Human Growth and Developement
1/131
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HAHP 2000: Test #1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Life Span Development
The pattern of movement or change that beings at conception and continues throuhgout the life span
Characteristicss in LifeSpan Development
Development is:
Lifelong, multidimensional, multidirectional, plastic, multidisciplinary, involves growth maintanence, co-construction of biology, culture and the individual and contextual
Normative age-graded influence
Similar for people in a similar age group
Normative history graded influences
Common to people of a particular generation
Non- Normative Life events
Unanticipated events
Lifespan expectancy
The average age a child born in a given year can expect to live to
Median Age for male
40.1
Median age for women
42.2
Biological processes change
Physical Nature
Cognitive process refer to changes in
thought, intelligence and language
Socio-emtional processes involve changes in
relationships, emotions and personality
Different ways to describe age
Chronological, biological, mental, psychological, social
Brad Meisner Research interest/focus
Age related stereotypes, Perceptions, attitudes and discrimination
Nature
Development primarily influenced by biological inheritance
Nuture
Enviornmental influences and experiences
Continuity
Development involve Gradual Cumulative changes
Discontinuity
Development involve distinct stages
Stability and Change
Become older renditions of our early experiences or do we develop into someone different from who we are at an earlier point in development
Methods of collecting data
observation, survery & interview, standardized test, case study, physiology measures
Research Designs
Quantitative Designs and Qualitative Designs
Quantitative Designs
Descriptive, Correlational, Experimental
Descriptive Research
Observe and record behavior
Correlational Research
Looks at strength of relationshop between two or more events and characteritics
Experimental Designs
Independent and Dependent variables; manipulate one or more variables and obserbe effects on behavior; hold other variables constant
Cross-sectional approach
individuals of different age are compared at one time
Longitudinal approach
same individuals are studied over a period of time
Sequential approach
Combined cross sectional and logitudinal design
Sigmund Freud Theory
Development primarily unconscious, development heavily influenced by emotions and early experiences with parents shape development
Erikson Psychosocial THeory
Primary motivation for behavior is social and developmental change occurs throughout the lifespan
Sensorimotor Stage (Piaget Cognitive Development)
Infact constructs understanding of the world by coordinating sensory experiences with physical actions (Birth to 2yo)
Preoperational Stage (Piaget Cognitive Development)
Child begins to represent the world with words and images, these words and images reflect increased symbolic thinking and go beyond the connect of sensory information and physical action. (2yo to 7yo)
Concrete Operational Stage
The child can now reasonably logically about concrete events and classify objects into different sets (7yo to 11yo)
Fromal Operational Stage
Adolescent reasons in more abstract, idealitic, and logical ways. (11yo to adulthood)
Vugotskys Sociocultural Cognitive THeory
Lev theory says social interaction and culture guide cognitive development. Knowledge is situated and collaborative.
Information Processing Theory
Human mind is an infromation processor and development is a continuous increase in capactiy for processign and storing information
Pavlov Classical Conditional Theory
Neutral stimulus acquires the ability to produce a behavioral response originally produced by another stimulus
Skinner’s Opernt Conditioning Theory
Consequences of behavior change likelihood of behavior future occrurence.
Rewards increase likelihood of reacrrence
Punishments decrease the chance
Bandura Social Cognitive Theory
Behavior, enviornment and cognition are key factor in development and they all influence each other
Ethology
Focuses on respones to enviornment, physiological makeup, communication, and evolutionary aspects.
Ethological Theory
Charles Darwin: Evolution and natural selection
Konrad Lorenz: Imprinting (connecting with the first thing seen as parent
John Bowlby: attachment
Humanist Approach
People strive to become the best they can be. Valus, intentions and meaning are important for understanding human behavior.
