Micro Chapter 7
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
The molecule that encodes all the instructions needed to produce a cell's components is ______.
Multiple choice question.
RNA
protein
DNA
DNA
The functional unit of a genome that codes for a product is a(n)______
gene
All DNA nucleotides contain the same deoxyribose and phosphate groups, but different ._________
nucleobases
RNA contains the sugar _____, which differs from its DNA counterpart by possessing _____ oxygen atom.
Multiple choice question.
ribose; one more
ribose; one fewer
ribulose; one fewer
ribulose; one more
ribose; one more
Regulating gene expression involves controlling mRNA synthesis and rapidly destroying mRNA transcripts.
True false question.
True
Fals
True
An essential macromolecule that encodes all of the information needed by a cell to synthesize its components is ._____
DNA
To initiate replication of a DNA molecule, specific proteins must bind to a specific DNA sequence called the ______.
Multiple choice question.
start sequence
origin of replication
beginning point
origin of replication
A ______ is a sequence of nucleotides that usually codes for one functional protein.
Multiple choice question.
gene
triplet
codon
protein
chromosome
genome
gene
DNA replication must occur prior to cell division to ensure that each new cell has a complete genome.
True false question.
True
False
True
Which of the following is found in all DNA nucleotides?
Multiple choice question.
the same sugar, but different phosphates and nucleobases
the same nucleobase and phosphate, but different sugars
the same nucleobase, but different phosphates and sugars
the same sugar and phosphate, but different nucleobases
the same sugar and phosphate, but different nucleobases
The pentose sugar in RNA is________ , while in DNA the pentose sugar is ________
ribose and deoxyribose
Why is regulation of gene expression important?
Multiple choice question.
The cell needs a "rest period" when making protein.
A cell does not need all of its encoded proteins at the same time.
A cell can only express certain genes at any one time.
A cell does not need all of its encoded proteins at the same time.
A replication fork is ______.
Multiple choice question.
a site where one DNA strand serves as a template for the synthesis of an RNA transcript
a structure formed only during replication of a circular chromosome
a Y-shaped structure where both DNA strands are be
a Y-shaped structure where both DNA strands are being replicated
In general, the chromosome of a bacterial cell is a _______ DNA molecule that is replicated _______.
Multiple choice question.
circular; bidirectionally from multiple origins of replication
linear; bidirectionally from one origin of replication
circular; bidirectionally from one origin of replication
circular; unidirectionally from one origin of replication
linear; bidirectionally from multiple orgins of replication
circular; bidirectionally from one origin of replication
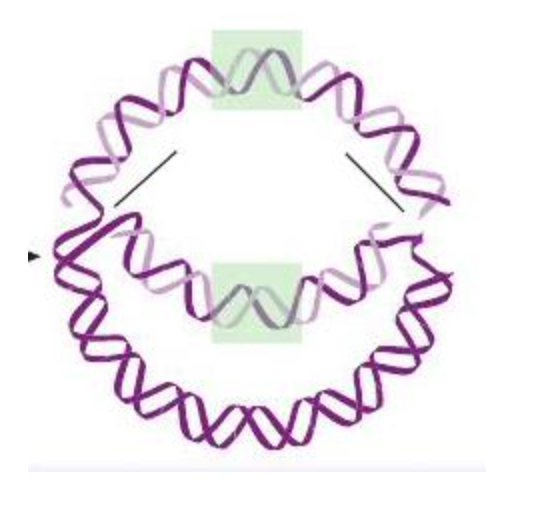
In this image of a bacterial chromosome replicating, the openings the labels are pointing to are called the _______ ________
replication forks
Cells duplicate their DNA before cell division using a process called DNA _________
replication
Because the newly made double helices are composed of one strand from the original molecule and one newly synthesized strand, DNA replication is said to be ._________
semiconservative
All DNA nucleotides contain the same deoxyribose and phosphate groups, but different ._______
nucleobases
How many template strands exist in a replication fork?
Multiple choice question.
only one
four
unlimited number
two
two
RNA contains the sugar _____, which differs from its DNA counterpart by possessing _____ oxygen atom.
Multiple choice question.
ribose; one more
ribose; one fewer
ribulose; one fewer
ribulose; one more
ribose; one more
A(n)_______ ________ is a Y-shaped point on a replicating DNA molecule where the DNA polymerases are synthesizing new strands of DNA.
replication fork
How many replication forks are formed from opening a section of a circular DNA molecule as part of DNA replication?
