Bio Lab Quiz (Labs 1-3)
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Biodiversity
includes all forms of life in its great diversity
Systematics
study of the diversity of organisms (both present and extinct) and their relationships
Taxonomy
aims at classifying and naming organisms
Phylogeny
representation of the evolutionary history of a group of organisms
tree indicates common ancestors and descendants (lineages)
Binomial nomenclature
each species name consists of two Latin words: the genus (group of species) and the specific epithet (species name)
Rules for binomial nomenclature
when writing: italics or underline
only genus name should be capitalized
genus can be abbreviated to a single letter (ex. H. sapiens)
Hierarchy of Taxonomic Classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phyla, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Which domain(s) contain(s) prokaryotic organisms?
Bacteria and Archea
Domain Bacteria
contains most diverse prokaryotes
most heterotrophic
unicellular organisms
Domain Archea
contains unicellular prokaryotes
less diverse than Bacteria
diff than Bacteria: due to diff in rRNA, plasma membrane, cell wall chemistry
Domain Eukarya
diverse unicellular and multicellular organisms
cells have membrane-bound nucleus
divided into 4 Kingdoms (Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia)
Derived characters
when a group has its own individual characteristics, divergence is presumed
Ancestral characters
characteristics shared by all groups, ancestor and descendants
Cladogram
same as phylogenetic trees
diagram that shows how organisms are related to each other
Taxonomic/dichotomous keys
enable to identify a specimen by comparing it, feature by feature, with alternative possibilities
each choice leads to another pair of statements until the organism can be identified by its taxonomic category
What do all cells have?
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
genetic material (DNA)
ribosomes
Shapes of Prokaryotes
Cocci (spherical)
Bacilli (rod-shaped)
Spirilla (spiral-shaped)
Protists
composed of eukaryotic cells
nucleus and membrane bound organelles
most are microscopic
Sessile
organisms that are not capable of moving from one place to another
Motile
organisms capable of moving from one place to another
Protists are also called…
algae: posses chloroplasts containing chlorophyll (can photosynthesize); autotrophs
protozoa: unicellular heterotrophs (use phagocytosis); possess flagella, cilia, pseudopods for movement
fungus-like protists: heterotrophic Slime + Water Molds that produce spores
Slime & Water Molds
known as oomycetes, have several similarities to fungi; decomposers or parasites; produce spores
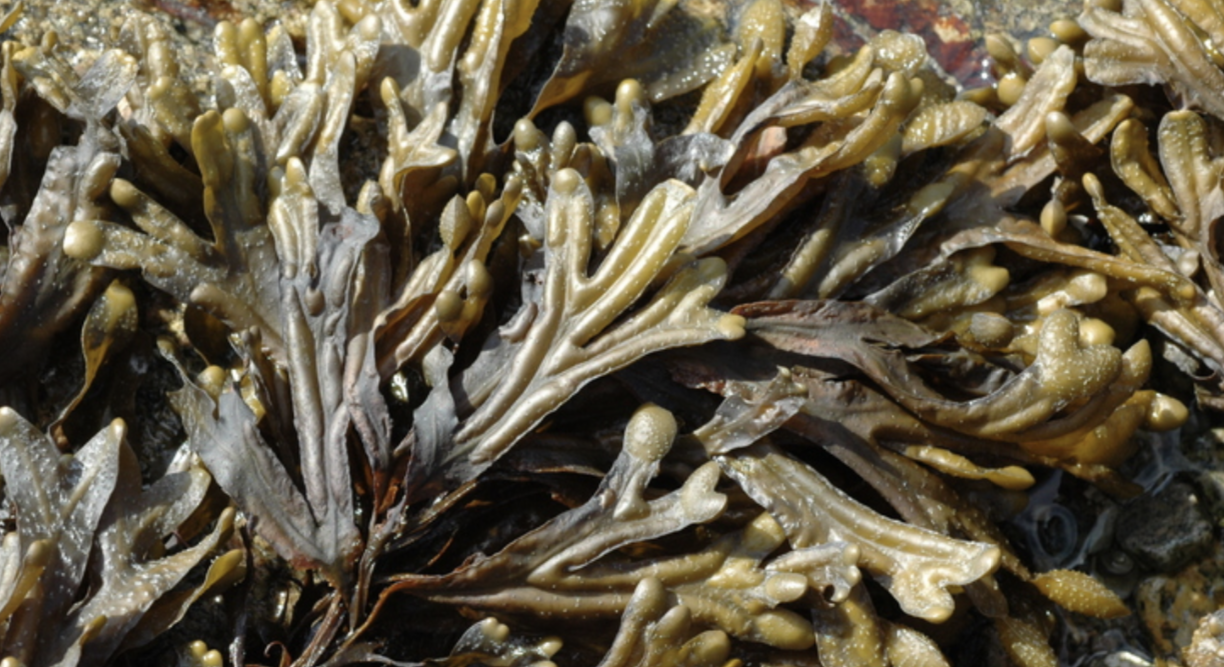
Fucus
macroscopic algae, multicellular, sessile, brown pigment, leafy, lives in salt water

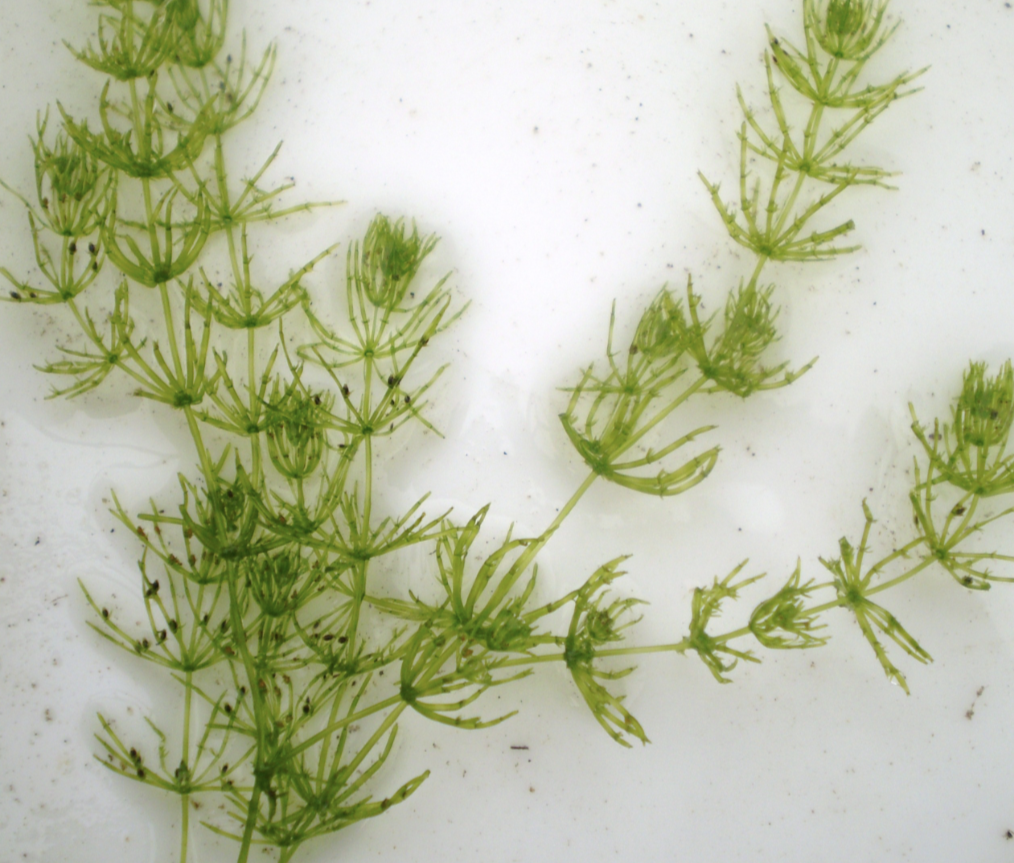
Chara
macroscopic, green pigment, lives in freshwater, multicellular

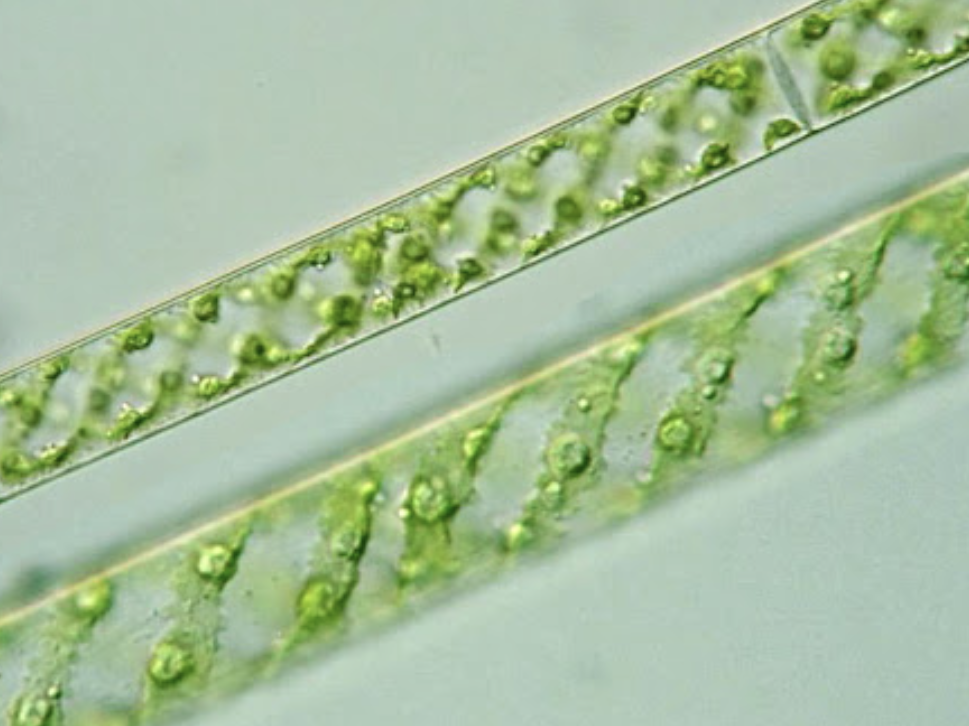
Spirogyra
microscopic, unicellular, green-rod like structures

