MLSP 5311 Final Exam
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Definition: Chromatography
A group of texhniques used to separate complex mixtures based on varied physical properties through a stationary and mobile mediums.
The ___ in chromatography is the substance or component that is being measured.
Analyte
The mobile phase in chromatography can be ___ or ___.
Liquid, gas
The stationary phase can be solid or ____.
Liquid
To achieve optimal separation, the compounds of interest must ___ in affinity for both phases in chromatography.
Differ
What are three common clean up specimen extraction methods?
Partition, adsorption, centufugation and precipitation
What is the extraction method of partitioning?
Separation between stationary and mobile phase - liquid/ liquid extraction such as orgainic and aqueous
The gas used in the mobile phase of chromatography must be..
Inert, having minimal interactions with specimen
In liquid chromatography, the various liquids ____ interact with the analytes
Do
Retention
When compounds absorb or partition to the stationary phase
Elution, or the alteration of the system to release the stationary phase can be done by:
Changing the temperature, mobile phase conditions, flow
Peak evaluation
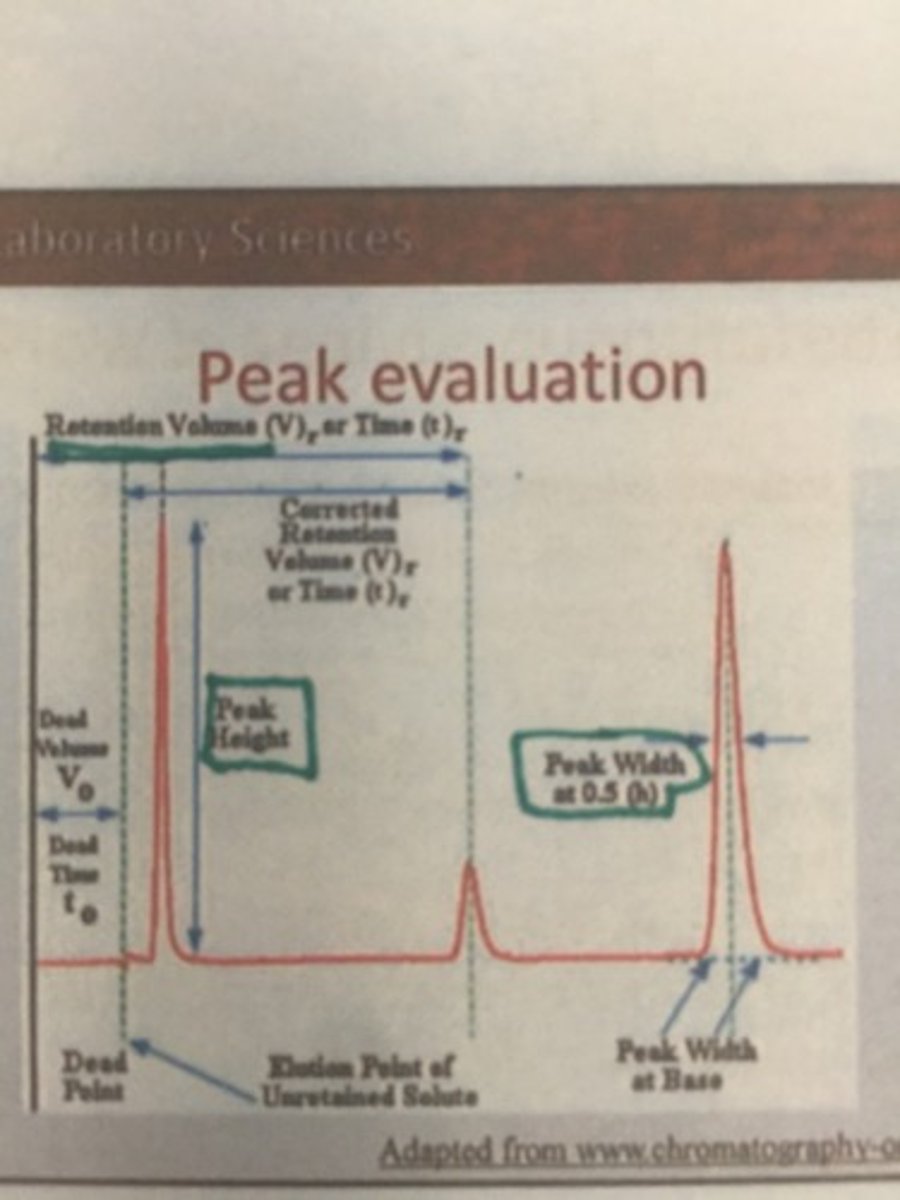
Co-elution
Where two peaks occupy the same space. This means minimal resolution
Examples of peaks

Name three factors that affect resolution :
Analyte factors such as similarity, system factors such as the phases, and the NTP or number if theoretical plates
As NTP increases, so does....
