Development Biology Lab - Gametogenesis and Fertilization
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
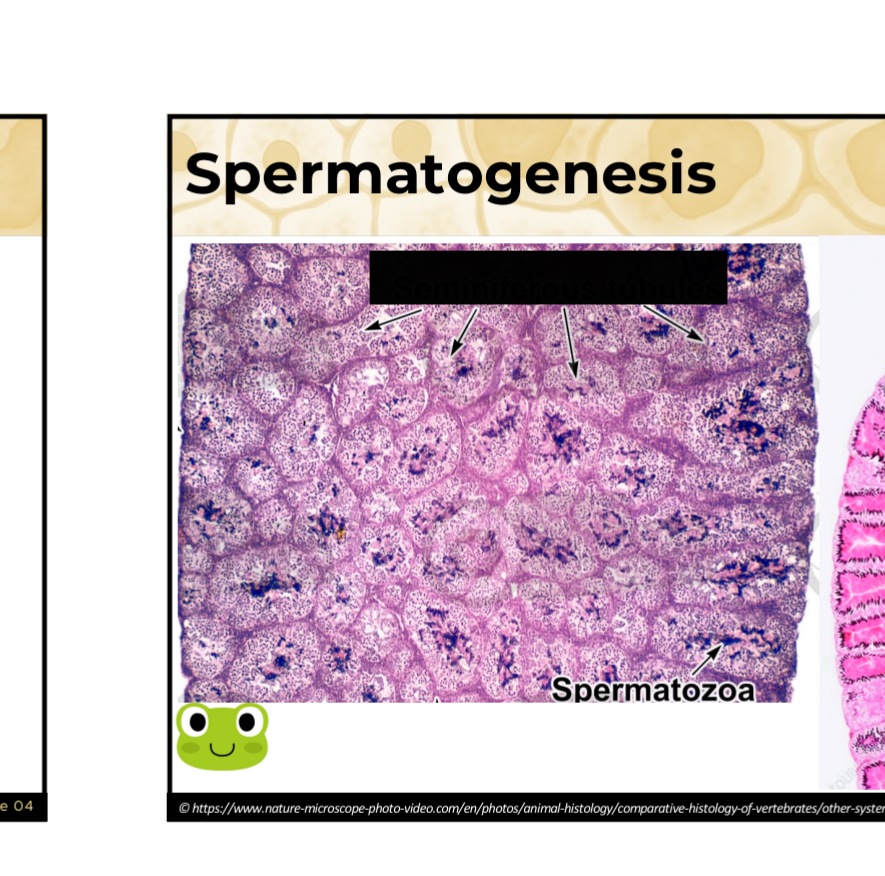
Identify the blanked out name for this component of spermatogenesis
Semineferous tubules
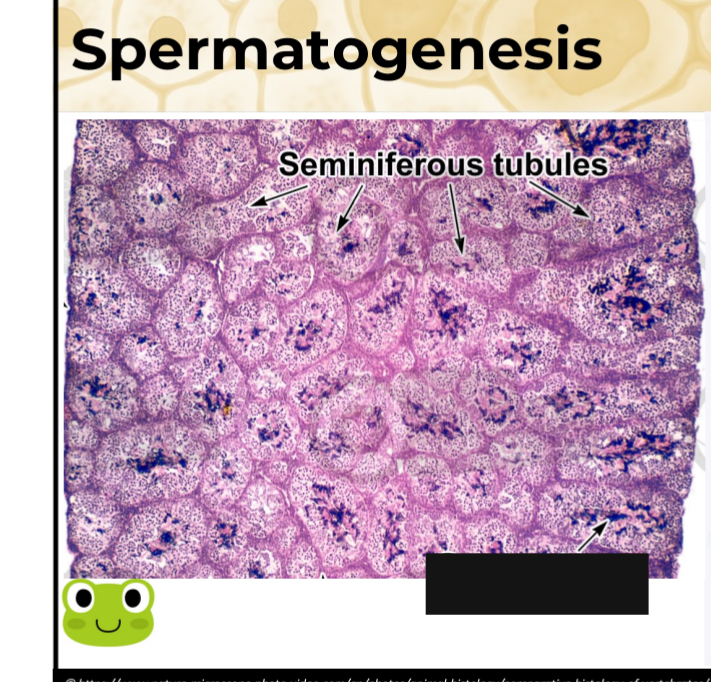
Identify the blanked out name for this component of spermatogenesis
Spermatozoa
Primary spermatocyte into secondary spermatocyte transition.
When the sperm becomes haploid from diploid.
Lumen
Haploid, light-shaded area where maturation begins.
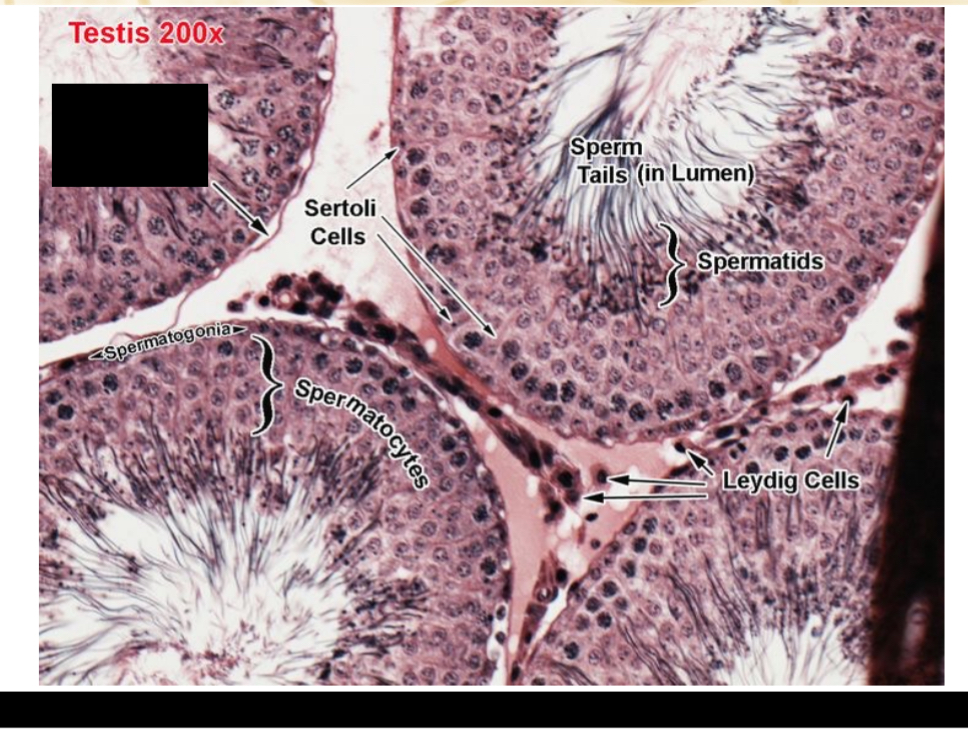
Identify the part, and its function.
Basement membrane. Diploid, where spermatogonia begins (primordial sperm creation)
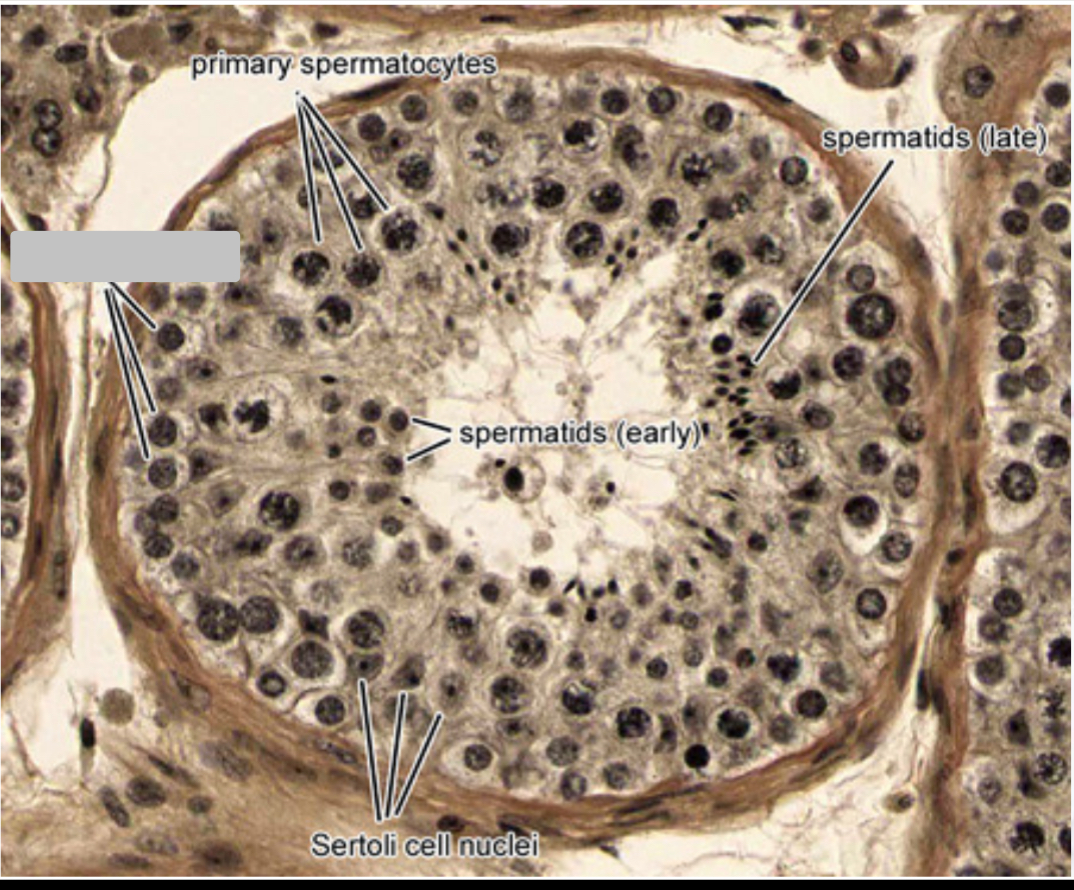
Identify the part, and its function.
