chemistry
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the key concepts related to atomic structure, including definitions of particles and properties.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Nucleus
The central part of the atom that contains protons and neutrons.
Proton
A positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
Neutron
A neutral particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
Electron
A negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus in electron shells.
Relative Mass of Proton
1
Charge of Proton
+1
Relative Mass of Neutron
1
Charge of Neutron
0
Relative Mass of Electron
Very small (often considered as zero).
Charge of Electron
-1
Volume of Electron Orbits
Determines the size of the atom.
Mass Concentration in Nucleus
Almost the entire mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
Standard Form
A way of expressing very large or very small numbers, such as 1 x 10^-14 m for the nucleus radius.
How to calculate relative atomic mass (Ar)

2 ways to separate soluble solids from solutions
Evaporation and crystallisation
What did Rutherford do
The alpha particle scattering experiment
Group 1 elements
Alkali
Features of alkali metals
Very reactive
Soft and low density
Increase reactivity as you go down
How do u calculate mr
Add up the Ar(relative atomic mass) of each element in the formula
What is the formula triangle
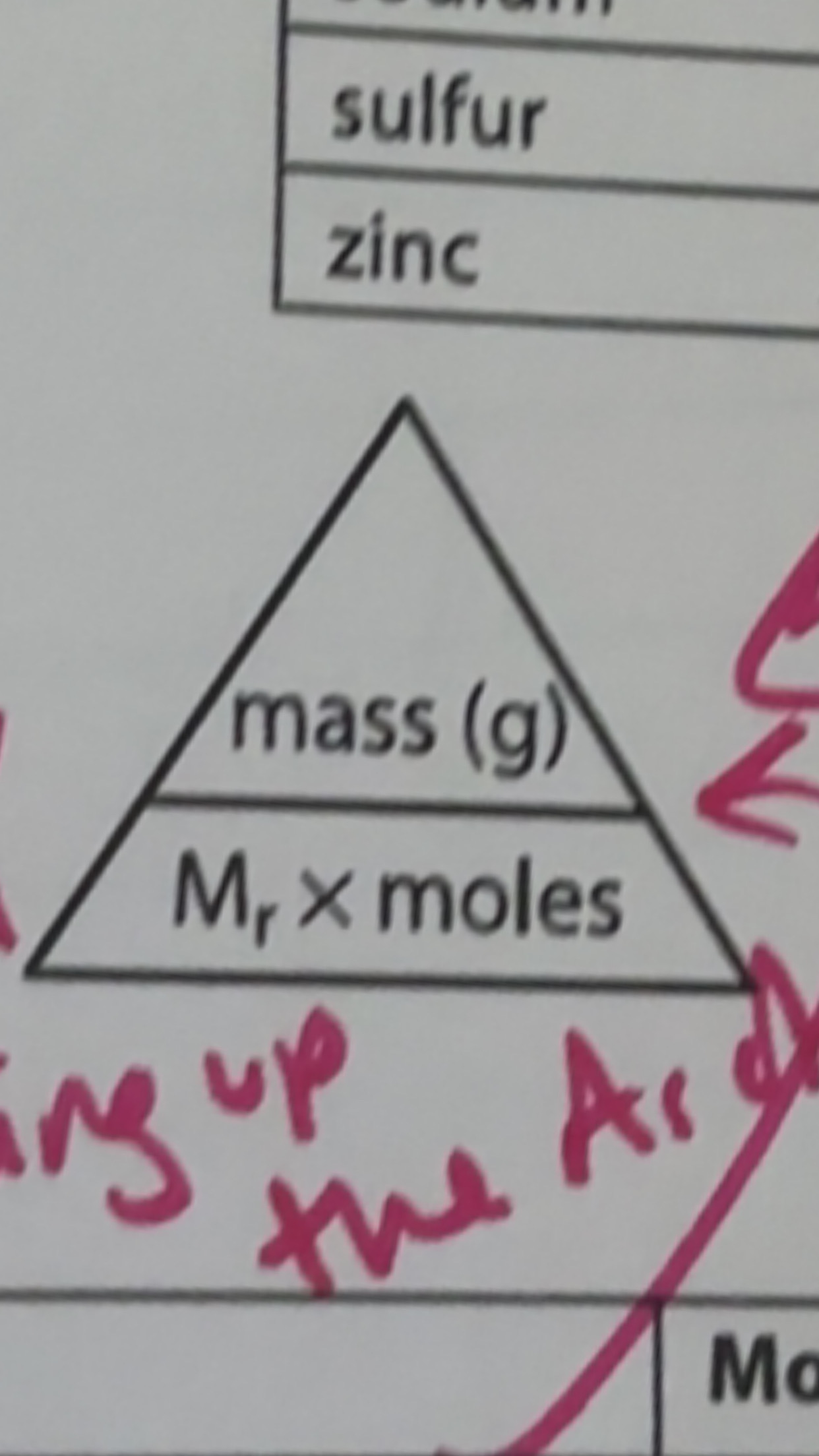
M.E.P.B
methane = c1 ethane=c2 propane=c3 butane=c4
Alkane general formula
CnH2n+2
The shorter the hydrocarbon chain
The more runny , less viscous