Reproduction in Female Domestic Animals
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Location GnRH
Produced in the hypothalamus.
Location LH
Produced in the anterior pituitary.
Location FSH
Produced in the anterior pituitary.
Location Progesterone
Produced in the corpus luteum.
Location Inhibin
Produced in granulosa cells.
Location Activin
Produced in granulosa cells.
Location Estradiol
Produced in granulosa cells.
Location Prostaglandins
Produced in the uterine endometrium.
Function Dopamine
Inhibits production of prolactin.
Function Oxytocin
Stimulates smooth muscle contractions of the uterus and milk letdown.
Function Prolactin
Causes mammary growth and milk production, inhibits dopamine.
Function FSH
Stimulates follicular growth, estradiol production by granulosa cells and induces granulosa cells to produce LH receptors.
Function LH
Follicle maturation and ovulation, progesterone secretion and CL maintenance, negative feedback on progesterone.
Function Progesterone
Maintenance of pregnancy.
Function Inhibin
Suppresses FSH.
Function Activin
Stimulates FSH.
Function TRH
Stimulates prolactin synthesis.
Function Estradiol
Negative feedback on FSH.
Function Kisspeptin
Induces GnRH release.
Function GnRH
Induces FSH/LH secretion.
Ferguson reflex
Pressure in the birth canal or on the cervix stimulates release of oxytocin to further stimulate contractions.
Follicular phase
Rising estrogen, intensifying LH pulses, LH surge, ovulation.
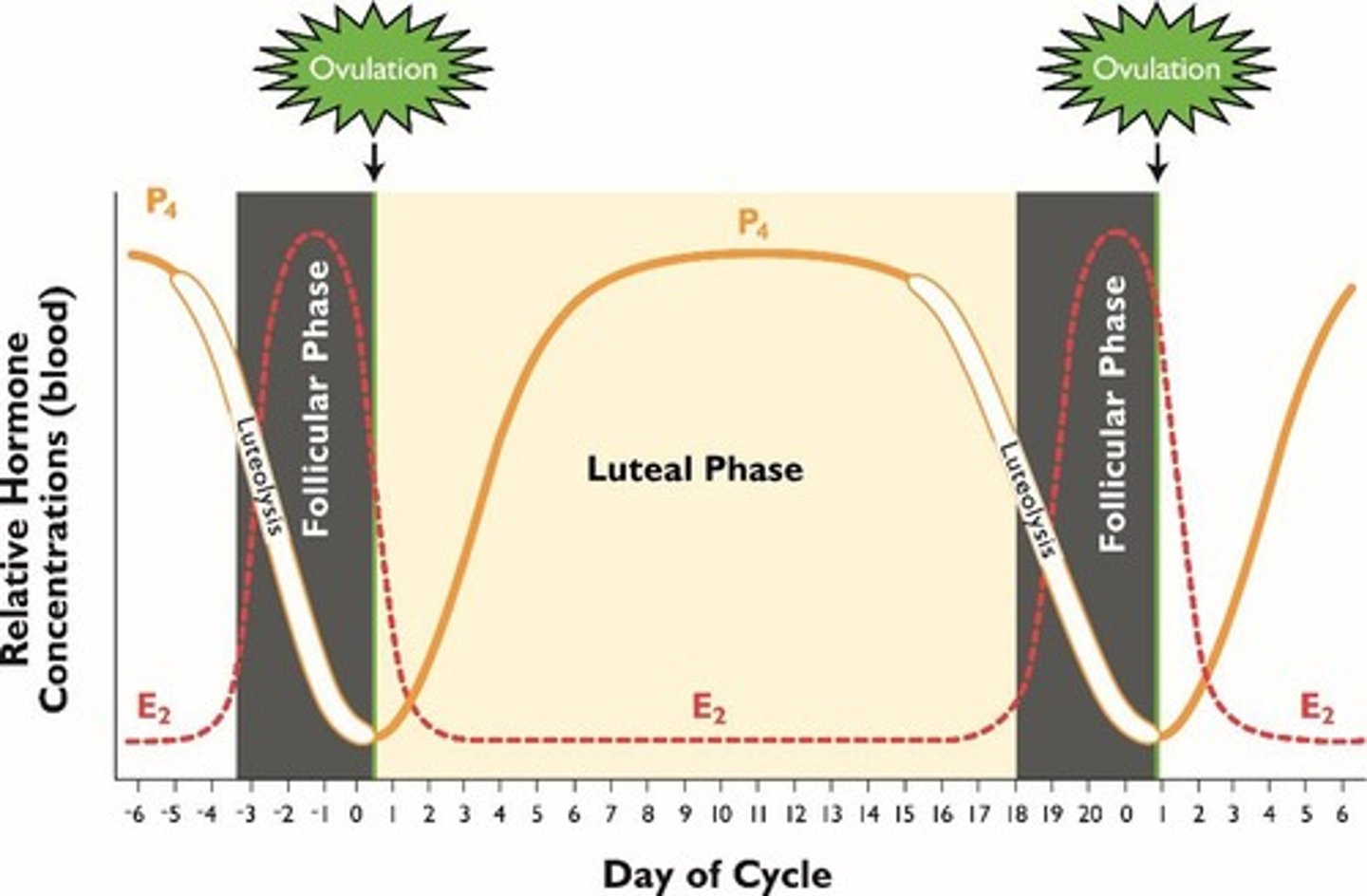
Luteal phase
Progesterone is higher than estrogen, inhibition of LH, no heat.
