3. innate & acquired immunity
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
innate immunity refers to _____
various physical, chemical, and cellular barriers that represent the first line of defense against infectious disease
uses proteins encoded in the germline (elements an individual is born with)
features of innate immunity
preformed or rapidly induced on short notice
no memory: NOT enhanced by prior exposure; same response each time
broad specificity → stimulated by structures that are common to groups of related microbes
LPS (gram - )
peptidoglycan (gram +)
features of acquired/adaptive immunity
specificity
memory
diversity
clonal expansion/contraction
specialization
non-reactivity to self
mechanisms/components of innate immunity
anatomic/physical barriers
physiologic & chemical barriers
cellular barriers
inflammatory barriers
what are epithelial barriers?
cells held together by tight junctions
skin
mucous membranes — conjunctiva, GI, respiratory, and urogenital tracts
external/first lines of defense
how do mucous membranes protect against microbes?
secretions → saliva, tears, urine, mucus
wash away/inhibit growth/trap microbes
cilia → muco-ciliary escalator
peristalsis in GI tract, coughing, sneezing removes microbes
gut stasis leads to microbial growth and infection
functions of epithelial barrier
physical barrier to infection
epithelial cells produce & secrete peptides antibiotics
intraepithelial lymphocytes kill microbes
defensins and cathalicidins are examples of what?
peptide antibiotics produced and secreted by epithelial cells
physiological/chemical barriers
fever
pH → stomach, vagina, skin
normal microflora → GI tract and skin
chemical mediators
defensins (secreted by epithelia)
hydrolytic enzymes of saliva
lysozyme in tears, sweat, and saliva
surfactant has antimicrobial properties
interferons
interfere with viral infection
anti-viral actions of type I interferons
paracrine signaling → virally-infected cell secretes interferons → induces antiviral state in nearby cells
activates NK cells
promotes CD8+ T cells/cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs)
highly conserved (maintained through evolution)
steps in phagocytosis
adherence and opsonization
ingestion
destruction
macrophages produce high levels of what substances that promote inflammation?
IL-1 (interleukin-1) & tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) — cytokines
adherence
microbes physically adhere to surface receptors on phagocyte
ex. lectin receptor, mannose receptor
opsonization
enhances phagocytosis
microbes are coated in protein that bind to receptors on macrophage/neutrophil cell membrane
antibodies → Fc receptors
complement proteins (C3b) → complement receptors
3 mechanisms of microbial destruction (phagocytosis)
lysosomal enzymes
reactive nitrogen intermediates → nitric oxide (NO)
produced by iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase)
reactive oxygen species (respiratory burst)
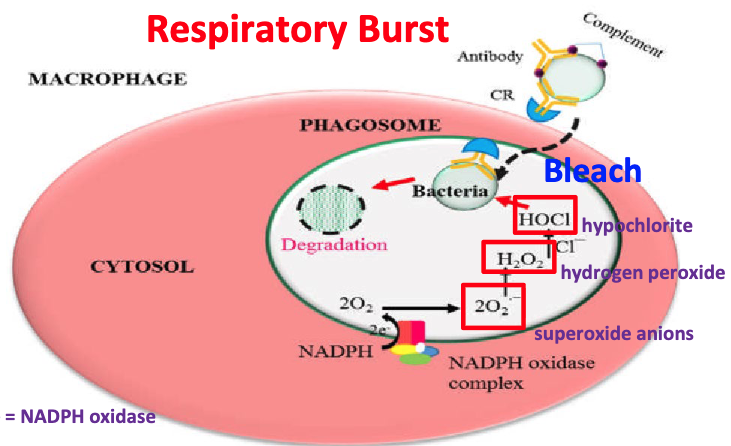
respiratory burst
production of reactive oxygen species to kill microbes
NADPH oxidase complex converts O2 → O2- superoxide anions → H2O2 hydrogen peroxide → HOCl hypochlorite (bleach)
neutrophil extracellular traps
mixture of cellular contents (chromatin, histones, cathepsins, elastase, myeloperoxidase) released right before neutrophil dies
traps nearby microbes → digested by enzymes