Central Dogma & Gene Expression (28-29)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is the genetic code?
A set of rules that determines how the sequence of nucleotides in DNA and RNA is translated into the sequence of amino acids in a protein.
How many different amino acids are used to build proteins?
20 different amino acids.
What are codons?
Sequences of three nucleotides that represent specific amino acids.
How many possible codons are there?
64 possible codons.
What does it mean that the genetic code is redundant?
A given amino acid can be encoded by more than one codon.
What does it mean that the genetic code is unambiguous?
Each codon specifies only one amino acid.
Is the genetic code universal?
Yes, the same codons code for the same amino acids in all organisms.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The process where DNA is transcribed into mRNA, which is then translated into protein.
What is transcription?
The process of copying DNA into mRNA.
What is translation?
The process of converting mRNA into a sequence of amino acids to form a protein.

What is the start codon and what does it code for?
The start codon is AUG, which codes for methionine.
What are the stop codons?
UAA, UAG, and UGA, which signal the end of protein synthesis.
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotes?
In the nucleus.
Where does translation occur in all cells?
At ribosomes.
What is the role of mRNA?
To carry genetic information from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
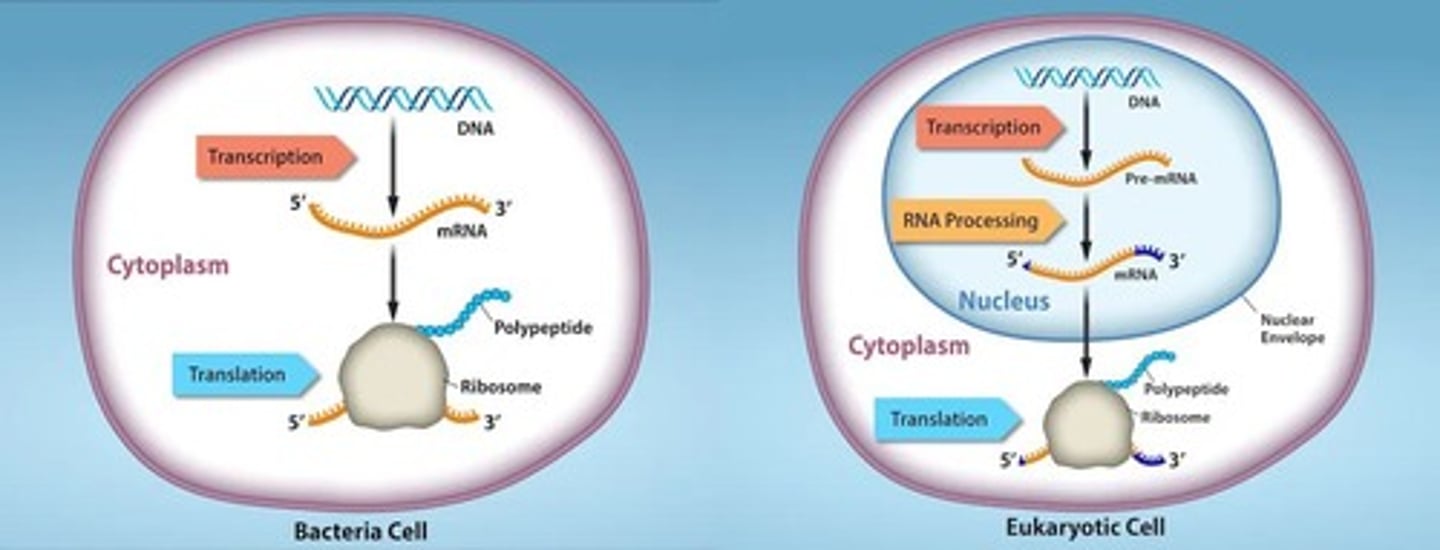
What is the relationship between the sequence of amino acids and protein function?
The sequence of amino acids determines the protein's structure and function.
What is the significance of the reading frame in translation?
The mRNA is read three nucleotides at a time, with no overlap, until a stop codon is encountered.