Volvox
microscopic, lives in a colony, algae, motile (flagella), green-pigment
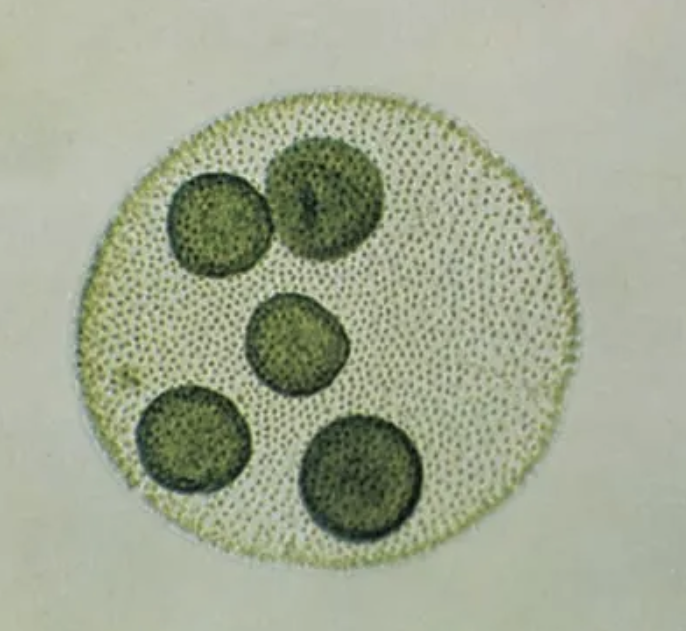
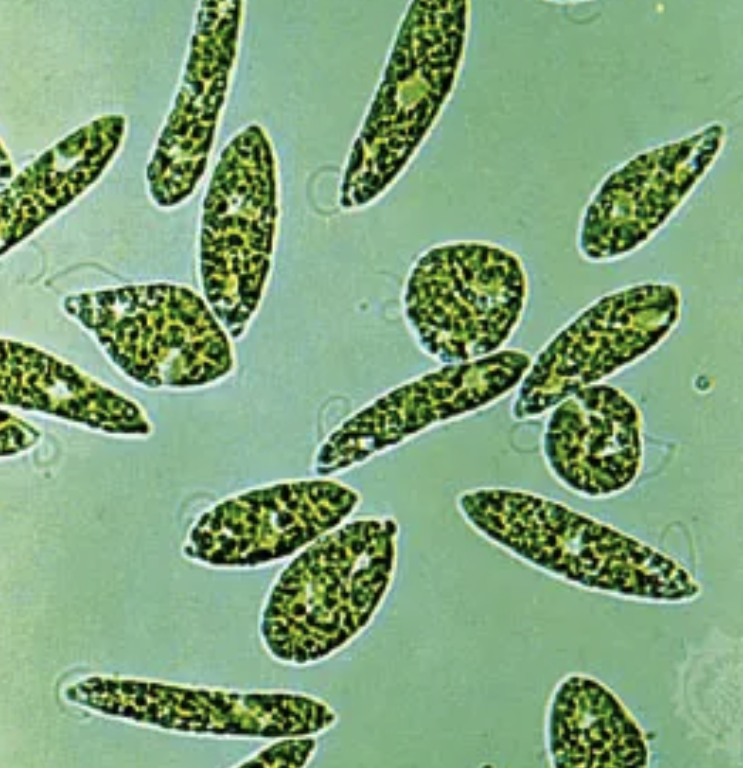
Euglena
microscopic, motile (flagella
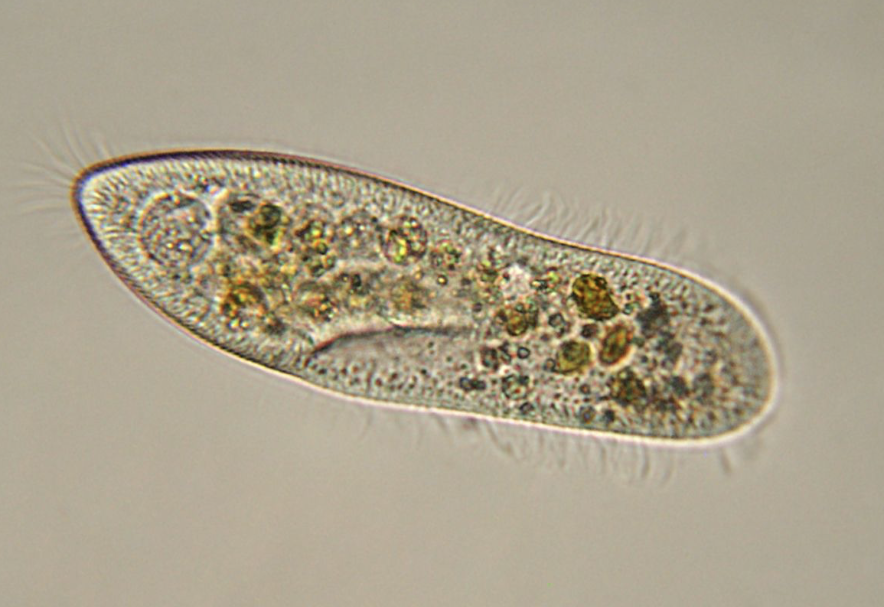
Paramecium
microscopic, protozoa, motile (cilia), unicellular, tan
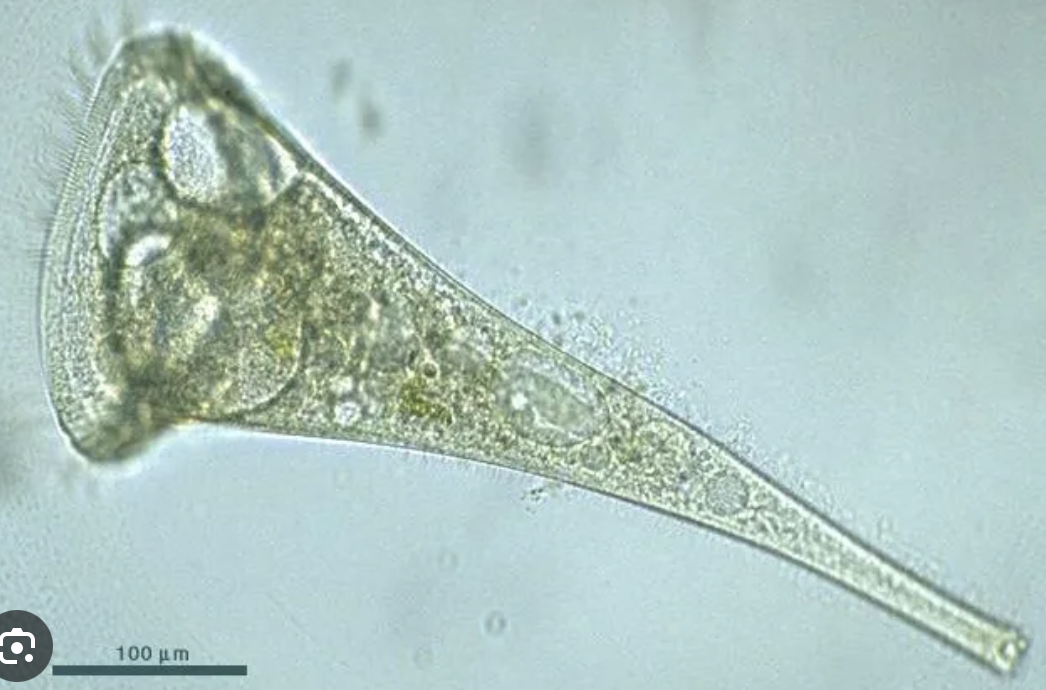
Stentor
microscopic, unicellular, protozoa, motile (cilia)
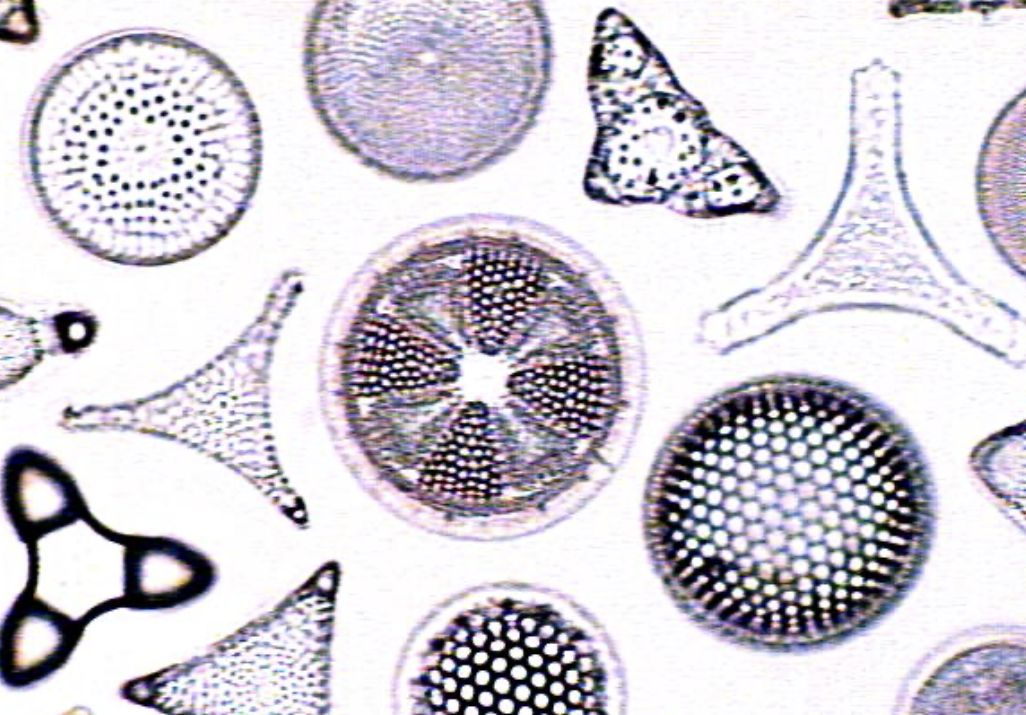
Diatoms
microscopic, freshwater, variety of geometric shapes, glass-like appearance
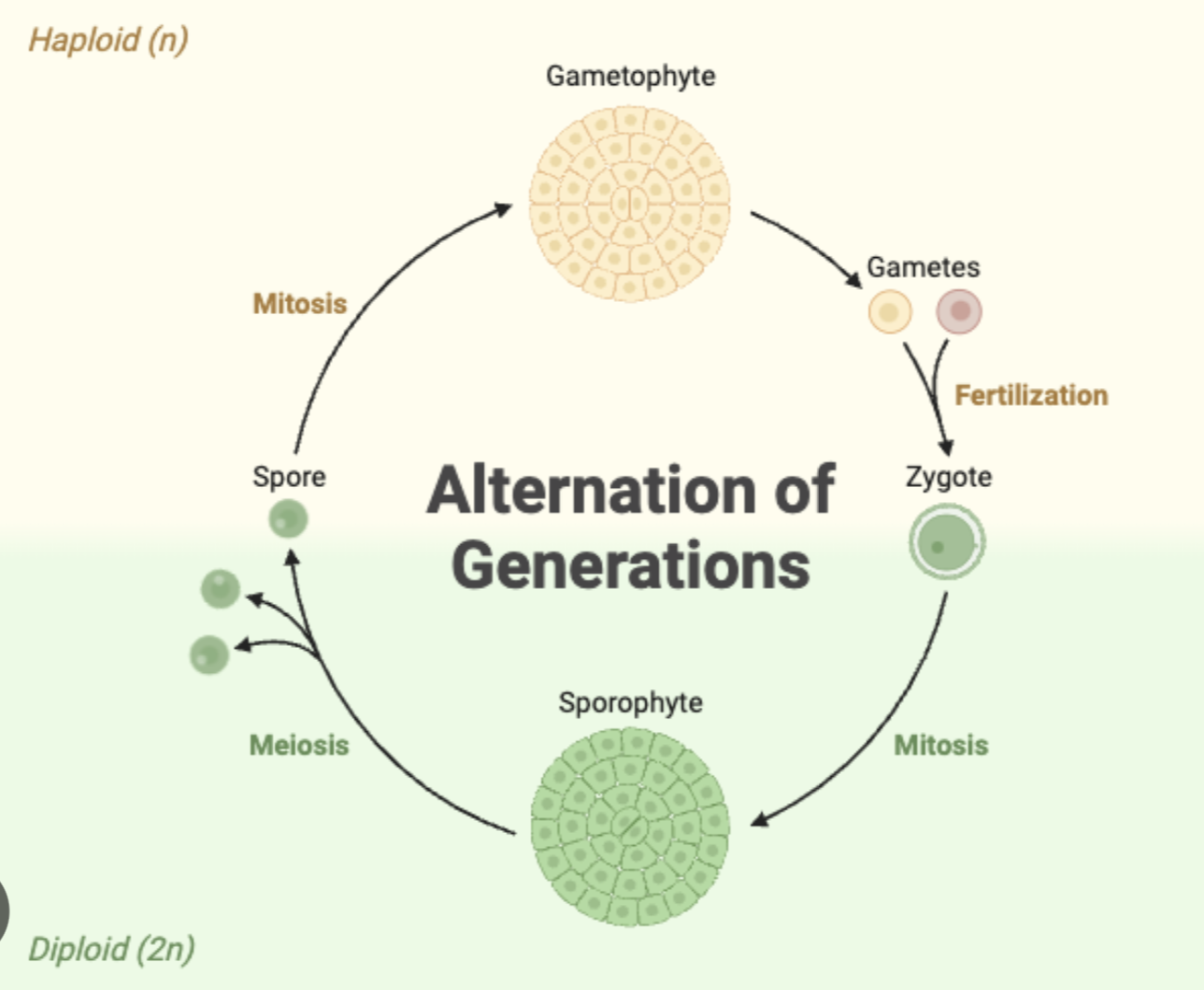
Alternation of Generations
plants that have both a multicellular diploid phase (sporophyte) and multicellular haploid phase (gametophyte)
Bryophytes
dominant gametophyte with dependent sporophyte
Lycophytes, Ferns, Horsetails
dominant sporophyte, both gametophyte and sporophyte can live independently
Gymnosperms, Angiosperms
dominant sporophyte with dependent gametophyte
Xylem
tissue in plants that transport water, cell walls make them rigid and strong
Phloem
tissue that transports sugars
Megaphylls
multiple leaf veins that branch out
Microphylls
only one leaf vein that does not branch out
Spores
haploid, grow into a new gametophyte, contains sporopollenin (prevents drying)
Seeds
product of fertilization, diploid embryo that grow into a new sporophyte, seed coat (hard covering that prevents drying)
Charophytes
aquatic
contains sporopollenin
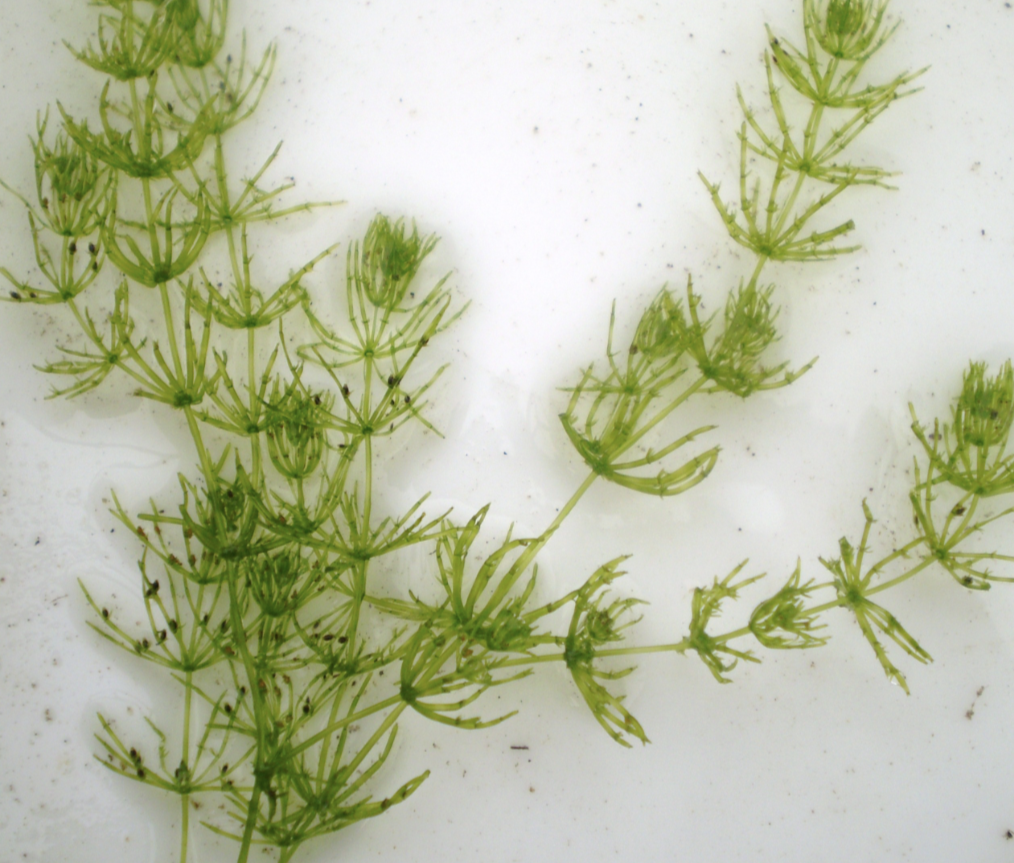