Selectivity
What are two qualities of a good chromatogram?
Tall thin peaks, good baseline resolution
How is an Analyte quantitated?
An IS or internal standard such as QC and calibrators
What are the advantages of using an internal standard in chromatography?
Accounts for losses and used for quantification
Peak height ratio equation

Affinity chromatography
Uses a tag such as an antibody to bind to the stationary phase. Then a buffer releases it from the column
Ion exchange chromatography
Analytes are separated by ionic charge with polar opposite beads. Then a buffer releases it
Steric Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
Separation based on molecular size. The beads have tiny pores in which small particles become trapped, large molecules move the fastest and elute first
TLC or thin layer chromatography
Two phases in which the solid can consist of silica or charcoal. Migration occurs with the solvent absobant into the solid phase
What is the Rf value and how is it calculated? (TLC)
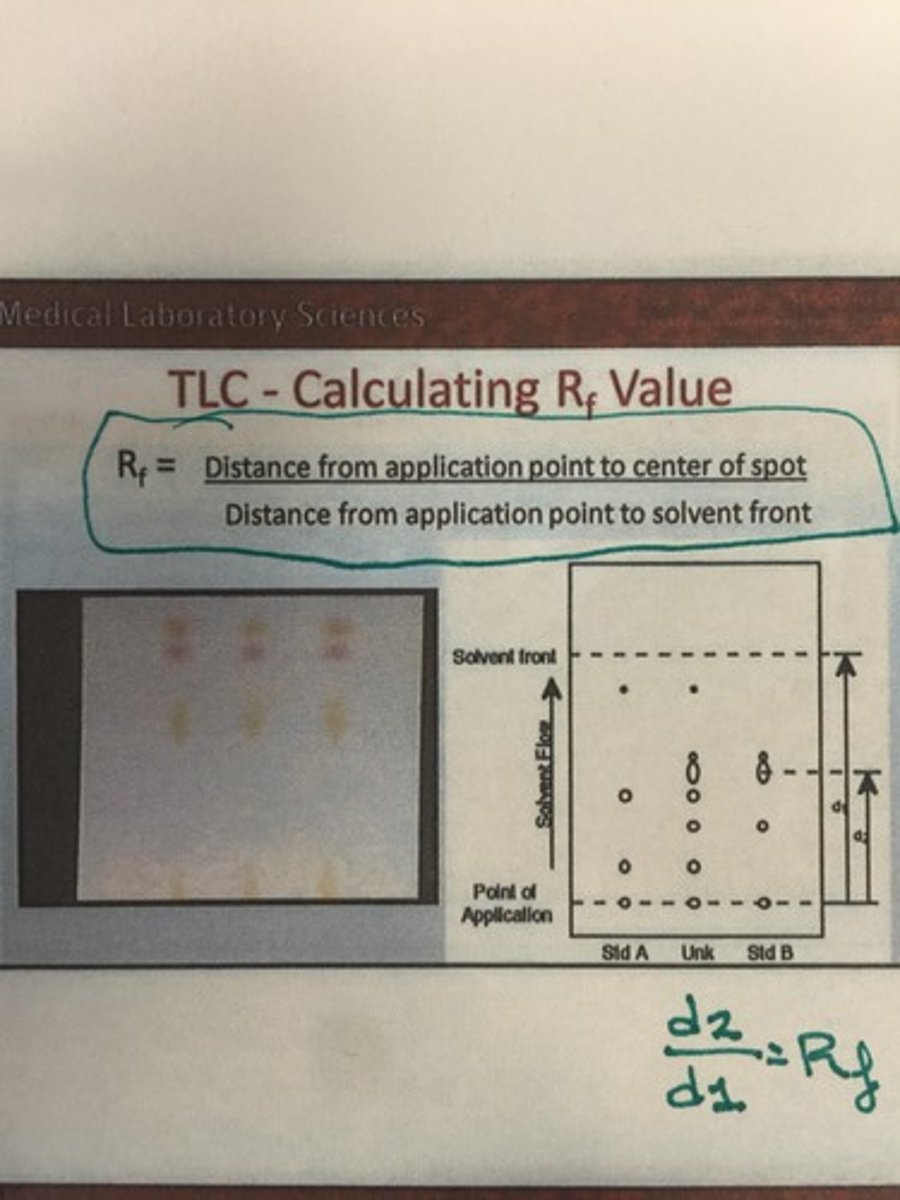
TLC is :
A. Quantifiable
B. Semi quantitative
B semi quantitative
What are two advantages and two disadvantages to TLC?
