Biology C4.2
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
define ecosystem
all the organisms and abiotic factors, eg water rock sunlight etc, in an area
whats the difference between open and closed systems
Open system:
resources (matter and energy) can enter and exit
Closed system:
energy can enter and exit, but not matter
define autotrophs and tell me the two main types of autotrophs
Autotrophs synthesize organic compounds from inorganic molecules using sunlight or inorganic compounds as energy sources.
→ photoautotrophs use sunlight
→ chemoautotrophs use chemical reactions (cave ecosystem, deep ocean)
what is something that rely on consuming other organisms or organic matter to obtain energy and nutrients for survival.
heterotrophs
define anabolic and catabolic reaction and describe what it does to energy when it occurs
anabolic reactions: building larger molecules with smaller molecules, energy stored
catabolic reaction: breaking down larger molecules into smaller molecules, energy release
what limits the length to food chains
Only 10-20% of energy moves from one level to the next, because:
movement (catching/ eroding predators) Loss of energy in the form of heat
Heat loss -
a consequence of energy conversion during cell respiration.
metabolism (meaning all the chemical reaction the body does) eg. Respiration
undigested waste - eg. barn owl would be bones, teeth, hair, etc
this energy loss restricts length of food chains
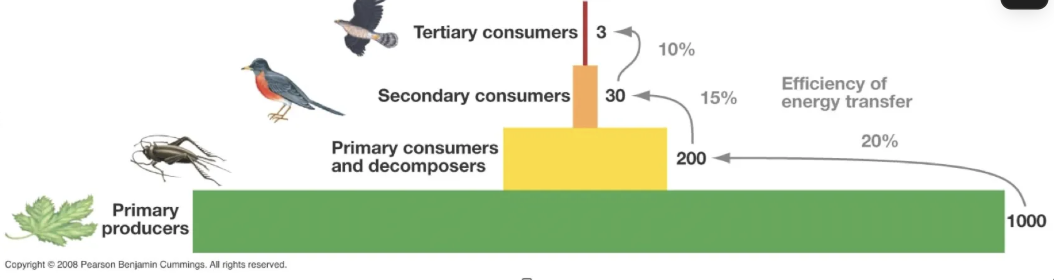
what is the unit for pyramids of biomass and pyramids of energy
energy= calories/kilocalories or joules/ kilojoules

tell me what a decomposer does and the two types of decomposers
Decomposers
break down dead organisms and organic matter, releasing essential nutrients back into the environment.
→ they exist at all trophic levels
Saprotrophs: Does external digestion (Fungi, bacteria), through secreted digestive enzymes into their environment
Detritivores: Feed on detritus (dead stuff) and do internal digestion (vulture, dung beetle)
define flux, sinks and sources, and give me 2 examples each
Flux: movement from one place to another,
includes: photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, combustion and carbon sequestration
Sink: an organism in an ecosystem that absorbs more carbon than it releases , not necessary long term, trees, ocean, soil, rocks, peat
Sources: releasing carbon from a sink/ reservoir
Burning fossil fuels
Respiration
Livestock + methane gas production
define anaerobic and methanogens
anaerobic: organisms that do not use oxygen to respire
eg anaerobic bacteria (methanogens) uses hydrogen uses hydrogen to break down organic molecules
Methanogens: bacteria that produces methane in anaerobic respiration
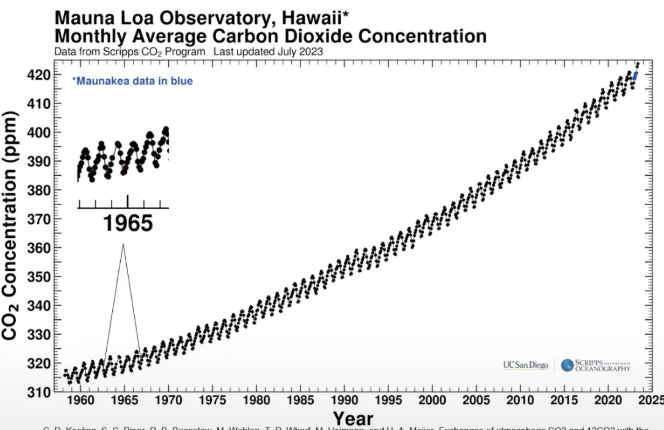
what is this called, tell me why is there an steadily increase and the fluxes in the increases
keeling curve’s steady increase shows the increase of CO2 throughout the years
the equal rise and fall shows, rising in the winter when leaves drop and CO2 storage in plants has decreased
drop in CO2 is during the summer when plants bloom and plants undergo more photosynthesis