How do you transcribe a DNA template strand into mRNA?
By using base pair rules, where A pairs with U and C pairs with G.
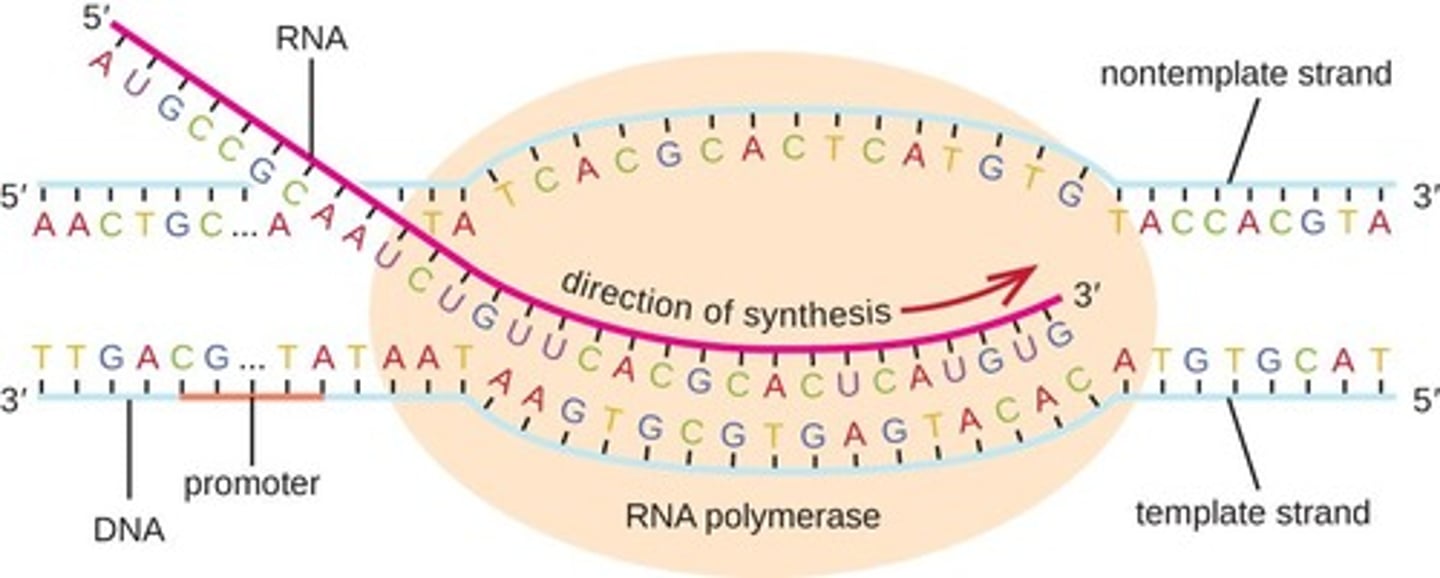
What is the process to identify the start and stop codons during translation?
Locate the start codon (AUG) to begin translation and identify stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) to end it.
What does the flow of information from gene to protein involve?
The flow involves DNA being transcribed to mRNA, which is then translated to form proteins.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of amino acids that make up the protein.
What is the role of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes facilitate the translation of mRNA into a polypeptide.
What is the significance of the genetic code chart?
It is used to translate the sequence of codons in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids.