Spermatogonia, progenitor sperm cell.
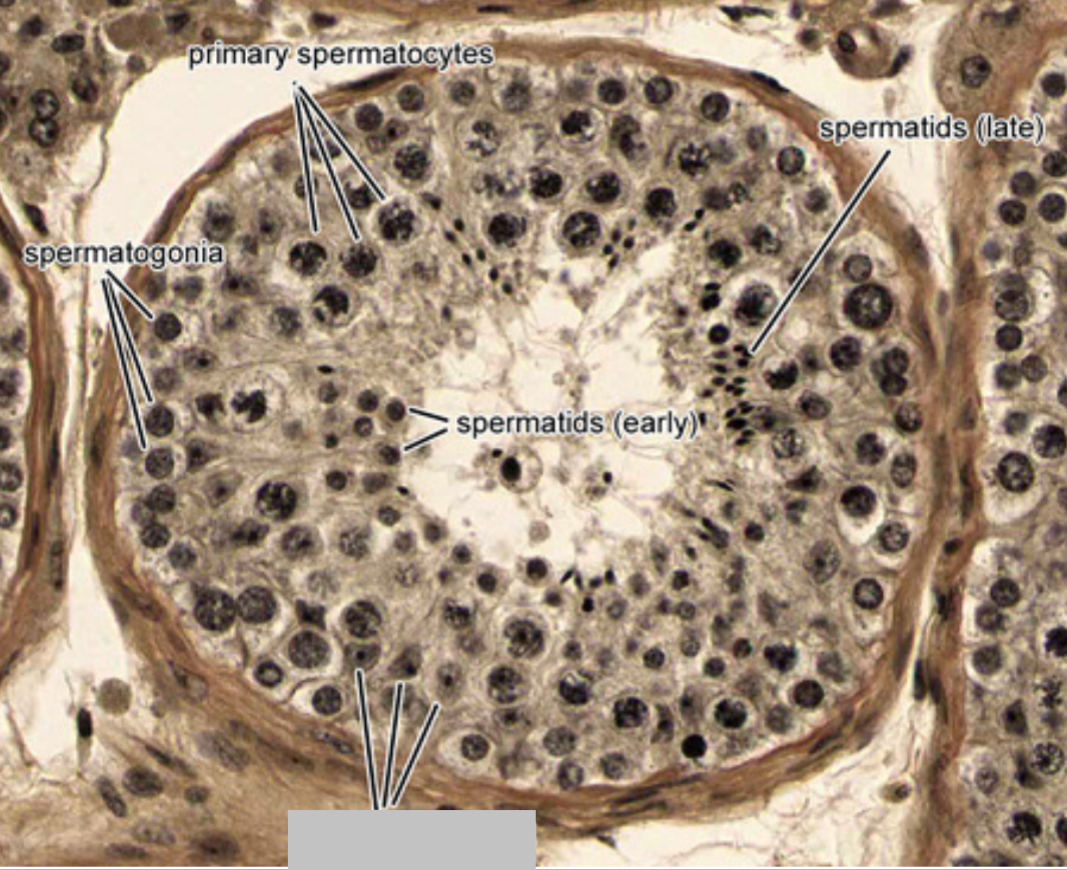
Identify the part, and its function.
Sertoli cell nuclei. Supports the development of sperm cells.
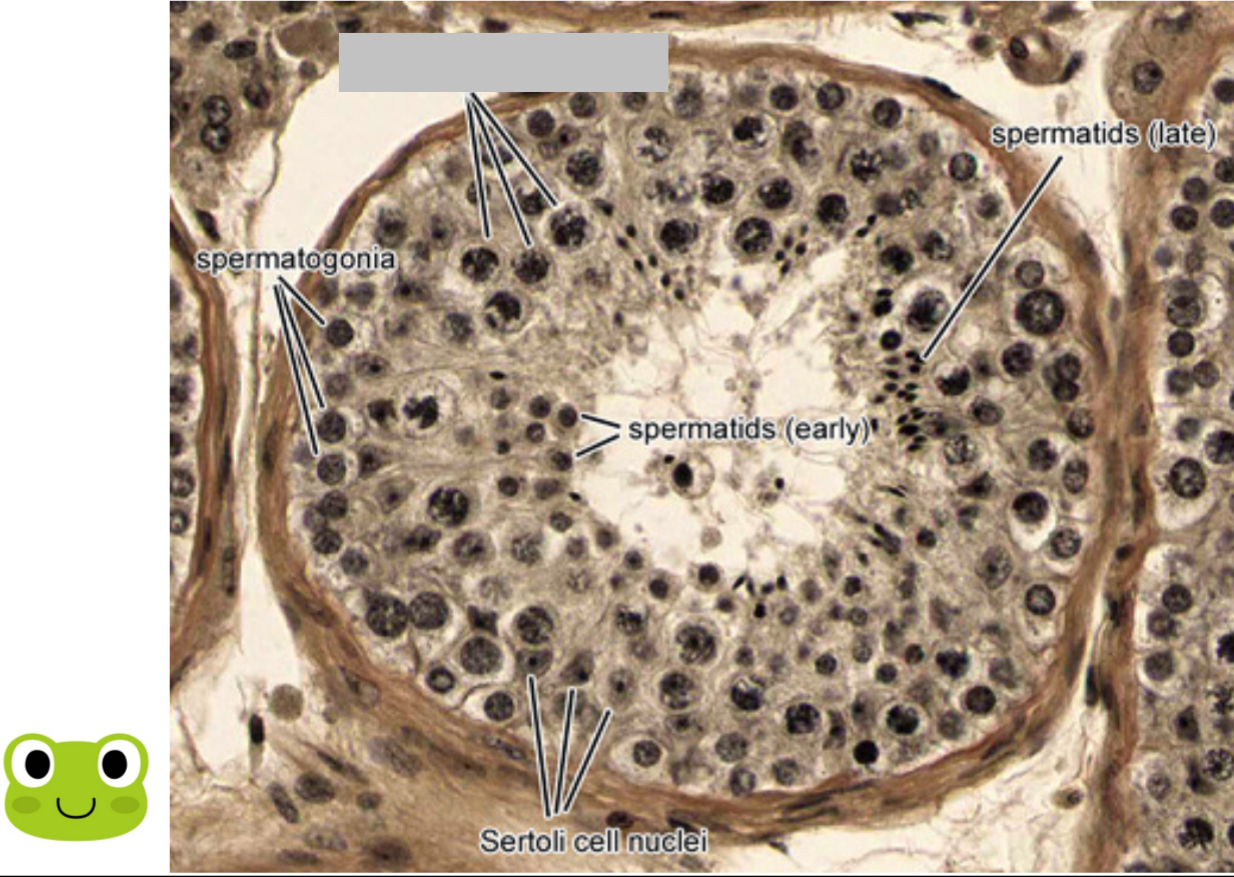
Identify the part, and its function.
Primary spermatocytes. Diploid
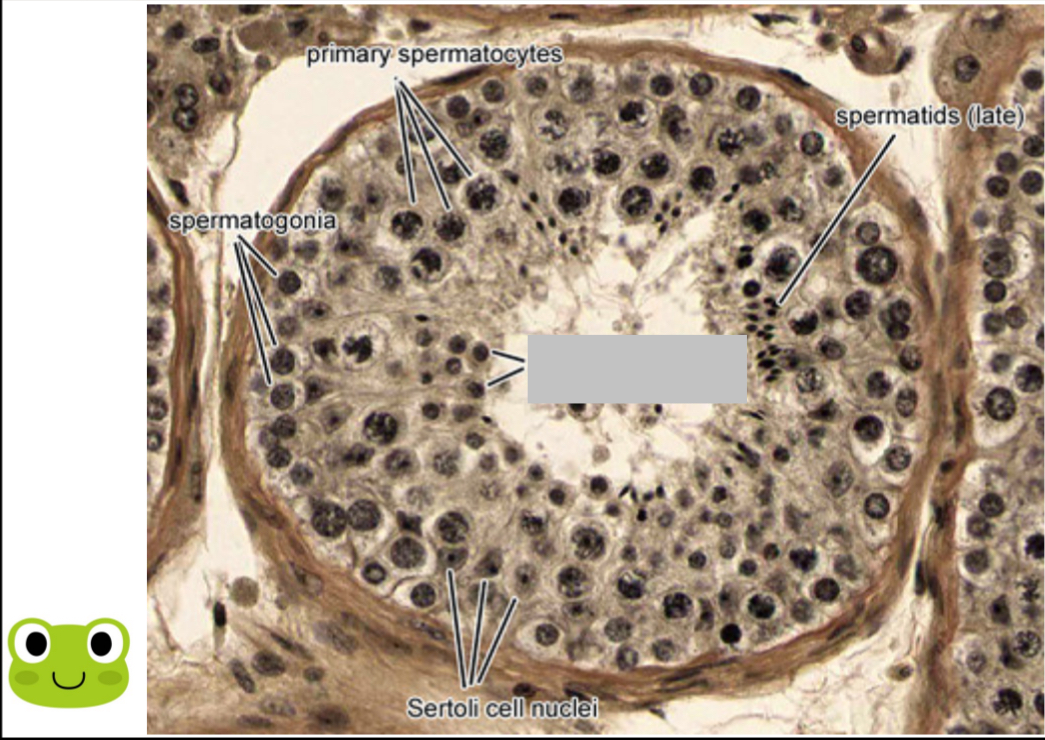
Identify the part, and its function.