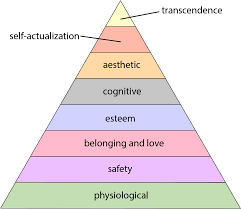
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Bronfenbrenner’s Bioecological THeory of Development
Emphasizes the effect of enviornmental and biological factors on development
Contemporary approaches to psychology
Dynamic Systems
Evolutionary Psychology
Neuroscience and Neuroplasticity
Positive Psychology
Eclectic Approach
Take most compelling and workable concepts from each theoretical approach
Natural Selection and Adaptive Behavior
Survivors are better adapted than non-survivors and survivorss pass on their genes
Evolutionary Psychology
the study of behaviour, thought, and feeling as viewed through the lens of evolutionary biology
Thrify Genotype
Certain populations may have genes that determine increased fat storage
Mitosis
Cellular material is duplicated and new cells formed
Meiosis
Sex cells divide and produce 4 new cells with 23 single chromosomes
Fertilization
female gamete and male gamete fuse to create a single cell, a zygote
Fraternal/dizygotic twins
Sepertate eggs and sperm
Indentical/monozygoic twins
single zygote splits into 2 gentically identical replicas
Dominant Recessive Gene Principle
One gene of a pair is dominant and one gene is recessive the dominant gene exerts its affects overriding the recessive gene. A recessive gene exerts its influence only if 2 genes are both recessive
X linked inheritance
Mutated Gene is carried on X chromosome
Down syndrome
extra chromosome cause mild to severe intellectual disabilities and physical abnormalties
Fragile X syndrome
abnormal X chromosome cause intellectual disabilites
Tuner syndrome
Missing X chromosome in females
XXY syndrome
An extra Y chromosome
Amniocentesis
amniotic fluid tested
ultrasound sonography
high frequency sound waves produces image of fetus
Chrorionic Villi Sampling
small sample of placenta tested
Maternal serum screening
blood test
Fetal MRI
detailed image of fetus organs
Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis (NIPD)
analysis of fetal cells in mother blood
Infertility
inability to conceive after 12 months of regular unprotected intercourse
Stem Cells
Biological cells that can divide and differentiate into specialized cell types and can renew to produce more stem cells. It can be take from bone marrow, adipose tissue and blood in the umbilival cord
Behavior genetics
looks at influence of heredity and enviornment on differences in human traits and assumes behaviors jointly determined by interaction of heredity and enviornment. Behavior genetics often uses twins or adoption situations to study the influence of heredity on behavior.
Germanial Period
The first 2 weeks after conception. The zygote is created, cell division increases and implantation occurs
Blastocyst
Inner layer of cells that develops during germinal period and becomes the embryo
Trophoblast
outer layer of cells that develops during the germinal period and provides nutrition and support for embryo
Embryonic Period
2-8 weeks and the rate of cell differentitation intensifies, support systems form and organs appear
Placenta
disk shpaed group of tissues in which small blood vessels from the mother and the offspring intertwine
Umbilical Cord
Contains 2 arteries and one vein that connect the baby to the placenta
Amnion
A bag/envelope that contains a clear fluid in which the developing embryo floats
Organogenesis
Organ formation that occurs during the first two months of prenatal development
Fetal Period
from 8 weeks to birth where growth and development continue and organ systems mature
Brain development during the 1st 2 trimesters
Basic architecture of brain assembled
Brain development in 3rd trimeester
Connectivity and functioning of neurons
Teratogen
any agent that can cause a birth defect or negatively affect cognitive and behavioral outcomes
Psychoactive Drugs
Affect nervous system
Psychoactive Drugs
Caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, cocaine, methamohetamine, marijuana, heroin
Other Teratogen
incompatible blood type (RH factor), enviornmental hazards and maternal diseases
Maternal factors
maternal age, diet, nutrition and exercise, maternal obesity and emotional states
Paternal factors
exposure to lead, radiation, pesticides, smoking, and age
Recommended range of total weight gain for <18.5 BMI
12.5 to 18kg
Recommended range of total weight gain for 18.5 to 24.9
11.5 to 16kg
Recommended range of total weight gain for 25.0 to 29.9 BMI
7.0 to 11.5kg
Recommended range of total weight gain for >30 BMI
5.0 to 9.0kg
Preterm and Low Birth weight infants
Low birth weight is <2.5kg and preterm infants are born 3 weeks before term
Long Term Outcomes for Low Birth weight infants
Brain damage, delay in language, low IQ scores and behavioral problems
Kangaroo Care
Sking to skin contact, it helps increase weight and improves breast feeding and less pain before procedures
Massage therapy
Improves weight gain and lowers stress
Describe what endocrine-disrupting environmental chemicals are and how they lead to weight gain. Give some examples of known endocrine-disrupting chemicals.
Endocrine-disrupting environment chemicals are natural or human-made chemicals that mimic, block, or interfere with the body’s receptors to make them think they are natural hormones. They disrupt the system of glands that release hormones into our bloodstream. Examples of these chemicals include DES, Tributyltin, and Bisphenol A (BPA).