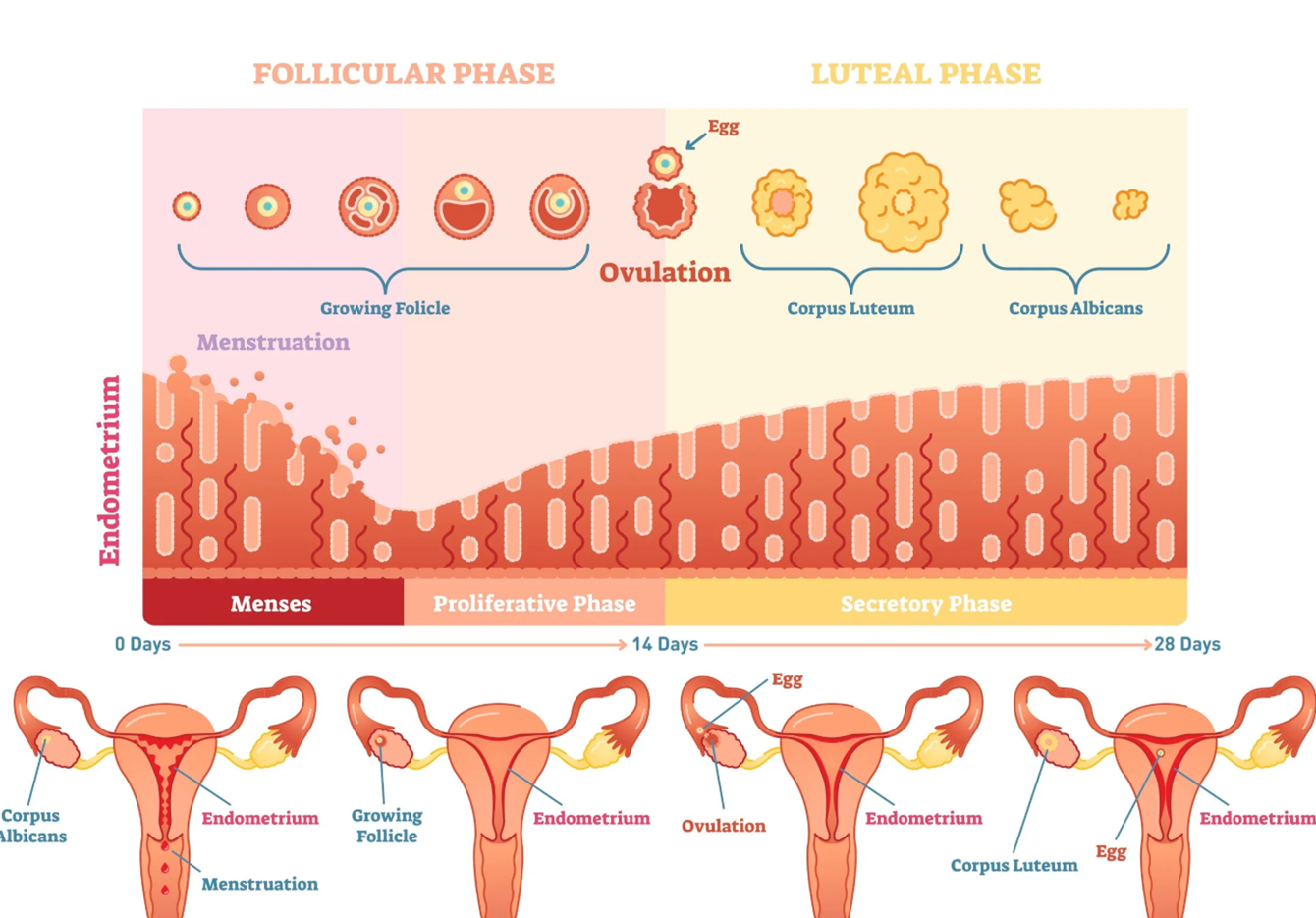
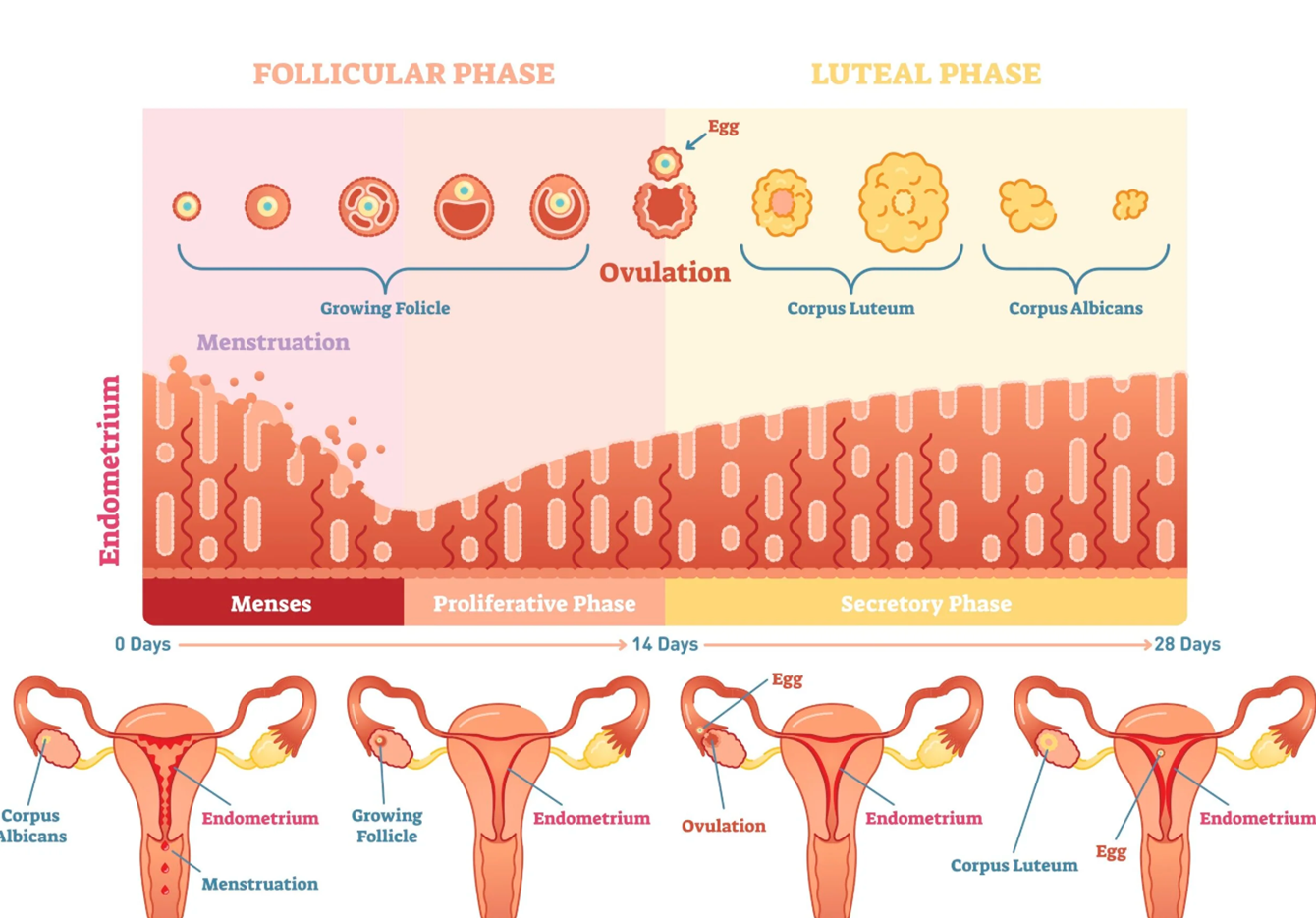
The change in the in the uterine limning, in the endometrium and the vagina
Why does the menstrual cycle occur?
in preparation for a developing embryo in case the egg released at the ovulation is fertilised and for the possible implantation of the embryo
What other cycle is close to the menstrual cycle?
Ovarian
Which hormones are the menstrual cycle mainly controlled by?
Oestrogen and progesterone
When does the menstrual cycle begin and end?
Puberty and menopause
When does menopause begin?
Menopause begins after menstruation has stopped for 12 consecutive months as a result of the ovaries ceasing reproductive hormone production, which also marks the end of the ovarian cycle
What happens when the follicle matures in the ovarian cycle?
Oestrogen causes the endometrium of the uterus to become thicker and softer
What structural changes occur in the endometrium post-ovulation?
The number of blood vessels and mucus-secreting glands increases
What does the endometrium secrete post-ovulation and what is it rich in?