Multiple choice question.
2
4
1
2
What enzyme synthesizes the short segments of RNA required to initiate DNA replication?
Multiple choice question.
DNA gyrase
primase
DNA polymerase
ligase
helicase
primase
DNA replication is described as being ______, because each new DNA molecule formed by the process has one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Multiple choice question.
complementary
conservative
antiparallel
semiconservative
semiconservative
After the initiation of replication of a bacterial chromosome, the enzyme _______ adds nucleotides to a growing strand.
Multiple choice question.
DNA polymerase
Primase
RNA polymerase
DNA ligase
DNA polymerase
The single-stranded DNA from which a new DNA strand is synthesized is referred to as the ______.
Multiple choice question.
origin of replication
complement
nucleotide
transcript
template
template
Which strand is replicated continuously during DNA replication?
Multiple choice question.
The lagging strand only
Neither the leading nor lagging strands
The leading strand only
Both the leading and lagging strands
The leading strand only
In DNA replication, the DNA strand that is synthesized continuously is the ______ strand, while the strand that is synthesized discontinuously is the ______ strand.
Multiple choice question.
leading; fragmented
leading; lagging
leading; Okazaki
lagging; leading
leading; lagging
To initiate DNA replication, short sequences of RNA are needed. These are called —————
primer
The DNA strand that is synthesized discontinuously during DNA replication, forming Okazaki fragments, is called the______ strand.
lagging
During replication, DNA polymerases ______.
Multiple choice question.
add nucleotides to the 3' end of the new DNA strand
add nucleotides to the 5' end of the new DNA strand
generate short stretches of RNA called primers to initiate replication
unwind the DNA double helix at the replication fork
add nucleotides to the 3' end of the new DNA strand
During transcription, RNA polymerase synthesizes ______ from a(n) ______ template.
Multiple choice question.
RNA; protein
RNA; DNA
DNA; RNA
RNA; RNA
RNA; DNA
In DNA replication, the synthesis of one new strand proceeds continuously as fresh template is exposed. This strand is known as the ______ strand.
leading
This is an image of a replication fork. The top (blue) arrow is pointing to the __________ strand, and the bottom (red) arrow is pointing to the_________ strand.
leading, lagging
What enzyme binds to a DNA promoter region to initiate transcription?
Multiple choice question.
DNA gyrase
RNA synthase
DNA polymerase
RNA polymerase
Primase
RNA polymerase
As part of DNA replication, Okazaki fragments are made during the synthesis of the ______.
Multiple choice question.
lagging strand in a discontinuous manner
lagging strand in a continuous manner
leading strand in a continuous manner
leading strand in a discontinuous manner
lagging strand in a discontinuous manner
After the initiation of replication of a bacterial chromosome, the enzyme _______ adds nucleotides to a growing strand.
Multiple choice question.
Primase
DNA polymerase
RNA polymerase
DNA ligase
DNA polymerase
An RNA transcript is a strand of RNA copied from an RNA template.
True false question.
True
False
False
The process of transcription stops when the RNA polymerase reaches a ______.
Multiple choice question.
terminator
promoter
ender
silencer
terminator
An RNA transcript is synthesized in the 3' to 5' direction.
True false question.
True
False
False
Transcription is carried out by an enzyme called .___________ ____________
RNA polymerase
The DNA strand that is synthesized discontinuously during DNA replication, forming Okazaki fragments, is called the ____lstrand.
lagging
The ______ DNA strand is used as the template for RNA synthesis.
Multiple choice question.
plus (+)
minus (-)
minus (-)
During what process is the information in mRNA used to make a protein?
Multiple choice question.
replication
transcription
translation
transduction
translation
RNA polymerase binds to a ______ to begin transcription.
Multiple choice question.
initiator
terminator
promoter
primer
promoter
RNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the ______ end of a growing strand.
Multiple choice question.
1'
3'
5’
3
What enzyme binds to a DNA promoter region to initiate transcription?
Multiple choice question.
Primase
RNA synthase
DNA polymerase
RNA polymerase
DNA gyrase
RNA polymerase
What are the three major structures directly involved in translation?
Multiple choice question.
DNA, mRNA and tRNA
RNA polymerase, DNA polymerase and ribosomes
Ribosomes, mRNA and tRNA
mRNA, Golgi and tRNA
Ribosomes, mRNA and tRNA
The ______ strand of DNA contains the same order of nucleotides as the corresponding RNA transcript.