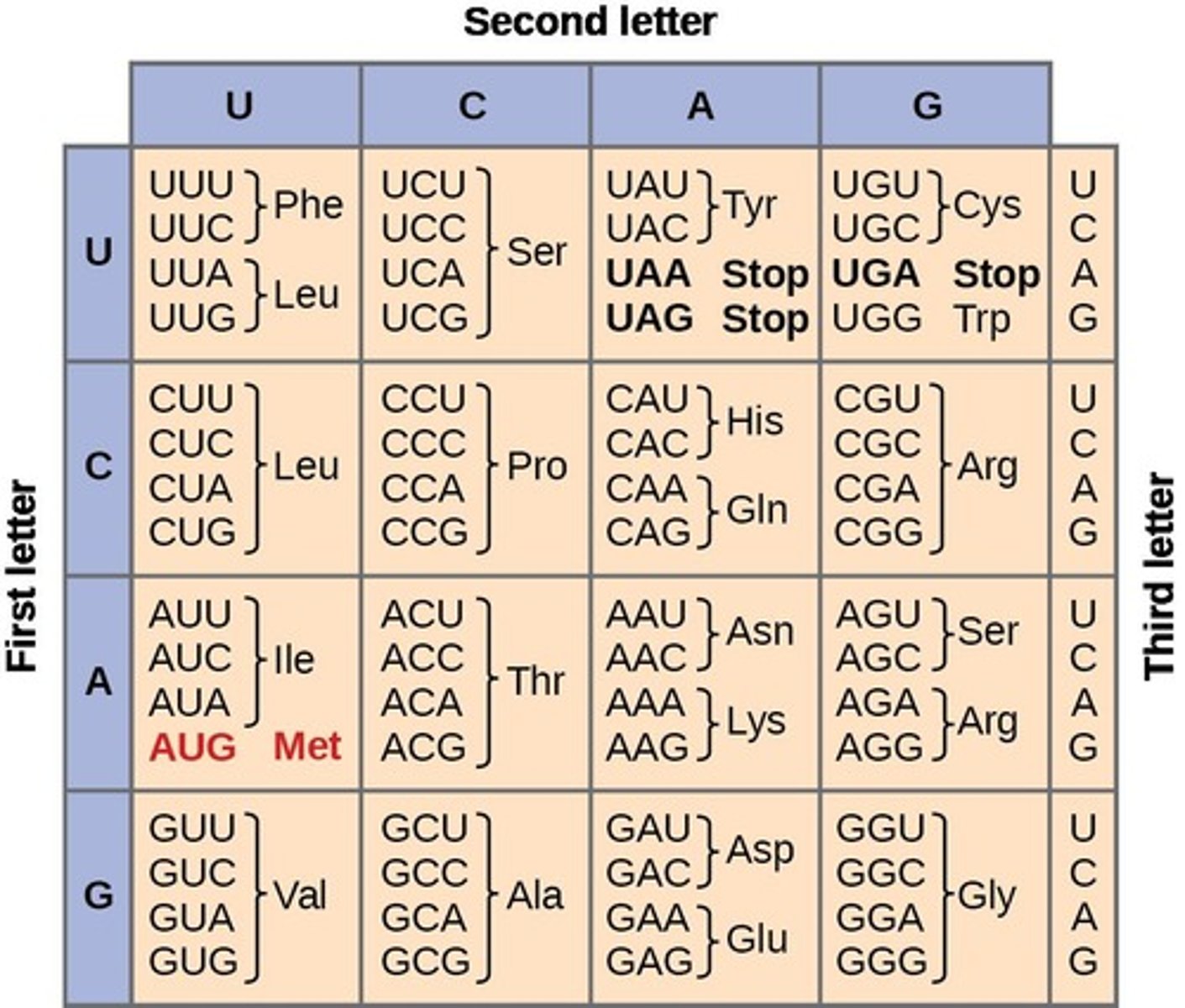
How does RNA differ from DNA in terms of nucleotide composition?
RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
What happens to mRNA after transcription in eukaryotic cells?
It is processed and transported into the cytoplasm for translation.
What is the function of proteins in cells?
Proteins perform most activities in a cell, including enzymatic reactions, cell signaling, and structural support.
