OpenSciEd 7.3 Metabolic Reactions
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
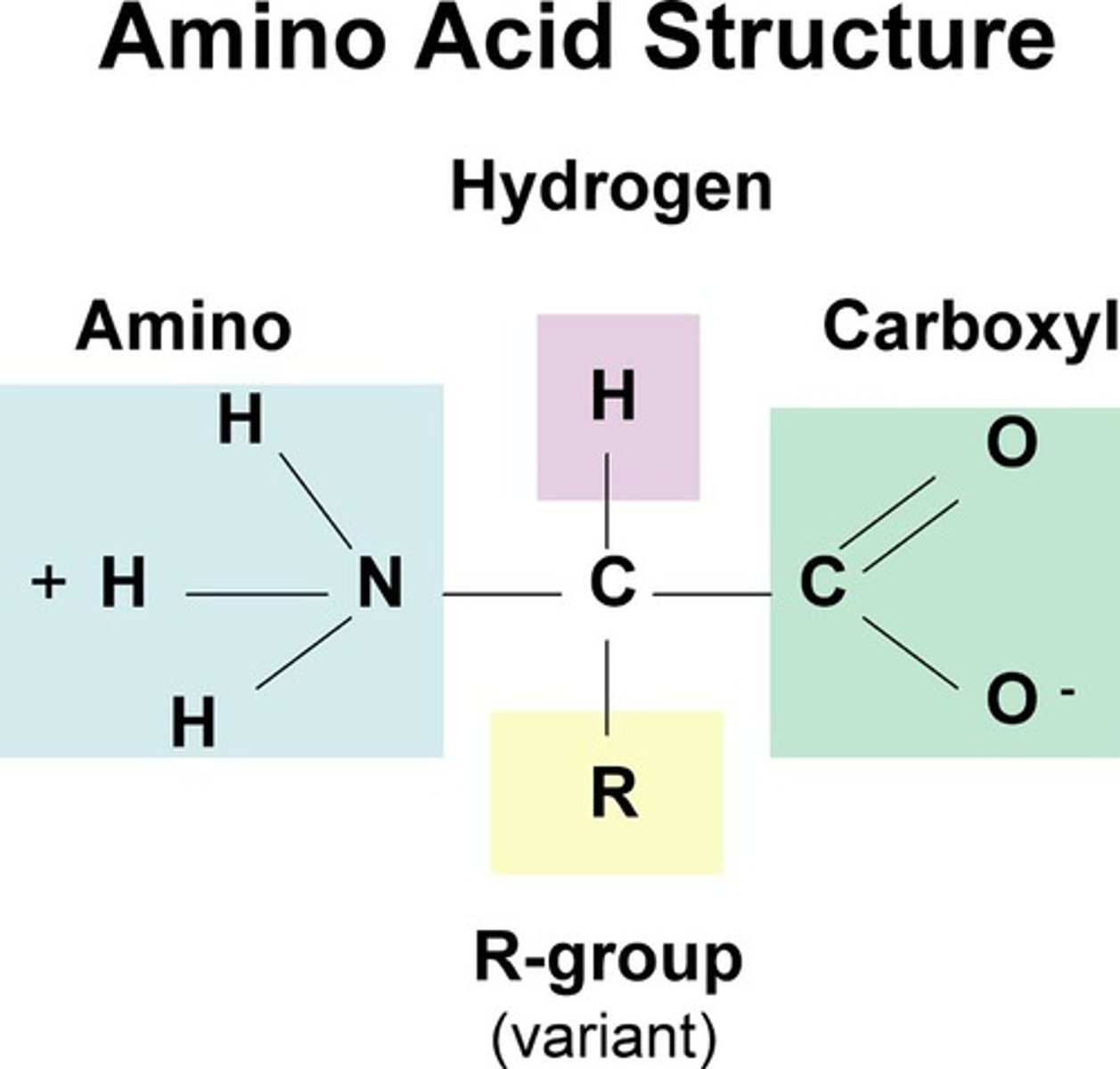
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
carbohydrate
compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; major source of energy for the human body

cellular respiration