Primordial follicle
Single layer of flat granulosa cells.
Primary follicle
Single layer of cuboidal granulosa cells.
Secondary follicle
Multiple layers of cuboidal granulosa cells.
Tertiary (antral) follicle
Presence of a fluid filled antrum, multiple layers of granulosa, theca cells, has FSH and LH receptors.
Theca cells function
Convert cholesterol into androgens.
Granulosa cells function
Convert androgens into estrogens (FSH).
What is a COC
Cumulus oocyte complex, oocyte surrounded by cumulus cells with zonal projections.
Describe the hormonal process of ovulation
LH surge stimulates relaxin and prostaglandins from the granulosa, connective tissue of the follicle weakens and leads to rupture.
Induced ovulation species
Cats, camelids, ferrets, rabbits.
Progesterone in dogs
Progesterone rises before ovulation.
CL regression hormone. What species do not use this hormone?
Prostaglandins; dogs/cats do not use this hormone.
Unilateral ovarian development species
Most avian.
Can you spay birds? Reptiles/chelonians?
No, but yes for reptiles/chelonian.
what is a Seasonal breeder? what causes changes in seasonal cyclicity?
Only breed during certain times of the year; changes in seasonal cyclicity caused by melatonin.
Determinate layer
Fail to lay additional eggs in the case of egg loss (chelonians, reptiles, budgies, parakeets, most avians; NOT CHICKENS).
What species do we do Ovariectomy and ovariohysterectomy? Advantages? Disadvantages?
Performed on large animals and small animals respectively; advantages include permanence and disease prevention, disadvantages include weight gain, incontinence, reduced estrogen.
how does Ovaban (megestrol acetate) work
Suppresses estrus, mammary development, weight gain, adrenal suppression in dogs.
what does Depo-Provera (medroxyprogesterone acetate) do?
Causes weight gain, adrenal suppression, mammary neoplasia, uterine disease (CEH/cystic endometrial hyperplasia and pyometra) in dogs.
what does Regu-Mate (altrenogest) do?
Blocks secretion of LH from anterior pituitary in horses.
Is Depo-Provera (medroxyprogesterone acetate) recomended in horses
Not effective/recommended.
Anti-progestins (e.g., RU-486) function
Binds the progesterone receptor and prevents action of natural progesterone (not often used in animals).
How do Androgens work?
Inhibits secretion of gonadotropins (LH/FSH) through negative feedback, decreases follicular development and inhibits ovulation.
What is Mibolerone? What are its functions and side effects?
Type of androgen contraceptive; decreases incidence of CEH/pyometra and mammary gland neoplasia in comparison to progestins; side effects include clitoral hypertrophy, discharge, increased aggression.
How do GnRH agonists work?
Have a higher affinity than natural GnRH, down regulates the anterior pituitary with large doses to reduce FSH and LH to prevent follicular development and ovulation.
how do GnRH antagonists work?
Bind to GnRH receptor, biologically inactive, rapid onset, short duration, prevents synthesis/secretion of FSH/LH to inhibit ovulation.
GnRH toxins
Bind to GnRH receptor and kill the cell, decreases FSH/LH.
how does the GnRH vaccine work?
Bound to a larger molecule; anti-GnRH antibodies bind circulating GnRH and prevent it from acting upon its receptor, thus preventing LH/FSH production; antibodies must wane before cyclicity returns; works in males and females.
how does the Zona pellucida vaccine work?
Antibodies against the ZP proteins block the sperm binding site to inhibit fertilization; does not influence ovulation or estrus; immune mediated pathology may occur.
How can you Induce ovulation
GnRH or GnRH agonists stimulate anterior pituitary release of LH to induce ovulation; LH and hCG also act like LH (requires ovarian stimulation for ovulation).
What is Superovulation
Causes ovulation of multiple follicles.
Hormones from dominant follicle
Inhibin and estradiol cause only one follicle to ovulate.
How to Induce superovulation
Administer exogenous FSH or eCG or prevent the action of inhibin through immunoneutralization to allow for the action of endogenous FSH.
What is one method of Synchronize estrus
Administer progesterone for 10-14 days to suppress LH (act as a fake CL); may also administer estradiol to suppress FSH; PGF would be administered at the end of treatment.
Cystic ovaries pathologies
Mostly in dairy cows with a mis-timed LH surge or insufficient estrogen production by the follicle; includes failure to ovulate, partial luteinization, persistent estrus, masculinized, persistent estrus/anestrus, elevated tail head, cystic endometrial hyperplasia, vulva enlargement.
Short cycling indication
Uterine infection or endometritis causing persistent release of PGF and CL lysis.