Multiple choice question.
plus (+)
minus (-)
plus (+)
is transcribed from a DNA template and translated during protein synthesis.
mRNA
is the process of decoding the information carried by mRNA to synthesize a protein.
translation
The ______ _____correlates a series of three nucleotides to one amino acid or a stop codon.
genetic code
The process of transcription stops when the RNA polymerase reaches a ______.
Multiple choice question.
promoter
terminator
silencer
ender
terminator
A(n_________) is the specific sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA that encode a particular amino acid or a stop signal.
codon
An RNA transcript is synthesized in the 3' to 5' direction.
True false question.
True
False
False
The genetic code is comprised of 64 different codons. Out of these, ______code a specific amino acid.
61
The process of translation requires the three major structures. What are they?
Multiple select question.
ribosomes
RNA polymerase
DNA polymerase
sRNA
tRNA
mRNA
ribosomes
tRNA
mRNA
The genetic code includes _______ stop codon(s).
Multiple choice question.
20
61
3
7
1
3
The function of mRNA is to ______.
Multiple choice question.
bring amino acids to the ribosome for transcription
serve as a template for protein synthesis
compose ribosomal subunits
serve as a template for protein synthesis
Information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins based on rules known as the ______.
Multiple choice question.
genetic code
RNA world hypothesis
central dogma
genetic code
Several codons code for the same amino acid, which is called the redundancy of the code. Because of redundancy, the genetic code is said to be degenerate.
True false question.
True
False
True
A codon contains how many nucleotides?
Multiple choice question.
1
It depends on the size of the gene
20
3
3
An mRNA sequence has ______.
Multiple choice question.
only a single reading frame, which must be used for translation
three potential reading frames, but only one is typically used for translation
three potential reading frames, and any one can be used for translation
three potential reading frames, but only one is typically used for translation
How many codons are used to specify the 20 possible amino acids?
Multiple choice question.
64
20
30
3
61
61
Protein synthesis involves ______, which align amino acids and catalyze peptide bond formation between them.
ribosomes rRNA
The signal to end protein synthesis is indicated by sequences called .__________ ________
stop codons
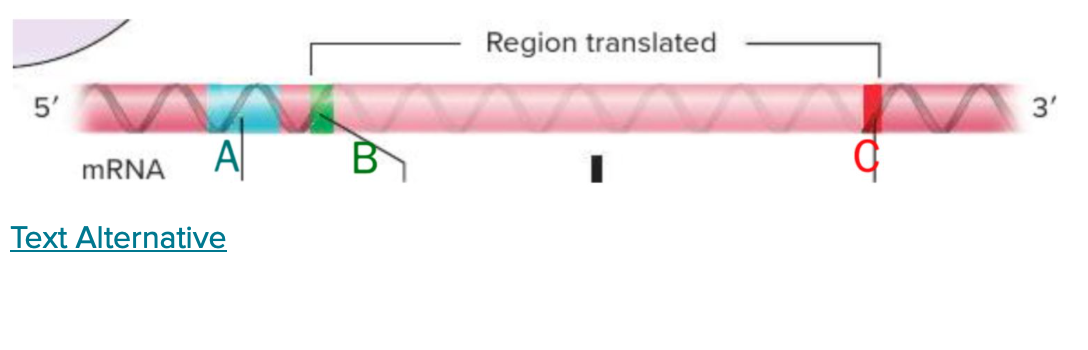
In this schematic of mRNA, label A points to the_____-binding site, label B depicts the______ codon, and label C highlights the_____ codon.
ribosome, start, stop
______is transcribed from a DNA template and translated during protein synthesis.
mRNA
Which type of RNA molecule is included in the composition of ribosomal subunits?
Multiple choice question.
mRNA
rRNA
tRNA
rRNA
Why is the genetic code said to be redundant?
Multiple choice question.
More than one codon can code for a specific amino acid.
It is no longer needed by cells: DNA can be directly decoded to make protein.
The code is universal: all living things use the same genetic code.
Any amino acid can be decoded from any codon.
More than one codon can code for a specific amino acid.
The function of a tRNA is to ______.
Multiple choice question.
compose ribosomal subunits
carry the amino acids used in translation
bring a ribosome to the amino acid
carry the amino acids used in translation
What is the outcome if translation begins at the wrong reading frame?
Multiple choice question.
DNA polymerase corrects the reading frame.
