Chemical Kinetics (Rates of Reactions)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
The rate of a reaction
Is the change in concentration of a reactant or a product per unit time
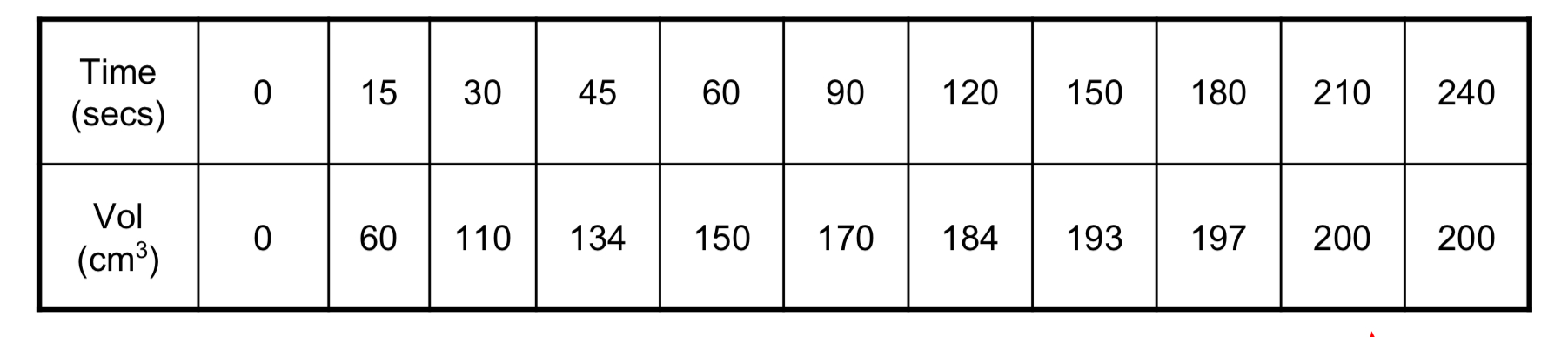
The average rate of reaction
Is calculated by dividing total volume by total time. Average rate = 200cm3/210s = 0.95cm3/s
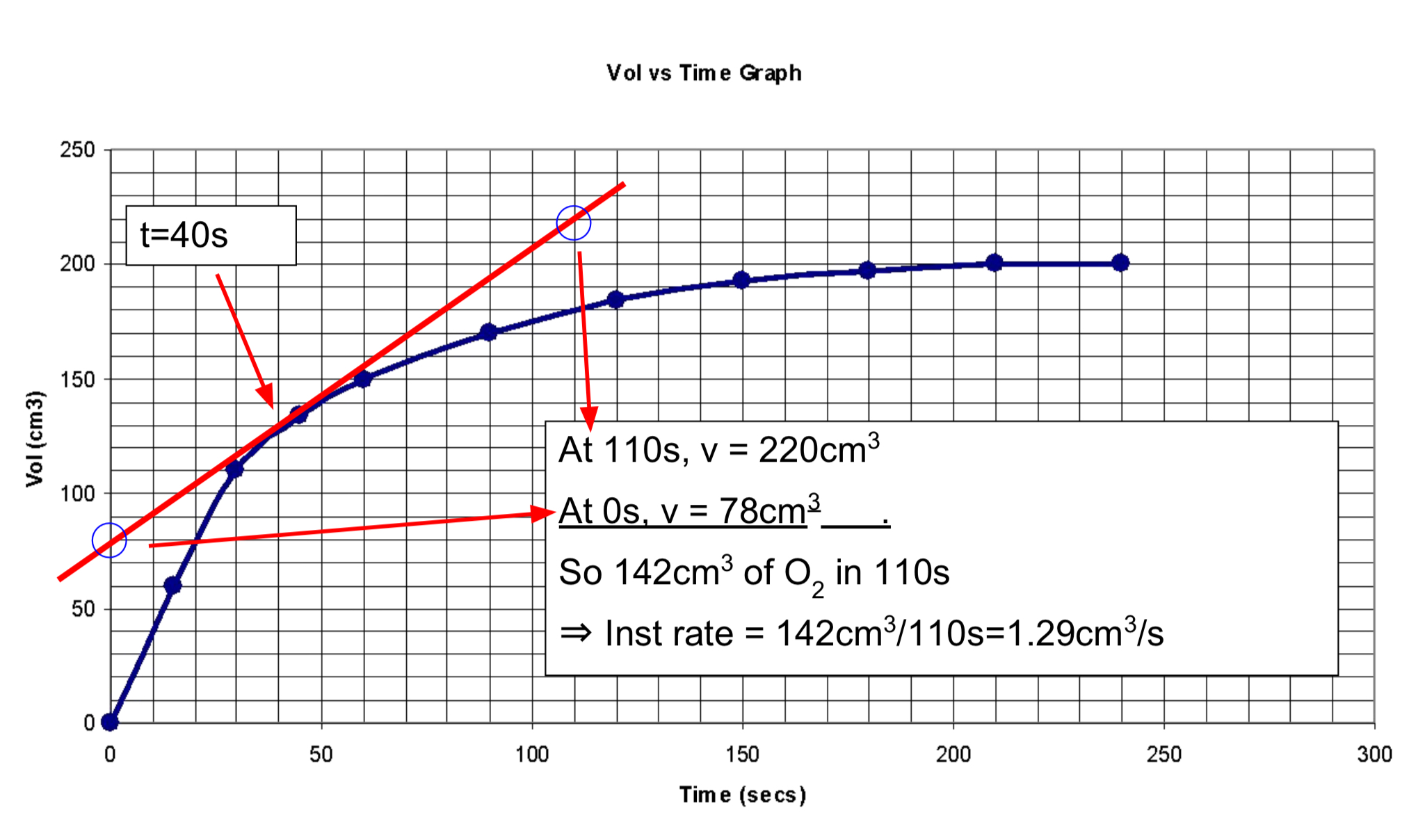
The instantaneous rate of a chemical reaction
Is the rate of that reaction at one moment in time. Draw a tangent to find it.
5 factors that can change the rate of a chemical reaction
1. Nature of Reactants
2. Particle Size
3. Concentration
4. Temperature
5. Presence of a Catalyst
Ionic substances
Fast reactions as lower activation energy is need as only the attractive force between ions needs to be broken
Covalent substances
Slow reactions as higher activation energy is need as bonds need to be broken in order to react
Particle size
Small particle size = greater surface area. Greater surface area = more collisions and more effective collisions. This results in a higher rate of reaction
Concentration
More particles increase the number of effective collisions, therefore, the rate increases. As a reaction proceeds the concentration of the reactants will decrease and so the rate of the reaction will decrease with time.
Temperature
Increase in the number of collisions due to the increased energy of the particles. Increased energy of the collisions means that more collisions reach activation energy
A catalyst
Is a substance that alters the rate of a chemical reaction whilst remaining chemically unchanged.
Heterogenous Catalysis
Where the reactants and the catalyst are in different phases
Homogenous Catalysis
Where the reactants and the catlayst are in the same phase
Autocatalysis
Where the catalyst is one of the products produced by the reaction itself.