Causes of pseudopregnancy
Inadequate PGF release, embryonic loss after maternal recognition of pregnancy, severe uterine pathology preventing the release of PGF.
Acute infection effect on PGF
Causes PGF release.
Chronic infection effect on PGF
Inhibits PGF release.
Effect of Fescue ingestion in cows
High dopamine, low prolactin, no milk production.
Phytoestrogens ingestion in cows/ewes can cause what
Causes CEH.
Can you tell systemically if a large animal has a uterine infection? Small animals?
Systemically undetectable in large animals, but detectable in small animals.
Pyometra stage in dogs
Occurs in diestrus.
What hormone is stimulated by high frequency pulses of GnRH?
LH
What hormone is stimulated by low frequency pulses of GnRH?
FSH
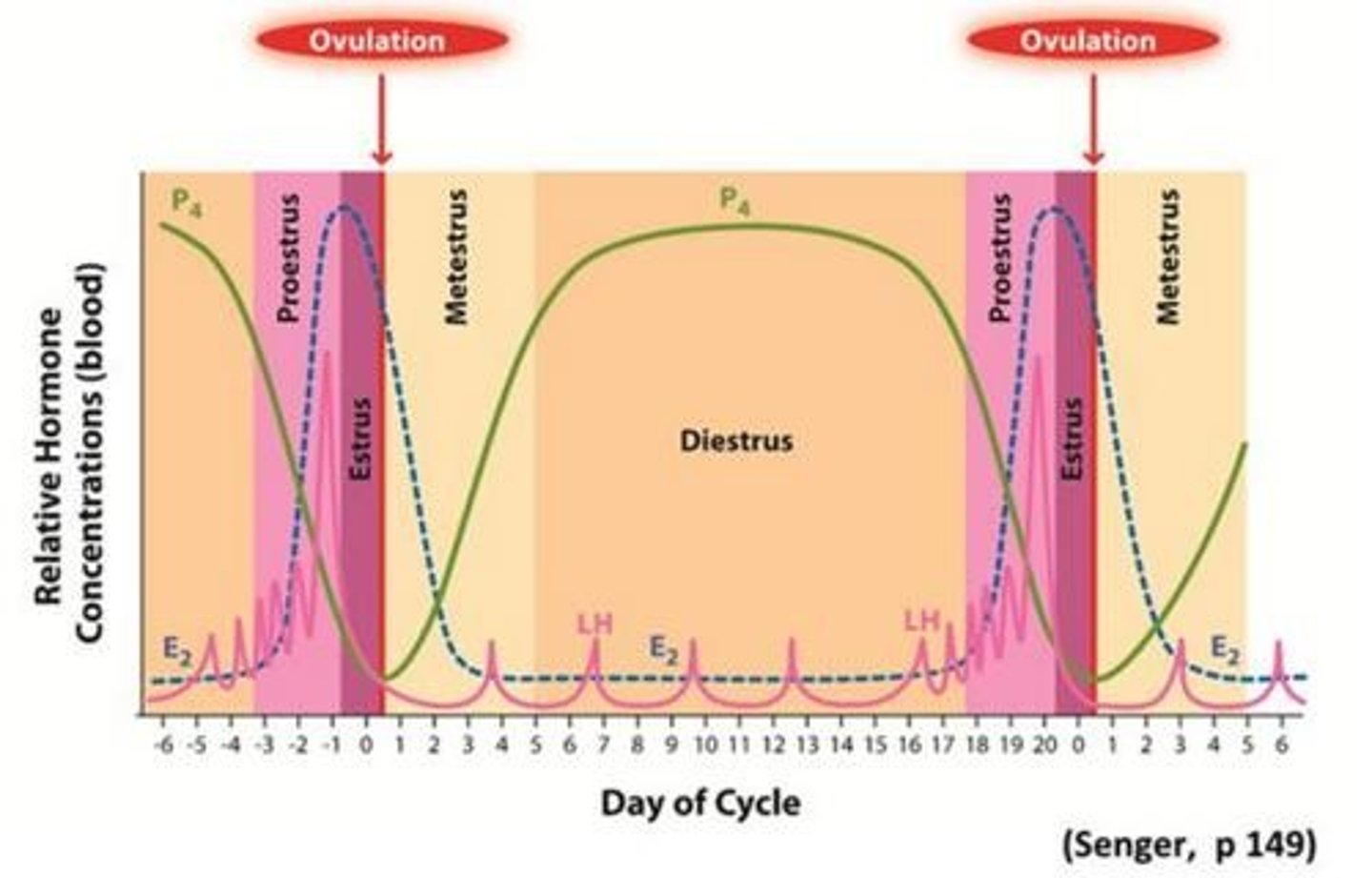
What hormone(s) are associated with proestrus
declining progesterone, increasing estradiol
What hormone(s) are associated with estrus
high estrogen
What hormone(s) are associated with metestrus
declining estrogen, increasing progesterone
What hormone(s) are associated with diestrus
high progesterone
What hormone(s) are associated with anestrus
low hormonal action
Is it a good idea to give a bird nesting materials or alter the light cycle?
Yes, it increases folliculogenesis