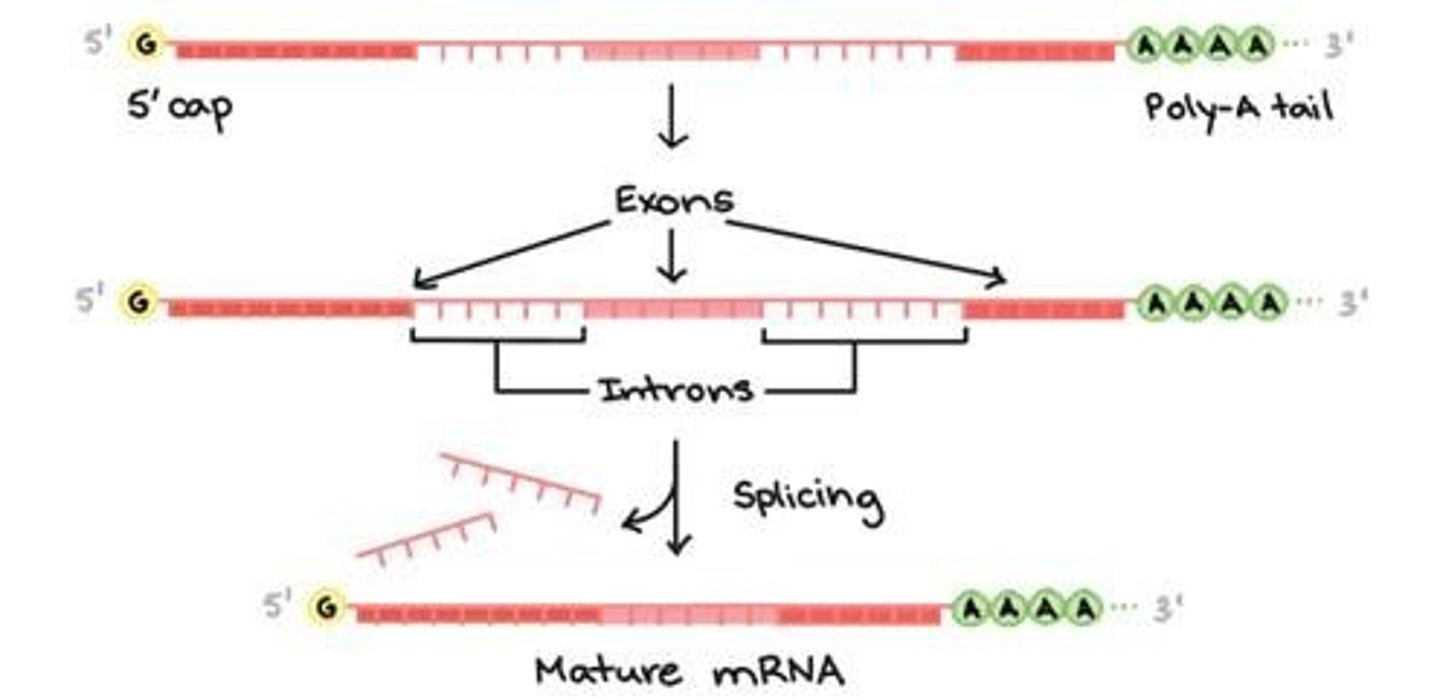
What is the initial product of transcription in eukaryotes?
Pre-mRNA, which must be processed to become functional mRNA.
What are the three main processing steps of pre-mRNA in eukaryotes?
Addition of a 5' cap, addition of a poly-A tail, and splicing out of introns.
What is the role of the promoter in transcription?
It serves as a recognition site for sigma factor and RNA polymerase to initiate transcription.
What happens during the initiation stage of transcription?
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, unwinds the DNA, and forms an open complex.
What occurs during the elongation stage of transcription?
RNA polymerase synthesizes the RNA transcript by sliding along the DNA template.
What is the termination stage of transcription?
RNA polymerase reaches the terminator, causing it and the RNA transcript to dissociate from the DNA.
What is the function of the sigma factor in transcription?
It helps RNA polymerase bind to the promoter and is released during elongation.
What is the difference between the coding strand and the template strand of DNA?
The coding strand has the same sequence as the RNA transcript, while the template strand is used by RNA polymerase to synthesize RNA.
What is the purpose of the 5' cap added to mRNA?
It protects mRNA from degradation and helps it find a ribosome for translation.
