A Level Physics - Gravitational Fields
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Gravitational field
a field created around any object with mass, extending all the way to infinity, but diminishing as the distance from the centre of mass of the object increases-its a region where an object experiences a non contact force
Gravitational field strength (g)
the gravitational force exerted per unit mass at a point within a gravitational field
Gravitational potential and it's equation
the work done per unit mass to bring an object from infinity to a point in the gravitational field
-in a radial field ( like Earth's) V(grav)=-GM/r
- the GP is negative, you have to do work against the gravitational field to move an object out of it
- the further you are from the centre of the radial field, the smaller the magnitude of Vgrav is
- at an infinite distance from the mass, the gravitational potential will be zero
Units of gravitational potential
Jkg-1
Gravitational potential energy
the capacity for doing work as a result of an object's position in a gravitational field
how does a planet orbiting the sun relate to gravitational potential energy
-if a mass is moved but the distance is kept the same, no work is done against gravity
- this happens when a planet moves around a star in a circular orbit, distance form the sun is kept constant
similarities between gravitational and electric fields
- grav field strength is force per unit mass and electric field strength is force per unit charge
- Newtons' law of gravitation is an inverse square law, as is coulombs law
- field lines for a point mass go towards the centre, as do the field lines for a negative point charge
- grav potencial (Vgrav0 is potencial energy per unit mass, is 0 at infinity, electric potential is potential energy per unit positive charge and is 0 at infinity.
- both have constants, one is very large though and the other is very small
differences between gravitational and electric fields
1) grav fields are attractive, electric fields can be attractive or repulsive
2) objects can be shielded from electric fields, not from gravitational fields
3) size of electric field depends on the medium between the charges, ( e.g. plastic and air) for grav forces this makes no difference
Escape velocity
the minimum velocity at which an object has just enough energy to leave a specified gravitational field
Newton's Law of Gravitation
Force between two particles is proportional to their masses & inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
Newton's law of gravitation equation
F = force between two point masses
M and m = masses
r = separation between masses
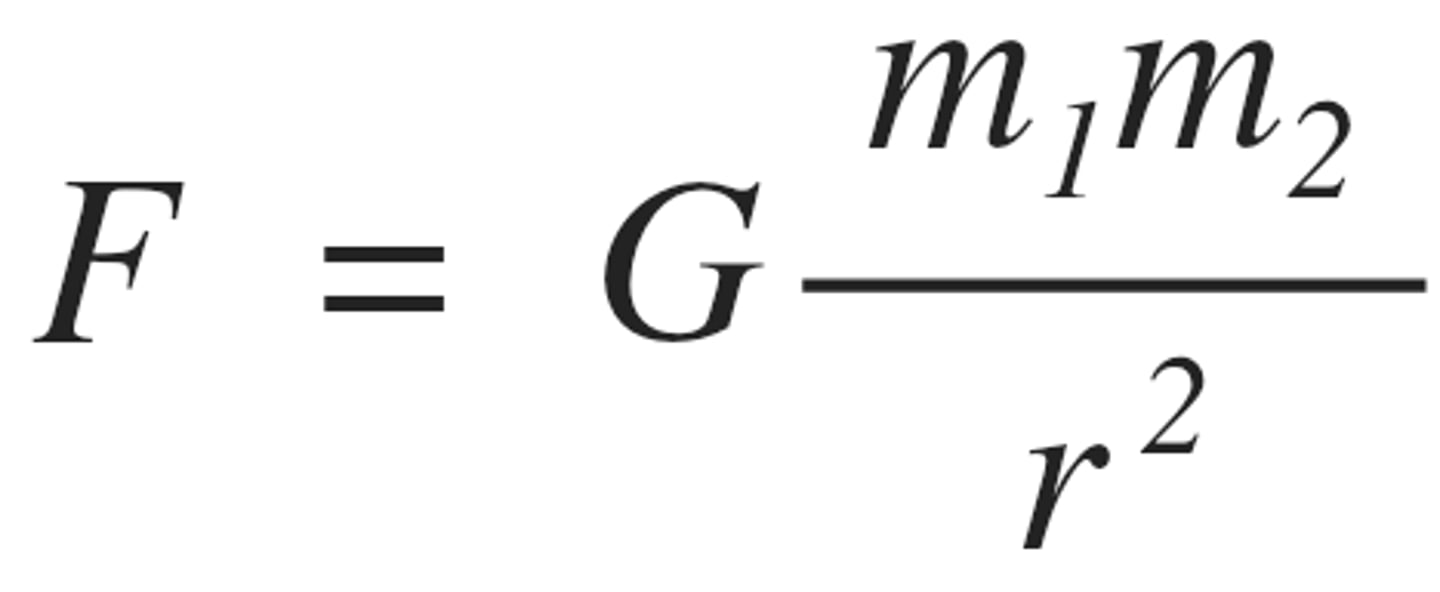
What does the inverse square law state?