A watery mucus rich in glycogen
What happens to the corpus luteum if fertilisation does not occur?
It degenerates due to decreasing levels of progesterone
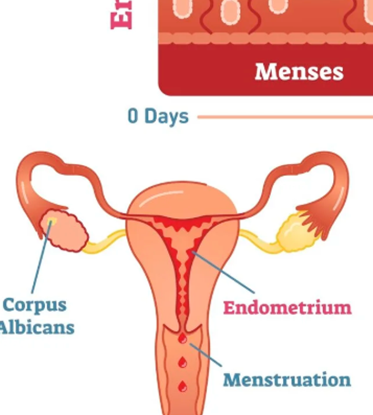
When does menstruation occur in relation to ovulation?
14 days post-ovulation
What is shed during menstruation?
The uterine lining, blood capillaries, mucous secretion, and cell debris via the vagina
Why does menstruation occur?
The egg is not fertilised by a sperm
When progesterone levels are low?
Day 1-4 because of the degeneration of the corpus luteum
When are oestrogen levels low?
Day 1-4
At day 1-4 what is happening in the ovarian cycle
It is in its early follicular phase
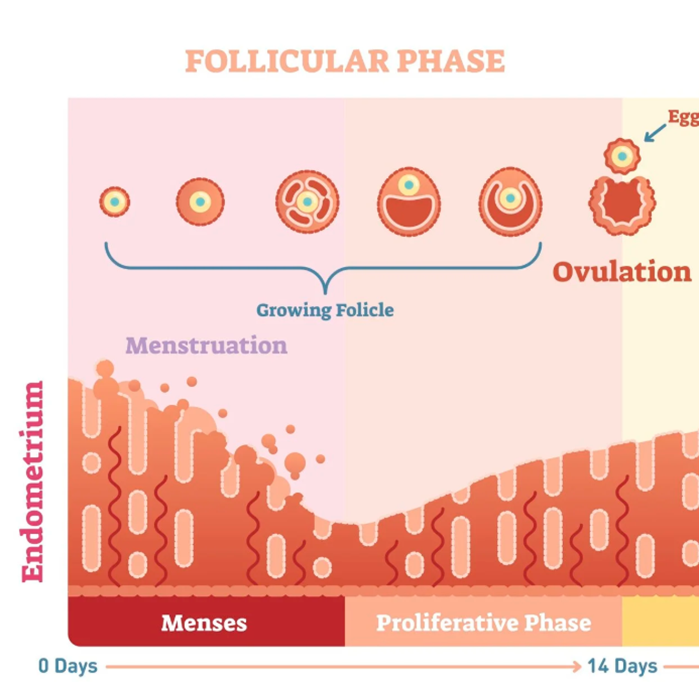
What is the proliferative phase and how long is it?
Pre-ovulation 5-12 days
How long is menstruation
Day 1 -4
What happens to the endometrium in the proliferative phase?
The endometrium begins to repair as the ovarian follicle develops and matures
What happens to oestrogen in pre-ovulation (proliferative phase) and why
Oestrogen increase because of the growing follicles allows the endometrium produced by the growing follicles allows the endometrium to thicken and grow
What other phase in the ovarian cycle in the proliferative phase?
Follicular phase
What days do ovulation occur?
13-15 days
What happens day 13-15 and what part of the cycle is it?
Increased oestrogen levels stimulate a spike in LH leading to rupture of the most mature follicle, releasing the egg into the uterine tube
How long is secretory phase?
16-20
What secretion occurs in 16-20
Secretion of the mucus by the endometrium, cervix and uterine tubes to aid in the movement of the unfertilised egg
What does the development of the corpus luteum do and when does it occur?
Produces high levels of progesterone and moderate levels of oestrogen, happens in the secretory phase 16-20 days
What do high levels of progesterone maintains?