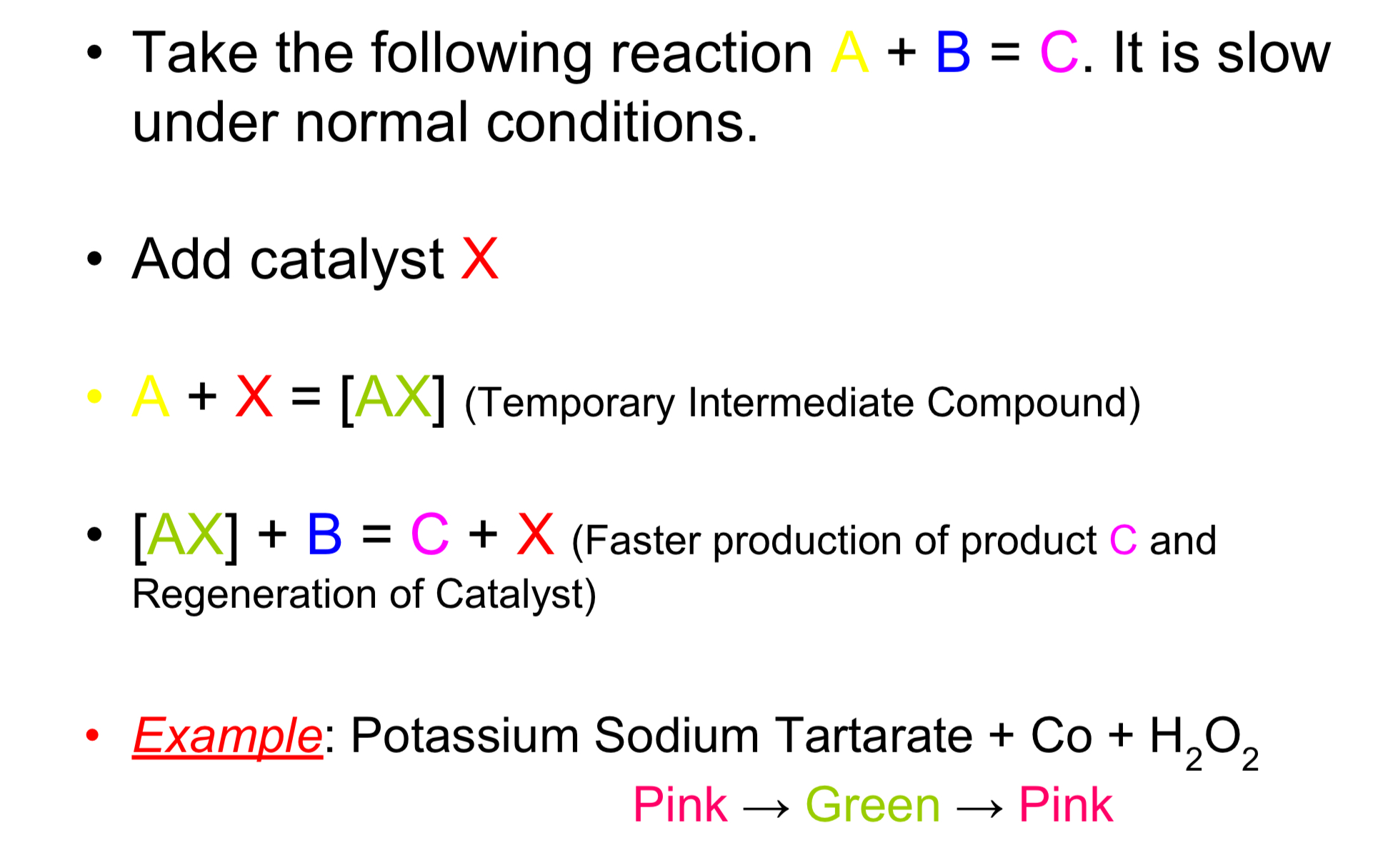
Intermediate Compound Formation Theory
One of the reactants forms an intermediate compound with the catalyst. The new compound reacts with the other reactant at a greater rate. As the product is formed the intermediate compound is broken down. The catalyst is returned chemically unchanged. Eg potassium sodium tartarate + Co + H2O2
Surface Adsorption Catalysis
The reactants, A and B, build up on the surface of the solid catalyst. (Adsorption) This increases their local concentration. Higher concentrations of reactants give rise to faster reaction rates. Product, C leaves the surface of catalyst (Desorption). Eg Pt solid catalyst used to add H2 to substances
Collision Theory
When a chemical reaction occurs as a result of a collision such a collision is called an effective collision.
Activation Energy
The minimum amount of energy required to produce an effective collision is called the activation energy of the reaction.
Endothermic reaction
Heat taken into the reaction from the environment. Products have more energy than reactants.
Exothermic reaction
Heat given out into the environment. Products have less energy than reactants.