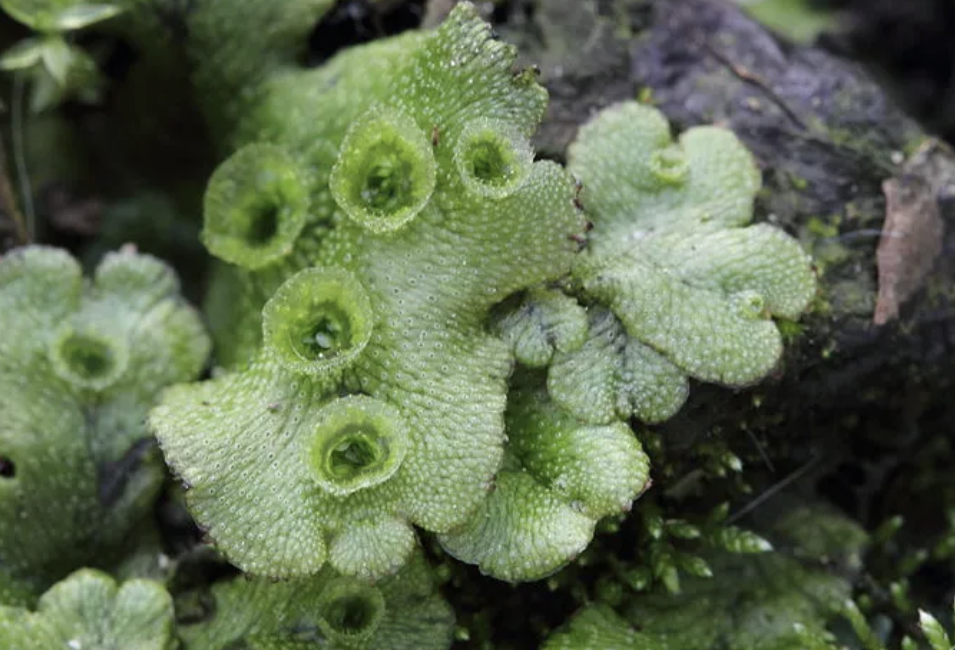
Bryophytes- liverwort
no vascular tissue
reproduce w/ spores

