AP HUG UNIT 4: Political Geography
1/97
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
the ability to decide and control internal affairs without outside interference
Sovereignty
a nation that has established sovereignty in an internationally-recognized defined space (Ex: Japan, Iceland, and Portugal because they are countries with a mostly homogenous population. Nigeria is NOT an example of a nation state)
Nation-state
a political state with multiple nations or ethnic groups with their own distinct cultures (Ex: Nigeria because it has 250 ethnic groups, U.K because it has 4 distinct nations, and Canada because of its English and French speaking populations)
Multinational state
a designated area within a country that has a degree of self governance (Ex: Tibet, Catalonia, and Sicily. Note: STATES CANNOT BE AUTONOMOUS REGIONS!)
Autonomous region
a nation that has not established sovereignty in an internationally recognized defined space (Ex: Roma, Flemish, Basques, Palestine, and Kurdistan because they have a nation but don’t meet the qualities of political states)
Stateless nation
a nation that is located in more than one separate political states (Ex: Kurdistan, Basque County, and Roma people since their nations inhabit multiple states)
Multistate nation
the principle that nations have the right to freely determine their political states and pursue their own development
Self determination
the process of a former colony gaining political independence from its ruling power
Decolonization
a country that was formally independent but under heavy influence or control of another country
Satellite state
the process of a central government transferring power and authority to a lower level of government
Devolution
the behaviour of groups claiming and defending a specific geographic area to establish control, identity, and resources
Territoriality
a place of physical congestion between wider regions of movement and interaction (Ex: Panama Canal, Strait of Hormuz, and Strait of Malacca because they’re places of movement and interaction.)
Choke point
the use of economic, political, and social pressures to control former colonies
Neocolonialism
a political boundary that existed before the cultural landscape emerged (Ex: the Canadian American border because it runs along the 49th parallel of latitude, which existed before the border was established in the 19th century)
Antecedent boundary
a political boundary established after a region has been settled (Ex: border between Northern Ireland and Ireland because it was drawn after settlers came to separate the Catholic south from the Protestant north)
Subsequent boundary
a political boundary that has been imposed on a region by an external authority often without regard for existing cultural and ethnic divisions (Ex: most of Africa and other colonized places)
Superimposed boundary
a type of political boundary that no longer functions as an official border but still holds historic significance (Ex: Berlin Wall in Germany, the Great Wall of China, and the Maxon-Dixon line in the U.S because even though they don’t function as borders anymore, they still have effects on the population)
relic(t) boundary
a political boundary defined and demarcated by straight lines or geometric shapes, often disregarding natural/cultural features of the landscape (Ex: Egypt and Sudan border because it follows the 22nd parallel north, U.S Canadian border, Algeria and Mali border, and Namibian border)
Geometric boundary
a type of subsequent boundary that takes into account cultural and physical landscapes (Ex: India and Pakistan border because it was created as a result of the partition of India to separate the majority Muslim population from the majority Hindu population)
Consequent boundary
a region that is politically fragmented and is caught in the middle of competing interests between larger, more powerful states
Shatterbelt
a political principle focused on the unification of groups who share ethnic or historical ties but are governed by different political entities (Ex: Russian-Ukrainian war because Russia claims Ukrainian lands are historical Russian. Balkan wars)
Irredentism
The international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities
UNCLOS
An area of the ocean extending up to 200 nautical miles from a country's coastline where the country can explore, extract minerals, and manage fish and energy
EEZ (Exclusive Economic Zone)
the manipulation of an electoral constituency’s boundaries so as to favor one party or class
Gerrymandering
the strategy of concentrating a large number of voters from an opposing party or group into a single district
Gerrymandering–Packing
the practice of splitting a group of voters with similar beliefs across multiple districts to dilute their voting power
Gerrymandering–Cracking
the practice of putting politicians from the same party who previously represented different districts into the same district so they have to run against each other
Gerrymandering–Hijacking
the practice of moving a politician's voter base to another district, leaving them stranded in a new district with less support.
Gerrymandering–Kidnapping
a political system where power is divided between a central government and regional subnational entities, like states or provinces (Examples: the U.S, Nigeria, India, and Belgium because power isn’t centralized in one government)
Federal state
a political system where the central government holds all power, with local governments only exercising authority that the central government chooses to delegate (Japan, China for some reason, Saudi Arabia, U.K)
Unitary State
the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide.
Globalization
the practice of multiple countries forming an organization for the benefit of all members
Supranationalism
a political supranational organization founded in 1945 with 193 that’s mission is to promote world peace, security, and human rights.
United Nations (UN)
a political and economic union of 27 European countries that have chosen to cooperate closely in various areas, including trade, governance, and social policy
European Union (EU)
a military/political supranational organization formed in 1949 as a military alliance for collective defense between North American and European countries. It was created in response to the Cold War, primarily to counter the perceived threat from the Soviet Union and to promote stability through mutual defense and cooperation.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
a trade agreement enacted in 1994 between the United States, Canada, and Mexico aimed at eliminating trade barriers and promoting economic cooperation. By reducing tariffs and allowing for the free flow of goods and services, NAFTA has significantly influenced trade patterns in North America, fostering economic interdependence and encouraging investment across borders.
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
a trade agreement that replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) to enhance economic cooperation among the three North American countries. It aims to address modern trade issues, promote fair labor practices, and ensure environmental protections, reflecting the changing dynamics of globalization and trade relationships in the region.
United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA)
an economic/political supranational organization of countries in southeast Asia set up to promote cultural, economic and political development in the region. ASEAN was officially formed in 1967 with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration.
Assoc. Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
a political/economic supranational organization consisting of 54 African states that aimed to advocate for peace, security, and stability on the continent through greater cooperation, economic development, and global integration
African Union (AU)
an environmental/political supranational organization that aims to foster cooperation with territory coordination, and interaction among Canada, Russia, the Arctic states the United States, with participation of and countries of Arctic indigenous northern Europe communities
Arctic Council
an economic supranational organization that's goal is to have countries agree to a set of fair and non discriminatory guidelines for international trade
World Trade Organization (WTO)
an economic supranational organization that focuses on the production of oil, or petroleum. It has twelve countries including Algeria, Angola (which joined in 2007), Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Venezuela
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
Which of the following is NOT a necessary criterion for a state?
Common culture and identity
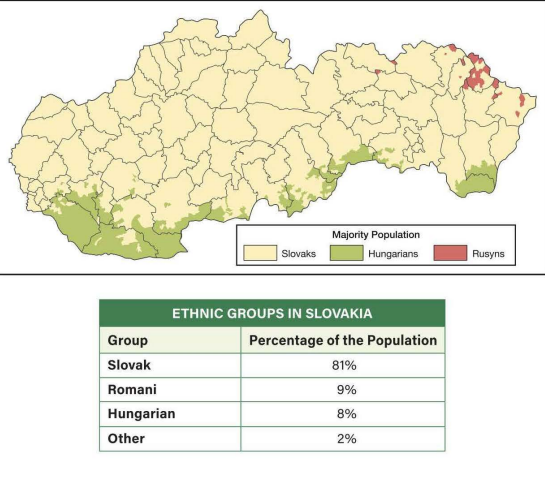
Which term best describes Slovakia?
