history of our planet week 5.2
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
causes of PETM, hominid and human evolution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Paleocene-eocene thermal maximum temperature change
+5 degrees C global warming within 20 Kyr
PETM - Volcanic trigger hypothesis:
A large flood basalt intrusion from Iceland hotspot began to open the north Atlantic 56.1Ma with splitting of the continents 55.5Ma
5-10 million km3 of basalts deposited in ~1myr intruded into fossil-fuel-rich sediments
This released co2, and thermogenic methane
Thermogenic methane is less 13^C depleted than biogenic methane/ hydrates hence more of it would be required to explain the δ^13C excursion
PETM - Methane hydrates:
Where the rest of the carbon needed for this 5*C increase in temp
Gas molecules trapped inside a frozen water lattice
]Sufficient methane trapped that they can be ignited
They form in the pore spaces in sediments
They occur in a layer in ocean sediments stabilised by high pressure (the large amount of sediment pushing down – will hold the gas in the lattic) and cold temperatures
Form at continental shelfs
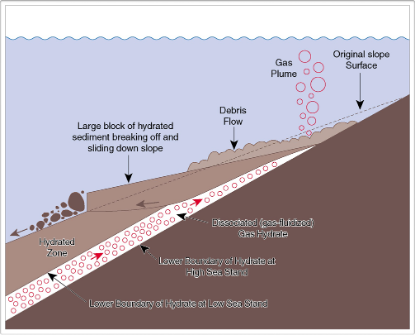
PETM - Methane hydrate destabilisation:
They can be destabilised by: - function of warming then destabilising of the sediments which was keeping it under pressure
Increasing temperature of overlying water
Depressurisation by lowering sea level,
(destabilise) slope failure
Hypothesis for PETM:
Warming of intermediate depth ocean waters destabilised mathen hydrate
Outgassing of methane added to warming causing more methane to be released
= a positive feedback
Total of 1500-4500 GtC of CH4 released in quite short of time
PETM - Champagne cork effect:
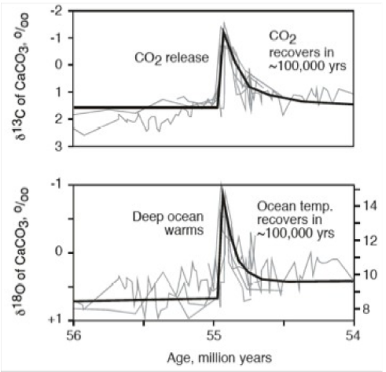
PETM - Timescale of recovery:
Methane is rapidly oxidised to CO2 in the atmosphere, warming the climate
It takes >100 kyr for ocean to be replenished with alkalinity from silicate weathering, drawing down CO2 and cooling the climate
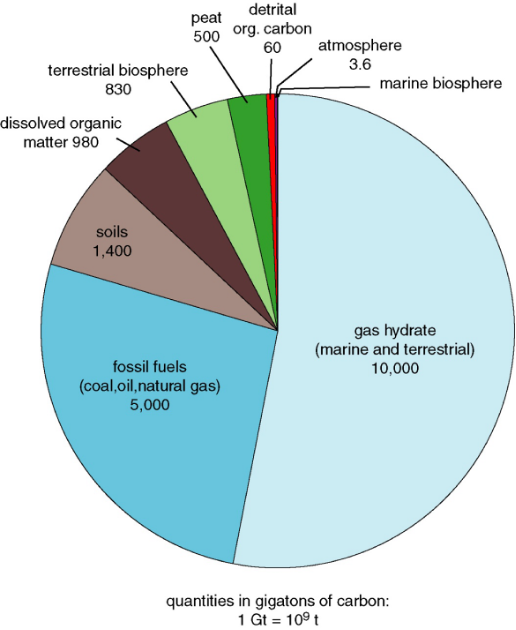
PETM - Gas hydrates today:
Estimates of total reservoir range from:
1000 GtC (milkov, 2004, ESR) to 10,000 GtC (kvenvolden, 1998)
1 GtC = 1 PgC = 10^15 gC
if this carbon were to be released it would seriously accelerate global climate change
Lessons from the PETM:
The amount of carbon released at the PETM is comparable to known fossil fueld reserves today and gave at least 5C long term warming
Models suggest that destabilisation of methane hydrates cold significantly amplify long term climate change
It will take at least 100Kyr for the carbon cycle and the climate to recover
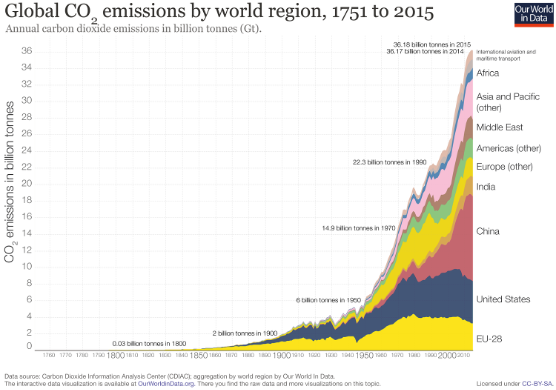
Most anthropogenic emissions have been since the 1990s
Cenozoic climate and co2:
Peak warmth ~ 50 Ma in Early Eocene then cooling begins
Possible co2 decline ?