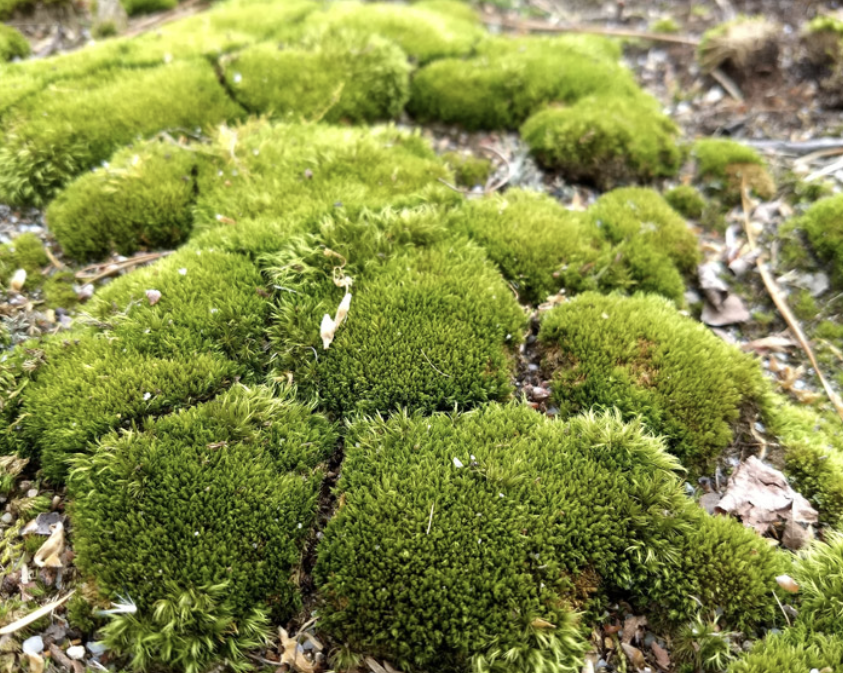
Bryophytes- mosses
no vascular tissue
reproduce w/ spores

Lycophytes
vascular tissue
microphylls
reproduce w/ spores
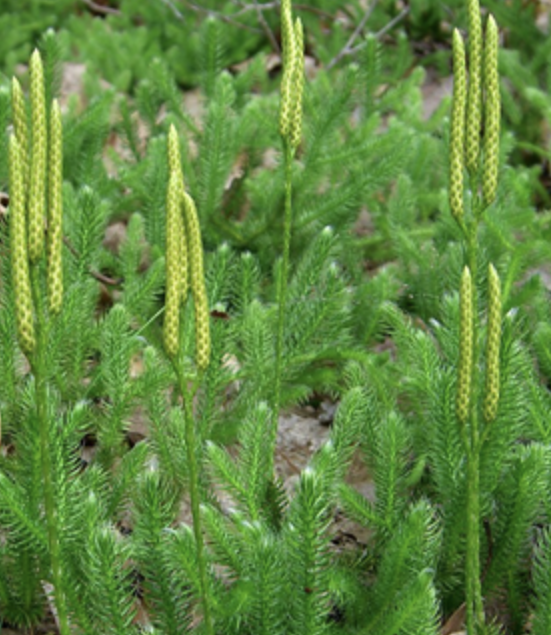

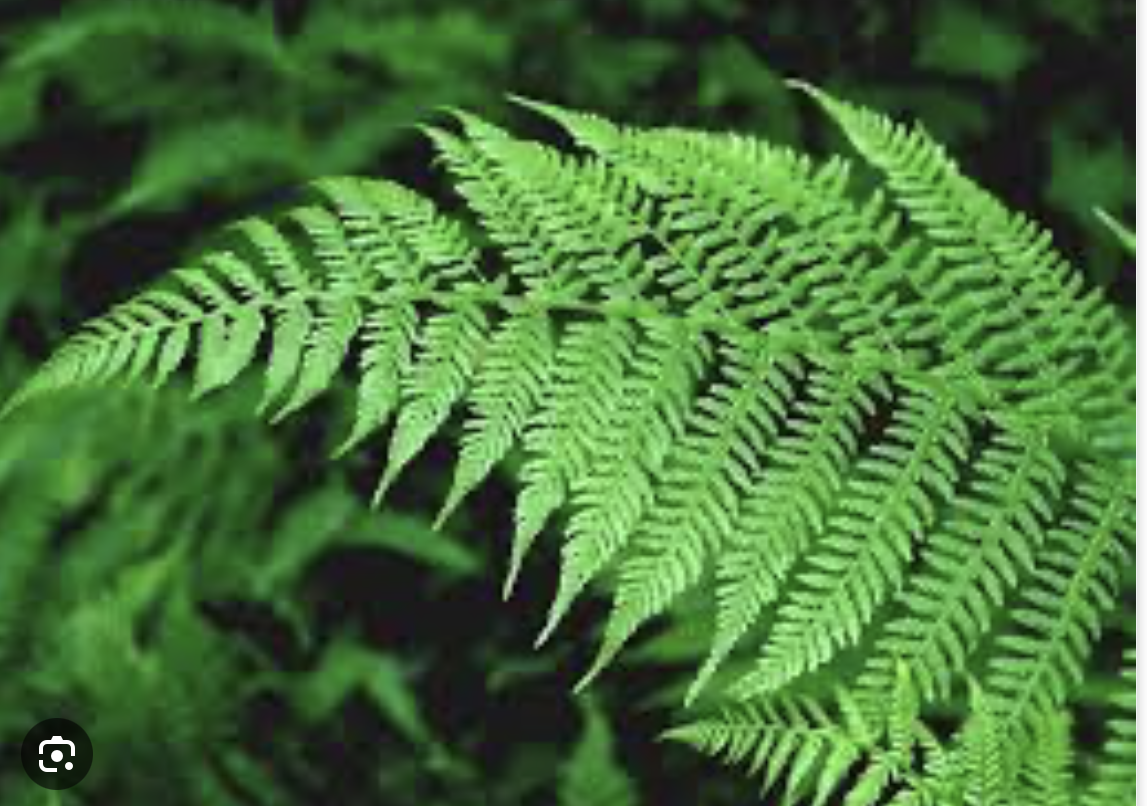
Ferns
vascular tissue
megaphylls
reproduce w/ spores
have sporangia on the backs of leaves

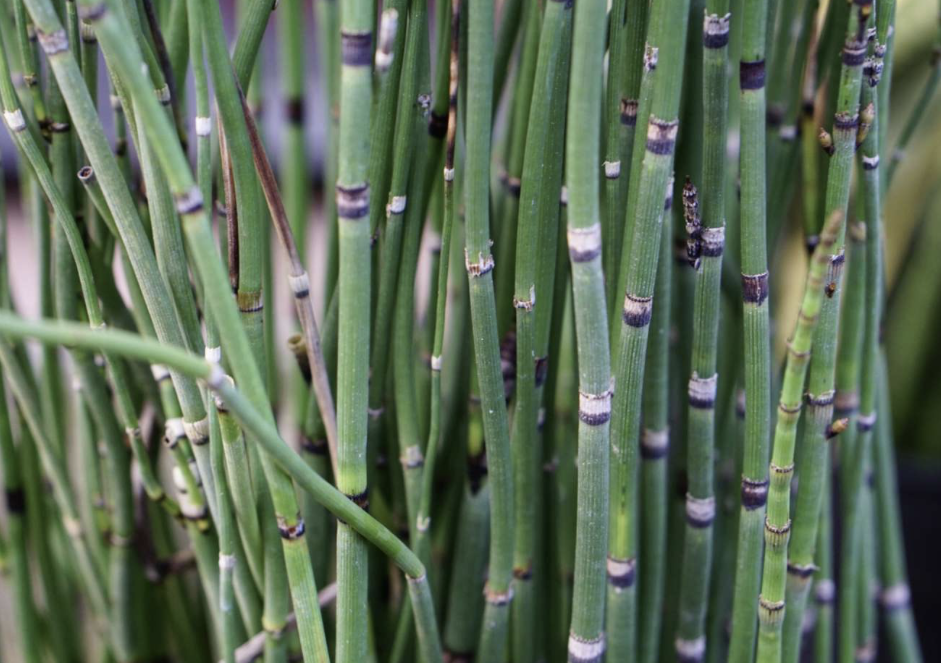
Horsetails
vascular tissue
silica in their cell walls
rigged stems
reproduce w/ spores

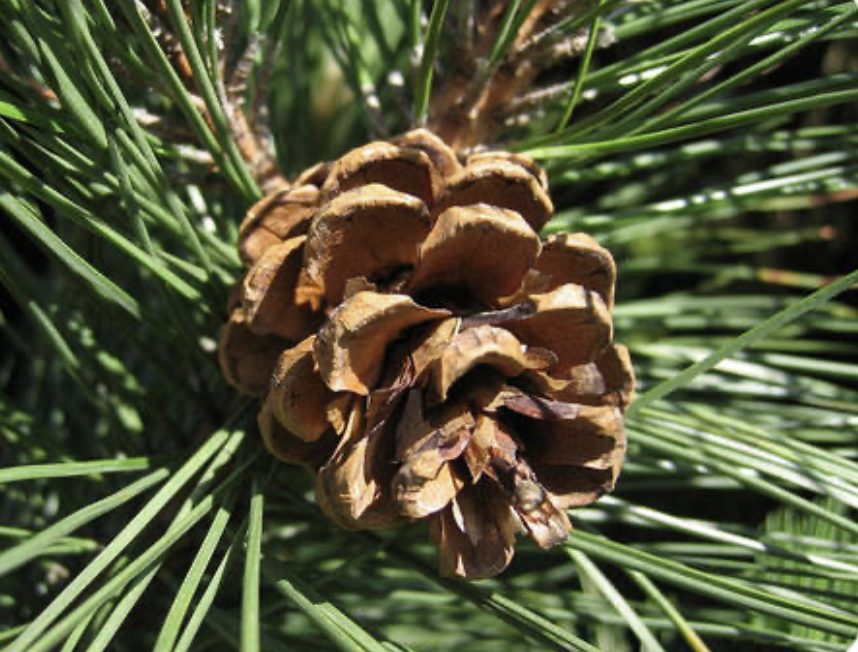
Gymnosperms- conifer
vascular tissue
megaphylls
reproduce w/ seeds
thin, needle-like leaves
male + female cones