Multinational state
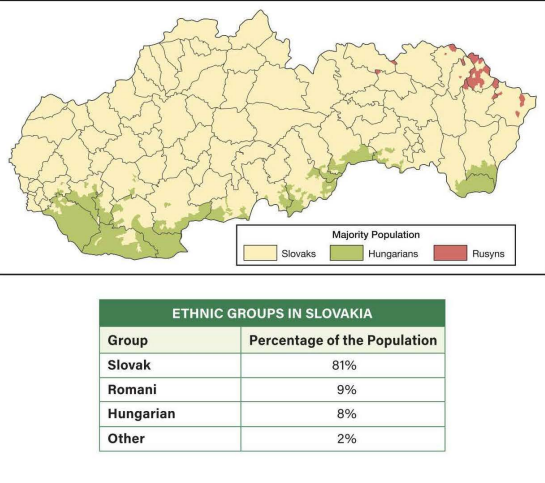
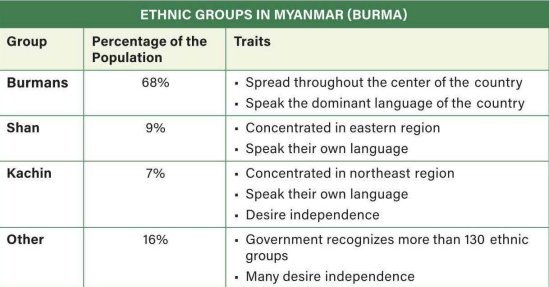
Which of the following best explains why the Romani ethnic group is identified on the chart but does not appear on the map?
The scale of analysis of the data reflects that the Romani are a large minority group but are not a majority in any religion
North Atlantic Treaty Organization
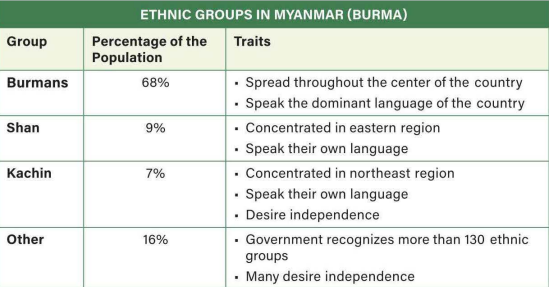
Which of the following would describe a positive development for a state that became independent through decolonization?
Establishing territoriality by claiming sovereignty over its lands

When Germany invaded Poland in 1939, it said it wanted to reunite the German minority living in Poland with Germany, this is an example of what?
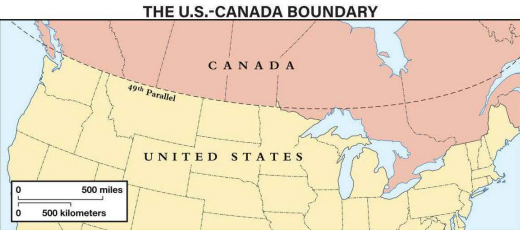
The formation of India and Pakistan in 1947 led to a new boundary between the two states. This boundary is best described as
a consequent boundary because the border was made along an already-existing cultural division
The Syrian Civil War erupted in 2011 and forced millions of refugees to flee into Turkey. The Turkish government was sympathetic to the refugees but became concerned about how many Syrians were crossing Turkey's border. Which type of border dispute describes this scenario?
Operational
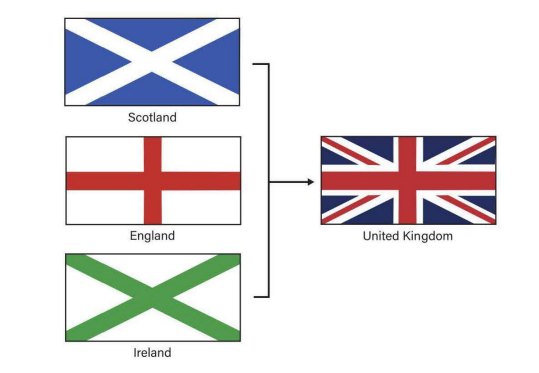
Notice how the crosses in the flags of Scotland, England, and Ireland are combined in the flag of the United Kingdom. Which process does this represent?
Which of the following terms best applies to what a country experiences when its unity is threatened by inequality or economic problems?
Centrifugal forces
Which provides the strongest support for the conclusion that Japan has few centrifugal forces?
Japan has a high degree of ethnic and linguistic homogeneity
Which is NOT an example of a centripetal force?
The Mindanao region of the Philippines has poor infrastructure and inadequate basic services.
Which of the following best describes the effect of globalization related to state sovereignty?