Early spermatid.
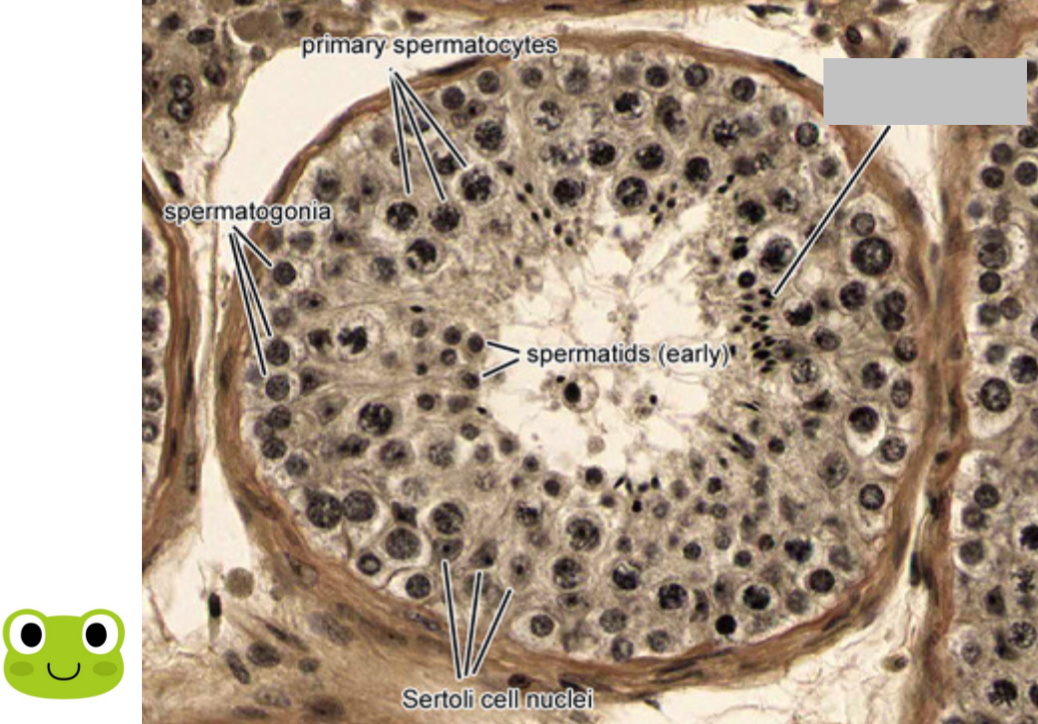
Identify the part, and its function.
Late spermatid. Smaller
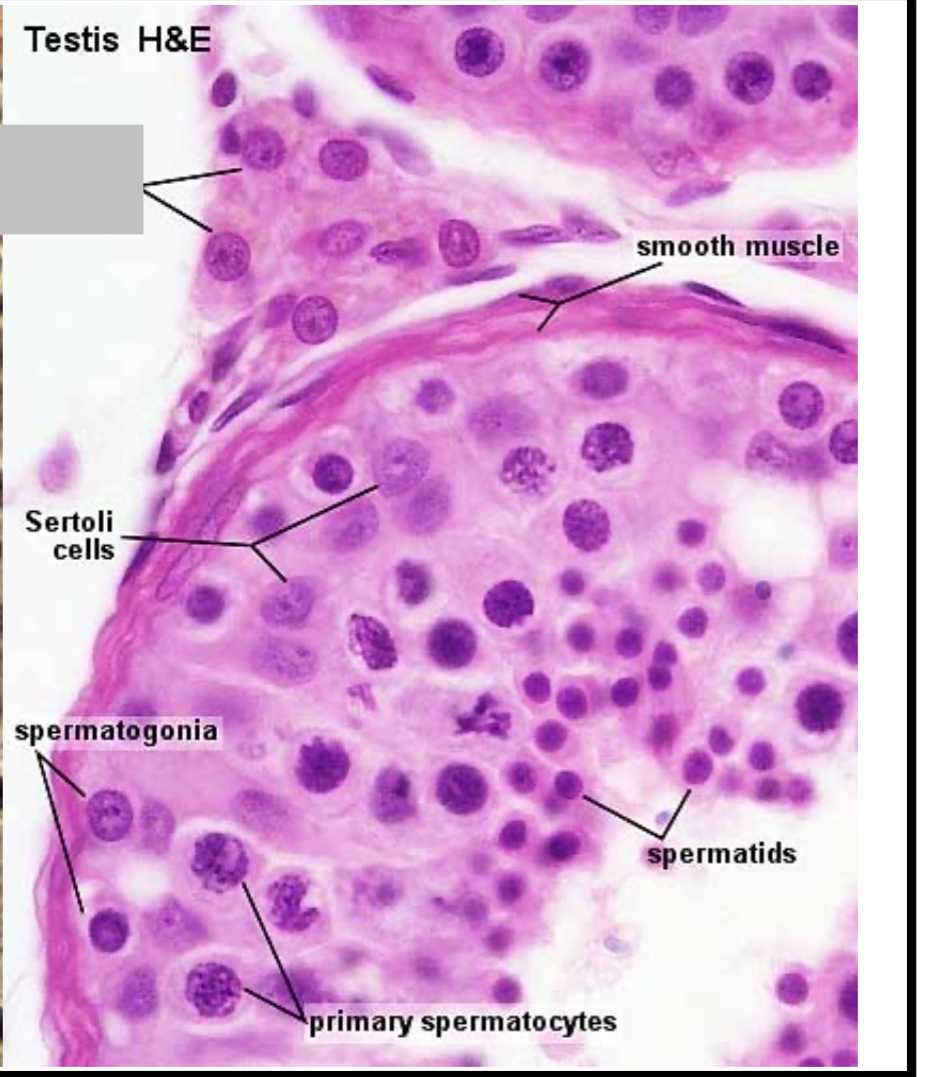
Identify the part, and its function.
Leydig cells. Produces and secretes testosterone.
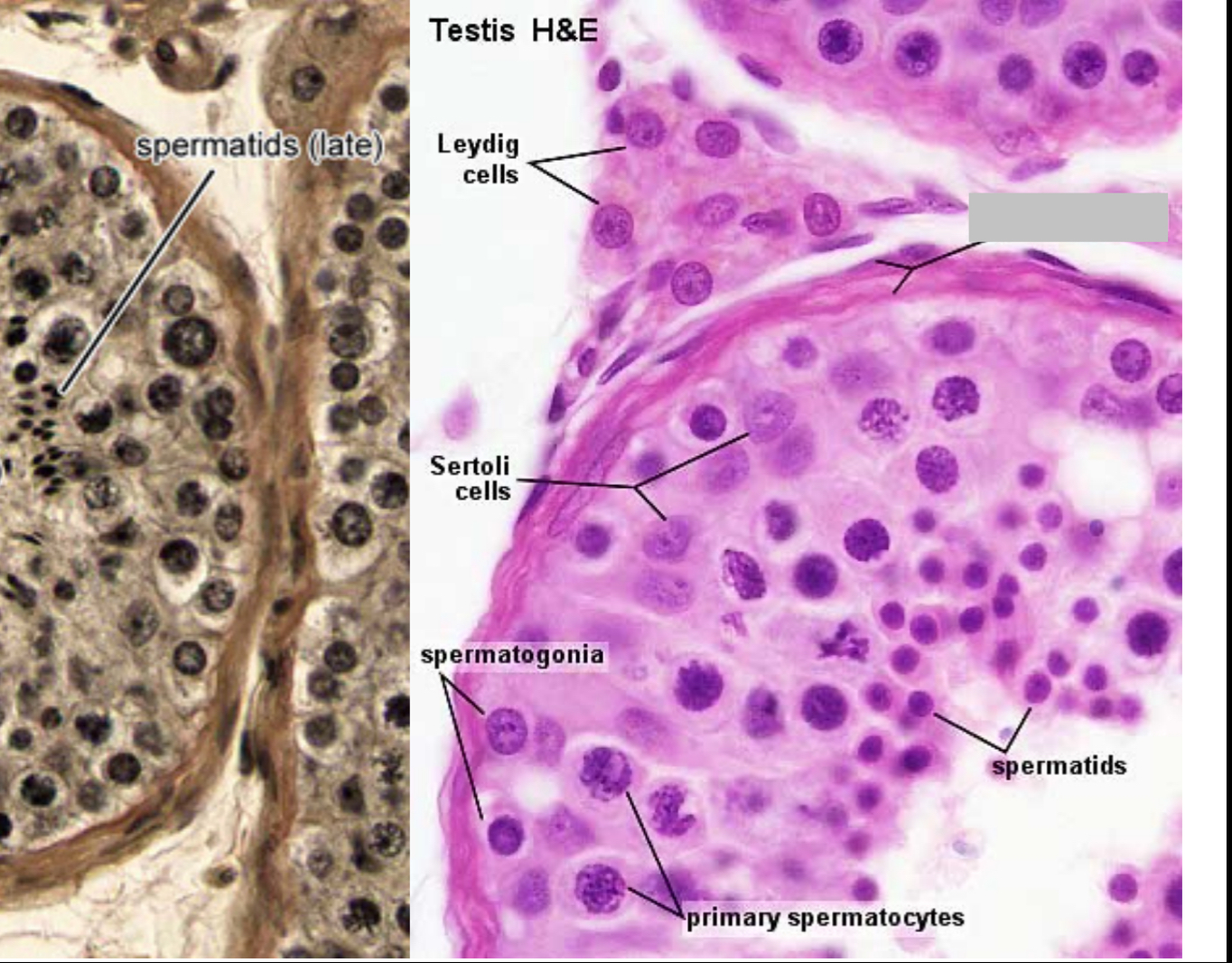
Identify the part, and its function.