if distance increases, then force F will decrease
- if distance doubles, then force will be 1/4 of its original strength
Fα1/r²
Planetary satellite
an body in orbit around a planet
Radial field
a symmetrical field that diminishes with (distance)^2 from its centre
gravitational field strength formula
and formula when you combine it with another
f=m1g + f=Gm1m2/r^2
you get g=Gm2/r^2
this equation works for point masses and for area around uniform spheres
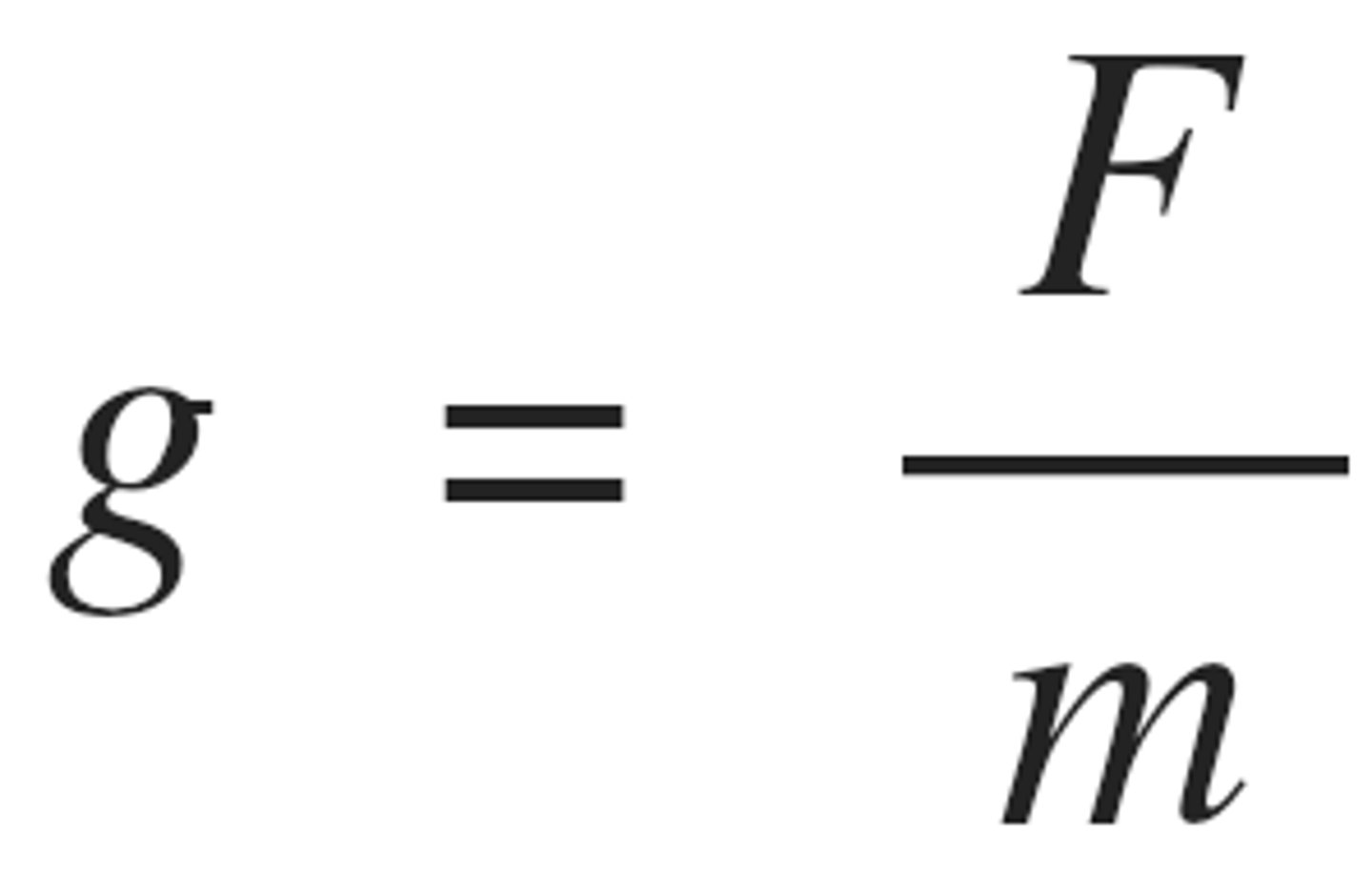
relationship between g and r in the Earth
- at earths centre g=0
g is then proportional to r as distance increases, it is a maximum on the surface, and then slowly decreases above the earth's surface due to the inverse square law
Gravitational field strength units
Nkg-1
What type of quantity is gravitational field strength?
