Stratified Epithelium
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
stratified cuboidal
lines salivary gland ducts/sweat glands
uncommon types of epithelium (has a very limited distribution)
only 2 layers with a basal layer of cells often appearing incomplete
salivary gland swelling
pathology associated with stratified cuboidal epithelium
clinical condition that can result from blockage of a duct/ducts, so that saliva is not able to exit into the mouth
causes: salivary stone (calculus)- forms from salts contained in the saliva
symptoms: pain when chewing, swelling that worsens just before mealtime, bacteria could grow
sometimes, a small stone may be ejected into the mouth without medical intervention
removal of a stone may require surgery or lithotripsy treatment by focused, high-intensity acoustic pulsing
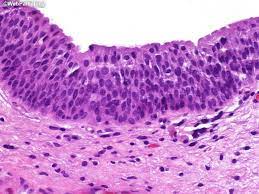
stratified columnar
located in the posterior surface of the eyelid, that is in contact with the surface of the eyeball, is lined by stratified columnar epithelium
also in exocrine glands
not common
trachoma
type of pink eye, stratified columnar in the palpebral conjunctiva of the eyelid
chronic conjunctivitis where the conjunctival epithelium surface suffers from inflammatory granulation caused by bacteria. often presents with keratoconjunctivitis
symptoms: tearing, discharge, photophobia, pain, and swelling of the eyelids, can lead to eye deformities, turned in eyelashes that scrape the cornea. (untreated- ulceration and infection in the cornea may occur which can lead to loss of vision if scarring happens in the center of the cornea)
lymphocytes and macrophages help with inflammatory process in the underlying connective tissue
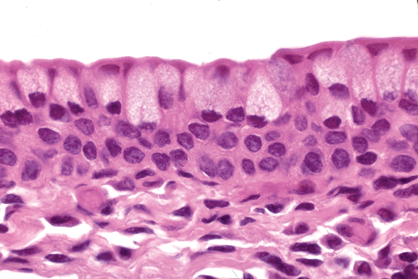
transitional epithelium
has the characteristic of being able to change shape to accommodate a volume change in the organ it lines
relaxed state= 4-6 layers
each surface cell appears umbrella/dome shaped
when stretched, the top dome-shaped cells become flat (squamous) and the epithelium becomes thinner
urothelium
location: kidney renal calyces, bladder, urethra,
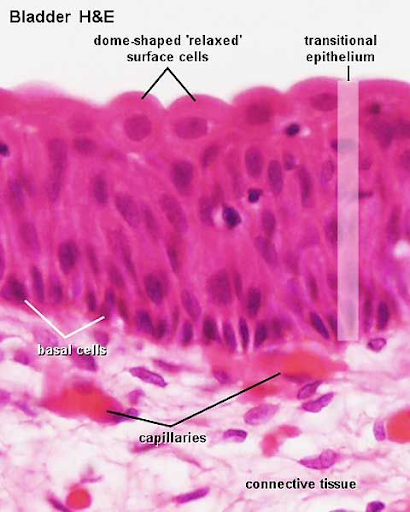
urothelium
the epithelium lining the urinary tract including the bladder, ureter, and major calyces of the kidney
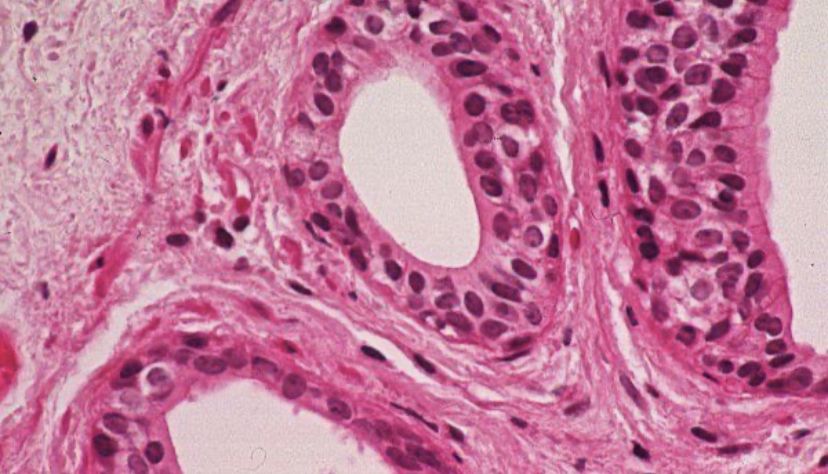
urothelial carcinoma
90%+ of bladder cancers originate in the transitional epithelium in the urinary system (most common is urinary bladder carcinoma)
generally in older men but may occur at any age
risks factors: smoking, exposure to radiation, infection by the parasite (schistosoma haematobium)
symptoms: painless gross hematuria (blood in pee that doesn’t hurt), frequency, urgency, dysuria (pain/burning)
treatment: transurethral resection (through the urethra), chemo, immunotherapy, radical cystectomy (remove bladder completely)
*high reoccurrence rate
cancer
uncontrolled growth, disorganization, lots of mitosis
keratinized stratified squamous
skin