Smooth muscle.
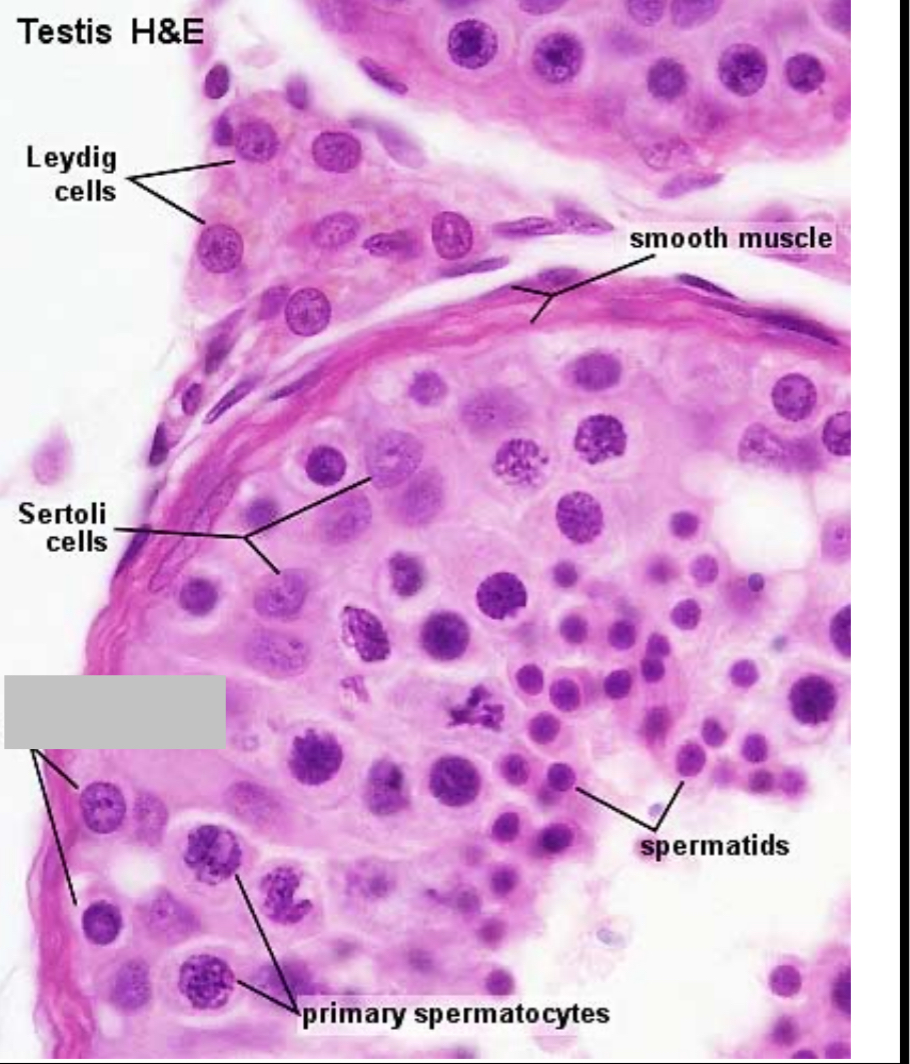
Identify the part, and its function.
Spermatogonia
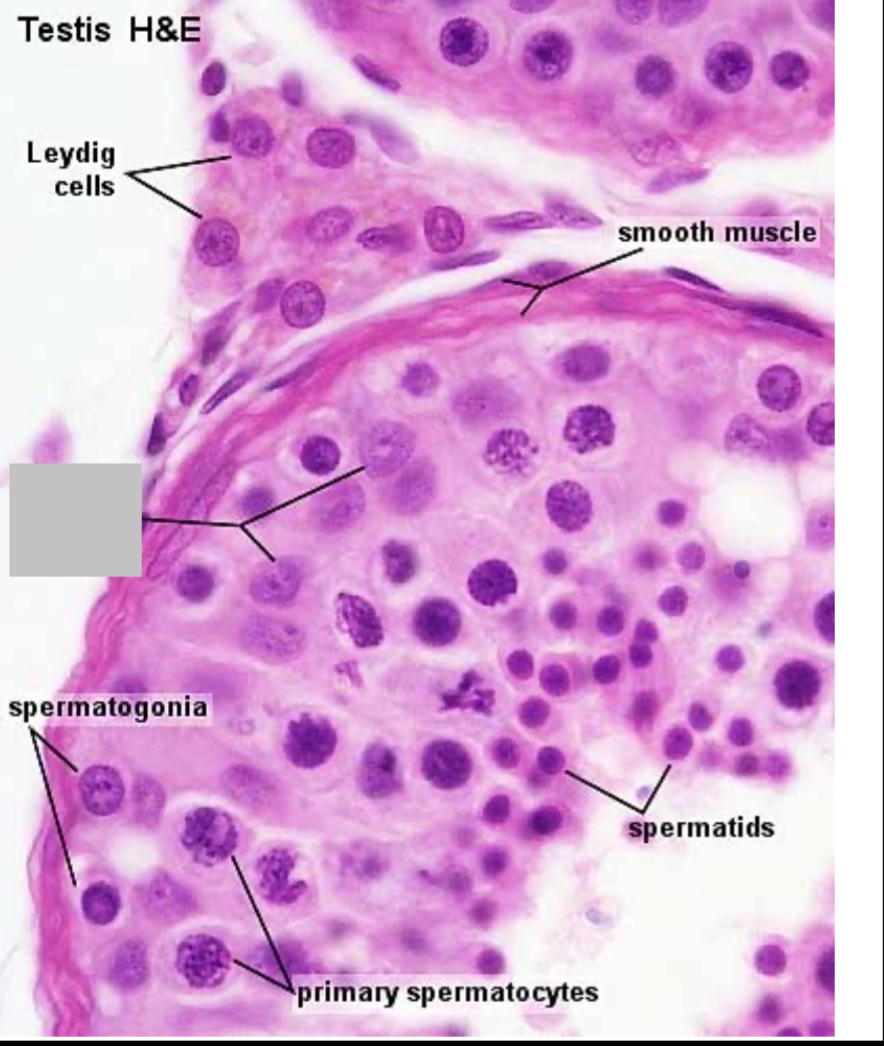
Identify the part, and its function.
Sertoli cells
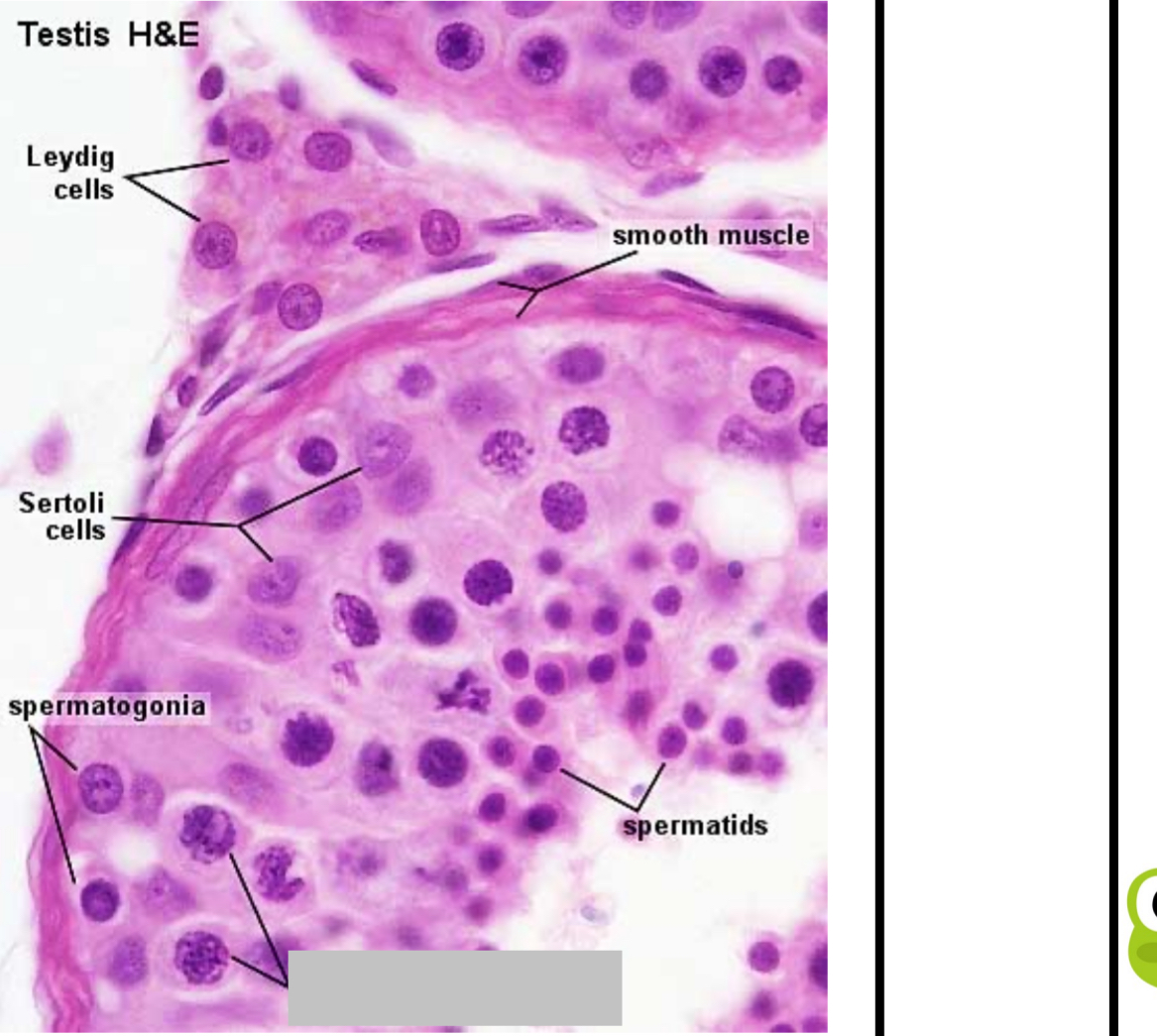
Identify the part, and its function.