vector
Which direction is gravitational field strength always in?
points towards the centre of mass of the object creating the field
Uniform gravitational field
field lines are parallel and equidistant, this happens on the Earth's surface, they are almost parallel, assume to field is uniform
Gravitational field strength in a radial field
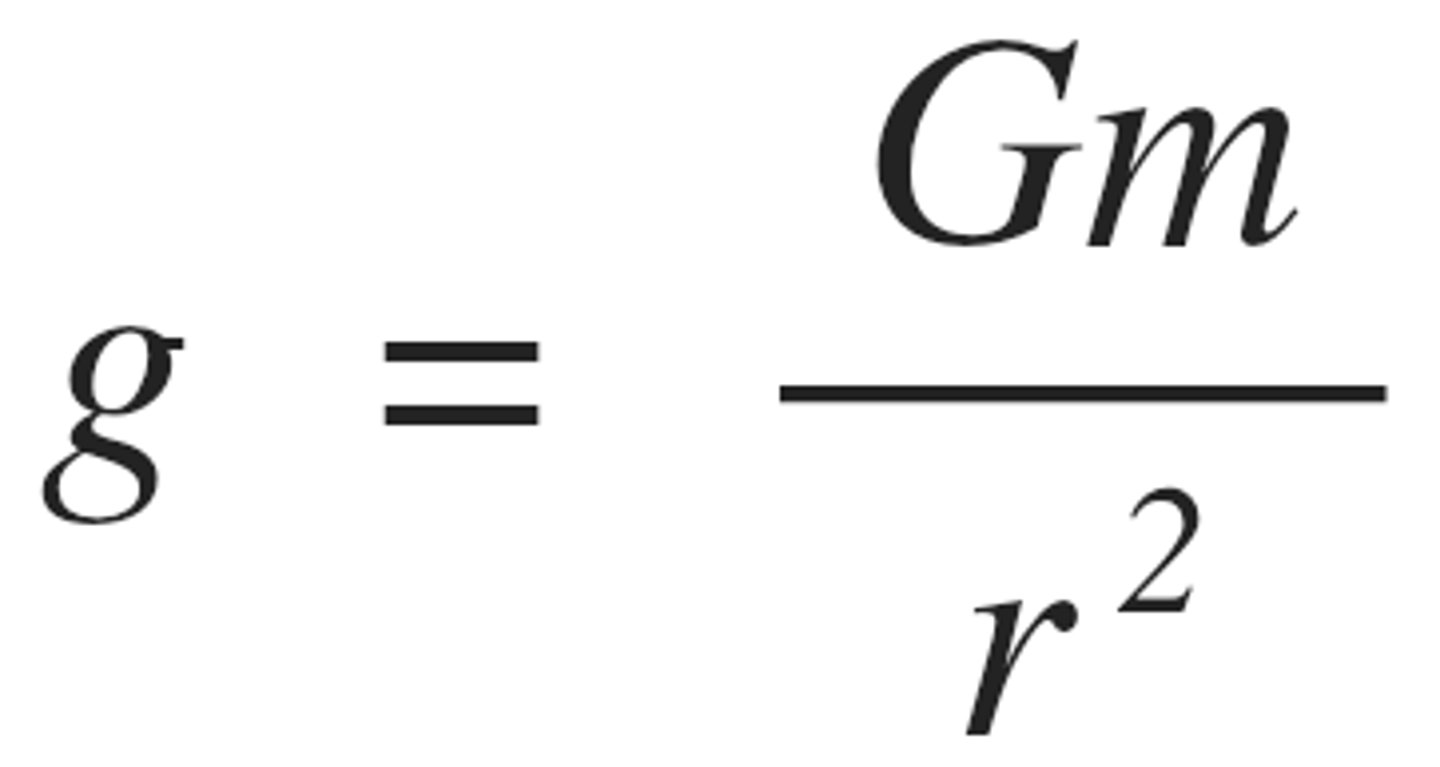
Mean distance between the Earth and the Sun
one astronomical unit (AU)
How do satellites stay the same height above Earth
satellites are always 'falling towards the earth' due to the earth's gravitational attraction. Because the satellite is travelling so fast, as it falls the earth curves away beneath it.