the process by which cells use oxygen to produce energy from food

chemical digestion
Process by which enzymes break down food into small molecules that the body can use
chemical reaction
process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals

Combustion
the process of burning something

diagnosis
Identification of an injury or disease
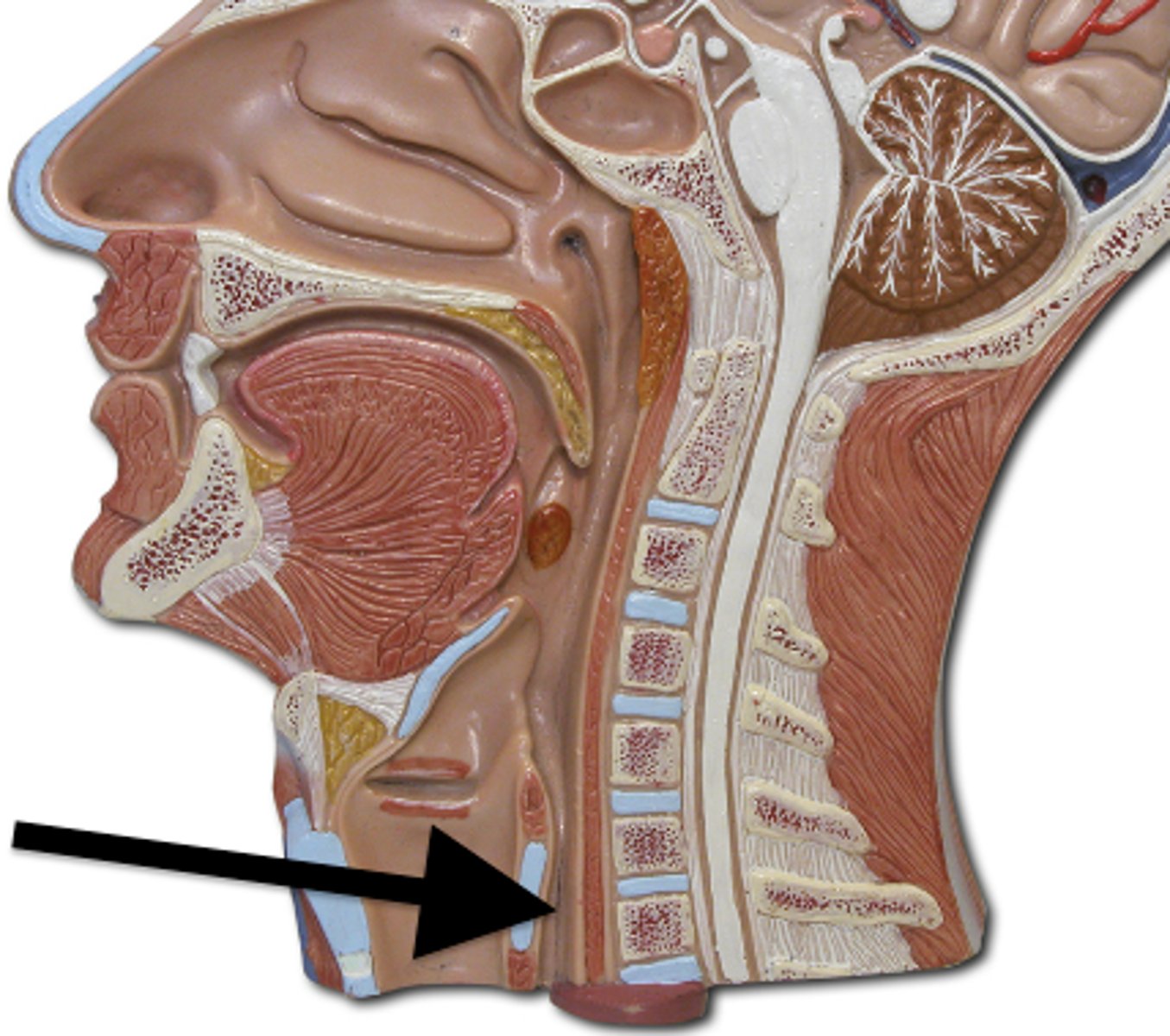
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
fatigue
Extreme tiredness, exhaustion

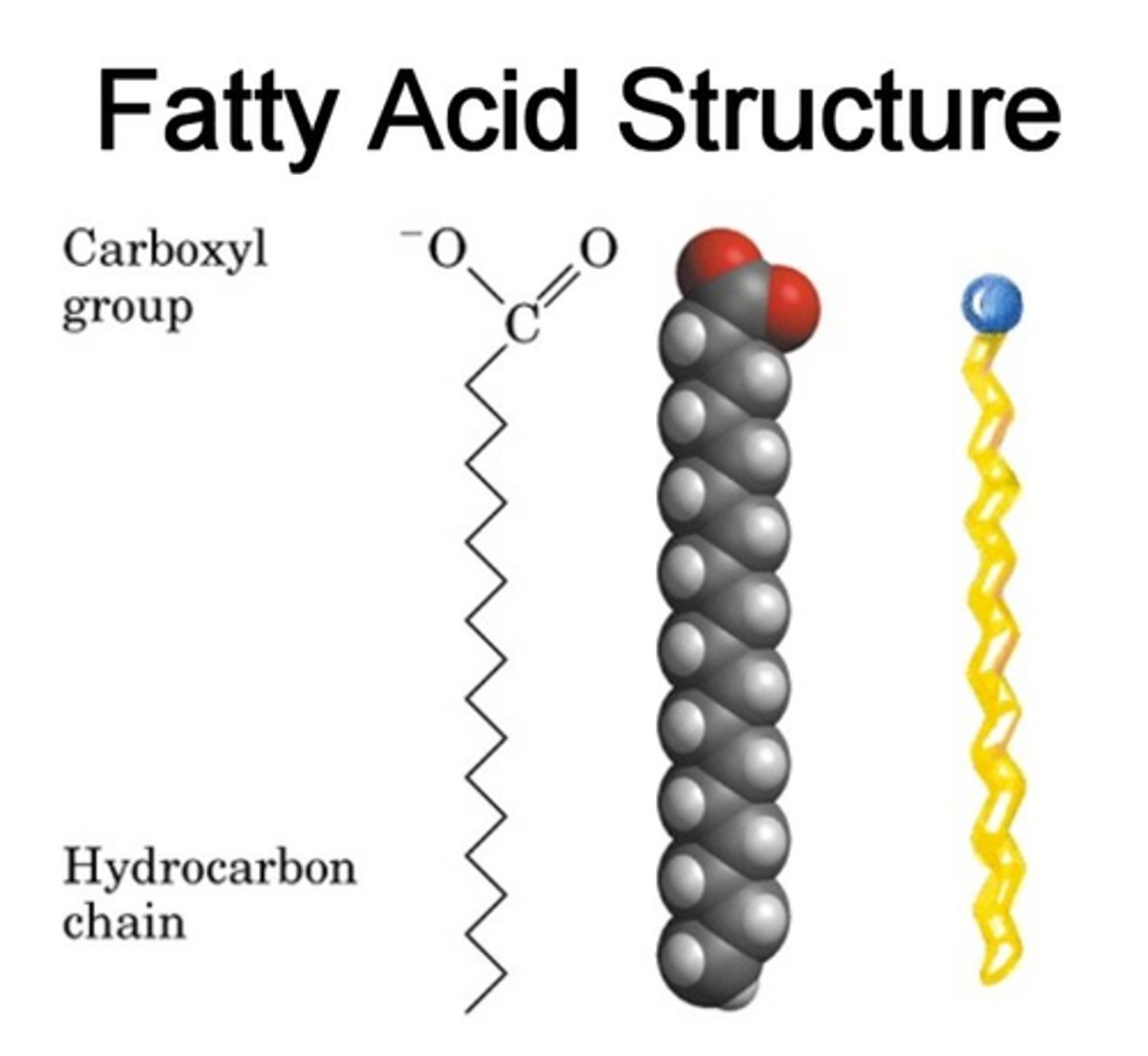
fatty acids
unbranched carbon chains that make up most lipids
Glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger.