Advatages: inexpensive, run multiple samples, easy, use of a densitometer
Disadvatages: lower sensitivity, semi quantitative
Parts of a gas chromatograph
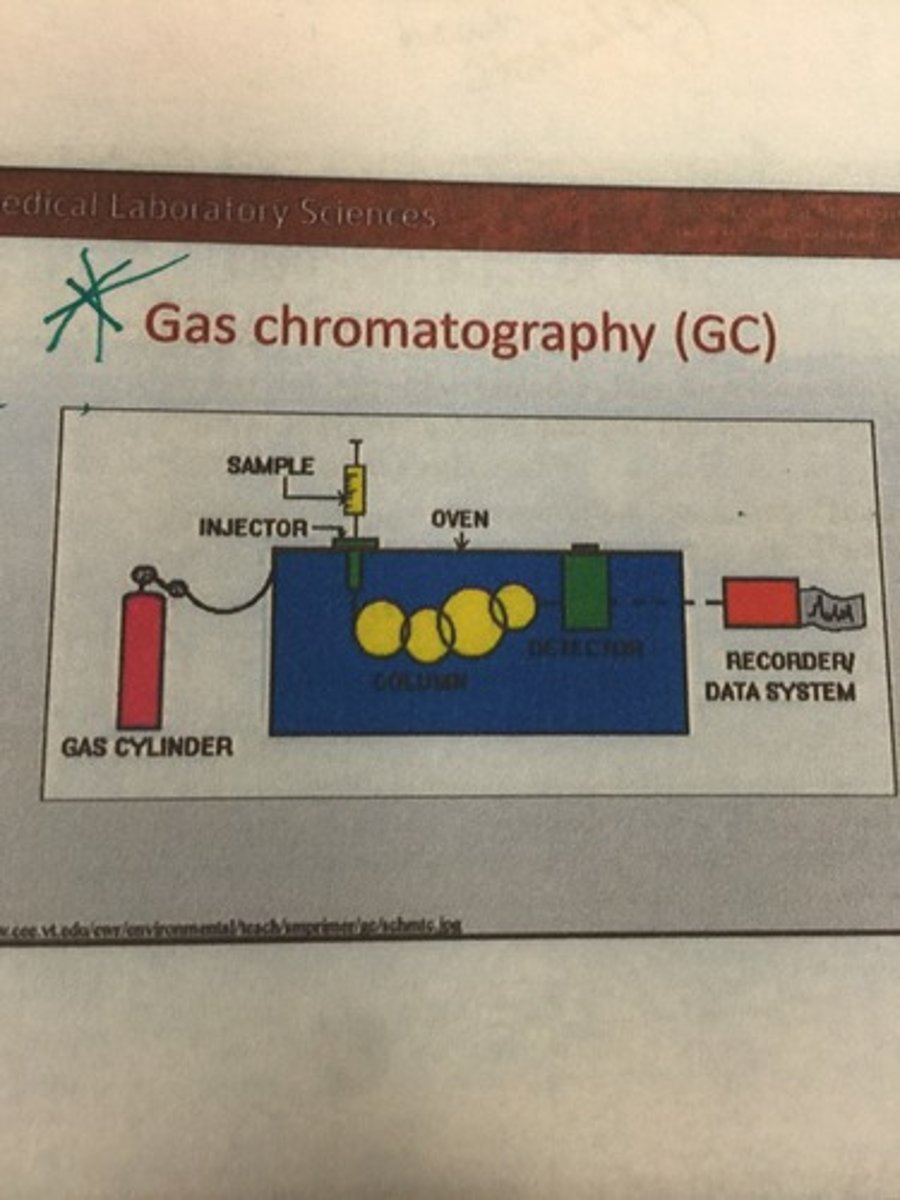
What three factors in gas chromatography affect elution?
