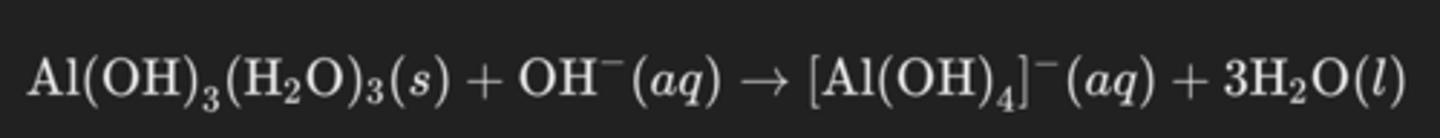AQA A level Chemistry 3.2.6 Aqueous ions
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What happens when a transition metal salt dissolves in water? (1)
The metal ion is surrounded by six water ligands, forming a metal aqua ion or hexa aqua ion
Write the equation for the formation of the hexa aqua ion of Fe²⁺ from Fe(NO₃)₂. (1)
Fe(NO₃)₂(s) + aq → Fe²⁺(aq) + 2NO₃⁻(aq), then Fe²⁺(aq) + 6H₂O(l) → [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺(aq)
What is the colour of the [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺ complex? (1)
Green
What is the colour of the [Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺ complex? (1)
Blue
What is the central metal charge of [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺, and what is its colour? (2)
- Central metal charge: Fe³⁺
- Colour: Purple (often appears brown due to [Fe(H₂O)₅(OH)]²⁺)
What is the colour of the [Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺ complex? (1)
Colorless
Define a Brønsted-Lowry acid. (1)
Proton donor.
Define a Brønsted-Lowry base. (1)
Proton acceptor
How does the charge on the central metal ion affect the acidity of a complex ion? (2)
- Higher charge increases charge density.
- This polarises the O-H bond more, increasing the number of H⁺ ions in solution
What is the typical pH of a solution containing [M(H₂O)₆]²⁺ ions? (1)
pH 6
What is the typical pH of a solution containing [M(H₂O)₆]³⁺ ions? (1)
pH 3
What is the typical pH of a solution containing [M(H₂O)₆]⁴⁺ ions? (1)
pH 0
What is the typical pH of a solution containing [M(H₂O)₆]⁺ ions? (1)
pH 7
How does Lewis acid theory define an acid? (1)
A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor
How does Lewis acid theory define a base? (1)
A Lewis base is an electron pair donor
What is a common example of a reaction involving a Lewis acid and a Lewis base? (1)
BH₃ + NH₃ → NH₃BH₃
In the reaction BH₃ + NH₃ → NH₃BH₃, identify the Lewis acid and the Lewis base. (2)
- Lewis acid: BH₃
- Lewis base: NH₃
What is the colour of the aqueous ion [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
Green solution
What happens when NaOH is added dropwise to [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (2)
- Fe(H₂O)₄(OH)₂(s) forms as a green precipitate
- Which turns brown on standing in air
What happens when an excess of NaOH is added to [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
No further change
What happens when NH₃ is added dropwise to [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (2)
- Fe(H₂O)₄(OH)₂(s) forms as a green precipitate
- Which turns brown on standing in air
What happens when an excess of NH₃ is added to [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
No further change
What happens when Na₂CO₃ is added to [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
FeCO₃(s) forms as a green precipitate
What is the colour of the aqueous ion [Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
Blue solution
What happens when NaOH is added dropwise to [Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
Cu(H₂O)₄(OH)₂(s) forms as a blue precipitate
What happens when an excess of NaOH is added to [Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
No further change
What happens when NH₃ is added dropwise to [Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
Cu(H₂O)₄(OH)₂(s) forms as a blue precipitate
What happens when an excess of NH₃ is added to [Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
[Cu(H₂O)₂(NH₃)₄]²⁺ forms as a deep blue solution
What happens when Na₂CO₃ is added to [Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺? (1)
CuCO₃(s) forms as a blue-green precipitate
What is the colour of the aqueous ion [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