States have given up some sovereignty in order to join supranationalistic organizations.ore isolated states
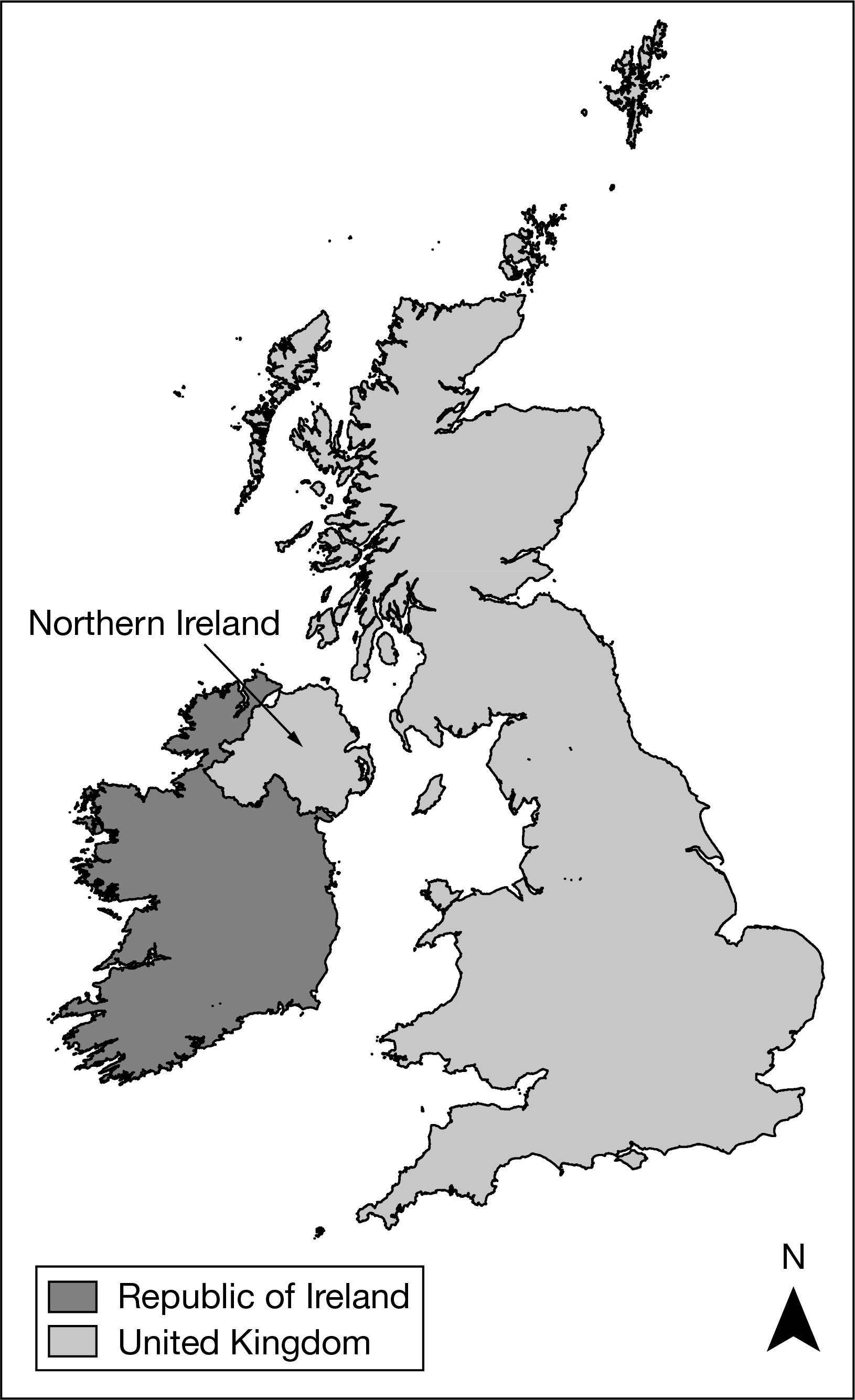
Based on the map, which of the following can be identified as a true statement about Northern Ireland?
It is physically separate from the rest of the United Kingdom, a multinational state.
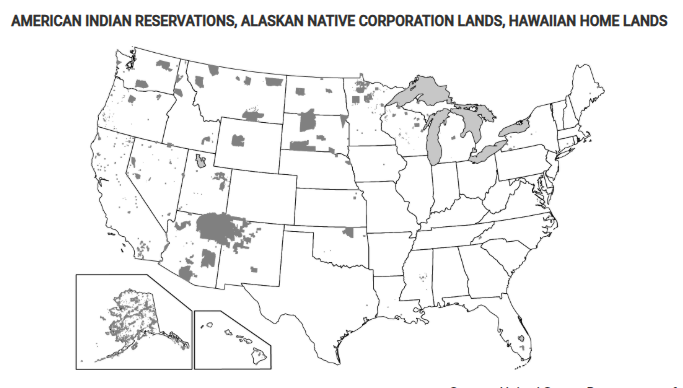
Which of the following terms identifies the type of regions shown in the dark gray-shaded areas on the map?
Semiautonomous regions
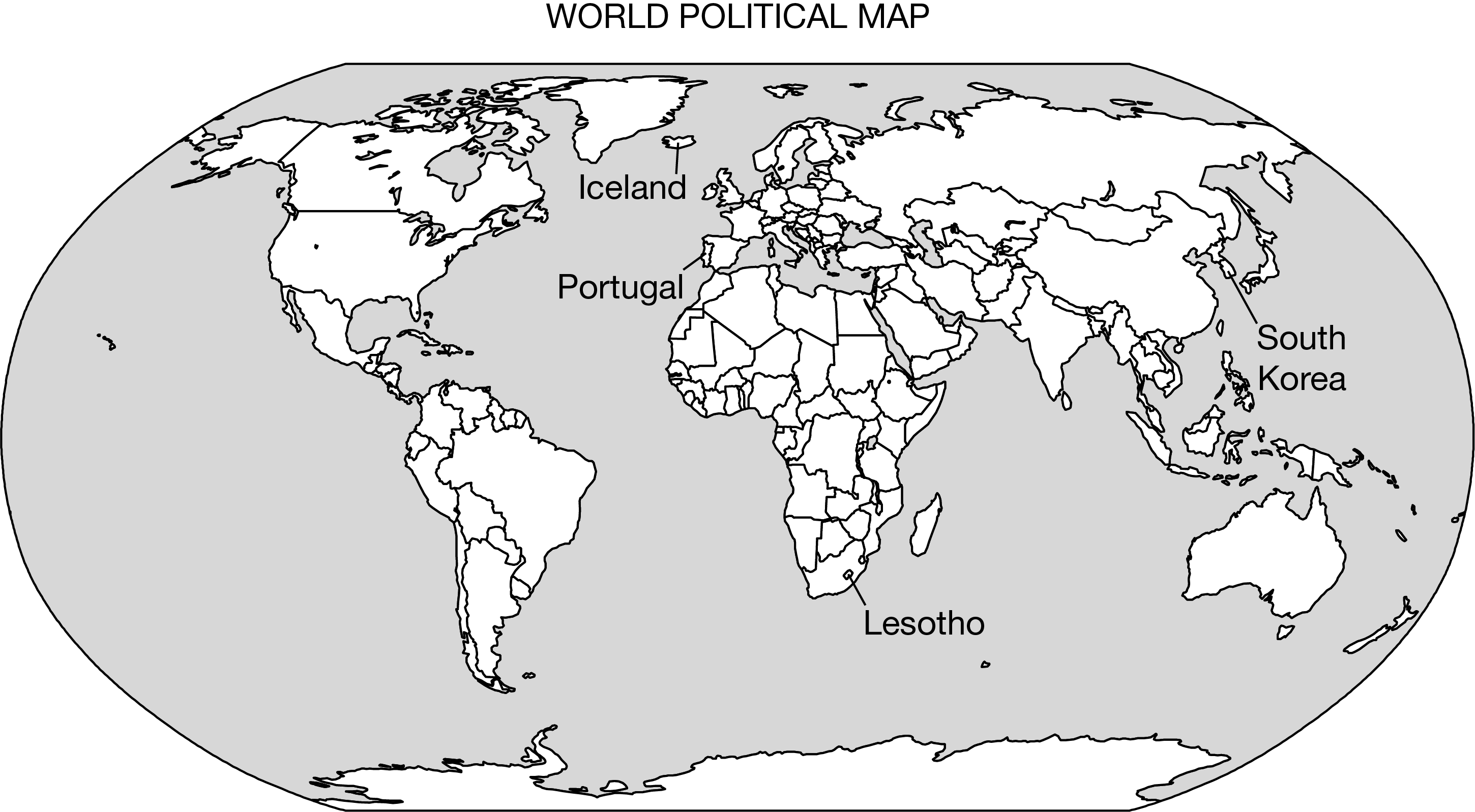
Owing to their localized geography or their locations on islands or peninsulas, many small political entities such as those labeled on the political map of the world can be identified as
nation-states
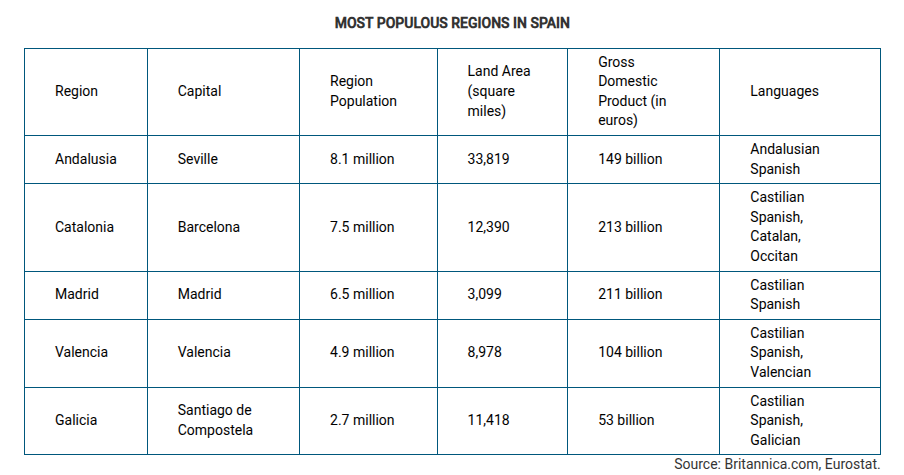
Which of the following best explains why the region of Catalonia in Spain could be a viable country?
