Kaap 309: Introduction to Skeletal System
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Primary Functions of Bones: What does it do?
Support
Protection
Movement (Anchorage)
Storage
Hematopoiesis
Hormone production
Support
Architecture for the body
Lower extremity (pillars)
Thoracic cage (walls)
Skull (enclosed room)
Protection
Bones protect vital organs:
Skull → brain
Thoracic cage → lungs & heart
Vertebrae → spinal cord
Movement
Bones serve as levers, and muscles attach via tendons
Type of movement is determined by joint types
Storage
Fat storage:
Stored as triglycerides in yellow bone marrow
Mineral storage:
Calcium and phosphate reservoirs
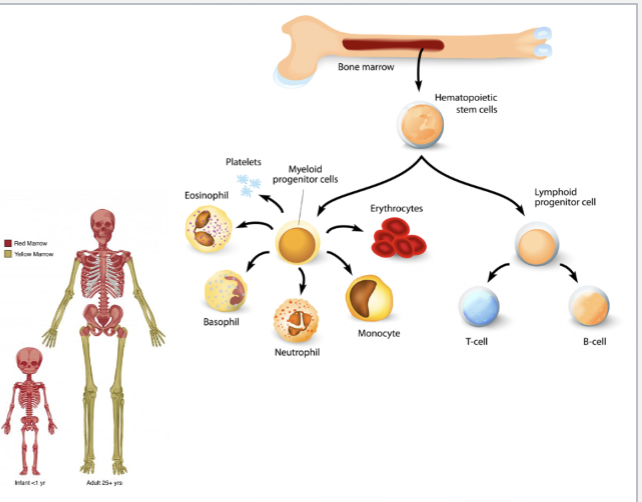
Hematopoiesis
Production of blood cells and platelets
Occurs in red bone marrow
Hormone production
Production of osteocalcin which regulates:
Insulin secretion
Glucose homeostasis
Energy expenditure
important for diabetes
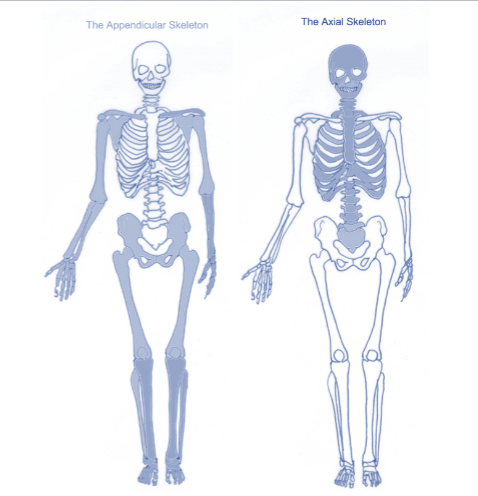
Classification of the Skeleton
Two Primary Regions:
Appendicular Skeleton
Limbs (upper/lower)
Limb girdles
Upper: scapula, clavicle
Lower: pelvis
Function: Movement and locomotion
Axial Skeleton (CORE)
Skull, vertebral column, rib cage
Function: Support and protection
Acronym: S.P.M.S.H.H. → “Some Powerful Moms Save Happy Homes.”
Function | Key Idea | Memory Image |
|---|---|---|
Support | Architecture for the body (pillars, walls, room) | Imagine bones as a house frame — legs are pillars, rib cage are walls, skull is a room |
Protection | Shield organs (skull → brain, ribs → heart/lungs, spine → spinal cord) | Think of armor protecting soft parts |
Movement (Anchorage) | Bones = levers, muscles = pulling ropes, joints = hinges | Picture a robot arm |
Storage | Stores fat (yellow marrow) + minerals (Ca²⁺, phosphate) | Think of bones as a pantry full of energy + minerals |
Hematopoiesis | Makes blood cells in red marrow | Red = blood! |
Hormone Production | Makes osteocalcin, regulates insulin, glucose, energy → links to diabetes | Picture a bone “chef” cooking up hormones for blood sugar control |
Acronym: “A for Arms, Ax for Axis.”
Skeleton | Includes | Function | Mnemonic |
|---|---|---|---|
Appendicular | Limbs + limb girdles (arms, legs, scapula, clavicle, pelvis) | Movement & locomotion | “Appendages help you move” |
Axial | Skull, vertebral column, rib cage | Support & protection | “Axis keeps your body upright” |