Primary spermatocytes
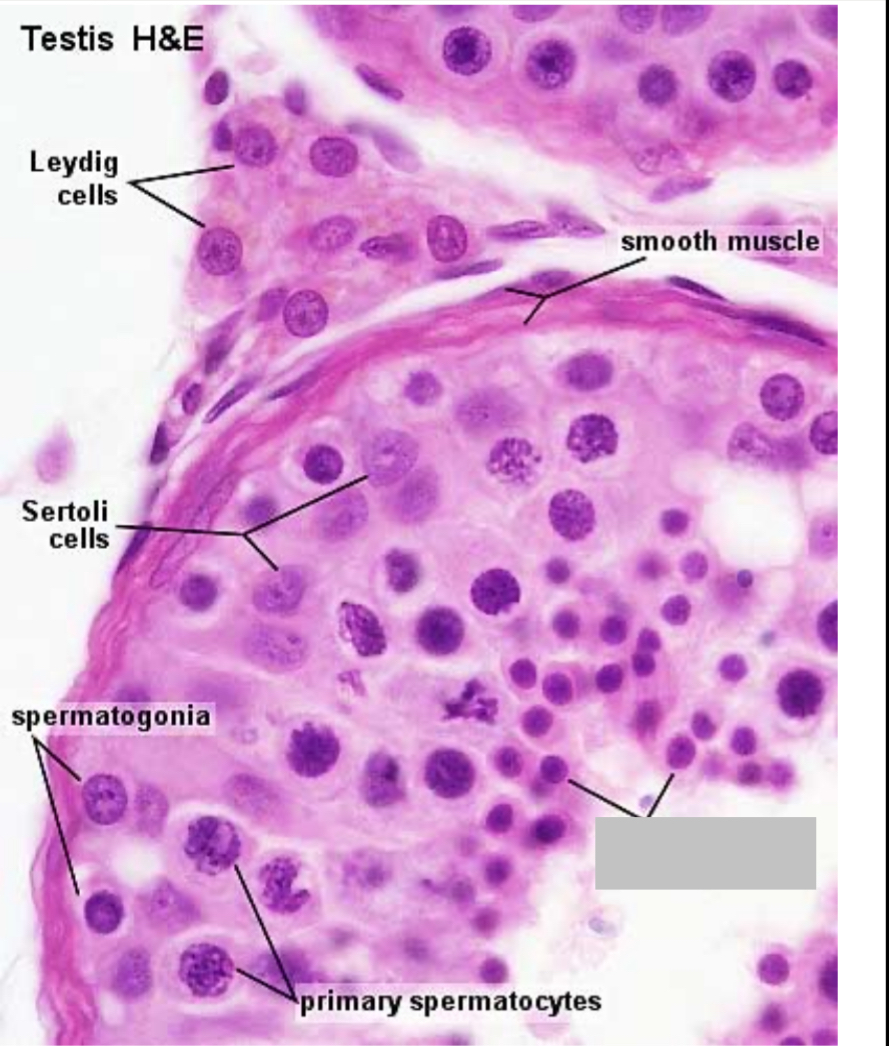
Identify the part, and its function.
Spermatids
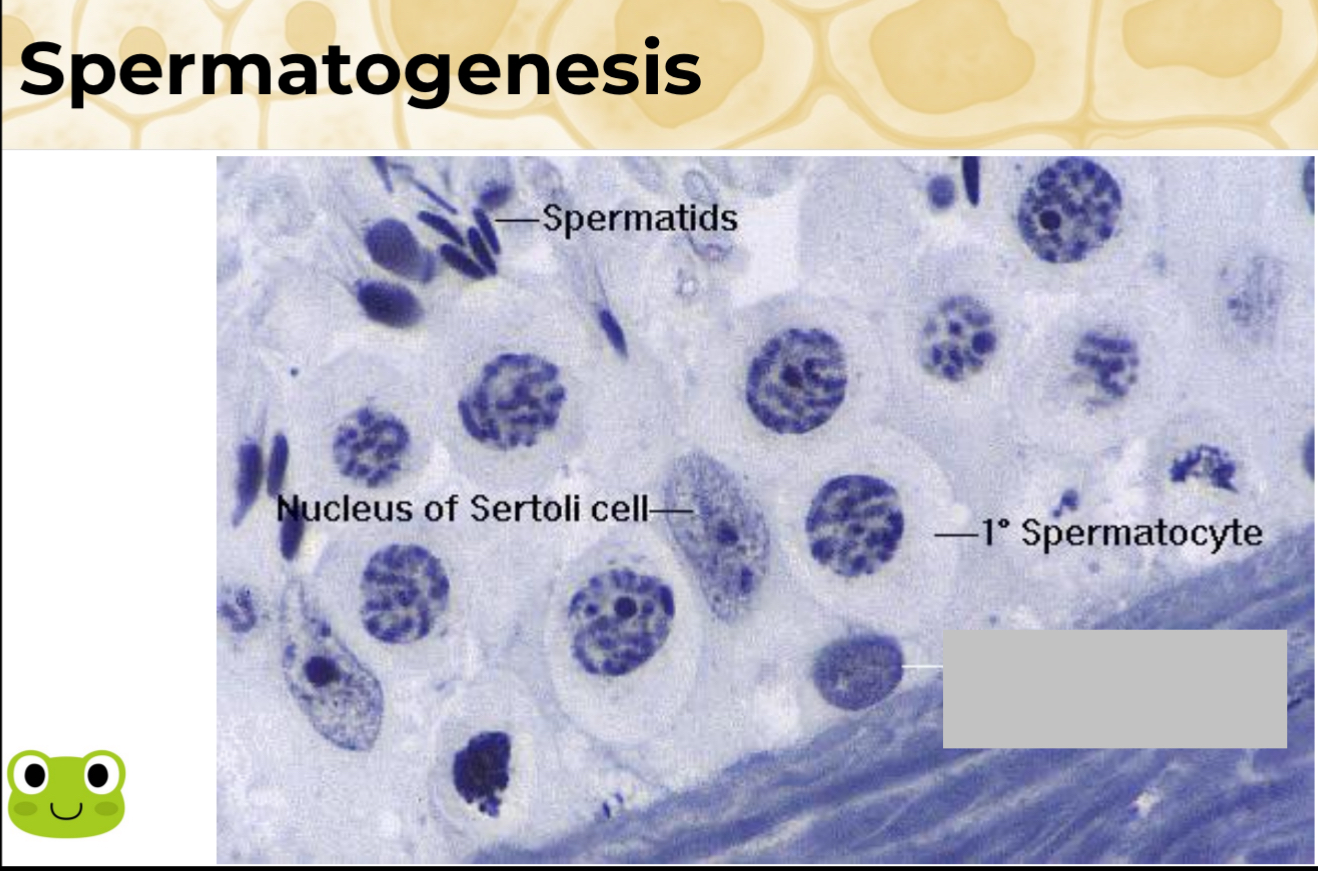
Identify the component
Spermatogonium
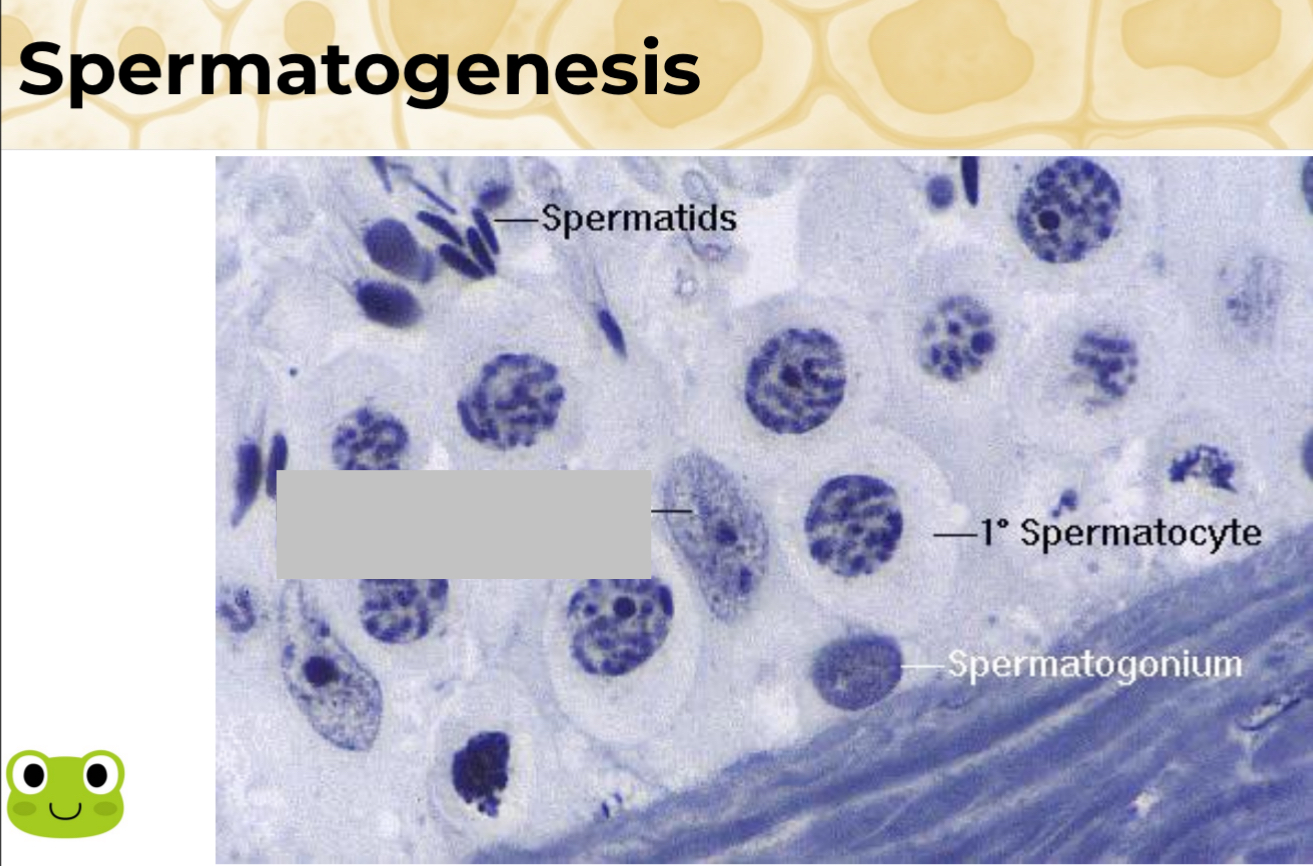
Identify the part, and its function.
