nervous tissue - anat
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
whats the nervous system
it is the control communications system of the body, it has functional divisions and structural divisions
what are the components of the structural division of nervous system
central nervous system: brain, spinal cord
peripheral nervous system:
cranial nerves: extend from the brain
spinal nerves: extend from spinal cord
ganglia: clusters of neuron cell bodies outside CNS
what are the components of the functional division of nervous system?
sensory input: afferent neuron, send signals toward the CNS
integration: interneuron
motor output: efferent neuron, send signals away from CNS
whats the difference between somatic and autonomic NS ?
somatic nervous system: provides conscious and subconscious control over skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system: controls internal/visceral functions largely outside our awareness
whats the difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
sympathetic nervous system: heart rate increases, pupils dilate, digestion slows down, breathing accelerates
parasympathetic nervous system: heart rate decreases pupils constrict, digestion stimulates, breathing slows
what are the 3 aspects of information processing ?
sensory (afferent) input travels from a sensory receptor
somatic reception
visceral reception
peripheral nervous system
integration of info in the brain or spinal cord and produces a response
central nervous system
motor (efferent) signals carried to the effector organ
somatic motor response of visceral motor response
peripheral nervous system
what are reflexes and the reflex arc ?
reflexes: are rapid, automatic motor response to stimuli (external or internal)
do not involve voluntary control of body
no integration in the brain, goes straight through the spinal cord
reflex arc: simple chain of neurons involved in reflexes
shows basic structural plan of nervous system
what are the two types of cells in the nervous system?
neurons: functional cells
send signals for sensory and motor functions
glial cells: support cells (help neurons function)
do not send signals
whats a neuron
it is the basic structural unit of the nervous system
approx 35-100 billion neurons in an adult
functions
conduct electrical impulses
extreme longevity
non-mitotic
high metabolic rate
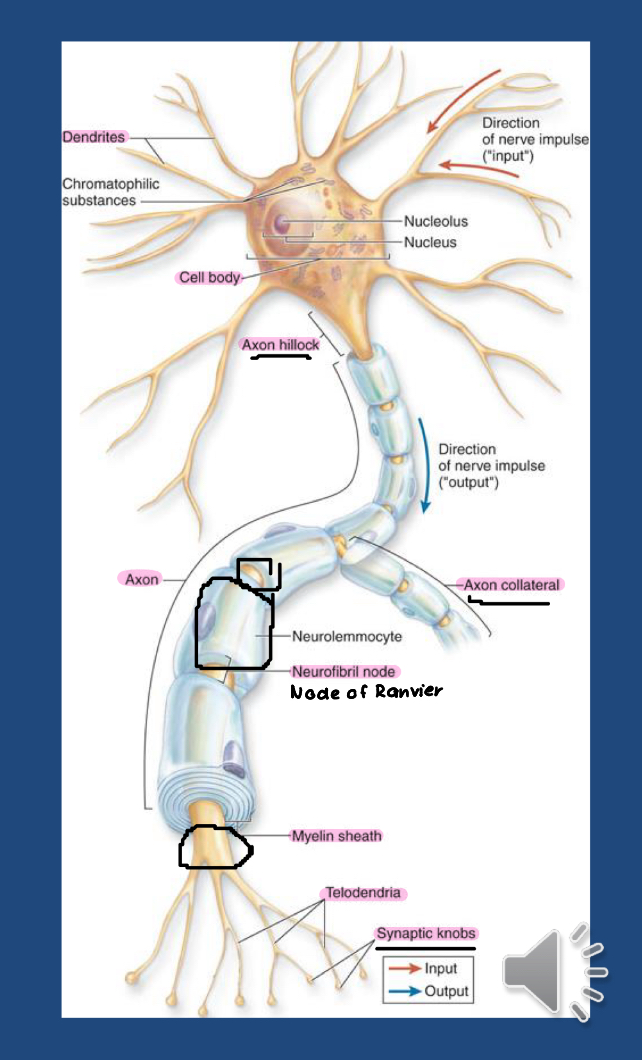
whats the anatomy of the neuron ?