Generally, a non-functional protein is made.
Redundancy in the code ensures that the same protein is always made.
Generally, a non-functional protein is made.
A tRNA has a(n) _______, a group of three nucleotides that is complementary to the codon of the mRNA.
anticodon
What are the roles of ribosomes in translation?
Multiple select question.
aligning amino acids and catalyzing the formation of peptide bonds between them
carrying information for the synthesis of a protein
Ribosomes detect sequences that indicate where translation should start and finish.
bringing amino acids to the site of protein synthesis
aligning amino acids and catalyzing the formation of peptide bonds between them
Ribosomes detect sequences that indicate where translation should start and finish.
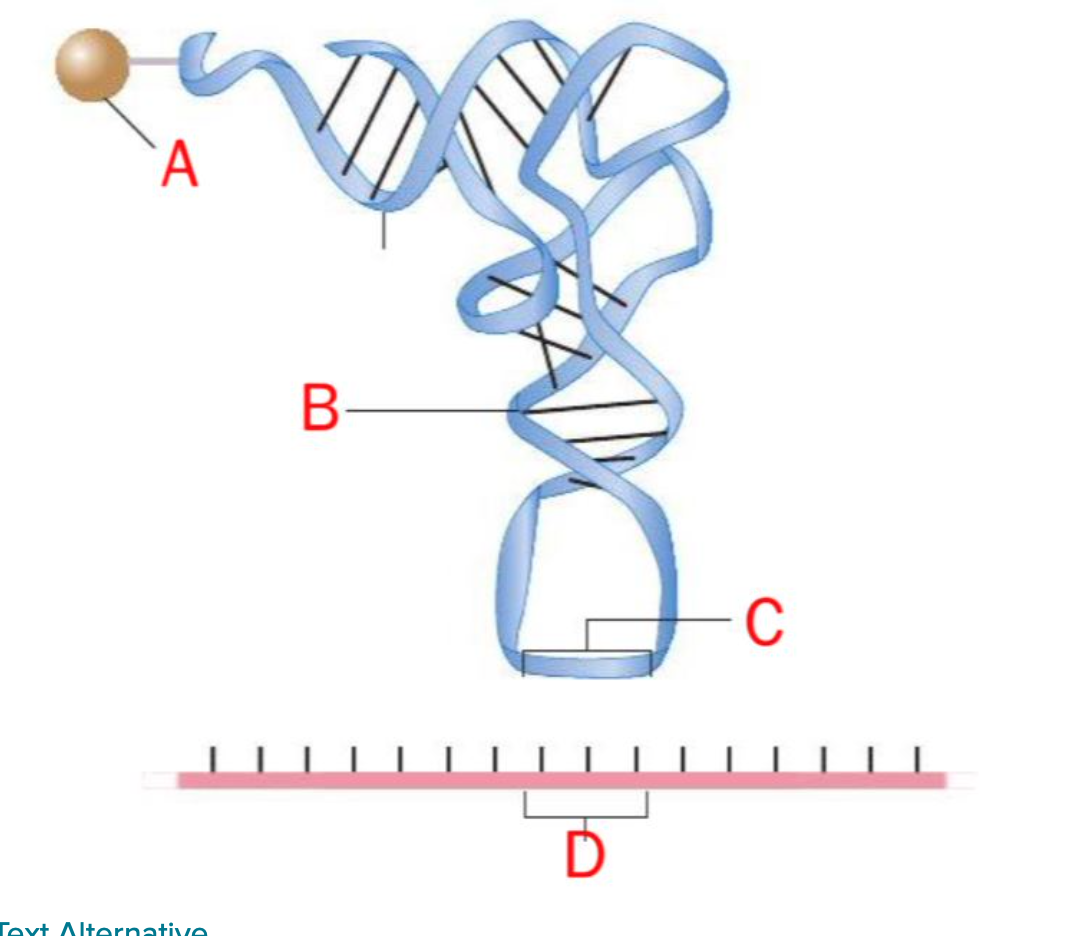
A; amino acid
B; Hydrogen bond
C;anticodon
D; codon
In bacteria, the ribosome starts to assemble at a sequence in mRNA called the _____ _____ site. Translation begins at the first AUG codon after that.
ribosome binding
The amino acid that is placed first during translation in bacteria is _______.