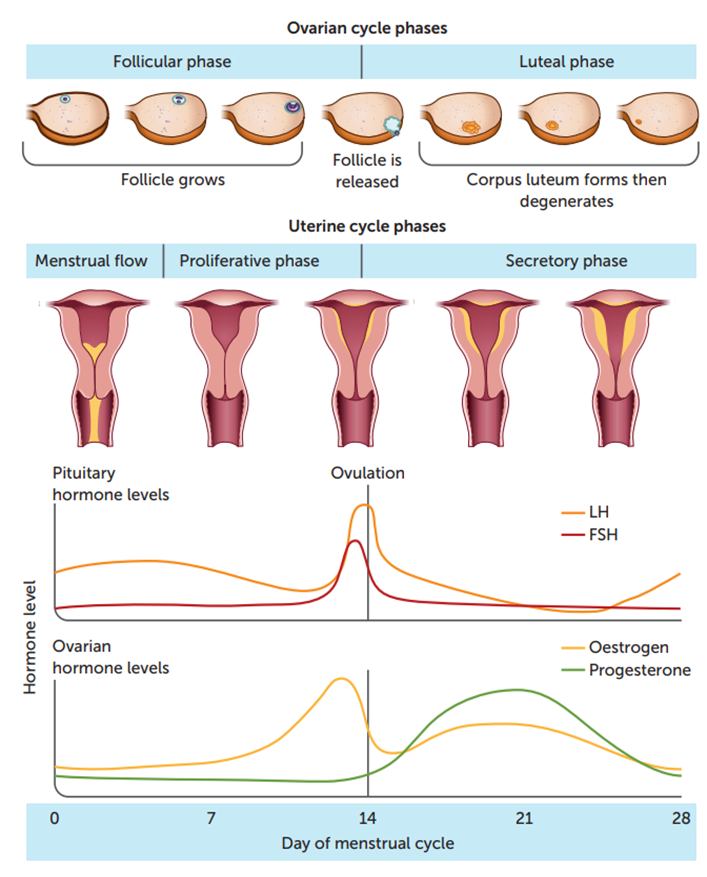
It maintains the endometrium
Secretory phase pre menstruation days 21-28
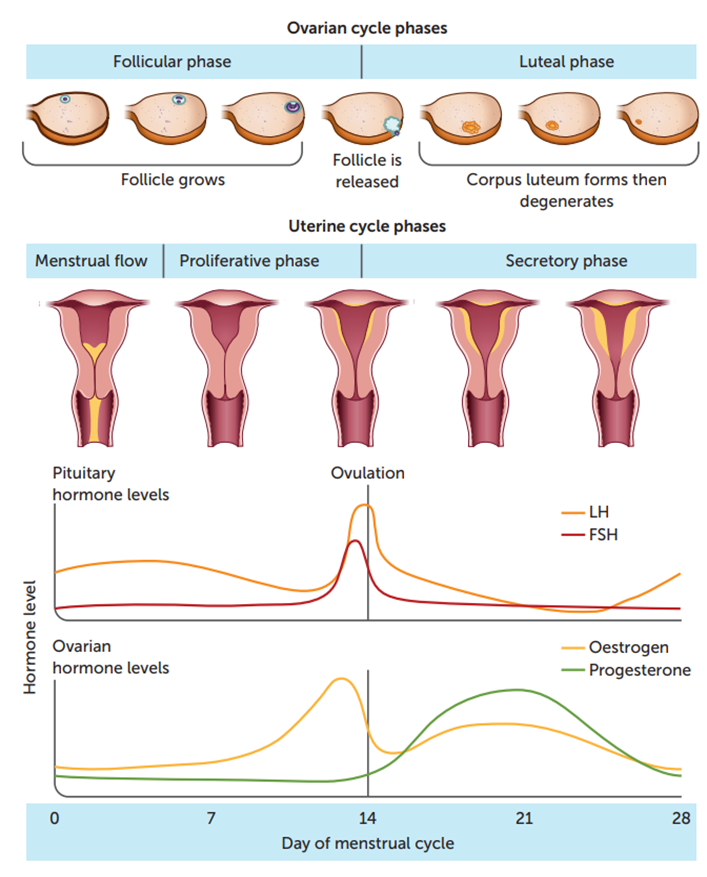
Degeneration of the corpus luteum resulting in declining levels of progesterone and oestrogen and the decline in hormone levels results in deterioration of the endometriu
Menstrual cycle
Development of secondary sexual characteristics
Secondary sexual characteristics are features that are associated with a sex however are not directly involved in reproduction themselves
They are induced by reproductive hormones testosterone in males and oestrogen and progesterone in females
Male
•Facial, chest and back hair
•Increase in the size of the larynx
•Increase in the length of the vocal cords
•Increased deepening of the voice and voice 'breaks'
e
Femal
•Enlarging of the breasts
•Broadening of the hips
•Deposition of fat
Both
•Pubic hair
•Armpit hair