Size, affinity, and boiling point
A low boiling point in gas chromatography will cause:
Faster elution into the mobile phase
Raising the temperature in gas chromatography will cause:
Decrease in retention time and sharper peaks
A longer column will allow for a ___ RT.
Longer
What is sample derivatization?
The chemical bonding of an analyte to a more volatile group to increase stability in a gas chromatography system
An example of sample derivatization is:
Oxycodone and TMS
What are five properties of a good GC detector
Sensitivity (proportional changes), selectivity (distinguishment), rapid responce, linearity (signal proportional to concentration), and stability (baseline noise).
GC Detector - Mass Spectroscopy (MS)
Very sensitive "Gold standard", ions are separated with a magnetic field m/z, *Expensive*
GC Detector - Flame ionization detector (FID)
A current generated by flame, sensitive, good for organic compounds
GC Detector - Nitrogen Phosphorous Detector (NPD)
Where Rb ions interact with the nitrogen or phosphorus in a compound. Less background, more sensitive
GC Detector - Electron Capture Detector (ECD)
A beta emitter, electrons are captured by halides resulting in a loss of current. Very sensitive, but also radioactive (Safety concerns)
Name five common compounds detected by gas chromatography:
-Alcohol levels
-Drugs
-Drugs of Abuse
-Toxins/Toxicology
-organic acids (metabolism errors)
What are the advantages to Gas chromatography?
High resolution and sensitivity, automated capability, low maintenance equipment
Name three disadvantages to Gas chromatography.
Need for extraction of specimens, volatile samples, time consuming
Samples for GC may require _____ or the being attached to a volatile analyte.
derivatization
What is high performance liquid chromatography or HPLC?
separation technique based on the solubility of the analytes in two liquids. The solid phase is usually silica coated and the mobile phases aqueous and organic
What is the major difference between GC and HPLC?
HPLC is done at lower temps, and the mobile phase is NOT inert. Little need for derivatization
Name three ways HPLC can be modified to change separation:
ionic strength, pH, Buffer type, ratios of water to organic solvent, temperature, and isocratic (ratio vs. gradient to manipulate elution)
The ___ ___ is the part of an HPLC that holds the mobile phase and usually has an inline filter to eliminate debris from the column.
solvent reservoir
The pump in a HPLC system ...
forces the mobile phase into the column. It is the most likely portion to need maintenance
The ___ ___ is the part of an HPLC that is a stainless steel tube(s) packed with the stationary phase that can be polar or non-polar.
analytical column
Three common detector systems for HPLC include MS, ___, ___, ___, and ___ detectors.
UV Spec, Fluorescence, Diode array, and Electrochemical
Compounds detected by HPLC include:
amino acids, anions, drugs, hemoglobin, vitamins, steroids
Name one advantage and one disadvantage to HPLC:
Advantages: nonvolatile, high resolution, and recovery of analyte
Disadvantage: Labor intensive, expensive
The ____ phase plays a larger role in HPLC then in GC.
mobile
What is the most common LC method?