Multiple choice question.
glycine
N-formylmethionine
N-formylglycine
methionine
N-formylmethionine
Each subunit of the ribosome is made up of______ and a type of RNA called_____ .
protein, ribosomal
Which type of RNA carries amino acids during protein synthesis?
Multiple choice question.
mRNA
rRNA
tRNA
tRNA
A codon and an anticodon base pair with each other because they have identical nucleotide sequences.
True false question.
True
False
False
Which of the following initiates translation?
Multiple choice question.
Amino acids are joined by peptide bonds.
Ribosomes assemble on the mRNA.
RNA polymerase binds the DNA promoter.
Ribosomes assemble on the mRNA.
A transfer RNA molecule is folded into a three dimensional shape held together by hydrogen bonds. On one end of this structure is the ______ (which binds to mRNA), and on the other end, a specific _____ _______ is attached.
anticodon
amino acid
Which of the following are true statements about events that take place during the elongation phase of translation?
Multiple select question.
Empty tRNAs leave the ribosome via the E-site.
Amino acids are joined together by the enzymes RNA polymerase.
A peptide bond is formed between amino acids on adjacent tRNAs.
tRNAs carrying amino acids occupy the A-site and the P-site of the ribosome.
Elongation starts at the promoter sequence of the DNA.
A peptide bond is formed between amino acids on adjacent tRNAs.
Empty tRNAs leave the ribosome via the E-site.
tRNAs carrying amino acids occupy the A-site and the P-site of the ribosome.
In prokaryotes, the first AUG after a ribosome-binding site typically functions as a(n) ___ codon . At other sites it simply encodes the amino acid ._____
start, met
Which of the following describes the termination of translation?
Multiple choice question.
A stop codon is reached and the polypeptide is released from the ribosome.
tRNA leaves the E-site on the ribosome.
A terminator sequence is reached and mRNA is released from the DNA template.
A stop codon is reached and the polypeptide is released from the ribosome.
Which type of RNA molecule is included in the composition of ribosomal subunits?
Multiple choice question.
mRNA
rRNA
tRNA
rRNA
The function of a tRNA is to ______.
Multiple choice question.
compose ribosomal subunits
carry the amino acids used in translation
bring a ribosome to the amino acid
carry the amino acids used in translation
Eukaryotic mRNA is first synthesized as an immature transcript called ______ ______. It has to be processed significantly before it forms mature mRNA.
pre mRNA
This figure highlights the _____ phase of translation in bacteria.
initiation
Microorganisms must adapt rapidly to changes in their environment in order to ______.
Multiple choice question.
communicate
infect
survive
die
survive
Translation terminates when the ribosome reaches a(n) ______codon, which is a codon not recognized by a tRNA.
stop
The transmission of information from outside a cell to the inside is known as ______.
Multiple choice question.
quorum sensing
signal transduction
two-component regulatory systems
antigenic variation
signal transduction
Some microorganisms can alter characteristics of certain surface proteins, allowing them to avoid detection by the host's immune system. This phenomenon is called ______.
Multiple choice question.
quorum sensing
antigenic variation
natural selection
phase variation
antigenic variation
What is the proper order of the following events in the expression of a eukaryotic gene?1. translation2. RNA processing3. transcription
Multiple choice question.
1, 3, 2
3, 1, 2
2, 3, 1
3, 2, 1
1, 2, 3
3,2,1
Enzymes that are synthesized constantly in a cell are called ._____
constitutive
All of the following are examples of means by which microorganisms can respond to changing environmental conditions EXCEPT ______.
Multiple choice question.
quorum sensing
two-component regulatory system
signal transduction
production of different ribosomes
production of different ribosomes
While standard sigma factors recognize promoters for genes that need to be expressed during routine growth conditions, alternative sigma factors ______.
Multiple choice question.
recognize different sets of promoters, thereby controlling expression of specific groups of genes
act by binding to the operator site and either blocking or promoting transcription
serve in the process of translating the mRNA into proteins
serve as backup regulators to control expression of these genes for routine growth in the absence of standard sigma factors
recognize different sets of promoters, thereby controlling expression of specific groups of genes
The lac operon only functions when ______ is present in the medium but ______ is absent from the medium.
Multiple choice question.
glucose; lactose
glucose; allolactose
lactose; maltose
lactose; glucose
lactose; glucose
Information is passed from the environment into the cell by a process known as signal _____
Transduction
Eukaryotic cells can regulate the levels of mRNA by destroying specific RNA transcripts through a process known as RNA , abbreviated ______RNAi.
interference