Catalonia is well developed economically compared to other regions in Spain.
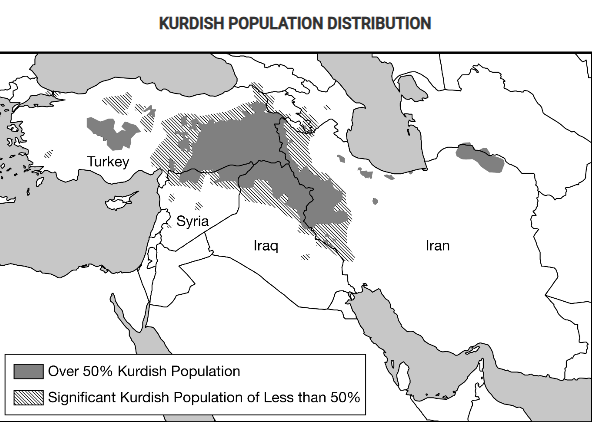
Based on the information in the map, what is the most likely outcome of the possible establishment of an independent Kurdistan for the Kurdish people?
The Kurdish people, seeking a state of their own with a majority Kurdish population, might secede from or rebel against the states labeled on the map.
Some territories within the Russian Federation are characterized by concentrated populations of ethnic groups and these areas function as autonomous republics. Which of the following best explains the political relationship between the autonomous republics and the central government of Russia?
The autonomous republics provide ethnic groups with some political control over their homelands while preserving Russia’s territorial integrity.
Which of the following best explains the effect of French language and culture on the federal state of Canada’s political power?
French language and culture act as a centrifugal force in Canada because independence movements in Quebec have attempted to secede the province from Canada.
Which of the following explains why Korea and Vietnam were viewed as shatterbelts during the Cold War?
Korea and Vietnam experienced conflict due to a dispute between global powers.
he former international border between East Germany and West Germany is best described as
a relict boundary
Which of the following describes an example of a consequent boundary?
Canada created the province of Nunavut to provide greater autonomy for the First Nations.
Which of the following is an example of a superimposed boundary?
The geometric boundary between Iraq and Saudi Arabia
The Berlin Conference established the borders of North African countries including Egypt, Libya, and Sudan. The landscape of these countries influenced the types of boundaries imposed by the European colonial powers. Which of the following boundary types best explains the influence of landscape on the political borders of the North African region?
Geometric, with straight lines, disregarding physical features or tribal cultural differences of the areas
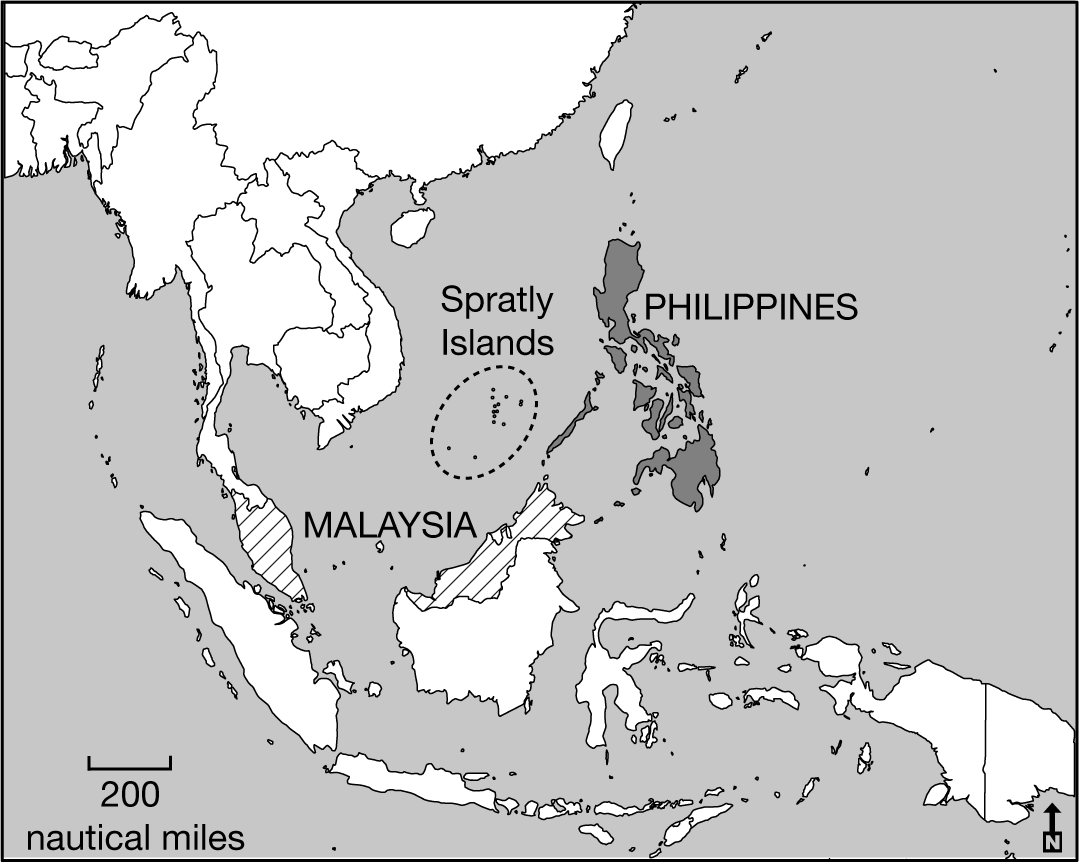
The Philippines and Malaysia lay claim to resources under and around the Spratly Islands. Which of the following best explains how the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) influences claims to the islands by both countries?