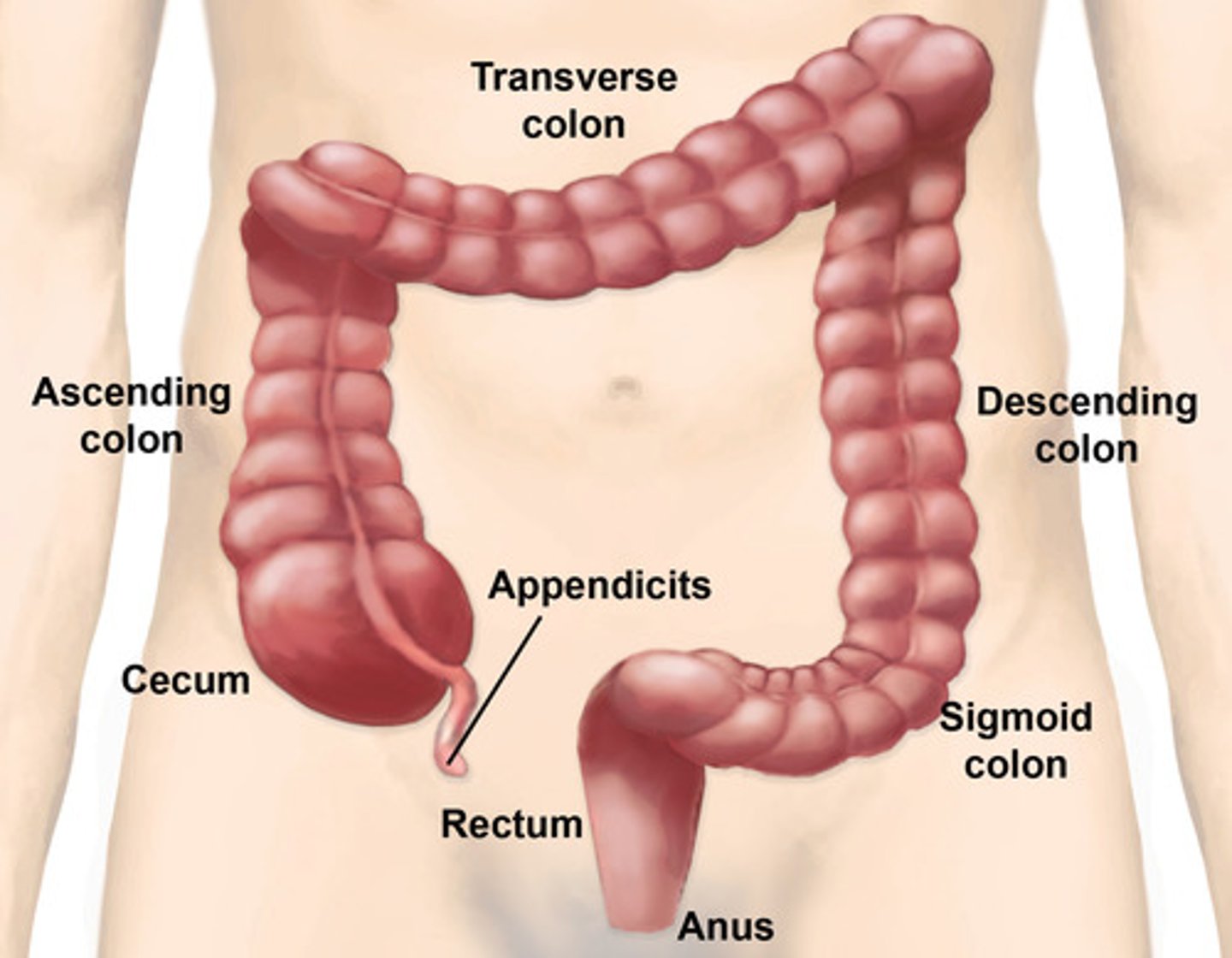
large intestine
The last section of the digestive system, where water is absorbed from food and the remaining material is eliminated from the body
mechanical digestion
physical breakdown of food

Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
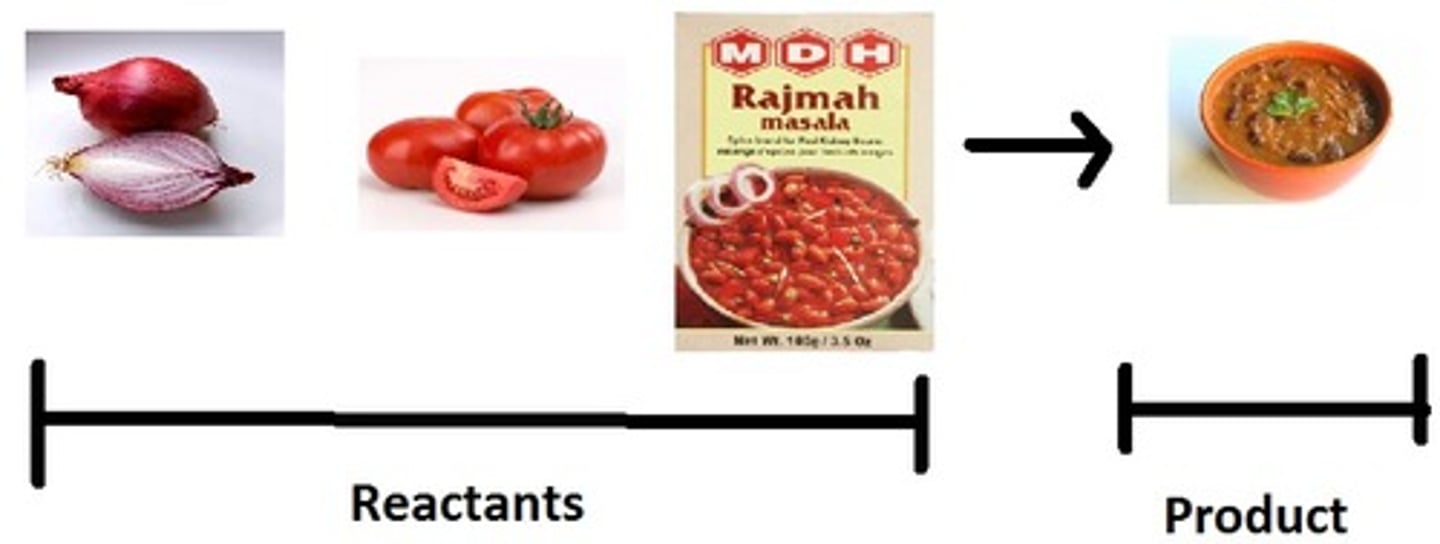
product
A substance produced in a chemical reaction

Protien
a class of nutients that builds body tissues and supplies energy. Protien is made of amino acids.