cell body (aka: soma): control center
contain nucleus and other organelles
dendrites
short small processes that branch from cell body
axon
long processes that leave the body
What are the structures of the axon
the axon is wrapped in myelin sheath
axon hillock: connection of axon to cell body
axon collaterals: branches that bud from axons
axon terminal (aka: telodendria): extensive branching at distal end of axons
synaptic knobs: extreme tips of axon terminals
node of ranvier: segment of axon between myelin sheath
myelination: process of wrapping axons with concentric layers of plasma membrane fro glial cells
what are the two components under impulse conduction?
action potential: when the voltage across the membrane changes
this is the signals that travels down a nerve
depolarization: sodium enters the cell and initializes an action potential
continuous conduction: transmission of an impulse that moves molecule by molecule along an unmyelinated axon
relatively slow transmission
whats saltatory conduction ?
the transmission of an impulse that skips from node to node along a myelinated axon
fast transmission
ex: walking fast = myelinated
whats an synapse?
a specialized junction between neurons and a subsequence cell
ex: other neurons, muscle cells or glands
area of communication
what are the 3 structures of the synapse ?
presynaptic neuron: carriers impulse towards synapse
ex: acetylcholine
synaptic cleft: narrow space between presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron
postsynaptic neuron: conduct impulse away from synapse
membrane has neurotransmitter receptors
what are the 3 types of synapses ?
axodendritic synapse:
between synaptic knob of presynaptic neuron and the dendrite of postsynaptic neuron
most common type
axosomatic synapse:
between synaptic knob of presynaptic neuron and cell body of postsynaptic neuron
axoaxonic synapse:
between synaptic knob of presynaptic neuron and postsynaptic axon
lest common type
what are the 3 structural classifications on neurons ?
unipolar neurons: neurons with short single process emerging from cell body, that branches like a T
peripheral processes: goes from dendrites of axon to cell body
central process: goes from cell body into the CNS
dendrites are short and multi-branched with receptive endings
bipolar neurons: have one axon and one dendrites extending from a single cell body
multipolar neurons: many dendrites and a single axon extending from the cell body
most common type of neuron
what are the 3 functional classifications of neurons ?
sensory neuron (afferent)
carry impulse from receptors to CNS
motor neurons (efferent)
carry impulse from CNS to muscles or glands
interneurons (association neurons)
lie entirely in CNS
carry out integrative functions such as decision making, processing, etc.
what are the classifications fo neurons ?
unipolar neurons are always sensory neurons
bipolar neurons are sensory neurons in special senses
multipolar neurons are interneurons and motor neurons
what are the 4 types of glial cells in the CNS
astrocytes:
involved in the blood brain barrier
contain glycogen and release glucose during period of high consumption
numerous other functions
microglial cells
least numerous glial cell in CNS
respond to infections by replacing into phagocytes
protect CNS from infection
ependymal cells
inner epidermis of the CNS
produce CSF which bathes the CNS for protection
oligodendrocytes
makes myeline in the CNS
myelin is fatty wrapping around axons in the CNS that provides insulation for quicker signaling
one cell can myelinate several neurons and several location of those neurons
what are the 2 glial cells in the PNS
satellite cells
flattened cells arranged around neuronal cell bodies in ganglia
supply nutrients to surrounding neurons
act as protective cushion around cells
schwann cells
myelinate axons in the PNS
one schwann cell myelinates one are of one axon
neurolemma: refers to the thin delicate outer layer of the schwann cell that remains after myelination, the inner layers become myelin
what are the functions of the myelin sheath in the CNS and PNS
CNS: one oligdendrocyte provides several segments of myelin on several neurons at once
PNS: each myelin segment represents one schwann cell
what are nerves and tracts
nerves: are bundles of parallel axons in the PNS
most nerves are mixed nerves: they contain axons of motor sensory neurons
tracts are a collection of parallel axons in the CNS
what are the structures of a nerve
nerves are split into multiple fascicles
blood vessels run throughout the nerve referred to as the vasa nervorum to provide nutrients to the cells
nerves have multiple CT wrapping enclosing
endoneurium: CT that surrounds each individual axon and its myelin sheath
perineurium: CT that surrounds individual fascicles
epineurium CT that surrounds the entire nerve