AP Biology Unit 1
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry of Life
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Polar
Polarity of water
Electronegativity
An atoms attraction for electrons
Covalent bonds
Bonds that share electron pairs
Polar molecules
atoms in a molecule have unequal pulls on electrons they share
Oxygen
In a water molecule has a slight negative charge
Hydrogen
In a water molecule that has a slight positive charge
Hydrophilic
Substances that are attracted to water
Hydrophobic
Substances that aren’t attracted to water
Specific heat capacity
water requires a high amount of heat energy to raise the temperature of a unit of a mass of water
High heat of vaporization
a large amount of energy is required to convert a liquid into a gas
Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen
Proteins are made of…
Amino acids
Monomers for proteins
Structure of proteins
Amino group on one side and a carboxyl group on another side
Carbon in the center bonded to a hydrogen atom
Variable R group
Cohesion
Attraction among molecules of the same substance (specifically water)
High surface tension
result of molecules being pulled close together due to hydrogen bonds at the surface
Adhesion
Attraction among molecules of different substances (specifically water)
Polar
Contains a lot of nitrogen and oxygen in comparison to other molecules
Acid
pH value less than 7
Base
pH value greater than 7
Neutral
pH value at 7
Non-polar
Contains a lot of carbon and hydrogen in comparison to other molecules
Acids
chemical substances that increase the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution
Bases
substances that increase the concentration of hydroxide (OH⁻) ions
Function
Structure of a protein determines…
Hydrogen ion concentrations
What pH measures
Hydronium
The ions that acids produce in water
Hydroxide
Ions that bases produce in water
Universal solvent
Water dissolves many substances (Ionic and polar molecules)
Aqueous
water-based solution
They separate into Ions
What happens when compounds dissolve in water
Polar covalent bonds
What are the intramolecular bonds in a water molecule
Stabilizes temperature
Due to hydrogen bonding, water can absorb energy and maintain relatively constant climate in land areas near large bodies of water.
Water expands when freezing
Due to hydrogen bonding, water can absorb energy and maintain relatively constant climate in land areas near large bodies of water.
Hydrogen bonds
Each water molecule can bond to 4 others through an attraction called
Atoms
Basic unit of matter and can combine through different types of bonding to form compounds
Ionic bonds
Bonds that occur when atoms form negatively charged particles by transferring electrons
Covalent bonds
Bonds that occur when atoms share electrons
C, H, O
most common elements that are used to form biological molecules of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucelic acids
Nitrogen
Element thats used to build proteins and nucleic acids
Phosphorous
Element that is used to form phospholipids and nucelic acids
Hydroxyl
-OH
Polar
Hydrophilic
Alcohol
-OH
Hydroxyl
Carboxyl
A carbon double bonded to an oxygen and bonded to an OH
Acidic
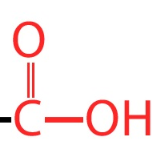
-COOH
Carboxyl
-CH3
Methyl
NH2
Amino acid
PO4
Phosphate group
Carbonyl
Carbon double bonded to an oxygen
C=O
Carbonyl
Monomers
Small repeating molecules used to create large polymers
Hydrolysis
Type of chemical reaction that is used to break down macromolecules into their smaller components
Dehydration Synthesis
Chemical reactions are used to construct macromolecules from smaller molecules with covalent bonds
1:2:1
Ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in carbohydrates
Simple sugars
Examples of carbohydrates
Function of carbohydrates
The energy contained can be released and used for essential cell processes
Glucose
Carbohydrate of most importance to living organisms
Starch
Consists of hundreds of glucose molecules
Starch
Primary energy storage for plants
Cellulose
Primary component of plant cell walls and other plant structures, single most abundant organic compound found on Earth
Chitin
A complex carbohydrate that forms the rigid outer skeleton of most insects and crustaceans
Glycogen
Primary energy storage for animals
Lipids
Nonpolar molecules that do not dissolve in water
Greasy to the touch
Can be a significant source of energy storage
Function of fats
Long-term energy storage and insulation
Function of sterols
Regulate growth and development
C, H, Small O
Composition of Lipids
Butter, lard
Ex. of saturated fats
Vegetables, olive oil
Ex. of unsatured fats
Function of fats
Absorbing some vitamins and minerals
Building and repairing cell membranes
Forming structures such as the myelin sheath
providing insulation
helping with muscle movement and blood clotting
Steroids
Fused ring structure; play a part in regulating growth and development
Cholesterol
Precursor molecule for steroid hormones
Phospholipids
Consist of glycerol linked to two fatty acid chains and a phosphate group, major component of the membrane that surrounds and contents of a cell an controls the flow of chemicals
Polarity of phospholipids
head region is hydrophilic
Tail region is hydrophobic
Amino acids
Monomers for proteins
Alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
shape of secondary structure of a protein