B3 - Consumer decision-making
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
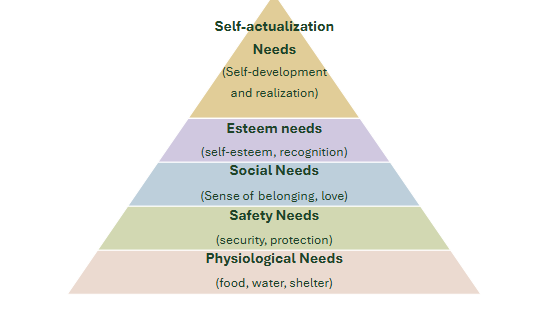
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Physiological needs: Food & water
Safety needs: Security, protection
Social needs: Belonging
Esteem needs: Self-esteem, recognition
Self-actualization needs: Self-development and realization
Steps in consumer making decisions
Need recognition
Information search
Information evaluation
Purchase decision
Post purchase evaluation
Needs vs wants vs demands
Needs: basic human requirement
Wants: needs to be directed towards specific objects that might satisfy the need
Wants backed by an ability to pay
Needs and watns model in the case of food
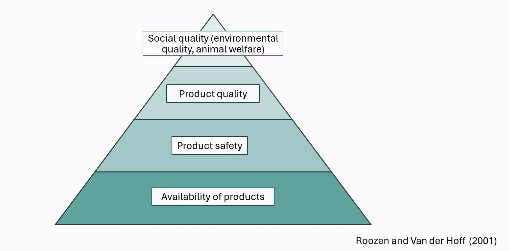
How do needs and wants differ in different situations
You don’t eat the same thing in a restaurant as at a movie theater.
What are the different roles that a decision-making unit consists of?
Initiators - recognize the need
Users - use the product
Influencers - influence on the decision
Decision makers - make the actual decision
Approvers - approve a purchase
Buyers - pay the purchase
Gatekeepers - authority to reject or accept products
Usually, different people play different roles, sometimes several at the same time.
These roles also can exist within a food company
What are the two processing systems used when making a decision?
System 1 | System 2 |
Automatic | Controlled |
Unconscious | Conscious |
Fast | Slow |
Emotional | Rational |
Intuitive | Analytic |
How to consumers derive information that help them make purchasing decisions
from their surroundings (shopping environment, product package)
Internal (memory) sources
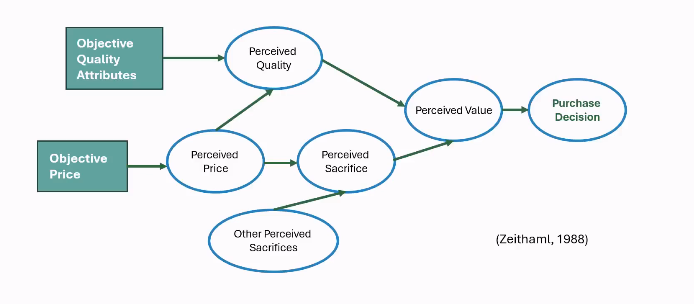
Customer value
Customer values differ from objective facts, as the customer value is much more about how things are perceived, which differs per customer.
How customer value is determined can be seen on the image.
Customer value is not only individual but also situational
Post-purchase evaluation
It is important that the product expectation are met
Consumers evaluate if expectations are met.
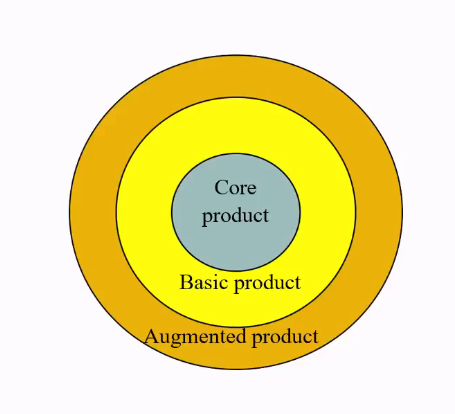
Analyzing food products
Core product (consumer benefit): problem-solving services or core benefits that consumers buy when they purchase a product
Basic (actual) product: a product’s parts, quality level, features, design, brand name, packaging and other benefits that combine to deliver core benefits
Augmented product: Additional consumer services and benefits built around core and actual products.
Example analyzing product: hotel
Core: you have a bed and are able to get comfortable sleep so you have enough energy for the next day
Basic: Bed, bathroom, shower, maybe breakfast, things that are expected.
Augmented: Fancy decor, a bar, things beyond expectations
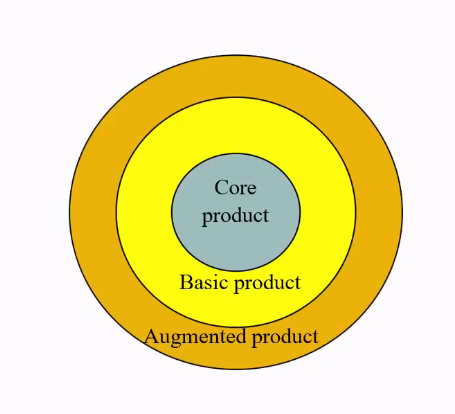
Core and basic products; Three-level analysis
Core product:
Benefit: The basic positive experience that a consumer gets when consuming the food
Basic product:
Attribute: the basic components of the food product that jointly shape the benefit
Characteristic: The technical elements of the food product that jointly shape the attribute.
Core and basic products; Three-level analysis Example froyo
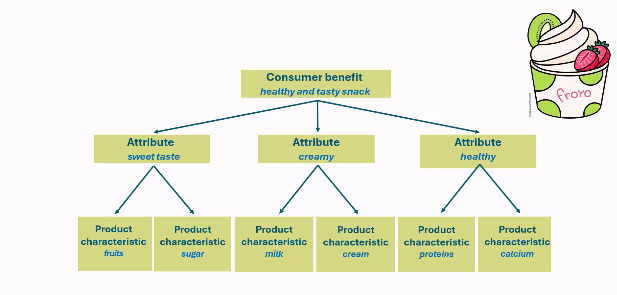
Types of attributes
Search attributes: easily observable, help consumers make the right choice
Experience attributes: only experienced during use of the product
Credence attributes: neither observable, nor experienced, consumers should believe that they are there (often production elements in chain)