Gymnosperms- ginkgo
vascular tissue
megaphylls
reproduce w/ seeds
fan-shaped leaves
separate male and female trees
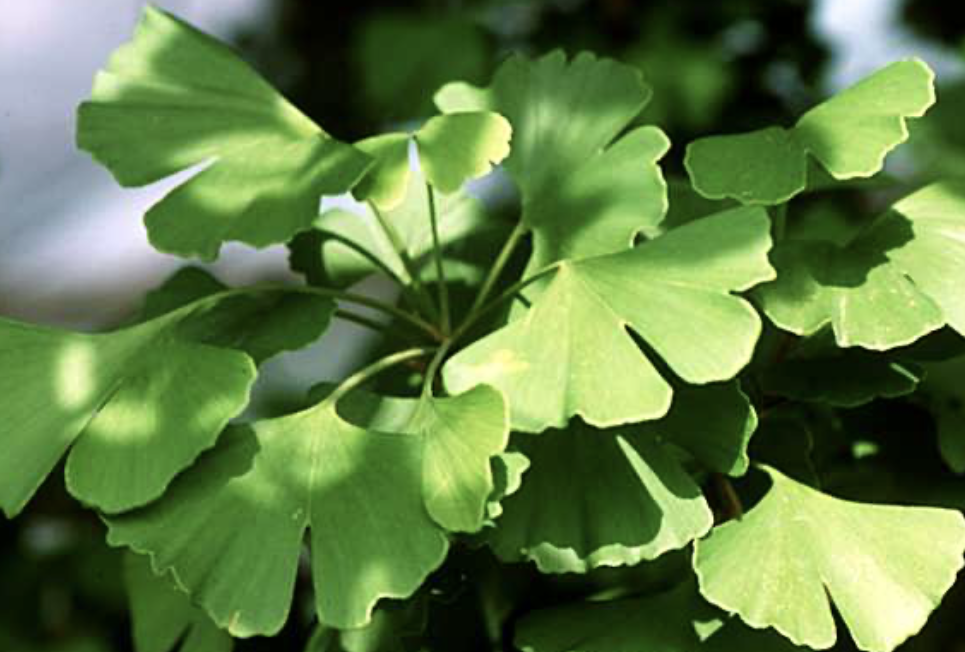

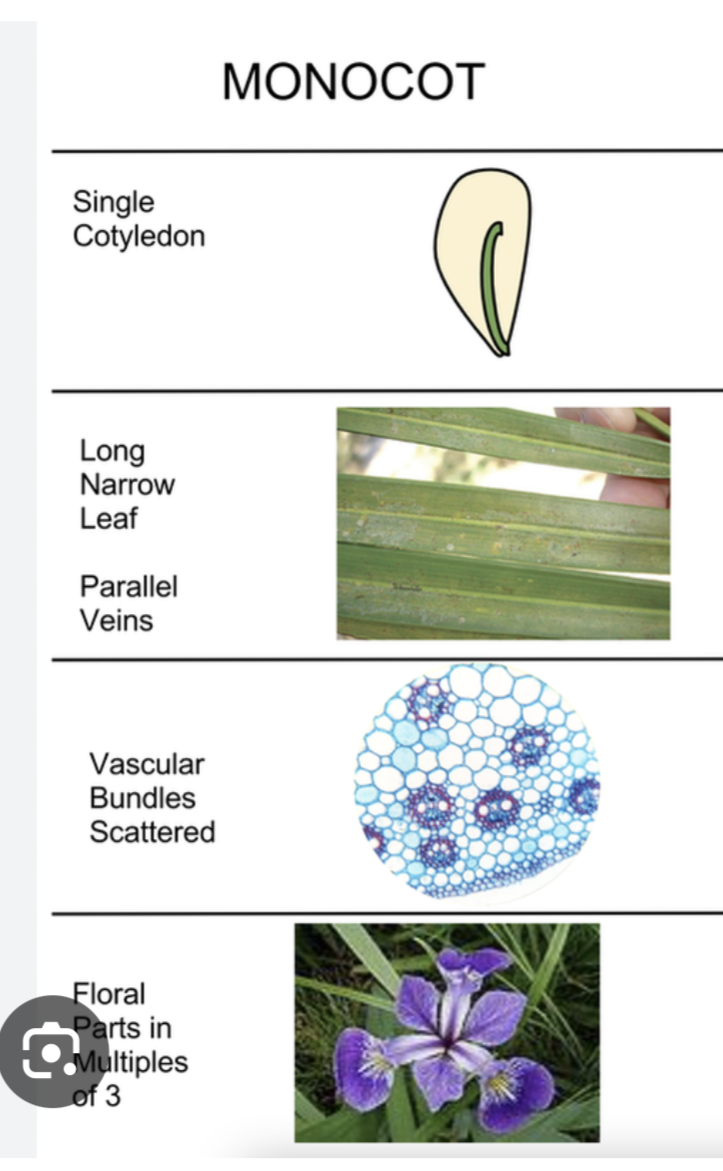
Angiosperms- monocot
vascular tissue
megaphylls
reproduce w/ seeds
have pollen, fruits and flowers
1 cotyledon
have flower parts in 3s
parallel leaf venation
fibrous roots
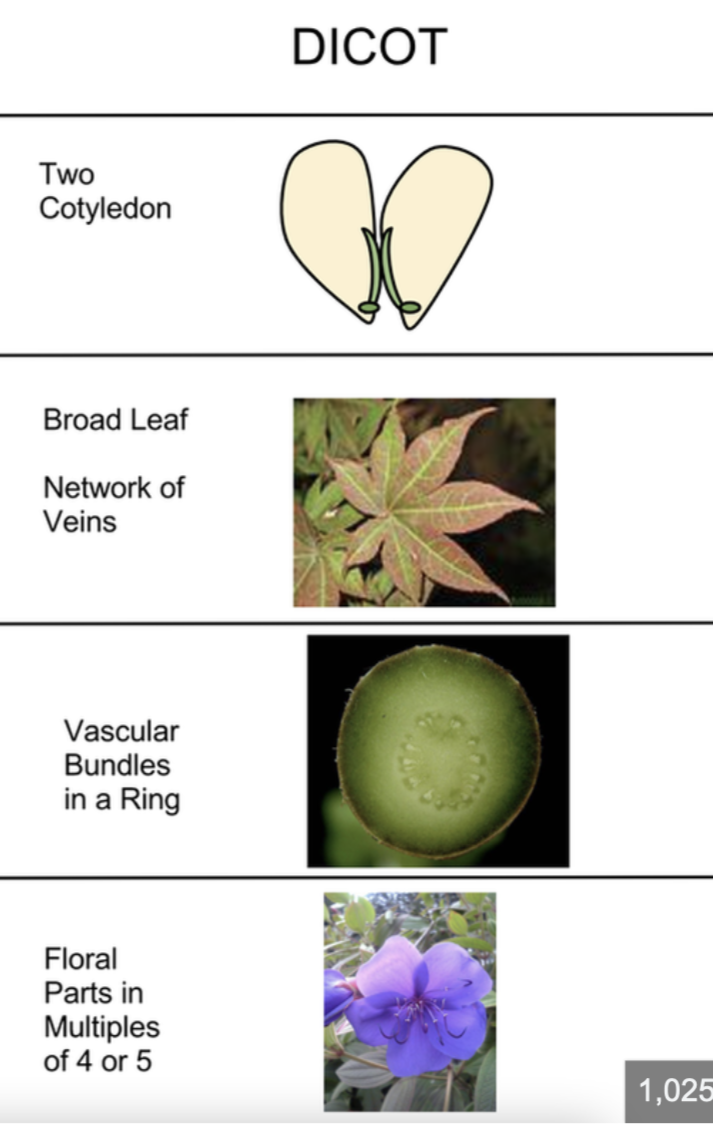
Angiosperms- eudicot
vascular tissue
megaphylls
reproduce w/ seeds
have pollen, fruits and flowers
2 cotyledon
have flower parts in 4’s and 5’s
reticulate leaf venation
taproots
Types of Symmetry
Asymmetrical: animals with no pattern or symmetry
Radial: longitudinal (up-and-down) symmetry
Bilateral: vertical plane cut from front to back separates the animal into roughly mirror-image right and left sides
Germ Layers
Endoderm: inner germ layer (radial sym.)
Ectoderm: outer germ layer (radial sym.)
Mesoderm: middle germ layer (bilateral sym.)
Diploblasts
animals that display radial symmetry with endoderms and ectoderms
Triploblasts
animals with bilateral symmetry with all 3 germ layers
Acoelomate
triploblasts that do not develop a coelom (internal body cavity derived from a mesoderm); mesoderm region is completely filled with tissue; ex: flatworms
Eucoelomate (or coelomate)
arises entirely within the mesoderm germ layer; ex: earthworms, snails insects, starfish
Pseudocoelomate
triploblasts that have a body cavity that is derived partly from mesoderm and partly from endoderm tissue; ex: roundworms
Protostomes
include phyla such as arthropods, mollusks, and annelids; mouth originates first
Deuterostomes
includes chordates and echinoderms; anus develops first then mouth
Gastrovascular cavity
only have one opening for digestion (mouth serves as anus- one long blind tube) ex: platyhelminthes, ctenophora, cnidaria
Alimentary canal
more advanced system; consists of one tube with a mouth at one end and an anus at other; ex: earthworms
Direct Diffusion
gas exchange across outer membranes that meet the oxygen needs of multicellular organisms; ex: cnidarians, flatworms
Skin
a dense network of capillaries lies just below the skin and facilitates gas exchange between the external environment and the circulatory system; ex: earthworms, amphibians
Gills
thin tissue filaments that are highly branched and folded, ex: mollusks, annelids, crustaceans
Diffusion
exchange of water, nutrients, and waste, as well as dissolved gases; ex: cnidaria, ctenophora
Open circulatory system
the blood is not enclosed in the blood vessels and is called hemolymph bc the blood mixes with the interstitial fluid; ex: mollusks, arthropods
Closed circulatory system
blood is contained inside blood vessels and circulates around the heart; ex: crustaceans, squid, octopuses
Water vascular system
system used by echinoderms, sea stars and sea urchins, for locomotion, food and waste transportation, respiration
Phylum Cnidaria
diploblast
radial symmetry
nematocysts
nutrients diffuse into body
gastrovascular system
Phylum Platyhelminthes
acoelomate
flatworms
gastrovascular system
Phylum Mollusca
mantle
open circulatory system
radula
shell
most respire w/ gills
Phylum Annelida
segmentation
dorsal blood vessels
closed circulatory system
Lophotrochozoa
most have a ring of tentacles around mouth (lophophore) and/or planktonic (trochophore) larval stage
Protostomia
blastopore becomes mouth
spiral cleavage
mosaic cleavage
Bilateria
bilateral symmetry
triploblastic
Anthozoa
phylum: cnidaria
only one polyp stage
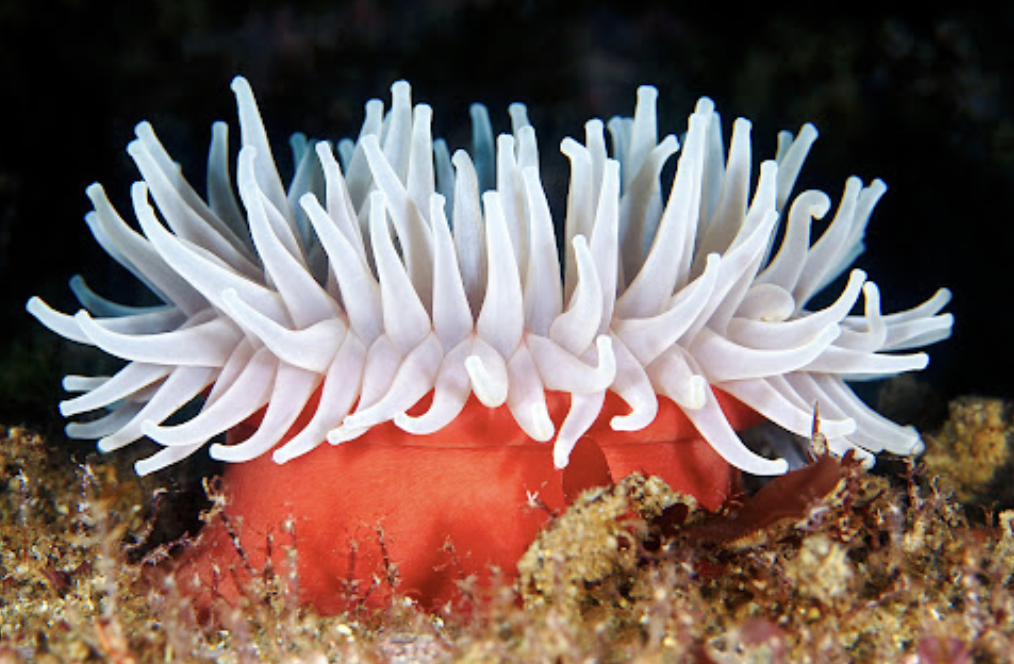