Reactant
A chemical substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction
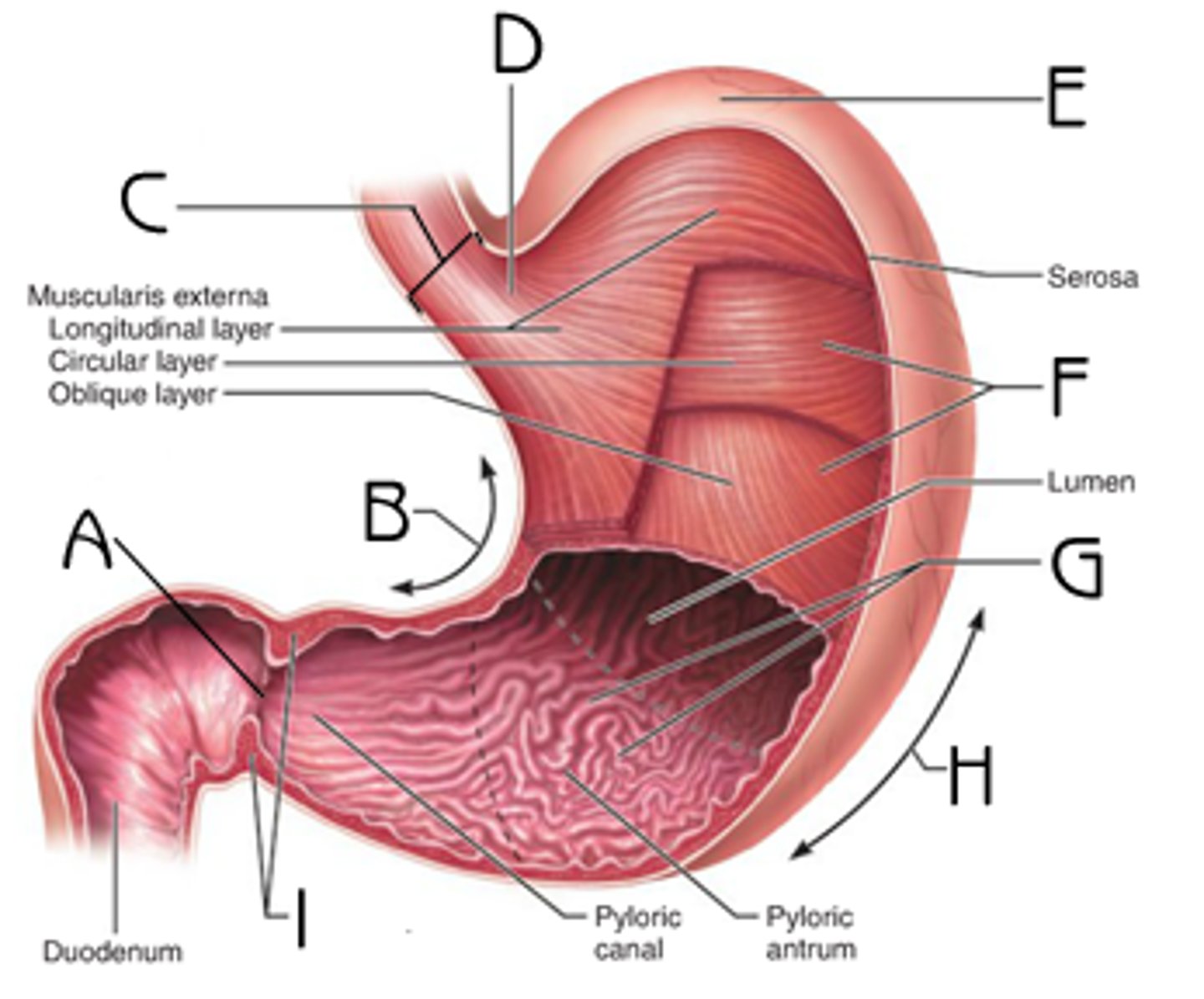
stomach
large muscular sac that continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of food
small intestine
The part of the digestive system in which most chemical digestion takes place.
nerve cells
fast cell communication, sends impulses through nervous system
circulatory system
(aka cardiovascular system) This system works as the transportation highway for the body. It consists of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It transports substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients in the body.
living things levels of organization
cells, tissues, organs, organ system
Organ
a structure composed of two or more tissue types that performs a specific function for the body
cells
The simplist level of organizations in humans;
system
set of organs tat work together to perform a specific function.
physcial change
Teeth chewing food into smaller digestible pieces is known as
enzymes
which example shows a chemical change to food during digestion?
mechanical digestion
by teeth
Lungs
Main organs of the respiratory system-balloons inflating or deflating can model this
nervous system
main organ-brain, regulates other systems
circulatory system
main organ-heart
respiratory system
main organ-lungs, supplies blood with oxygen
System
group of interdependent organs with similar functions
tissue
group of cells with similar structure or function
organ
group of tissues that work together to perform closely related functions
cell
structure and functional unit of all living things
circulatory system
works with digestive system to transport nutrients