The claims to the Spratly Islands by both the Philippines and Malaysia overlap due to exclusive economic zones up to 200 nautical miles from their coasts.
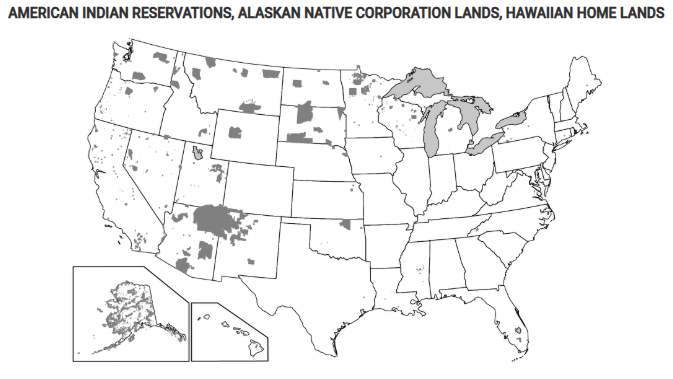
Which of the following best explains the governance of the shaded areas shown on the map?
These areas show where indigenous peoples have a limited amount of self-government at a national scale.

Which of the following is the correct organizational scale for the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)?
Supranational
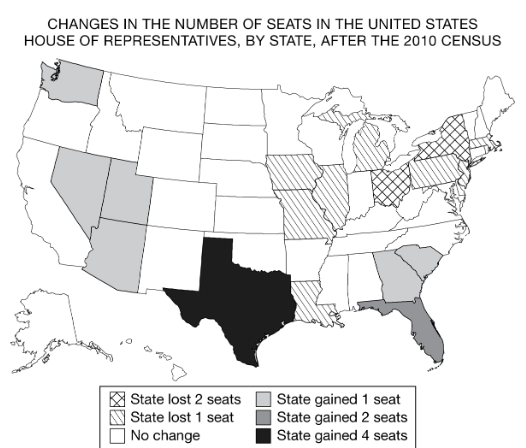
In the United States House of Representatives there are a fixed number of 435 seats divided among the states based upon each state’s relative population size. Changes in the number of representatives, as shown on the map, affect politics at which of the following scales?
National
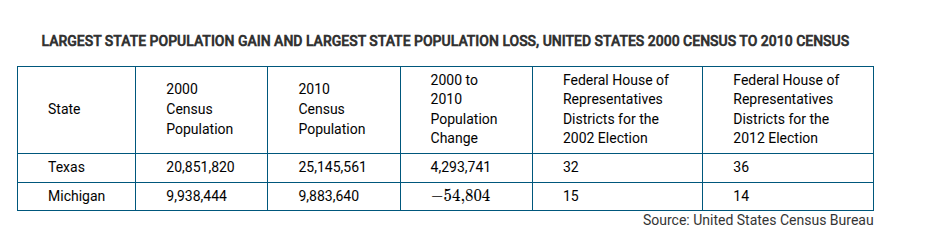
The examples in the table show states that gained or lost United States House of Representatives districts based on 2010 census data. The states were required to revise district boundaries based on census data.
Using the data in the table and the description, which of the following identifies the scales of analysis that are reflected in this redistricting?
Local representation in the national legislature
Which of the following describes typical characteristics of federal states?
A large land area and multiple ethnic groups
Which of the following describes a federal form of governance?
Multiple substates have local control and are unified to pursue common goals at the national level.
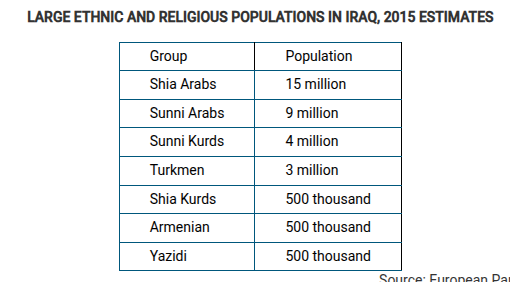
Based on the data in the table, which of the following is a possible impact of ethnic and religious diversity in Iraq?
Ethnicity and religion lead to devolutionary pressures in the country by politically dividing regions.
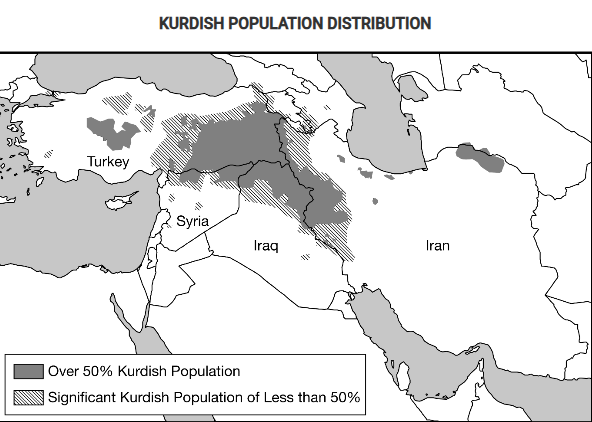
Based on the map, which of the following best explains the implications of physical geography as the Kurds continue to struggle for an independent state in their ethnic homeland?
Most areas with a Kurdish majority population are landlocked and therefore dependent on good relationships with their neighbors in order to access trade and prosper economically.
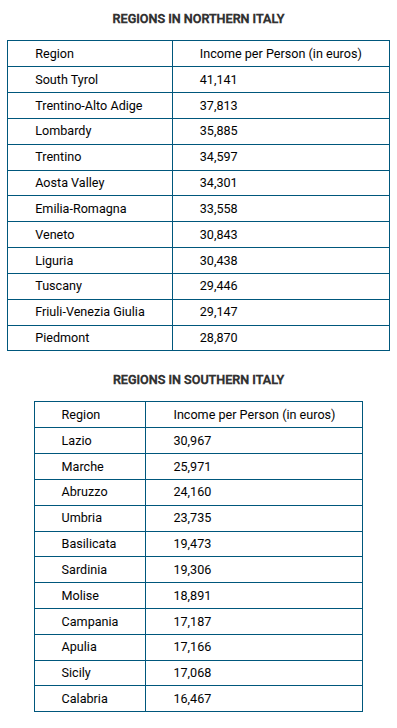
Which of the following possible political effects is implied by the data in the table?
