py435 exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:34 AM on 9/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
psychology
the study of mind and behavior
2
New cards
motivation
the desire to make us do something for pleasure or displeasure
3
New cards
drive
internal sensation that fuels the motivational state
4
New cards
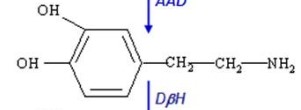
dopamine
phenylalanine -\> tyrosine -\> 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine
5
New cards
Norepinephrine
phenylalanine -\> tyrosine -\> 4-dihyrdoxyphenylalanine -\> dopamine
6
New cards
serotonin
tryptophan -\> 5-hydroxytryptophan
7
New cards
epinephrine
phenylalanine -\> tyrosine -\> 4-dihydroxypehnylalanine -\> dopmaine -\> norepinephrine
8
New cards
how many neurons does the brain have
86 billion
9
New cards
what are nerves
elongated axons that end at muscles and organs
10
New cards
what information do nerves convey
sensory (afferent): messages to the brain
motor (efferent): messages away from the brain
motor (efferent): messages away from the brain
11
New cards
peripheral nerves
somatic and autonomic
12
New cards
somatic
muscles and what you can do (voluntary)
13
New cards
autonomic
activating functions we do not have to think about (involuntary) (automatic)
14
New cards
what two nervous systems are in the autonomic
sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)
15
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
feel it; fight or flight
16
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
at work when you are relaxing; stores energy
17
New cards
endocrine system
a group of grands that secrete chemicals called hormones
18
New cards
exocrine galnds
produce and deliver secretions directly to where they are used (does not travel through bloodstream) (goes through ducts)
19
New cards
endocrine glands
secrete hormones into the bloodstream to be carried to where they are needed
20
New cards
name 2 pituitary glands/hormone/function
anterior pituitary gland:
prolactin: production of breast milk
posterior pituitary gland:
oxytocin: induces social bonding, labor, and release of breast milk
prolactin: production of breast milk
posterior pituitary gland:
oxytocin: induces social bonding, labor, and release of breast milk
21
New cards
name 2 other glands/hormone/function
ovaries- estrogen: produces secondary sex characteristics in females
testes- testosterone: produces secondary sex characteristics in males and females
testes- testosterone: produces secondary sex characteristics in males and females
22
New cards
what are the four basic drives
feeding, fleeing, fighting, fornicating (mating)
23
New cards
too much Acetylcholine (ACh)
death
-black widow spider poison
-nerve gas
-pesticides
-black widow spider poison
-nerve gas
-pesticides
24
New cards
too little Acetylcholine (ACh)
death
-botulism: improperly canning preserves
-d-tubocurare: a paralytic (botox contains small amounts of this)
-can effect memory
-calaber bean
-botulism: improperly canning preserves
-d-tubocurare: a paralytic (botox contains small amounts of this)
-can effect memory
-calaber bean
25
New cards
homeostasis
state of steady conditions maintained by living systems
26
New cards
negative feedback
regulates body hormones (ex. sweating keeps body cooled)
27
New cards
three main parts of the brain tree
forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
28
New cards
two main parts of the forebrain
telencephalan and diencephalan
29
New cards
three main parts of the telencephalan
cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system
30
New cards
four main parts of the cerebral cortex
frontal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, paritial lobe
31
New cards
three main parts of the basal ganglia
caudate, gleubus pollidus, putamen
32
New cards
seven main parts of the limbic system
nucleus accumbens
fornix
mammilary glands
amygdala
hippocampus
cingulate cortex
septum
fornix
mammilary glands
amygdala
hippocampus
cingulate cortex
septum
33
New cards
two main parts of the diencephalan
hypothalamus and thalamus
34
New cards
main part of the midbrain
mesencephalan
35
New cards
three main parts of the mesencephalan
reticular formation, ventral tegmental area, periaquaductal gray matter
36
New cards
two main parts of the hindbrain
mylencephalan, metencephalan
37
New cards
main part of the mylencephalan
medulla oblongata
38
New cards
two main parts of the metencephalan
cerebellum, pons
39
New cards
what are the brain protectors
skull
cerebrospinal fluid
meninges
ventricles
cerebrospinal fluid
meninges
ventricles
40
New cards
what does the cerebrospinal fluid do
cushions the brain
41
New cards
what causes chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)
a lot of continuous 'blows' to the head
42
New cards
symptoms of CTE
- first is personality changes
- memory loss
-suicidal behaviors
- abnormal gait
- memory loss
-suicidal behaviors
- abnormal gait
43
New cards
what is abraham maslow known for
hierarchy of needs
44
New cards
what is the hierarchy of needs
1. physiological needs: eating/warmth/etc
2. safety needs: security/protection
3. love and belonging: partner/group
4. esteem needs: confidence
5. self-actualization needs: highest potential
2. safety needs: security/protection
3. love and belonging: partner/group
4. esteem needs: confidence
5. self-actualization needs: highest potential
45
New cards
what is charles darwin known for
structure dictates function
46
New cards
what is sigmund freud best known for
said we are motivated by unconscious desire and urges
47
New cards
what is walter cannon best known for
homeostasis; fight or flight
48
New cards
what is edward throndike best known for
we are motivated to do things based on their consequences
49
New cards
what is pavlov best known for
learning is shaped by the environment
50
New cards
what is donald hebb best known for
everything is a result of reactions and messages in the brain
51
New cards
what is percy julian best known for
researched soy and callabar beans; birth control
52
New cards
what did Yerkes/Dodson find?
arousal and performance depended on the task (mice experiment)
53
New cards
what did dement/kleitman find
noticed humans go through regular sleep patterns
54
New cards
Who is Randy Gardner?