Purple solution (may appear yellow-brown due to [Fe(H₂O)₅(OH)]²⁺)
What happens when NaOH is added dropwise to [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
Fe(H₂O)₃(OH)₃(s) forms as a brown precipitate (may look orange-brown)
What happens when an excess of NaOH is added to [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
No further change
What happens when NH₃ is added dropwise to [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
Fe(H₂O)₃(OH)₃(s) forms as a brown precipitate (may look orange-brown)
What happens when an excess of NH₃ is added to [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
No further change
What happens when Na₂CO₃ is added to [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (2)
- Fe(H₂O)₃(OH)₃(s) forms as a brown precipitate
- CO₂ gas is evolved
What is the colour of the aqueous ion [Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
Colourless solution
What happens when NaOH is added dropwise to [Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
Al(H₂O)₃(OH)₃(s) forms as a white precipitate
What happens when an excess of NaOH is added to [Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
[Al(OH)₄]⁻ forms as a colourless solution
What happens when NH₃ is added dropwise to [Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
Al(H₂O)₃(OH)₃(s) forms as a white precipitate
What happens when an excess of NH₃ is added to [Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
No further change
What happens when Na₂CO₃ is added to [Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺? (1)
Al(H₂O)₃(OH)₃(s) forms as a white precipitate, and CO₂ gas is evolved
Write the reaction for [Fe(H2O)6]²⁺ with NaOH(aq) dropwise. (1)
[Fe(H2O)6]²⁺(aq) + 2OH⁻(aq) → Fe(H2O)4(OH)2 + 2H2O(l)
Write the reaction for [Fe(H2O)6]²⁺ with NH3(aq) dropwise. (1)
[Fe(H2O)6]²⁺(aq) + 2NH3(aq) → Fe(H2O)4(OH)2 + 2NH4⁺(aq)
Write the reaction for [Fe(H2O)6]²⁺ with excess Na2CO3(aq). (1)
[Fe(H2O)6]²⁺(aq) + CO3²⁻(aq) → FeCO3(s) + 6H2O(l)
Write the reaction for [Cu(H2O)6]²⁺ with NaOH(aq) dropwise. (1)
[Cu(H2O)6]²⁺(aq) + 2OH⁻(aq) → Cu(H2O)4(OH)2 + 2H2O(l)
Write the reaction for [Cu(H2O)6]²⁺ with NH3(aq) dropwise. (1)
[Cu(H2O)6]²⁺(aq) + 2NH3(aq) → Cu(H2O)4(OH)2 + 2NH4⁺(aq)
Write the reaction for [Cu(H2O)6]²⁺ with NH3(aq) in excess. (1)
Cu(H2O)4(OH)2 + 4NH3(aq) → [Cu(H2O)2(NH3)4]²⁺(aq) + 2H2O(l) + 2OH⁻(aq)
Write the reaction for [Cu(H2O)6]²⁺ with Na2CO3(aq). (1)
[Cu(H2O)6]²⁺(aq) + CO3²⁻(aq) → CuCO3(s) + 6H2O(l)
Write the reaction for [Fe(H2O)6]³⁺ with NaOH(aq) dropwise. (1)
[Fe(H2O)6]³⁺(aq) + 3OH⁻(aq) → Fe(H2O)3(OH)3 + 3H2O(l)
Write the reaction for [Fe(H2O)6]³⁺ with NH3(aq) dropwise. (1)
[Fe(H2O)6]³⁺(aq) + 3NH3(aq) → Fe(H2O)3(OH)3 + 3NH4⁺(aq)
Write the reaction for [Fe(H2O)6]³⁺ with Na2CO3(aq). (1)
2[Fe(H2O)6]³⁺(aq) + 3CO3²⁻(aq) → 2Fe(H2O)3(OH)3 + 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
Write the reaction for [Al(H2O)6]³⁺ with NaOH(aq) dropwise. (1)
[Al(H2O)6]³⁺(aq) + 3OH⁻(aq) → Al(H2O)3(OH)3 + 3H2O(l)
Write the reaction for [Al(H2O)6]³⁺ with NaOH(aq) in excess. (1)
Al(H2O)3(OH)3 + OH⁻(aq) → [Al(OH)4]⁻(aq) + 3H2O(l)
Write the reaction for [Al(H2O)6]³⁺ with NH3(aq) dropwise. (1)
[Al(H2O)6]³⁺(aq) + 3NH3(aq) → Al(H2O)3(OH)3 + 3NH4⁺(aq)
Write the reaction for [Al(H2O)6]³⁺ with Na2CO3(aq). (1)
2[Al(H2O)6]³⁺(aq) + 3CO3²⁻(aq) → 2Al(H2O)3(OH)3 + 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
Why is aluminium hydroxide classified as an amphoteric hydroxide? (1)
It reacts with both acids and bases to form different soluble species
What happens when aluminium hydroxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid? (2)
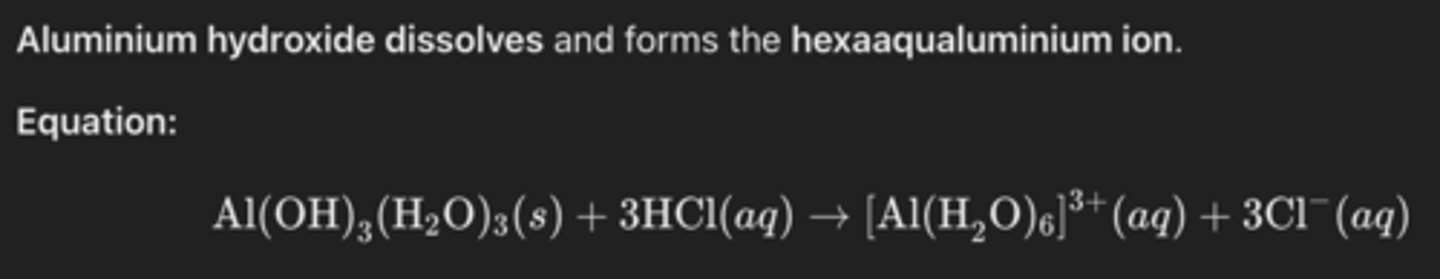
What is the ionic equation for aluminium hydroxide reacting with hydroxide ions? (1)