The high level of economic difference between the regions in Italy acts as a devolutionary force.
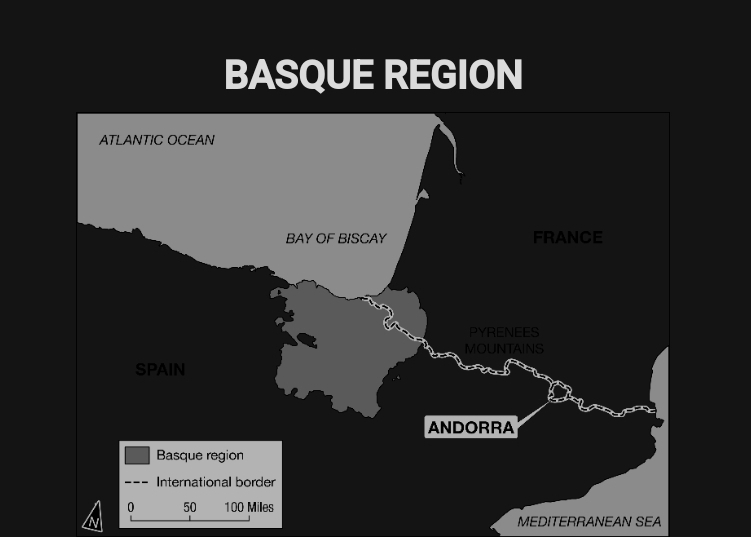
Local and regional autonomous governments and a separatist militia group have been established within the Basque region shown on the map. How do these local and regional governments compare with the national governments of Spain and France?
Local and regional governments create the potential for conflict and act as a centrifugal force within the larger independent states.
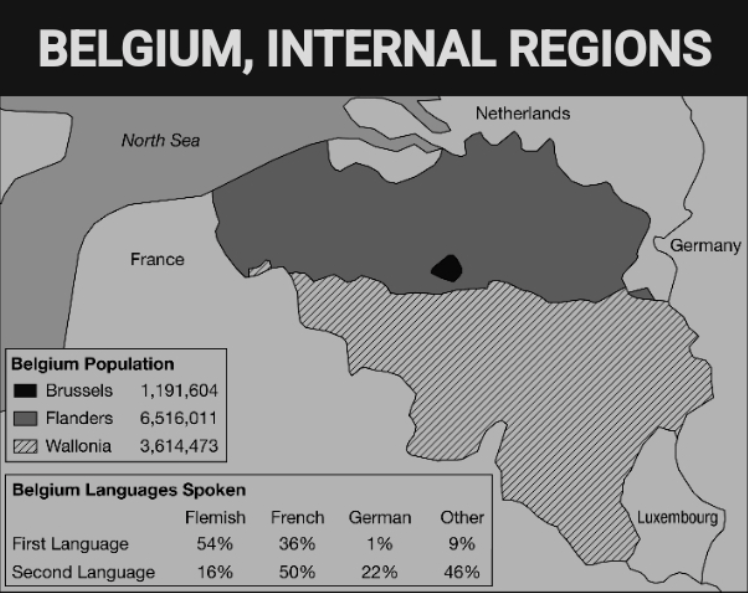
Some communities along the internal border between Flanders and Wallonia are required by Belgian federal law to have bilingual local governments, with road signs and government publications in Flemish and French. Some nearby communities refuse to permit a census of language users because they are concerned that the results will trigger federal requirements for a bilingual local government.
Which of the following geographic concepts best explains the efforts to preserve a single official language in such communities?
Territoriality, because communities are expressing power and political control over the landscape.
FALKLAND ISLANDS
United Kingdom
Name: Falkland Islands
Distance to the United Kingdom: 6,250 nautical miles
Dates of Control: 1765–1767, 1771–1774, 1833–1982, 1982 to present
Argentina
Name: Islas Malvinas
Distance to Argentina: 182 nautical miles
Dates of Control: 1770–1881 (as Spanish Viceroyalty of Río de la Plata), 1829–1831 (Argentina, onward), 1832–1833, three months in 1982
The Falkland Islands War took place in 1982 between Argentina and Great Britain, when Argentina’s military invaded the small British overseas territory in the South Atlantic Ocean. British forces reclaimed the islands after a short war.
Using the information shown, which of the following geographic principles explains the conflict in the Falkland Islands?
Overlapping claims of sovereignty
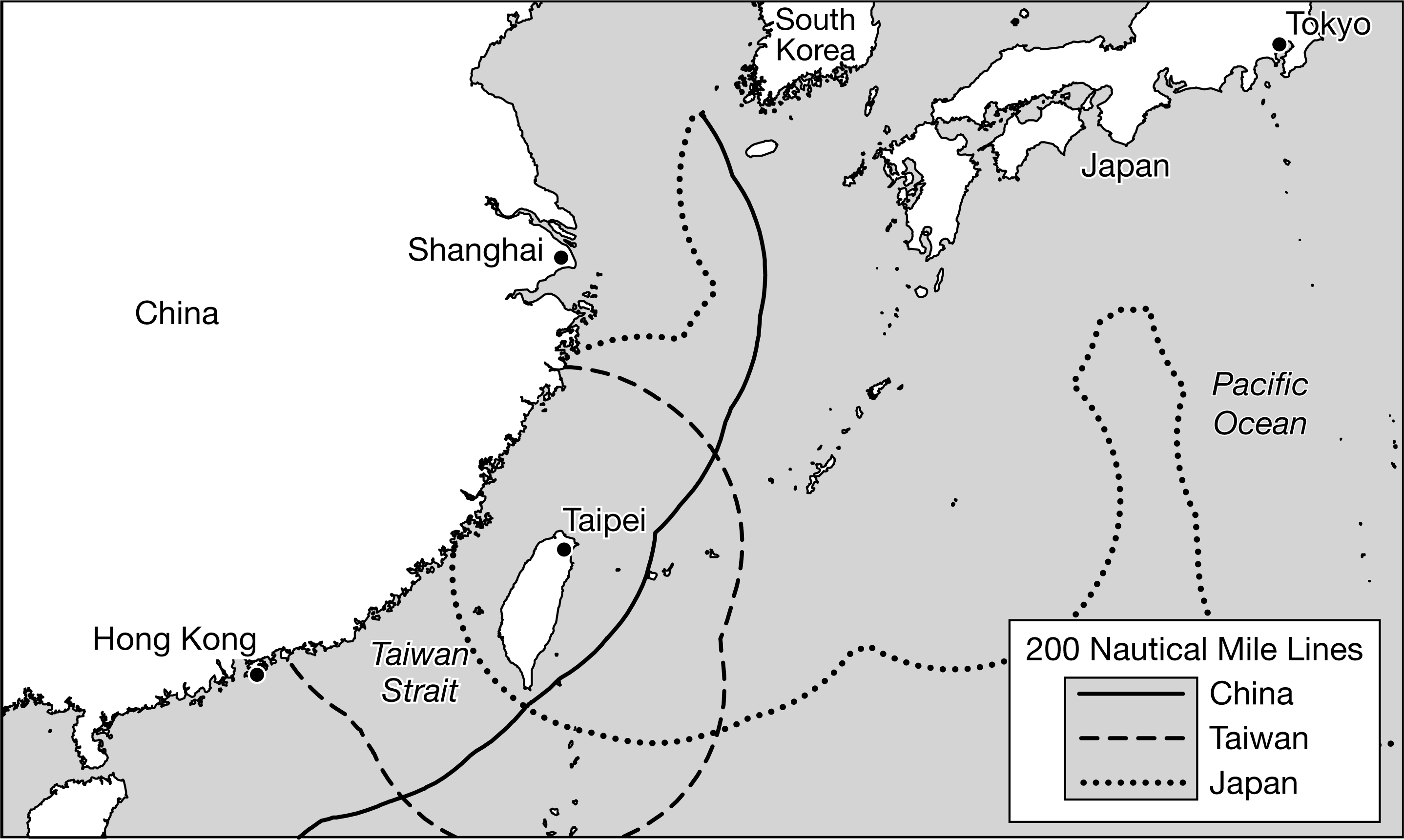
The map shows the Taiwan Strait. Which of the following best explains the global geopolitical significance of the Taiwan Strait?