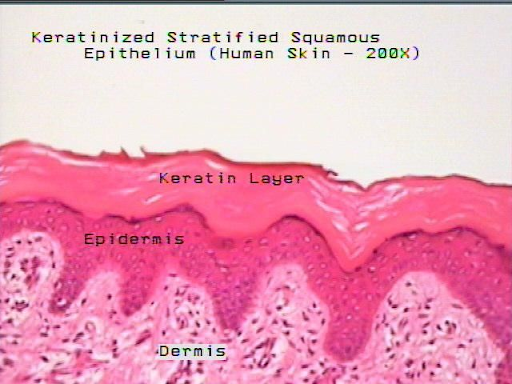
layers of the skin
epidermis
dermis-connective tissue
subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis)- fat cells
2 parts of the skin
skin of the palms and soles (thick skin)
skin on most other body surfaces (thin skin)
histology of the skin
epidermis- stratified squamous
dermis- connective tissue
top layer consists of dead cells (corneocytes) which lack a nuclei
the cells of outer layers of the epithelium are flattened
the middle most basal layers of cells are polyhedral or cuboidal
only cells in the deppest layer are in contact with the basement membrane
the interference between the epithelium and the underlying connective tissue is expanded dermal papille and rete ridges throughout most of the epithelium
psoriasis
pathology of keratinized stratified squamous. common chronic inflammatory skin disease typically chracterized by pink-to salmon-colored plaques with silver scales and sharp margins
symptoms and signs: itching, joint pain, nail pitting, nail discoloration
cause: genetic component, immunologic reactions
pathology: thickened epidermis, extensive overlying parakeratontic scales (keratin on top of epidermis with nuclei), neutrophils may migrate into the epidermis to form microabscesses , neutrophils may also form micropustules
remission, partial remission, chronic
common (3% of population)
can be anywhere
microabsscesses
within the parakeratotic area of the stratum corneum layer
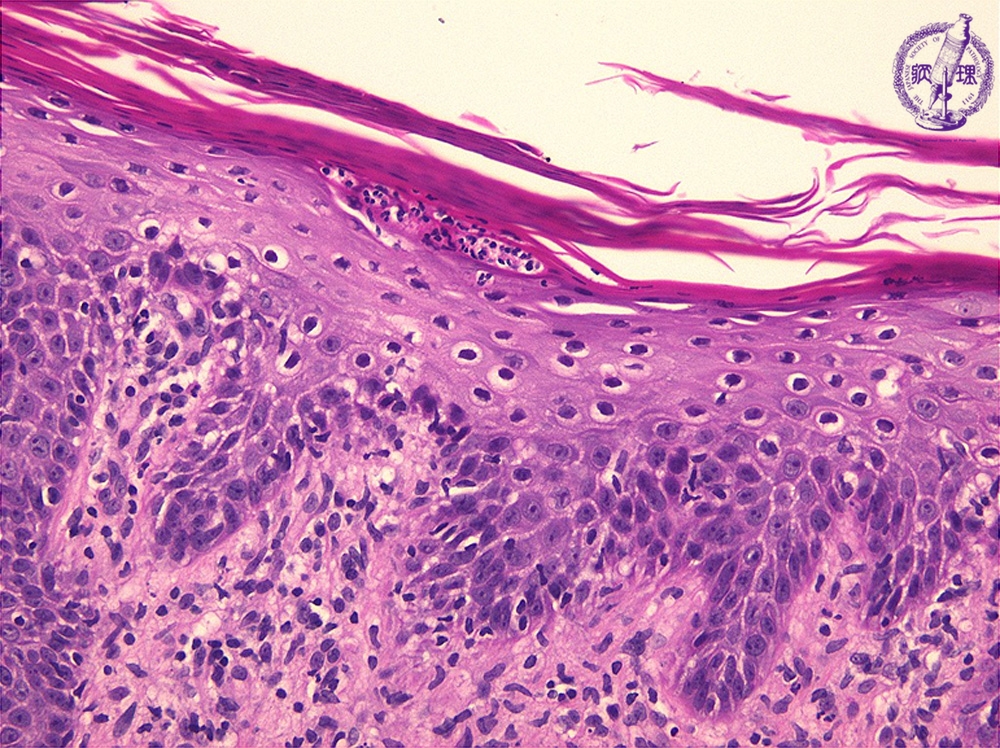
micropustules
located in the stratum granulosum and spinosum layers
bullous pemphigoid (BP)
pathology of kertainized stratified squamous. rare autoimmune skin condition characterized by fluid-filled blisters (bulla). typically affects older individuals
may initially manifest as itchy, scaly lesions in the nonbulbous phase
in the bulbous phase, tense fluid-filled blisters form preferentially on the flexor forearms, inner thighs, and lower abdomen
causes: uncertain, but it appears to be related to radiation exposure, medications, vaccinations
histology: the blister is formed by separation of the epidermis at the subepidermal interface. immunoflourescence microsopy shows linear deposits of C3 and/or IgG in the basement membrane
nonkeratinized stratified squamous
usually wet on its surface
found in the mouth, the oropharynx, the vocal cords, the vagina, and the esophagus
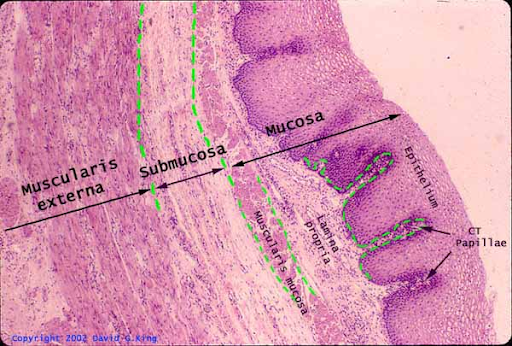
barrett syndrome
condition characterized by the development of intestinal metaplasia where the stratified squamous epithelium is replaced by simple columnar epithelium
causes: patients with long histories of gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) and heartburn
histological features: goblet cells, plasma cells (pink, lots of mitochondria, excentric nucleus, inflammatory cells (lymphocytes and plasma cells))
complications: patients have a high risk of developing cancer of the esophagus
commonly seen in middle aged white men