Reverse phase
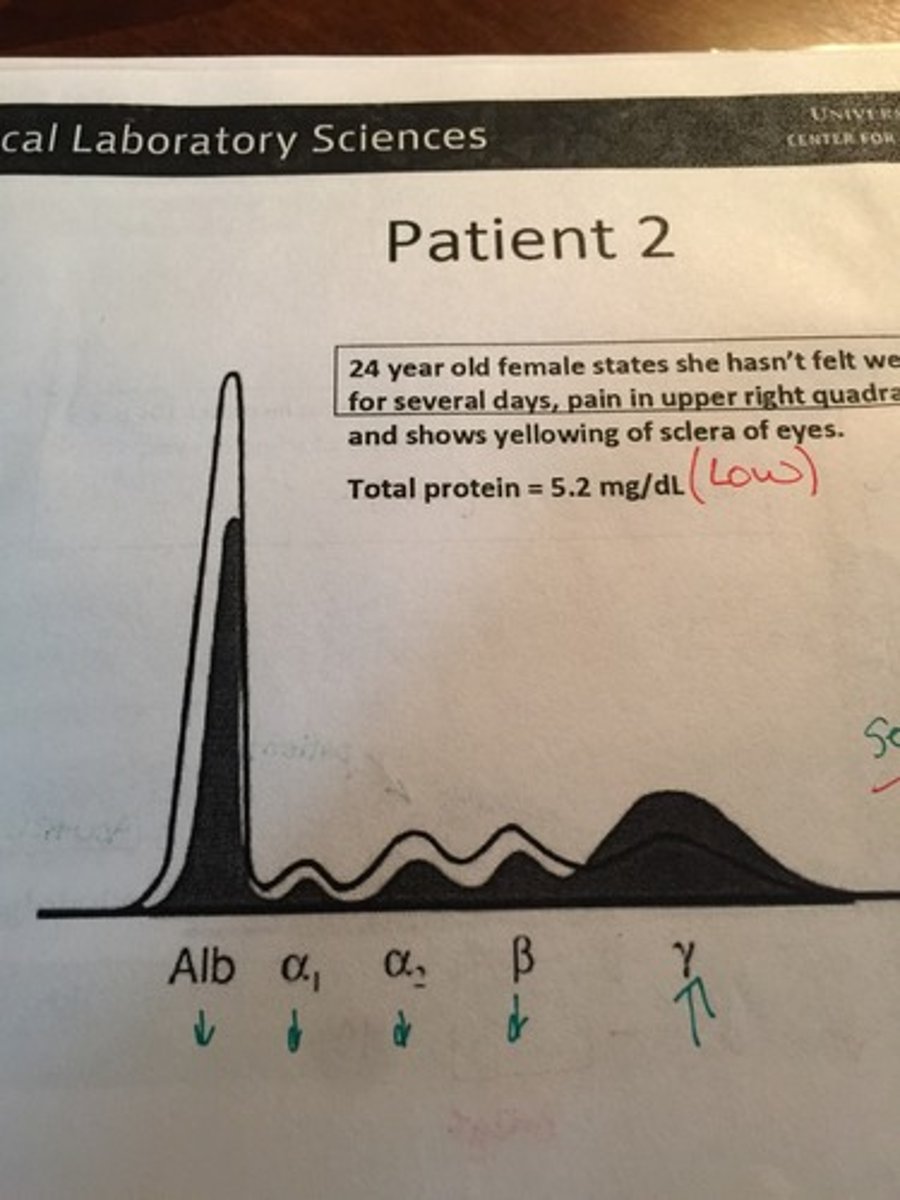
Acute Cirrosis HRE
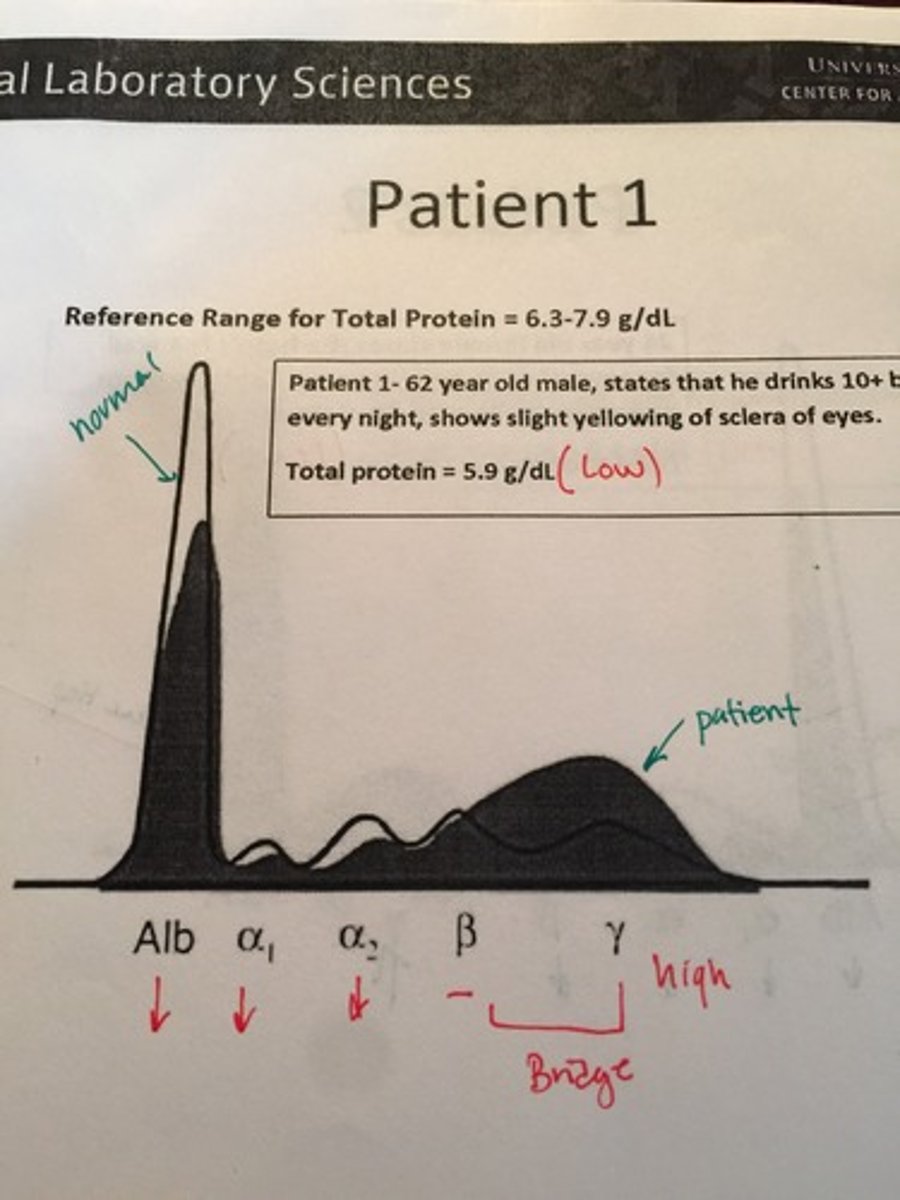
Severe Hepatitis HRE
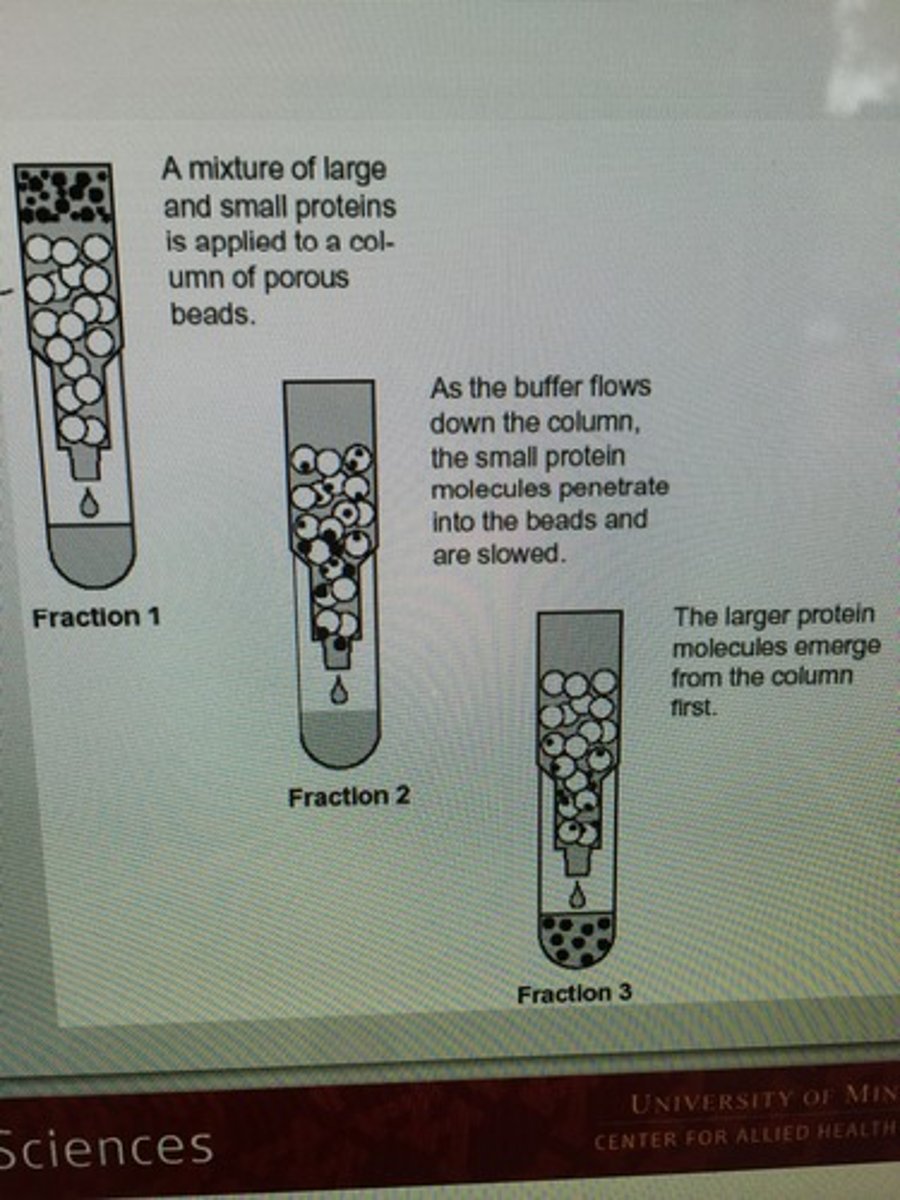
Column bed
The mass of beads packed into the column 'solid phase'
Fractionate
The ability to separate molecules of varying sizes from a mixture
Exclusion limit
The upper limit in size for molecules that cannot penetrate the pores of the beads
SEC Image
In SEC, hemoglobin has a __ color and a weight of __ daltons
Brown, 65,000
In SEC, B12 is __ in color and weighs __ daltons.
Pink, 1,350
The exclusion limit for the hemoglobin/b12 was __ daltons
60,000
Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein that transports oxygen where the central atom is ___.
iron
In the cellulose acetate electrophoresis when the amount of serum was raised 6x, what occurred in the results?
a decrease in resolution of both the densitogram and the acetate strip
Sickle cell anemia is a ___ mutation where glutamic acid is substituted with valine.
point
Vitamin B12 is crucial in brain functioning and is involved in the metabolism of every cell. It contains the metal element ____ centrally.
Cobalt (Co)
B12 is a coenzyme for MUT (Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase) for the TCS cycle (tricarboxylic acid [aerobic]) and MTR (methyl transfer enzyme) (homocysteine to methionine)