Nucleus of Sertoli cell.
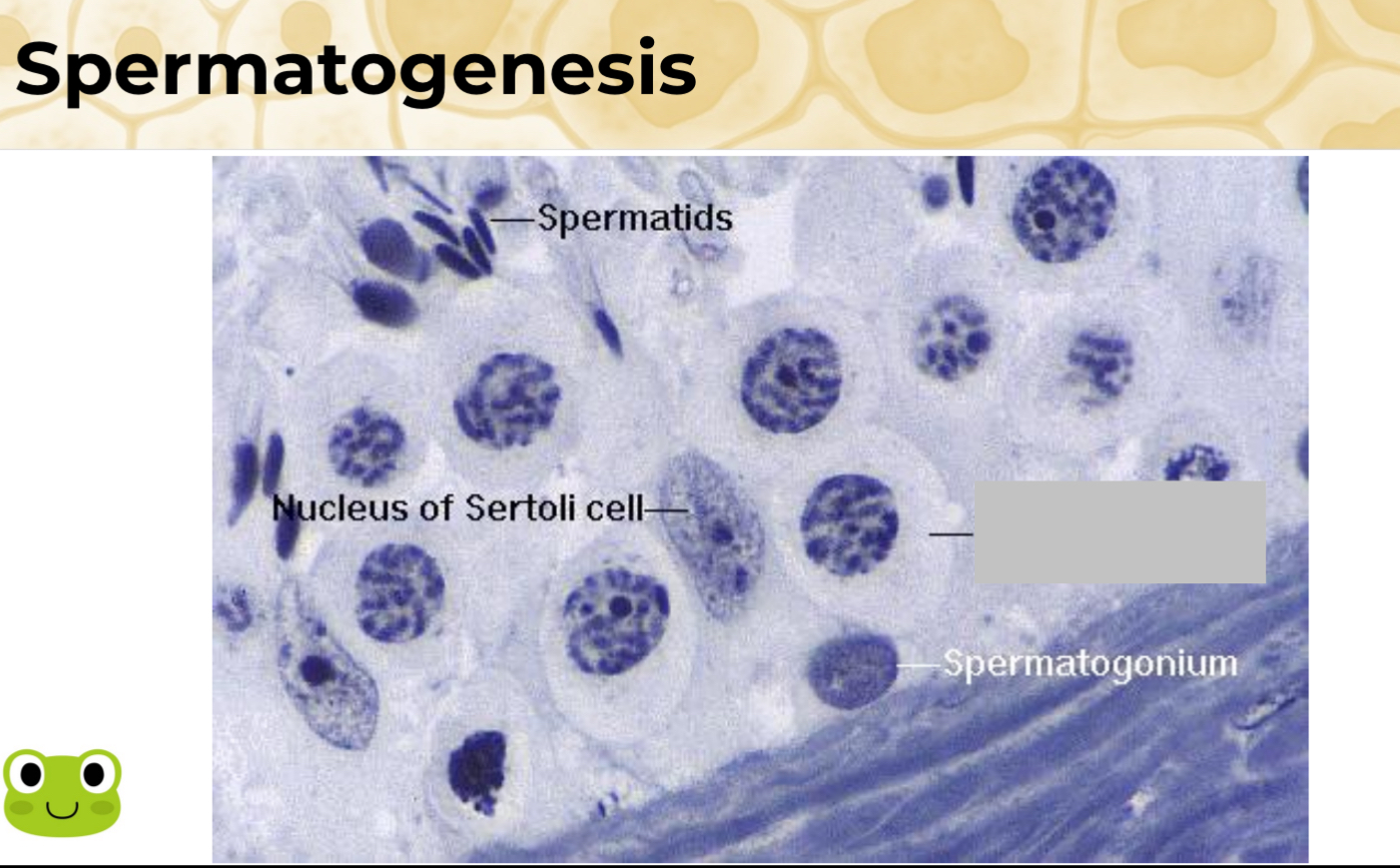
Identify the part, and its function.
Primary spermatocyte.
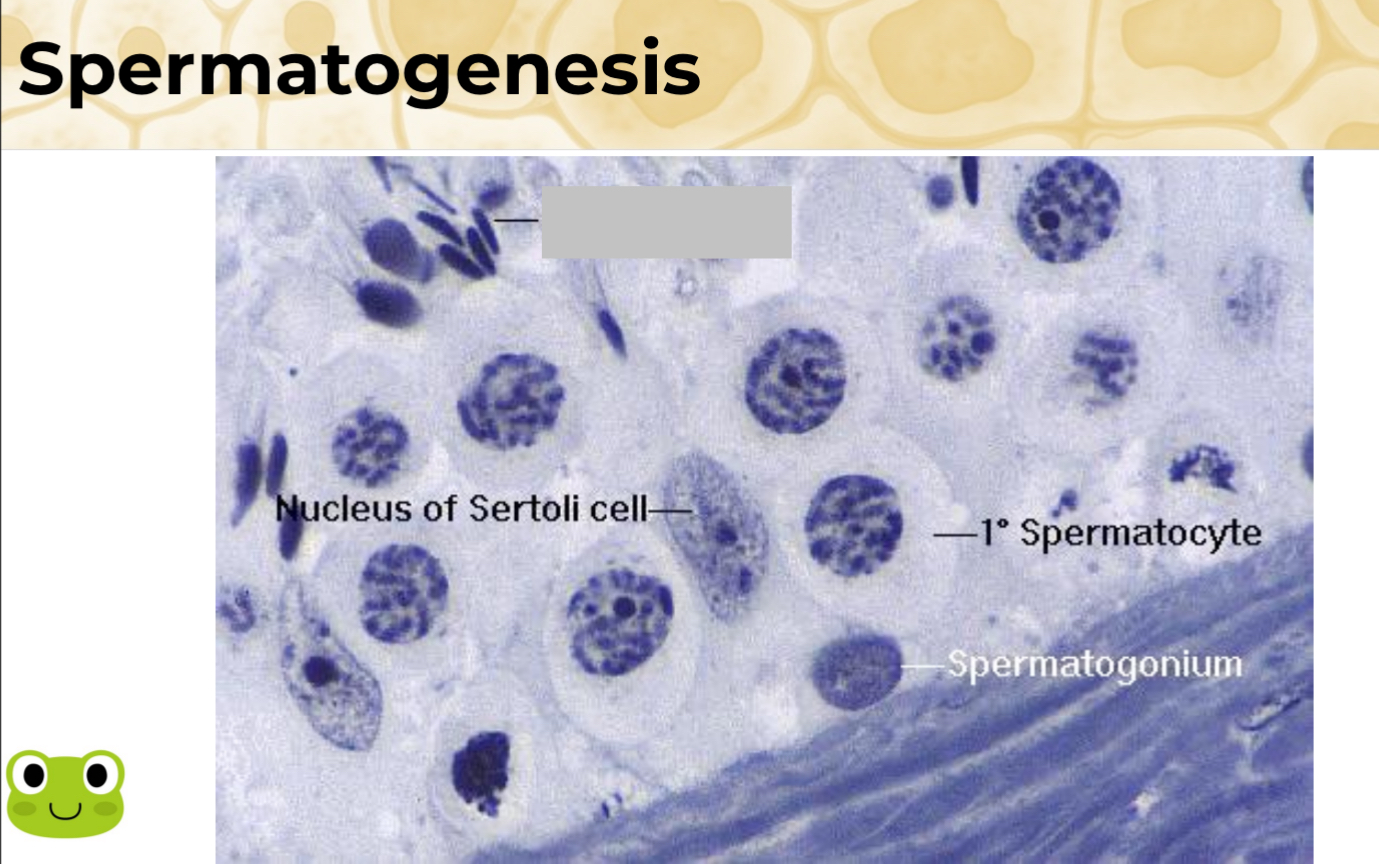
Identify the part, and its function.