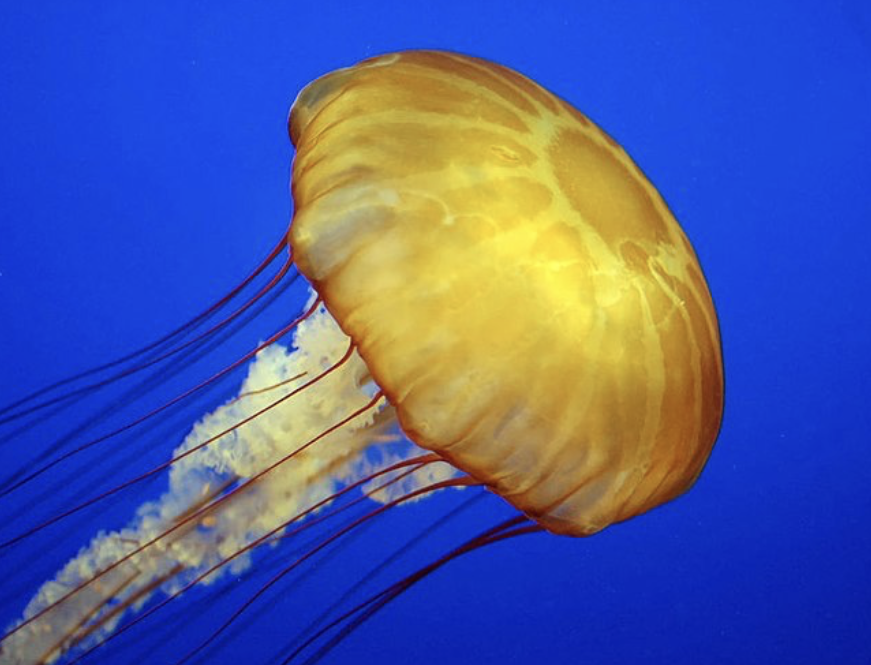
Medusozoa
phylum cnidaria
medusa and polyp stages