Abrupt growth of Antarctic ice sheet growth 34 Ma at Eocene – Oligocene boundary
Possible co2 peak ?
No clear cooling in Oligocene, But rapid co2 decline
Miocene climatic optimum ~ 15 Ma before further cooling
stable, low co2 since 24 Ma
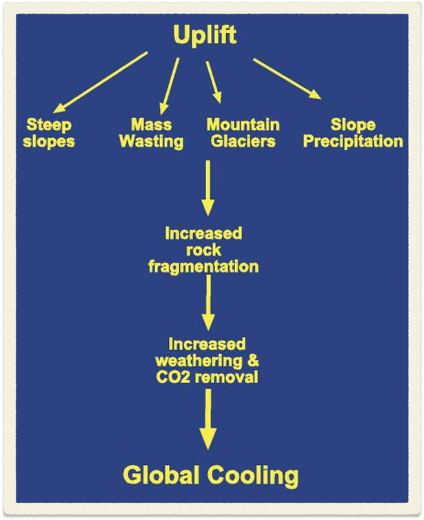
Himalayan uplift hypothesis
Raymo and ruddiman 1992:
Uplift of the Himalaya/ Tibetan plateau caused increased rates of weathering
This decreased atmospheric co2 thus cools the planet
This should have caused a negative feedback response
Lower co2 and temp reduce silicate weathering until it again matches degassing
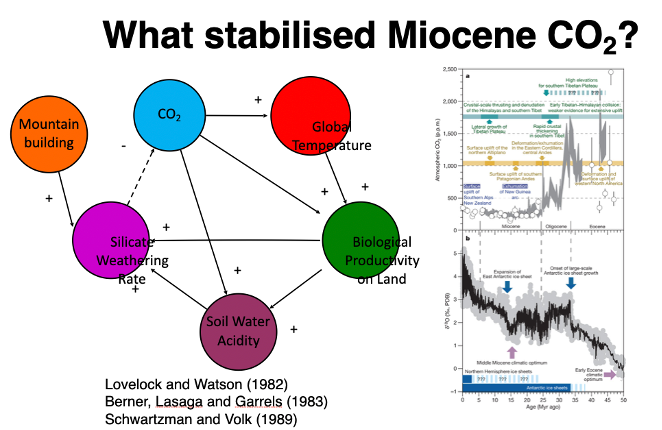
What stabillised Miocene CO2:
If co2 drops too low then the majority of (‘C3’) plants cannot photosynthesise
At 200-250ppm co2 during the Miocene upland vegetation was near co2 starvation
Pagani et al (2009) argues this limited the effect of plants on weathering, holding co2 stable
Great rift valley:
Savannah habitat
Divergence from chimpanzees ~6 Ma
Up to 5 genera:
Ardipithecus 5.8-4.4 Ma
Australopithecus 3.9-3 Ma
Praeanthropus?
Paranthropus ~2 ma
Homo ~ 2ma
Rise of grasslands: Characteristics:
-33% of vegetated land
Low to moderate rainfall
]High Si weathering
Promote glazing and fires
Rise of grasslands: 3 stages of spread:
Eocene/ oligocene 33 Ma: Desert grasslands
Early Miocene 17 Ma: Ungulates; horse, antelope
Late Miocene 7 Ma: C4 grasses
Stone tools, homo habilis 2.5Ma
Literally ‘handy man’
Better classified as Australopithecus habilis
Prey for large cats
The first tool makers used for scavenging
Stones moved < 13 km range of an individual
Indicates planning but not group activity