Spermatids
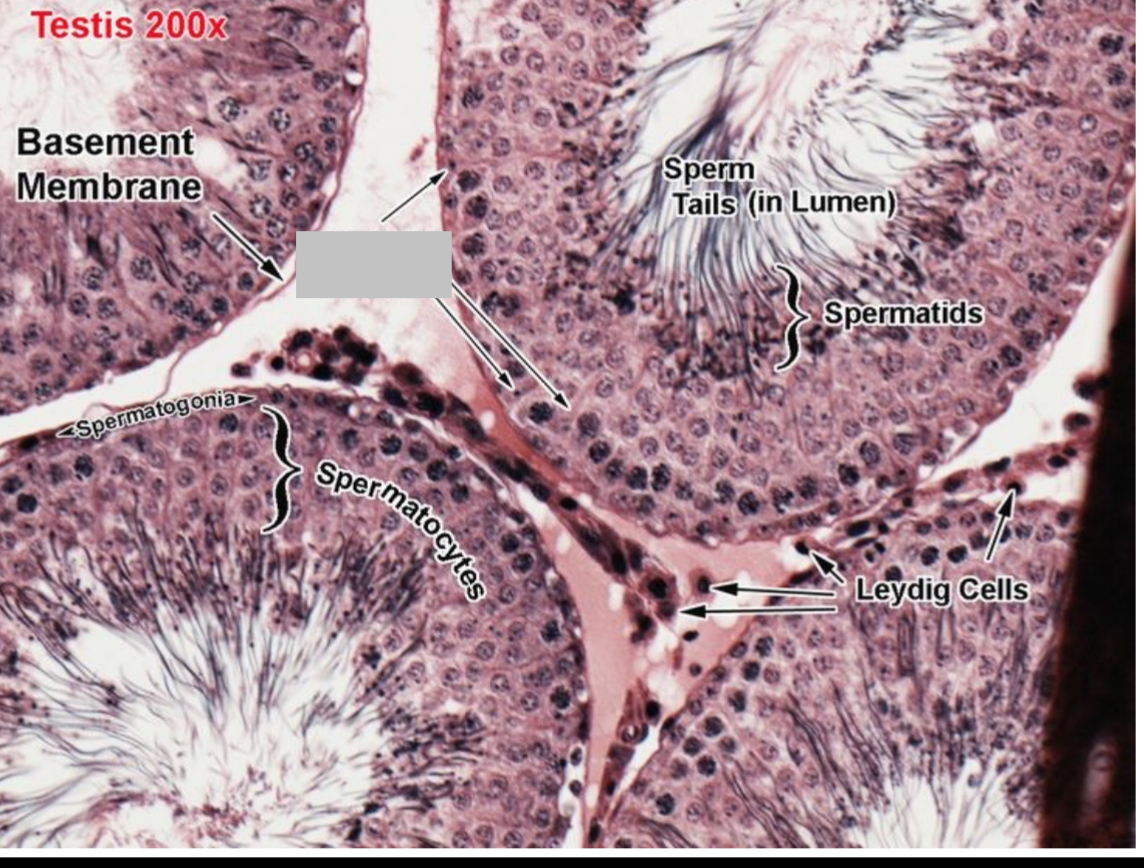
Identify the part, and its function.
Sertoli cells
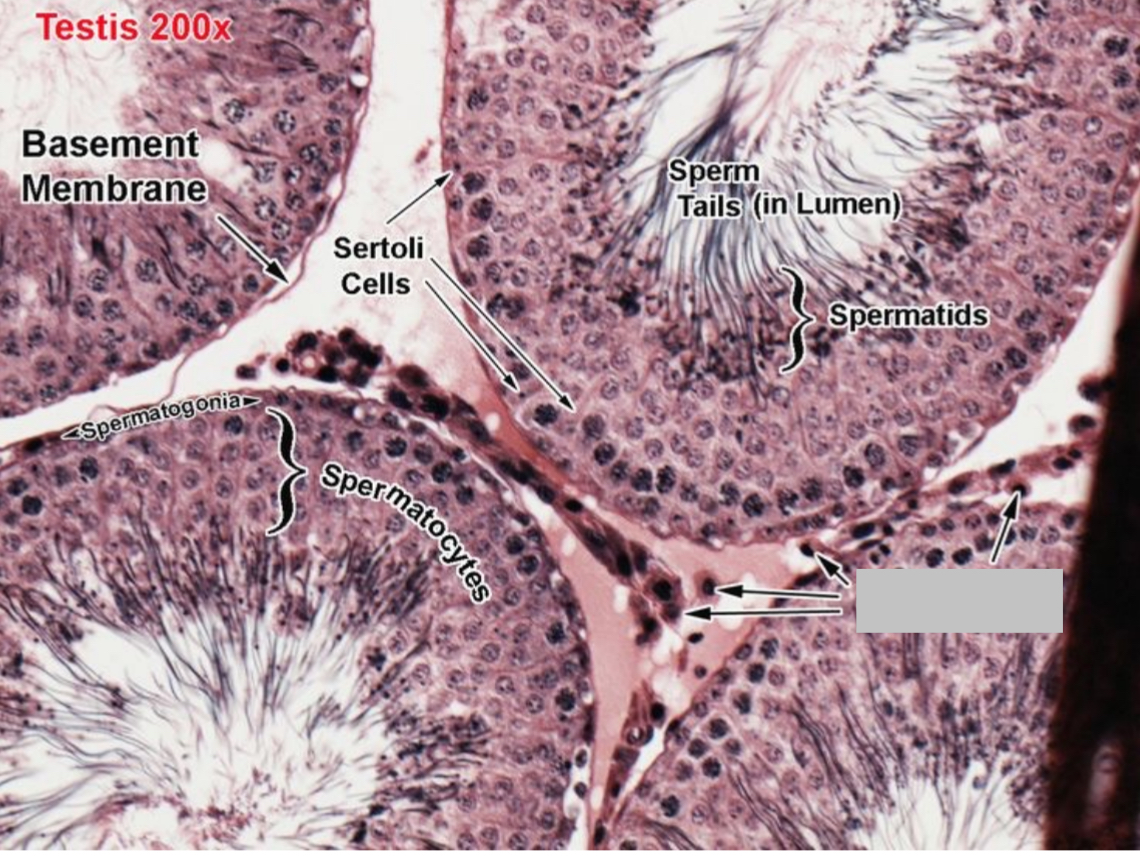
Identify the part, and its function.
Leydig cells
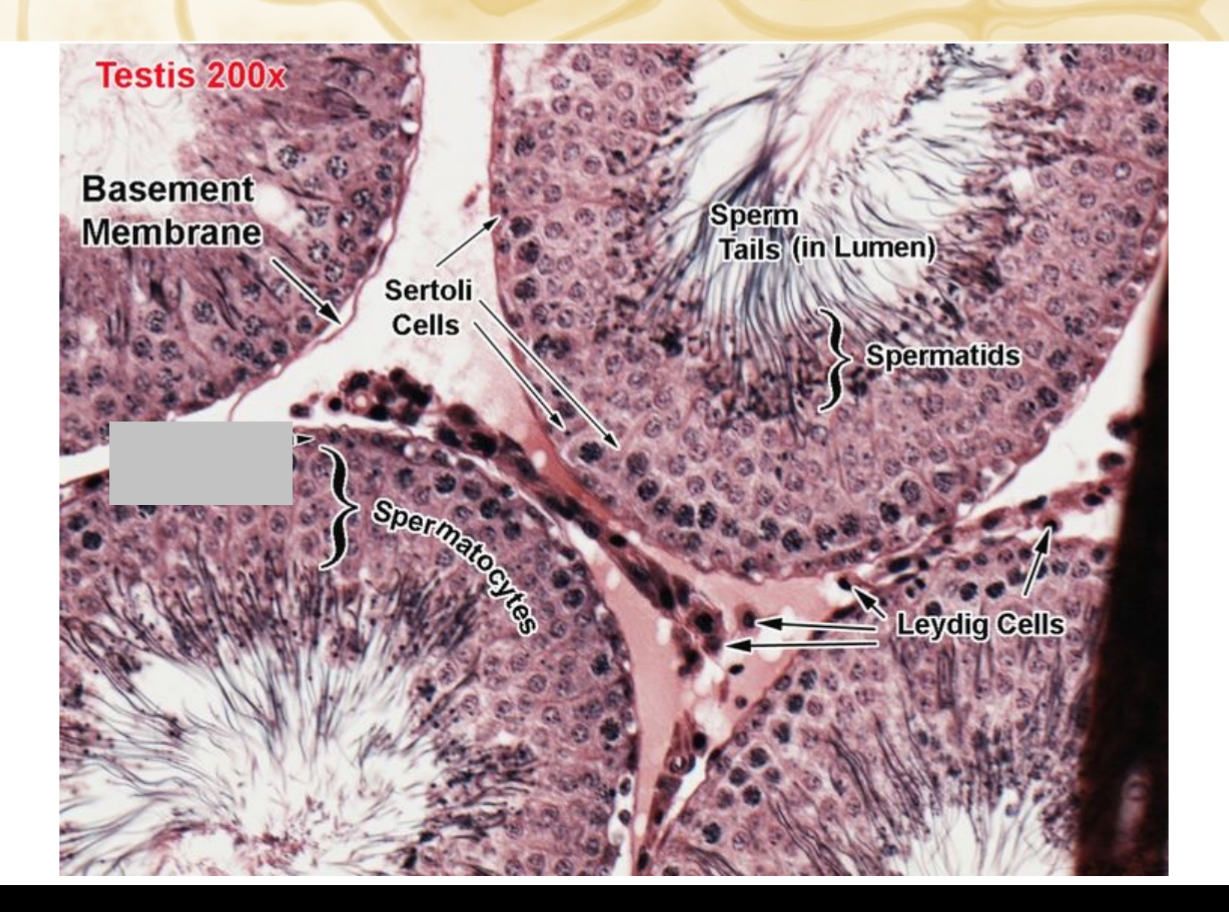
Identify the part, and its function.