The Taiwan Strait is a militarily strategic chokepoint that China and Taiwan claim as territory.
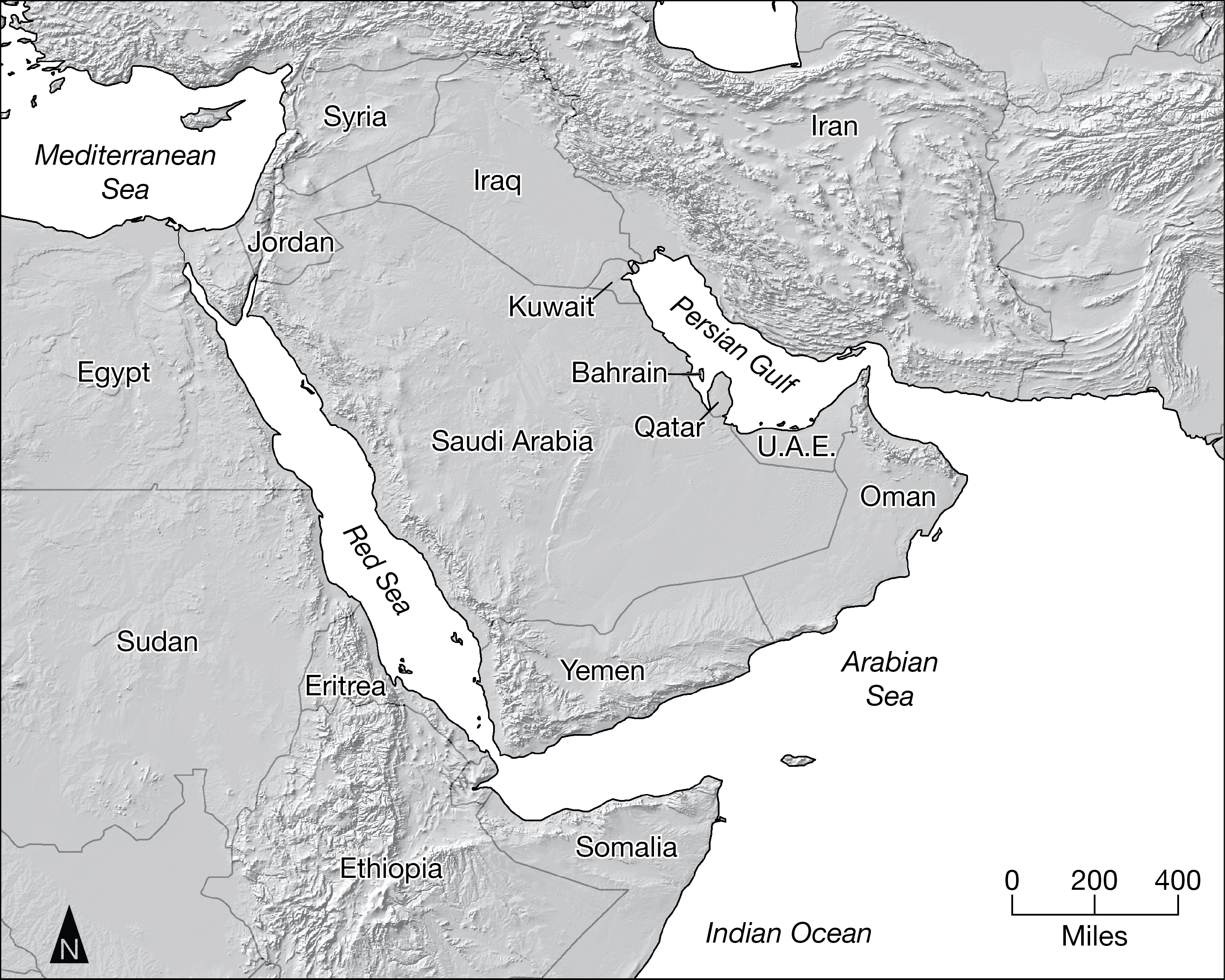
Which of the following statements is helpful in explaining why Iran and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) are able to assert some control over the export of oil from the Persian Gulf oil-production region?
Their location along the choke point of the Strait of Hormuz allows them to influence ship movement into and out of the Persian Gulf.
Which of the following best explains the primary function of international political boundaries?
Boundaries limit sovereignty and determine the extent of a state's power within the global political system.

The photograph shows guards at the Truce Village of Panmunjom within the demilitarized zone (DMZ) that divides the Korea Peninsula into North Korea and South Korea. The DMZ border was agreed upon as part of Korean Armistice Agreement at the end of the Korean War in 1953. Which of the following best explains the effect of the DMZ on the Korean Peninsula as a culture region?
The Korean people are divided into a multistate nation that has a common heritage and ethnicity.