Man who set the record for sleep deprivation - 11 days (proved brain does not make up for sleep deprivation)
55
New cards
what did Michel Jouvét do
- injected precursor to increase 5-HTP to increase serotonin in brain (in Raphé)
- injected 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine to increase dopamine to increase wakefulness and decrease REM (in reticular formation)
- injected physostigmine to increase ACh to increase REM (pons)
- injected 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine to increase dopamine to increase wakefulness and decrease REM (in reticular formation)
- injected physostigmine to increase ACh to increase REM (pons)
56
New cards
reticular formation/reticular activating system
arousal and awake
57
New cards
raphé
activated in order to sleep/inhibits movement during REM
58
New cards
Pons
control REM sleep
59
New cards
sleep functions
restoration theory; adaptation theory; facilitation of learning and memory consolidation theory; REM improves learning that involves emotions
60
New cards
Restoration theory
sleep repairs the wear/tear of activity
61
New cards
adaptation theory
sleep to stay out of harms way
62
New cards
facilitation of learning and memory consolidation theory
babies, concentration, test-taking
63
New cards
REM improves learning that involves emotions
need REM to consolidate emotion
64
New cards
four main sleep disorders
insomnia, sleep apnea, sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), narcolepsy
65
New cards
insomnia
trouble falling asleep/staying asleep
66
New cards
Sleep Apnea: Obstructive
obesity and alcohol caused; breathing is obstructed
67
New cards
Sleep Apnea: Central
brain fails to initiate breaths
68
New cards
Suden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
death of a healthy infant because of inability to move if face is obstructed while sleeping
69
New cards
narcolepsy
sleeping at inappropriate times; caused by lack of orexin
70
New cards
sleep attack (narcolepsy)
fall asleep when sitting or not moving; just for a few minutes
71
New cards
Cataplexy (narcolepsy)
Attacks of paralysis like those in rem (looks like fainting)
72
New cards
circadian rhythm
cycles every day/ every 24 hr (sleep wake cycle); internal clock; pineal- melatonin- controls this
73
New cards
zeitgeber
external or environmental cues that can help synchronize circadian rhythms
74
New cards
EEG
electroencephalogram; activity in brain
beta, alpha, theta, delta are the wave patterns
awake: beta
resting/drowsy: alpha
beta, alpha, theta, delta are the wave patterns
awake: beta
resting/drowsy: alpha
75
New cards
SWS disorders (slow wave sleep)
nocturnal enuresis, somnambulism, pavor nocturnus
76
New cards
nocturnal enuresis
bed wetting
77
New cards
somnambulism
sleepwalking
78
New cards
pavor nocturnus
night terrors
79
New cards
drive reduction theory
an explanation of motivation based on the notion that consummatory behavior meets an underlying need, reducing the motivation for that behavior
80
New cards
sociobiology
the application of darwinian theories of evolution to the study of social and reproductive behavior
81
New cards
neocortex
concerned with sensory awareness and voluntary control of movement
82
New cards
circumventricular organs
group of brain centers around outside of the blood brain barrier that permit the passage of hormones secreted by the hypothalamus
83
New cards
supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei
synthesizes and transports vasopressin; produces posterior pituitary hormones
84
New cards
antidiuretic hormone
controls water secretion by the kidneys
85
New cards
gonadotropic hormones
anterior pituitary hormones acting on the gonads
86
New cards
adrenocorticopic hormone (ACTH)
anterior pituitary controlling sections of the adrenal cortex
87
New cards
glucocorticoids
adrenal cortical hormones involved in regulating metabolism
88
New cards
mineralocorticoids
steroid hormones secreted by adrenal cortex involved in water and electrolyte balance
89
New cards
diurnal
being active during daylight hours
90
New cards
nocturnal
being active during nighttime hours
91
New cards
free-running rythm
circadian rhythm that emerges when an animal is kept isolated from external cues
92
New cards
zeitgebers
an environmental stimulus that entrains circadian rhythms
93
New cards
ultradian rythms
biological rythms that occur more than once within a 24 hour period
94
New cards
basic rest-activity (BRAC)
a 90 minute cycle that can describe the process of sleep as well as other processes
95
New cards
infradian rythm
rhythms that are longer than 24 hours (mentrual cycle in humans)
96
New cards
circannual rhythms
behavior of animals and birds throughout the year
97
New cards
suprachiasmatic nucleus
cicadian rhythm regulation
98
New cards
electroencephalogram
recordings of cerebral activity
99
New cards
electroencephalograph (EEG)
machine responsible for recording brain activity
100
New cards
dopamine