Turbellaria
phylum platyhelminthes
has eyespots
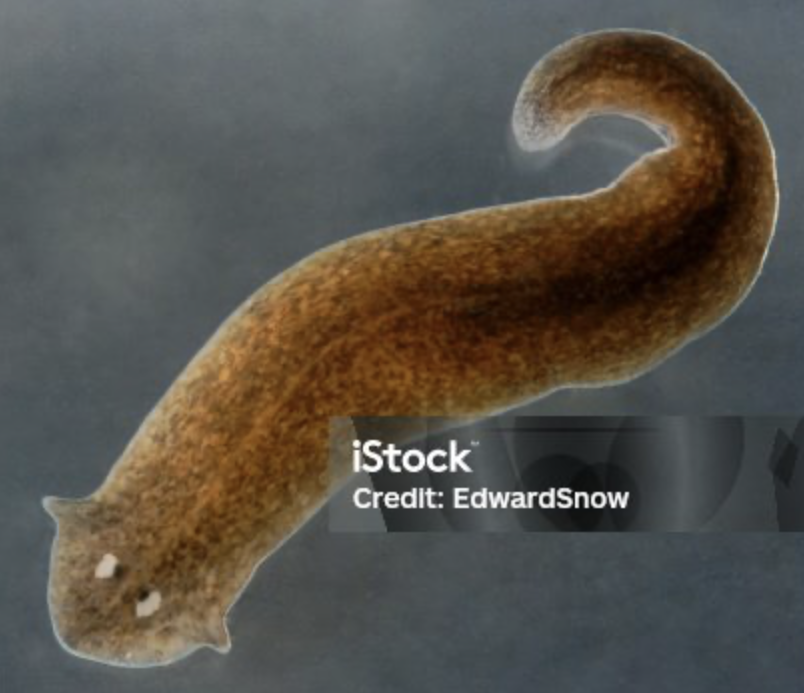
Trematoda
phylum platyhelminthes
parasitic
two suckers attach to host’s guts/lungs
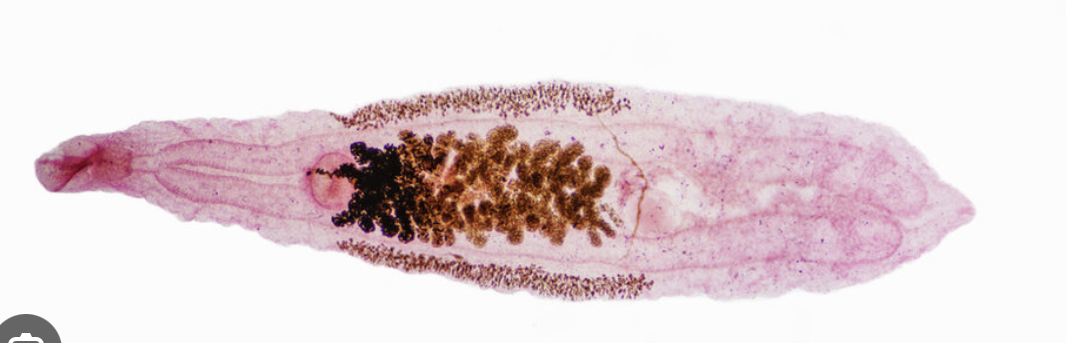
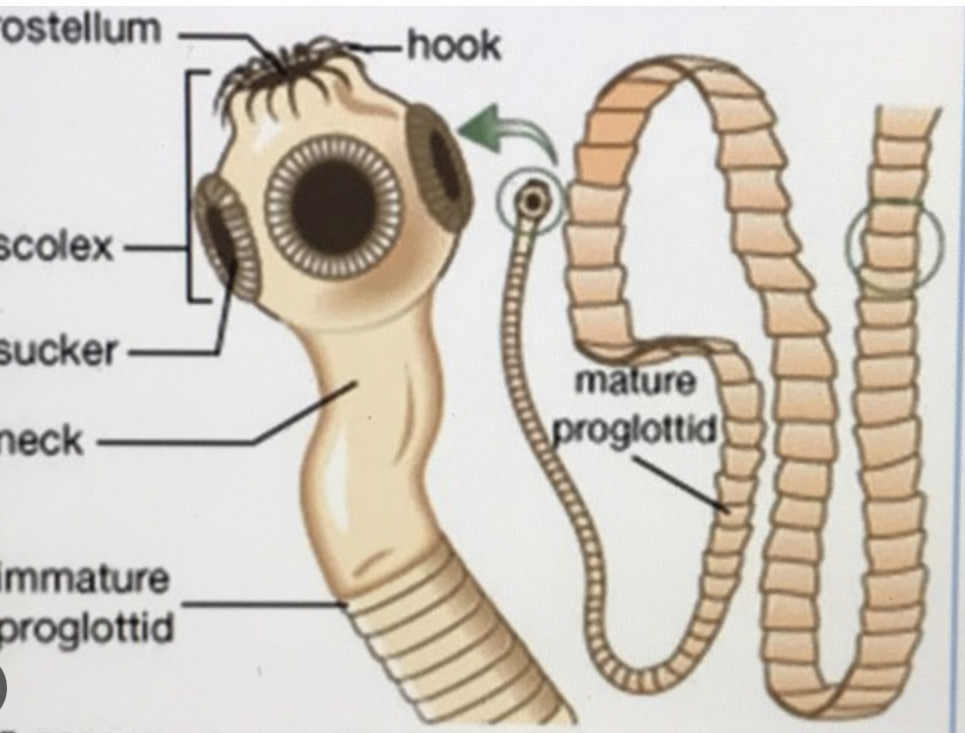
Cestoda
phylum platyhelminthes
parasitic
scolex (suckers w/ hooks)
Gastropoda
phylum mollusca
one shell
some live on land
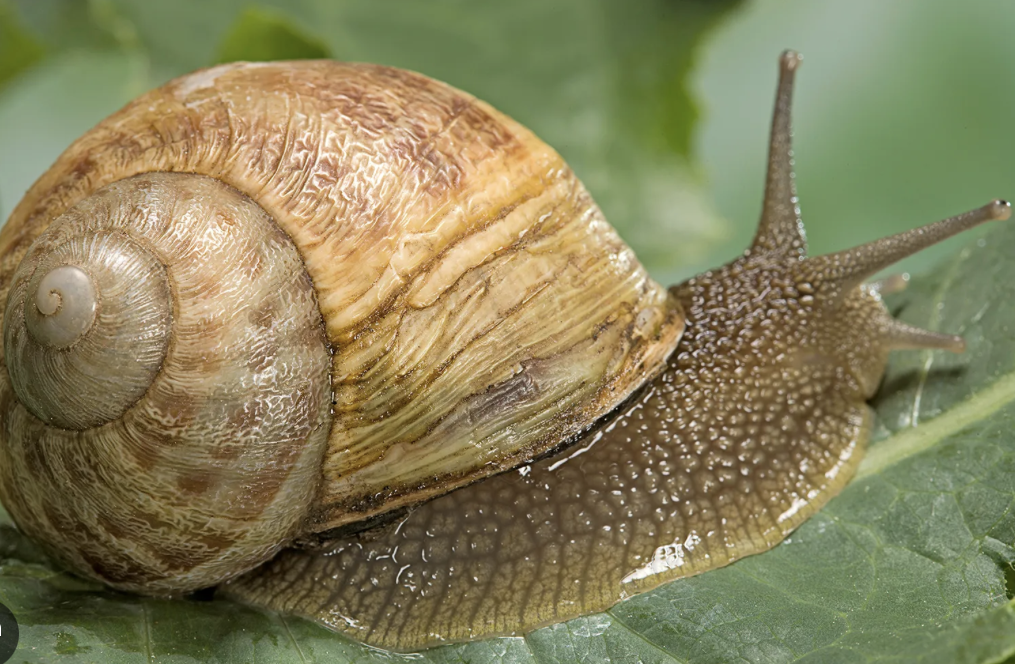

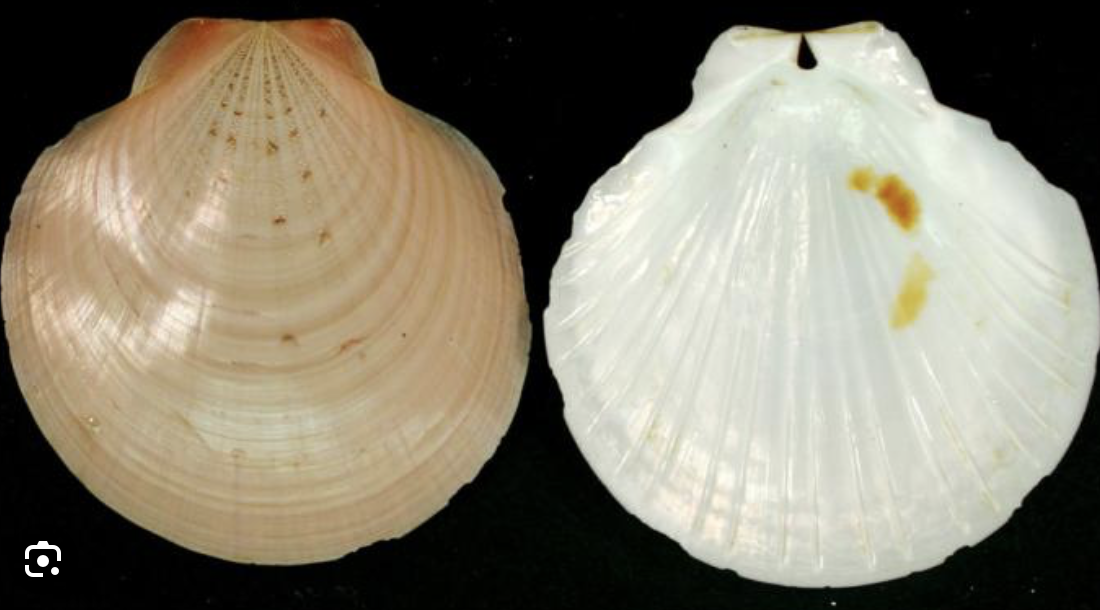
Bivalvia
phylum mollusca
muscular foot
two shells
filter feeders

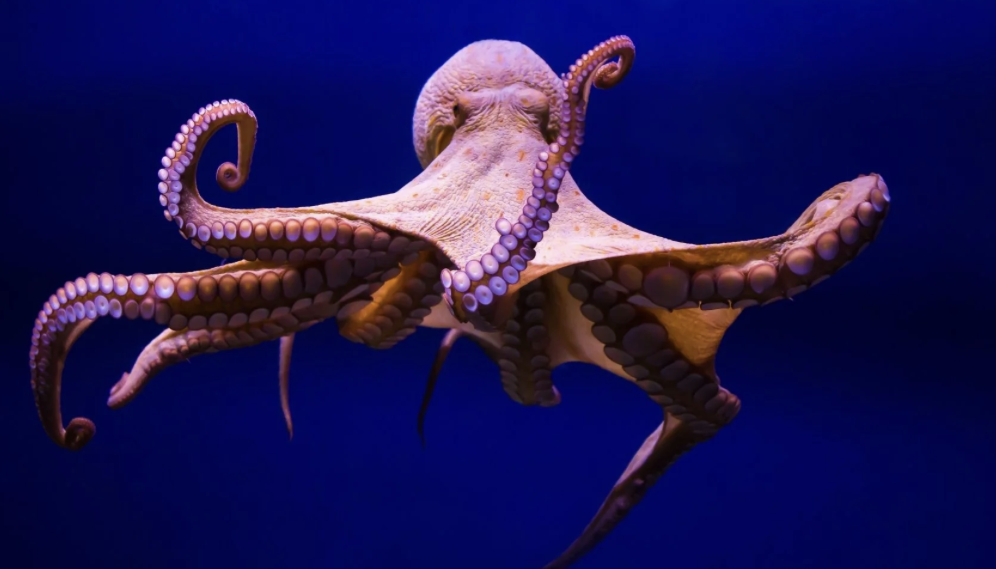
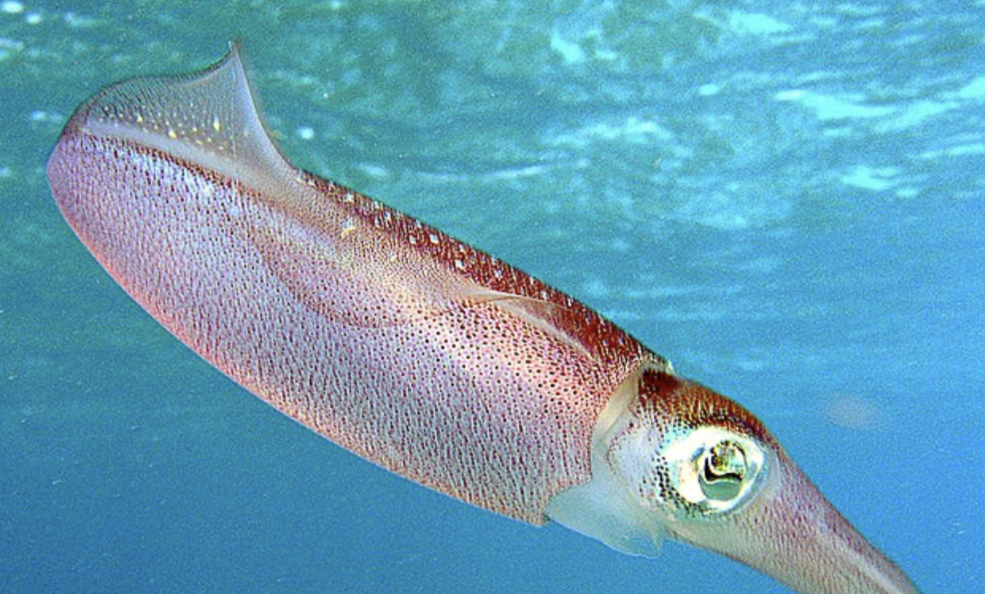
Cephalopods
phylum mollusca
shell- internal, external, or none
well-developed eyes
tentacles with suckers
beak (w/ radula)
ink sac
closed circulatory system replaces open system

