2.3- Garbage and Static keyword
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Examples of Garbage:
●What happened in Main?
○First we defined an attribute called a, which was of type Number
○On the next line we create a new Number object on top of a
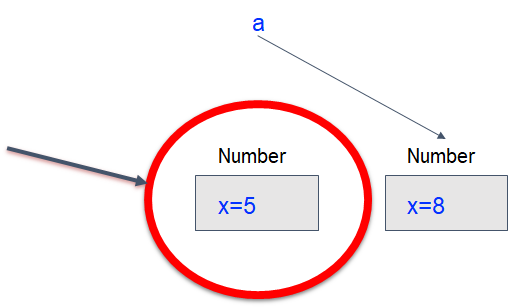
●What happened to the Number object that contained 5?
●It’s gone!....Sorta
class Number {
int x=7;
public Number(int x) {
this.x=x;
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Number a = new Number(5);
a = new Number(8);
}
}
What is a garbage collector?
●A task that runs in the background.
●Any object that you create that is no longer in use, is cleaned up by the garbage collector
○There is no guarantee of when it will be cleaned up
○If the garbage collector is too aggressive it could hinder performance of your program, so it tends to run when your program is waiting on something like user input.
Let’s look at this example:
●This number object is no long referenced by any variable
●It is considered garbage
●Soon the garbage collector will come along and remove it.
What if you needed a “shared” variable?
Imagine you write a set of classes to mimic a fast-food restaurant.
One class you write is fryCook. Your restaurant has 3 fryCook objects.
Each fryCook produces a new set of fries every 15 seconds.
Where should you store the fries?
One option is each fryCook has their own ArrayList of fries
This isn’t great for the person packing orders, because they have to ask each fryCook if they have any Fries.
Another option is that all fryCooks share an ArrayList of fries, that they can put their fries into.
Now the order packer just look in the shared ArrayList
This could be implemented as a static ArrayList in the fryCook class.
Static Variables/Attributes
●Unless you specify otherwise, all attributes in objects are independent from each other.
○i.e. object a and object b both have name attributes, but their values are independent.
●A static variables (a.k.a class variables) is shared among all instances of a class.
○i.e. object a and object b both have a maxHeight variable, that holds the SAME value in both objects because it’s shared.
■If a updates the static attribute, both a and b see the change.
●A variable become static by adding the reserved word static
○e . g. static int noOfCars =0;
●Constants (final) are often declared static since you only need one copy of the constant.
Example of static attributes:
class Dog {
static int dogCounter = 0; // Shared by all dogs
private int dogID; // Each dog has its own copy
Dog() {
dogID = dogCounter++;
}
}
Dog d1 = new Dog();
// d1’s ID is 0, dogCounter is now 1
Dog d2 = new Dog();
// d2’s ID is 1, dogCounter is now 2
Why use a static variable?
Probably the most common example is when you need to count how many objects of a given class are created, or you need to number those objects.
Think of KSU IDs.
Each Student/Faculty/Staff is a separate object
Thus each person needs their own unique ID in their object
However, somewhere you must keep track of the last ID you assigned.
This would be the static variable in your class KSU
class KSU { public static int next_id=0; private int id; public KSU { id=next_id++; } }
Static Methods
●A Static method (A.K.A class method) are invoked through a class name
●An object is not instantiated
●A method becomes static by adding the static reserved word to the method header:
○public static int carCount ()
●The main method in Java is static:
○public static void main()
●A static method can access only static variables and local variables
Static Method Example
class Dog {
static int dogCounter = 0;
private int dogID;
Dog() {
dogID = dogCounter++;
}
static void allowed() {
dogCounter *= 2;
}
static void notAllowed() { // Won’t compile
dogID = 10;
}
}
Dog d1 = new Dog();
d1.allowed();
Dog.allowed();
Dog.notAllowed(); // Why doesn’t this work?
Adding methods to your main class
•You may have noticed that if you add a method to your main class, you have to declare it static.
•This is because the main method is static, so everything it calls must be static.
Static Variables - Example
public class factoryWorker {
private String name;
private int empId;
private static int nextId = 1;
public int getId() {
return empId;
}
public void setId() {
empId = nextId; // set id to next available id
nextId++;
}
public static int getNextId() {
return nextId; // returns static field
}
}
public class StaticTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
factoryWorker fw = new factoryWorker();
int n = factoryWorker.getNextId();
System.out.println("Next available id=" + n);
}
}
Commonly used Static Method
Math Class
abs ()
min()
max()
sqrt()
Integer Class
parseInt()
Double Class
parseDouble()