True
Ampholyte (zwitterion)
a net neutral charge
If the pH < pI, the protein has a net ___ charge.
positive
If pH is > pI, then the protein has a net ___ charge.
negative
if pH=pI, then the protein has a net charge of ____.
zero
pI=
1/2 (pK1 + pK2)
Henderson Hasselbach Equasion
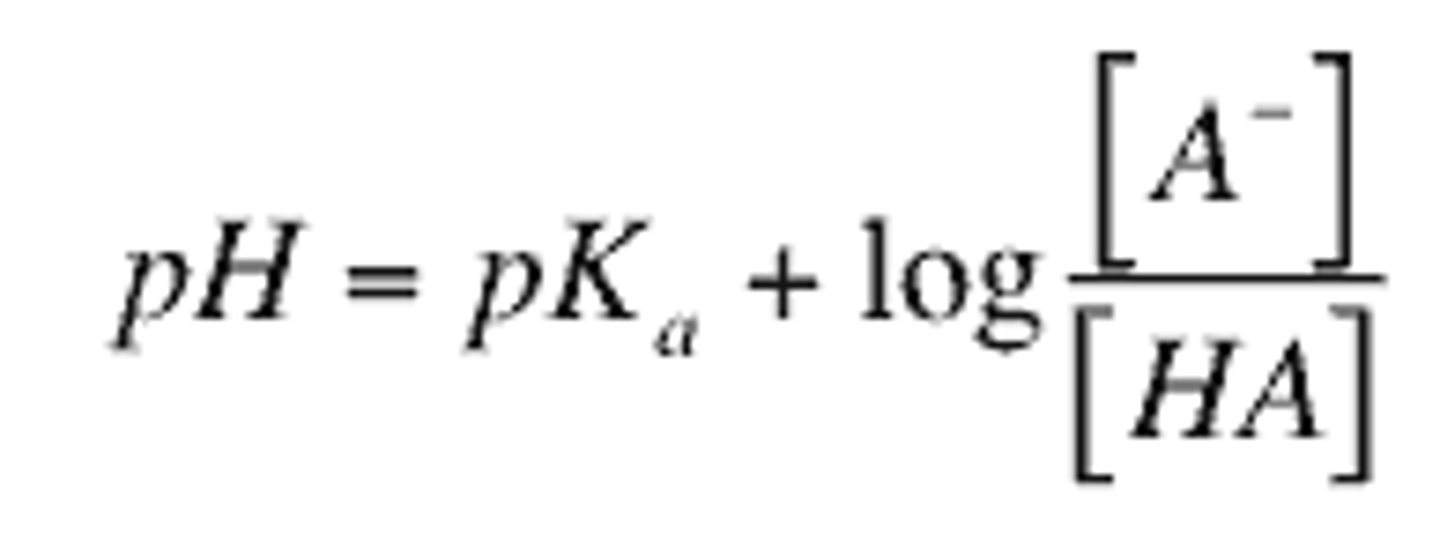
Isoelectric Focusing (gel)
separates proteins based on pI, a pH gradient is utilized by use of small polyanions and cations on opposite sides and the sample is placed in the middle. Proteins separate out on the gel.
Isoelectric focusing is used in the determination of a1-antitrypsin and genetic variants of enzymes and ___.
hemoglobin variants
Abnormal hemoglobin can be separated by varied pI, normal hemoglobin include:
A, A2, F (fetal)
Can urine have a protein pattern done on it?
Yes. as well as CSF
Immunofixation can be done on protein electrophoresis to...
help distinguish an abnormal protein, its done in two stages
Buffer in serum protein electrophoresis need to have on optimal ionic strength (concentration pH 7-9) Why?
Too low and the migration will occur too quickly, causing increased diffusion. Too high and the migration will be too slow, leading to increased resolution
Name three protein SDS troubleshooting issues:
over application, dirty application, electrode placement, buffer issues such as precipitation, no migration
2D Gel protein electrophoresis
Uses two properties of proteins to separate them even more, usually by pI and size exclusion. IEF to SDS
Western Blot is used commonly in the identification of proteins by _____ ____. Its main use is in HIV positive ELISA result confirmation.
antibody specificity
In the Western blot, protein are first extracted and then separated using _____.
SDS-PAGE
In western blot, the sds page gel is blotted onto a ____ membrane.
nitrocellulose
The nitrocellulose membrane in western blot is blocked using...?
milk powder
In the Glucose assay, what was the final product that resulted in a color being produced?
iminoquinone (red-violet color)
A trend in QC is most likely caused by:
a. improper dilution
b.electronic noise
c. miscalibration
d. reagent deterioration
d. reagent deterioration
A calcium standard is incorrectly diluted so that it contains 10.8mg/dL instead of 9.4mg/dL. How would this appear on a LJ plot?
downward shift, all samples would have lower then expected because the standard is lower then expected.
Is the lab accession number the same as a patient ID?
No, it is unique to the lab.
icteric sample
an interfering factor

When is method evaluation utilized in the lab?
when a new instrument is purchased, and when a new testing method is used
What is a recovery study?
When a sample is spiked with an aliquot of analyte to see how much is recovered in the presence of other compounds in a matrix. it is expressed in a percentage (ideal is 100%)
What is the parameter for recovery testing in dilution of the sample?
10%
What is an Interference study?
they are to determine the effect of a specific compound in the assay such as hemolysis, icterus, or preservatives. It is "bias" or the change due to the interference.
What are the three types of testing levels in a medical lab?
Waived (little harm to patient, accurate), Moderate (automated methods), and Highly complex (manual methods and those with complex interpretation)
What are the primary steps and purpose to method selection?
Cost reduction, improved quality and efficiency/ information should be gathered and analyzed such as QC, cost, calibration, etc.
What are the steps to Method evaluation? (2)
1. Analysis of standards and control ranges.
2. precision and accuracy
In a precision study, the controls should be run...
2x2x10 or two controls, twice a day, for ten days
How is accuracy tested in method comparison studies?
Recovery, interference, and COM (comparison of methods)