Spermatogonia
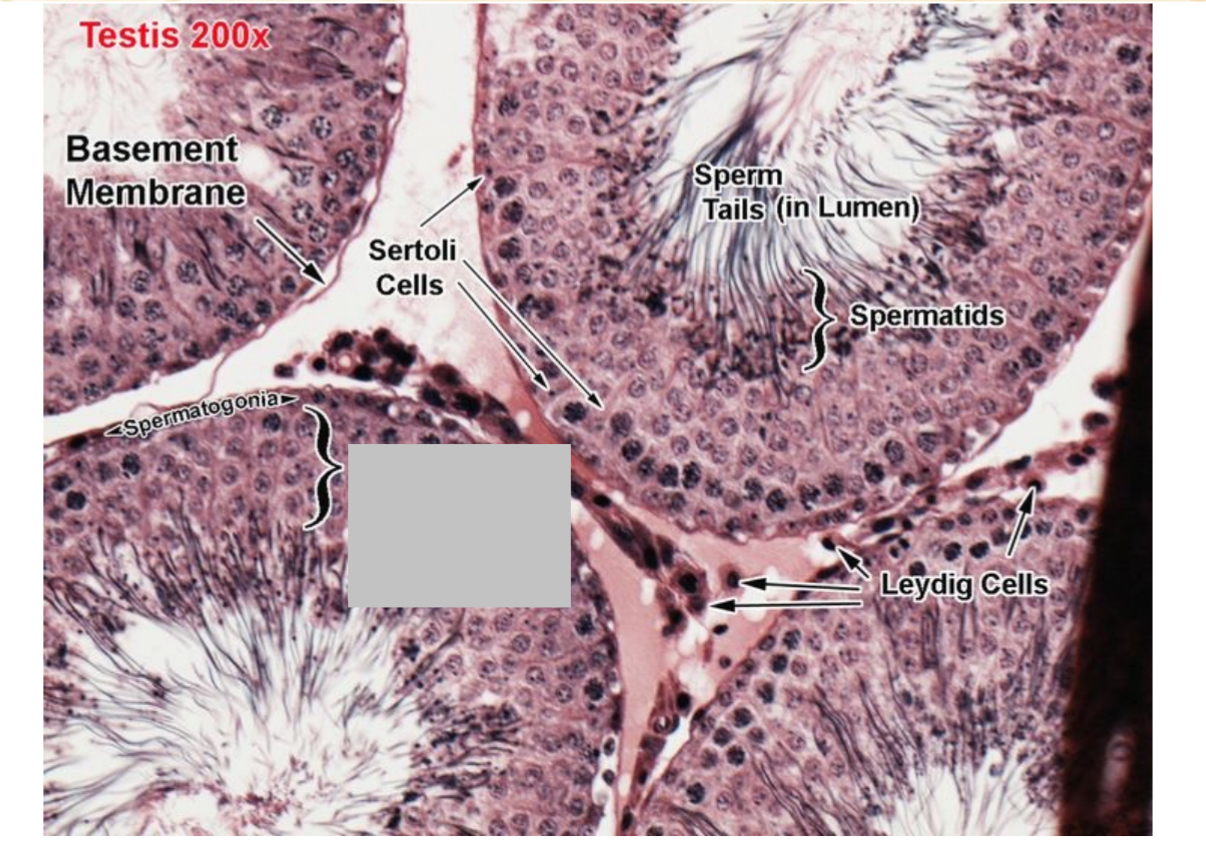
Identify the part, and its function.
Spermatocytes
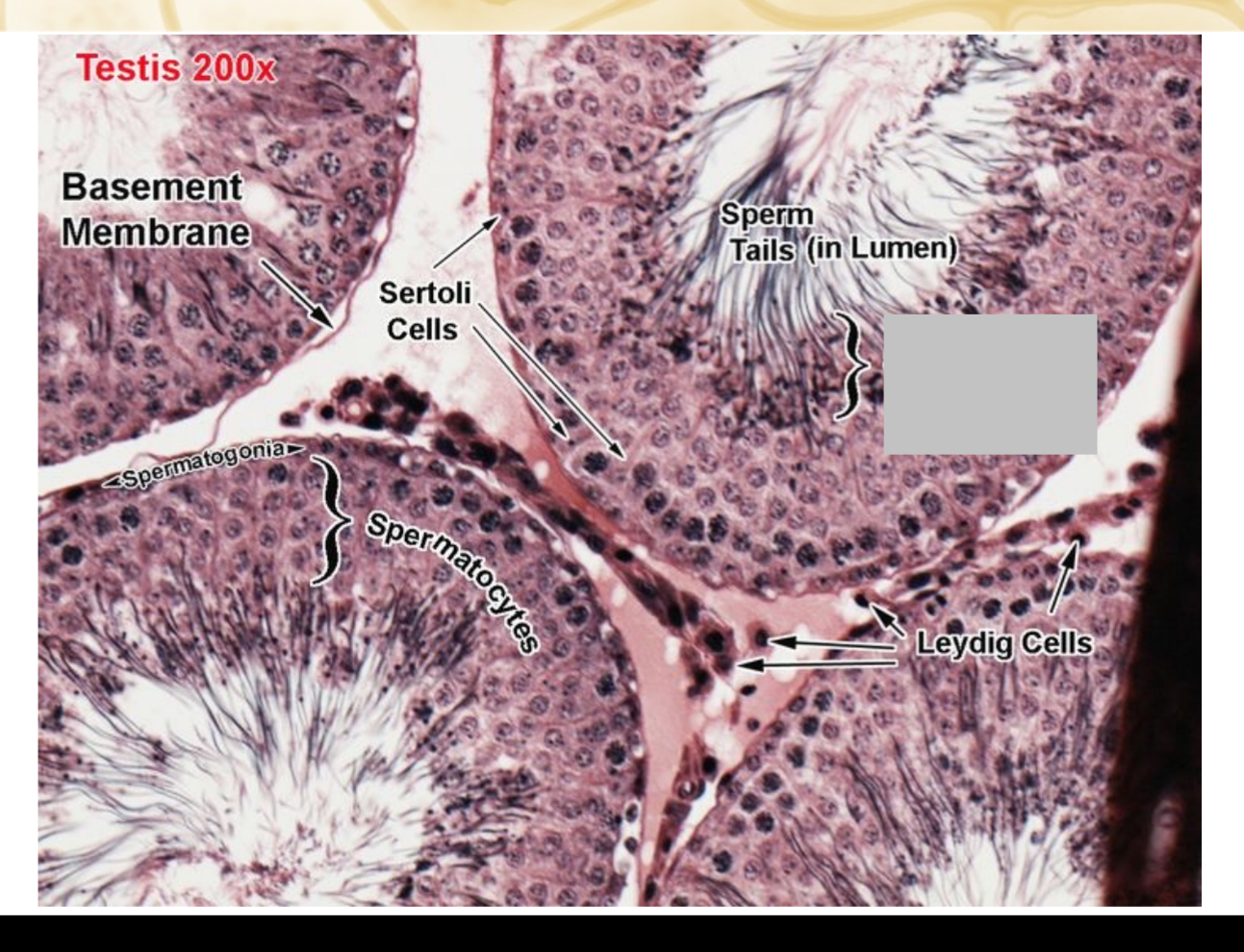
Identify the part, and its function.
Spermatids
Differentiate frog and rat spermatogenesis
Frogs is more oval/goblet-shaped, Rats are more pyramidal, more uniform organization.
Differentiate Leydig and Sertoli Cells
Leydig cells are extracellular, and their purpose is to secrete testosterome
Sertoli cells are close to the cell membrane, and provide nutrients/aid growth of sperm
Zona Pellucida
Barrier of Follicle. Prevents polyspermy fertilization
Corona Radiata
Outside of zona pellucida. Egg’s protein supply
Primordial follicles
Near wall, germinal epithelium. Primary oocyte
Primary follicle
2 Layers/Organized layer of follicle cell surrounds primary oocyte.
Secondary or antral follicle
Small antrum, formation of zona pellucida and corona radiata
Mature or graafian follicle
Large antrum. Will be realeased into ovarian duct
Corpus luteum
Secretes estrogen and progesterone. Remaining cells left behind by egg/follicle. Darker in color
Corpus albicans (white)
Lighter. Dying Corpus luteum