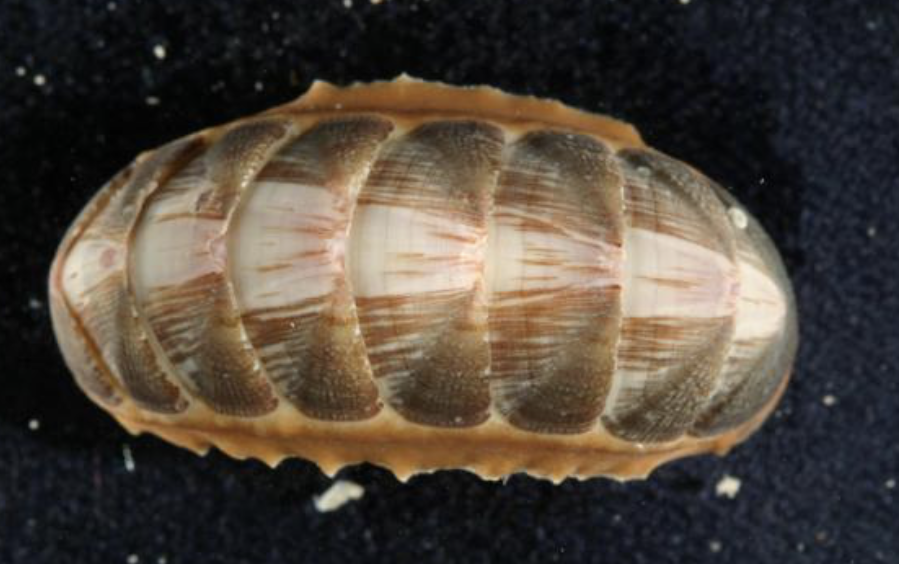
Polyplacophora
phylum mollusca
8 plates cover the dorsal surface

Polychaeta
phylum annelida
developed head
parapodia

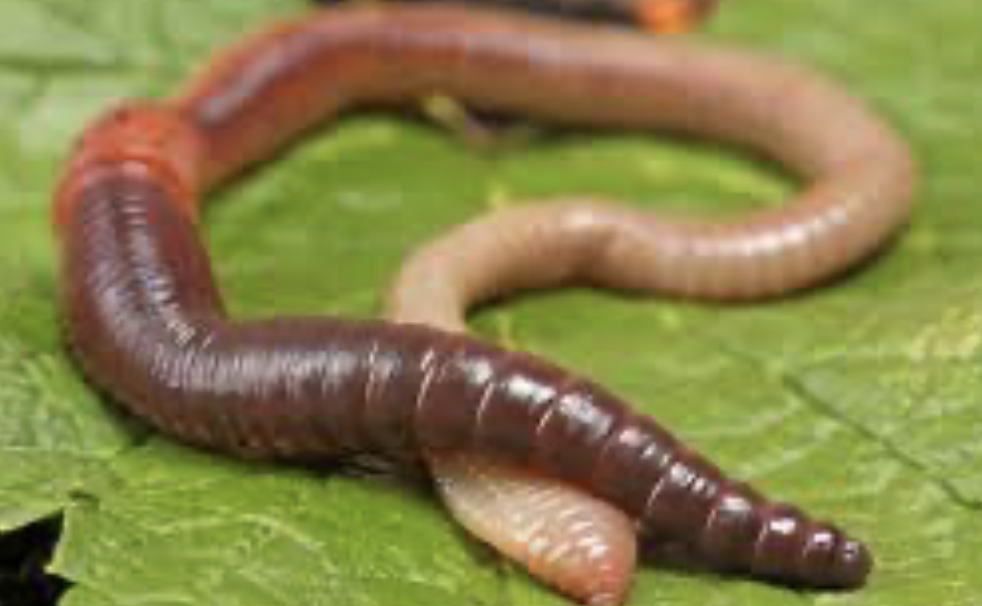
Oligochaeta
phylum annelida
cuticle
clitellum

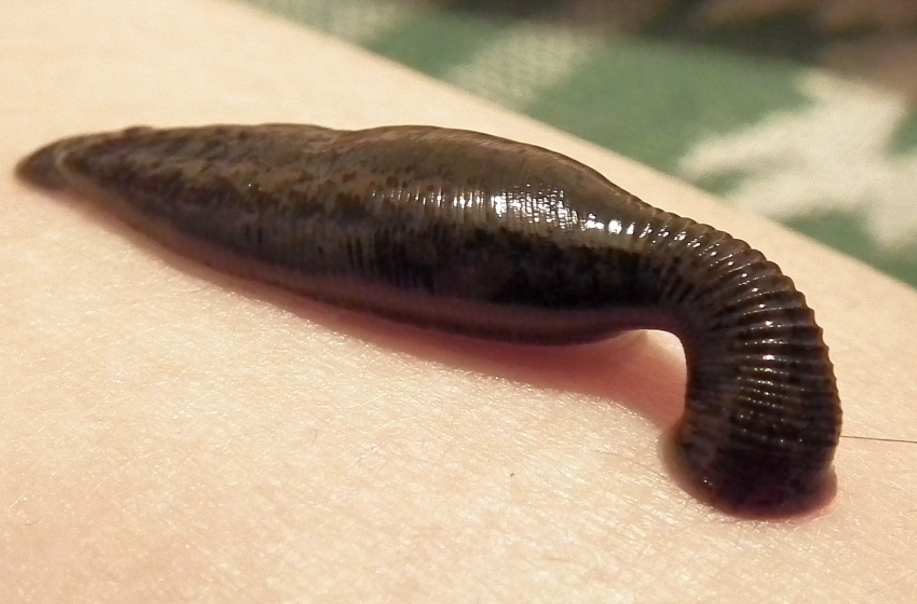
Hirudinea
phylum annelida
two suckers- 1 anterior, 1 posterior
many are blood sucking parasites

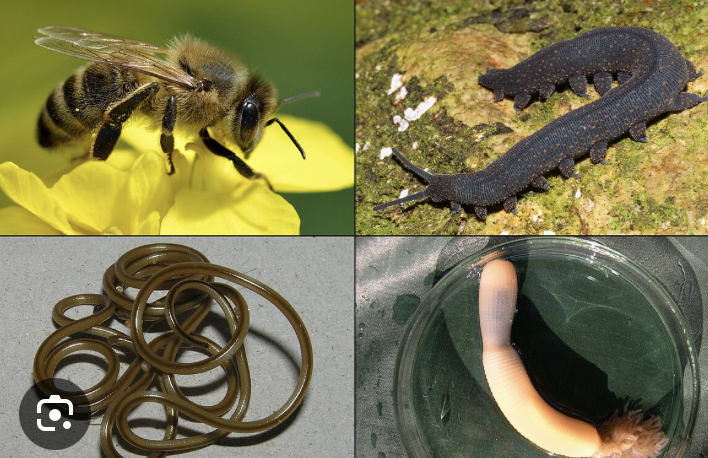
Trematoda + Cestoda both have…
gastrovascular cavity lost
complex life cycle with intermediate hosts
proglottids
Endoderm
the innermost layer of cells or tissue of an embryo in early development
Ectoderm
outermost germ layer
Superphyla Lophotrochozoa
ring of tentacles around mouth
planktonic larval stage

Superphyla Ecdysozoa
thick cuticle (or exoskeleton) that can be molted, shedding a tough external coat as they grow
includes phylum nematoda and arthropoda

Ecdysis
molting
Phylum Nematoda
round worm
pseudocoelomate
cylindrical body
Phylum Arthropoda
segmentation
jointed appendages
tagmata
contains chelicerata, myriapoda, crustacea, hexapoda
Phylum Echinodermata
water vascular system
endoskeleton- calcareous ossicles covered in epidermis
Deuterostomia
mouth forms second
blastopore becomes anus
opposite in protostomia
contains phylum echinodermata and chordata
Phylum Chordata
notochord
dorsal hollow nerve chord
pharyngeal slits
post-anal tail
endostyle/thyroid gland
Chelicerata
has two tagmata
chelicerae (mouthpart/jaw)
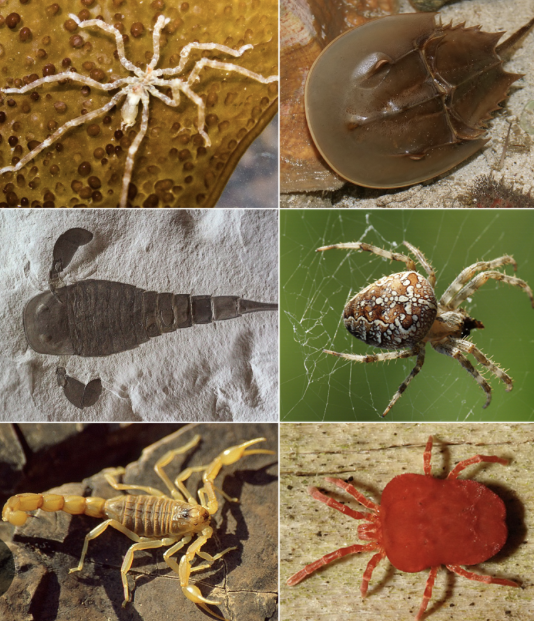

tagmata
grouping of segments