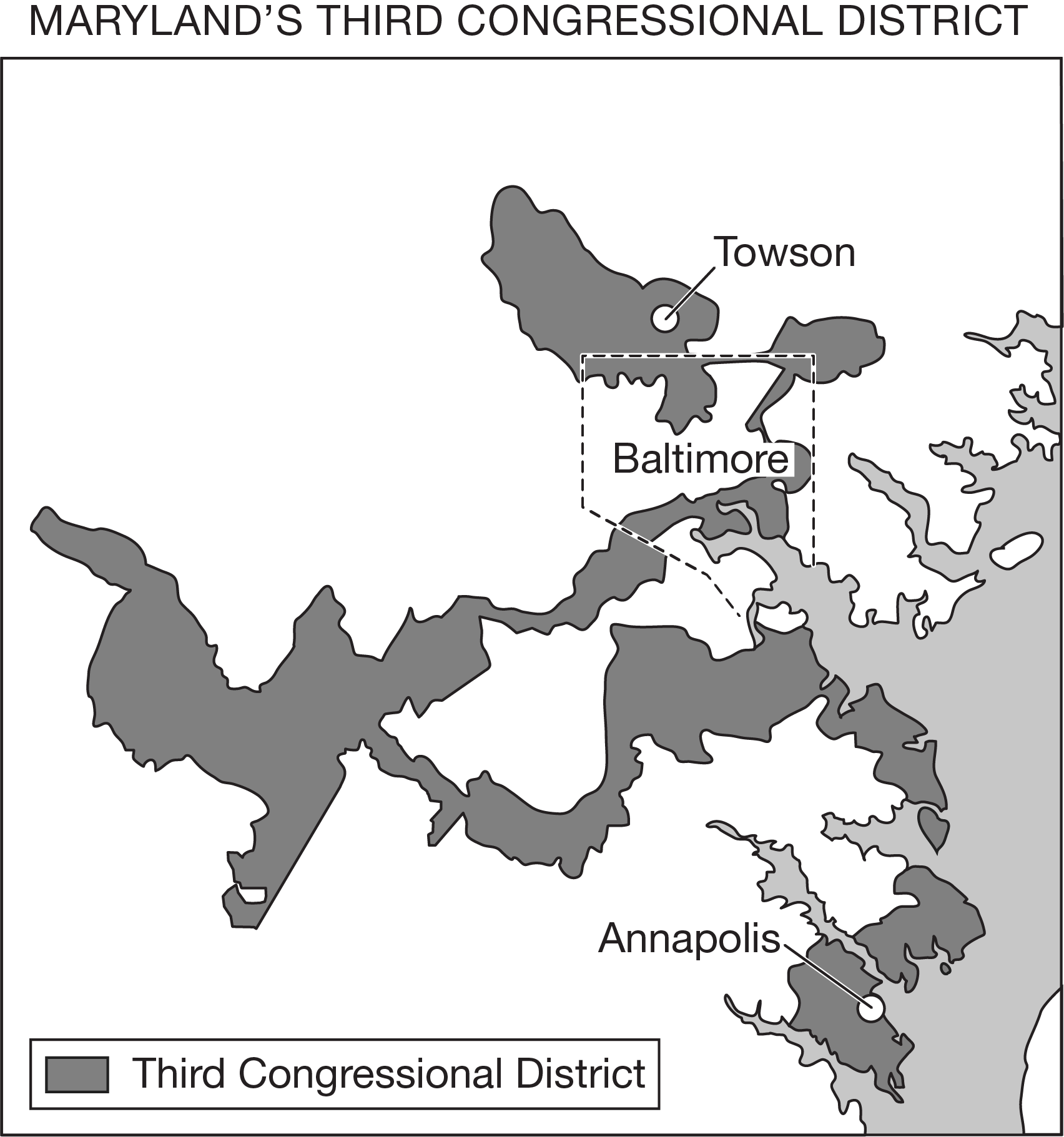
Residents of Maryland’s Third District could legally challenge the redistricting of the area shown on the map because they identify it as being
a gerrymandered boundary that guarantees a political party’s seat within the United States House of Representatives
Which of the following statements accurately compares the processes of devolution and supranationalism that challenge the sovereignty of Canada?
Centrifugal forces are present in Quebec, whereas the free-trade agreement between the United States, Canada, and Mexico challenges the Canadian government’s independence on a national level.
Which of the following technological examples is best used to compare the effects of local-scale and global-scale political challenges to state sovereignty?
Cell phone use weakening corrupt governments
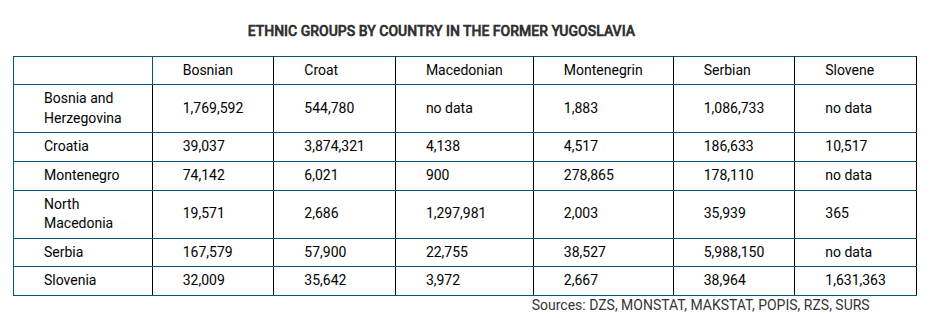
Which of the following best explains the political pattern shown in the table?
The devolution of Yugoslavia occurred primarily along national lines, resulting in countries with a defined ethnic majority.
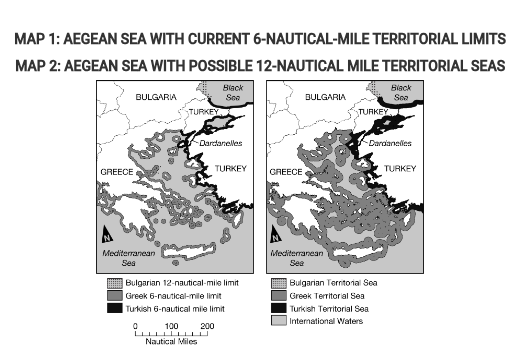
In 1982 the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) established freedom-of-navigation rights and defined territorial waters as a 12-nautical-mile limit from the coast where individual states have political and economic sovereignty. However, Greece and Turkey still only claim a 6-nautical-mile territorial sea.
If Greece and Turkey adopted the UNCLOS system and expanded their territorial seas to 12 nautical miles, as shown in Map 2, which of the following would be true for a Turkish-owned oil tanker sailing into Greek territorial waters?
The ship could be stopped by Greece’s Coast Guard for safety and environmental inspections.
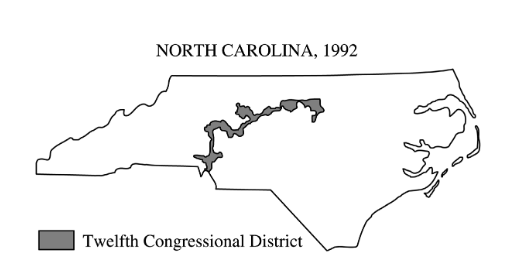
The shape of North Carolina’s Twelfth Congressional District, shown above, is most likely the result of
gerrymandering