What is the significance of the poly-A tail in mRNA processing?
It stabilizes the mRNA and aids in its export from the nucleus.
What are introns and exons in the context of mRNA?
Exons are coding sequences that remain in the mRNA, while introns are non-coding sequences that are removed during splicing.
What is alternative splicing?
A process that allows multiple mRNA variants to be produced from a single gene, leading to different proteins.
What is the direction of RNA synthesis during transcription?
RNA is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction.
What is the role of the hairpin structure in transcription termination?
It causes RNA polymerase to detach from the DNA, ending transcription.
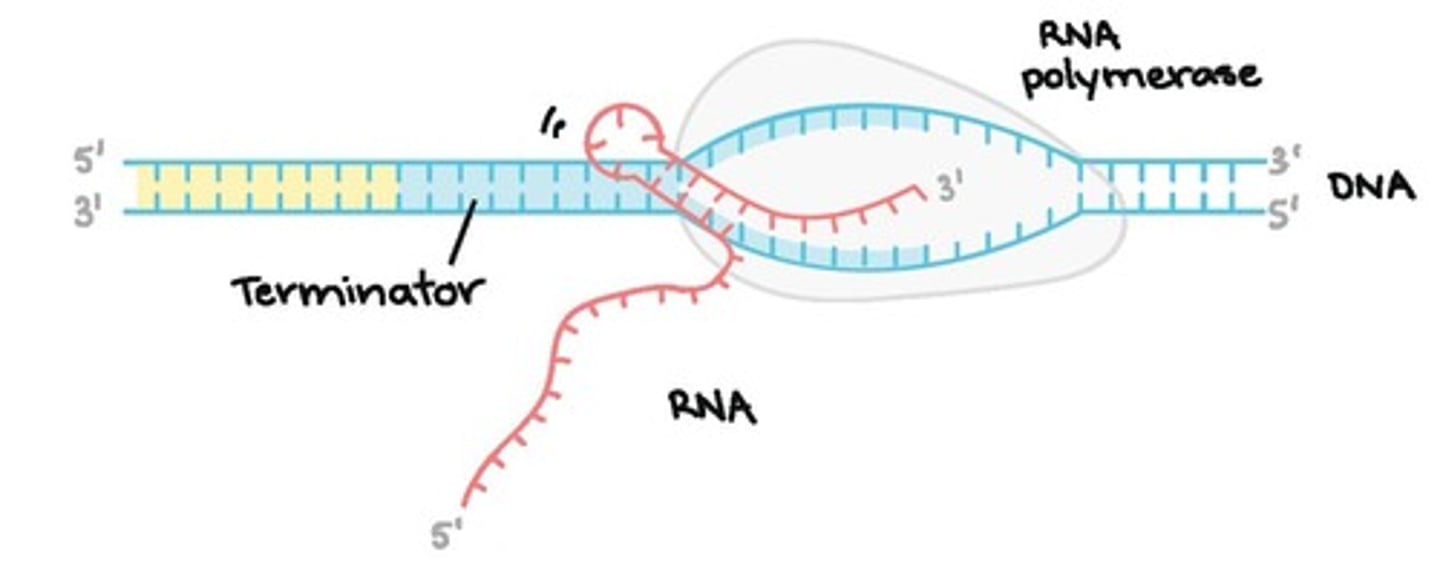
In prokaryotes, where does transcription and translation occur?
Both occur in the same location, as prokaryotes lack a nucleus.
What is the holoenzyme in the context of RNA polymerase?
It is the complex formed by the core enzyme and the sigma factor.
What are the consensus sequences recognized by the sigma factor?
-10 and -35 regions in the promoter.
What happens to the sigma factor after initiation of transcription?
It is released as RNA polymerase begins elongation.
What is the function of RNA polymerase during transcription?
It synthesizes RNA by adding complementary nucleotides to the growing RNA strand.

What is the relationship between transcription and the flow of genetic information?
Transcription is the first step in the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.