speed required for a satellite to have a stable orbit
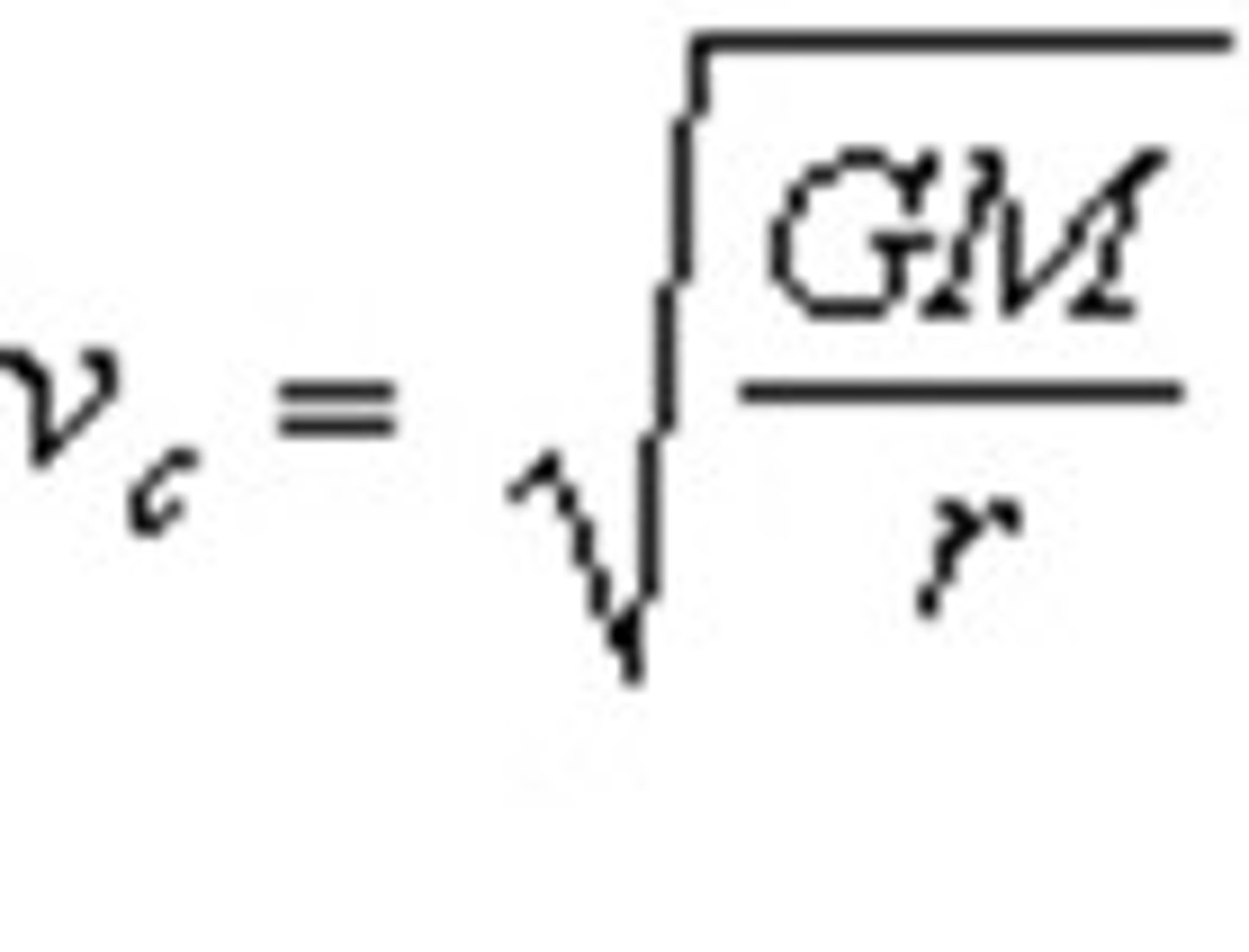
what does speed of an orbit depend on
radius and the mass of the larger body
Uses of satellites
communications (TV)
military
scientific research - looking down at the earth and outwards towards the universe
weather and climate
gps
Geostationary satellites
in orbit above the earth's equator
rotate in the same direction as the earth, stay above the same point on the earth
have orbital periods of 24 hours
how do forces from circular motion relate
F=mv²/r and ω=v/r
this means that ω²=v²/r²
this can be rearranged so that v²=ω²r²
substitute this in to get F=mω²r²/r which gives F=mrω²
whats the equation linking period T with distance, r
T=2π/ω (period taken for 1 orbit) and Gm1m2/r²=m1rω²
cancel m and substitute on 2ω/T
Gm2/r²=r4π²/T²
therefore
T²/r³=4π²/Gm2
in this equation 4π²/Gm2 are constants, so T²/r³ have the same value for all satellites
Polar orbits
offers a complete view of the earth over a given period of time
Why is gravitational potential negative?
gravitational potential is zero at infinity, because it requires no work to bring it from infinity to that position, so all values of gravitational potential are negative
What type of quantity is gravitational potential?
scalar
Gravitational potential energy formula
E = mVg
Escape velocity formula
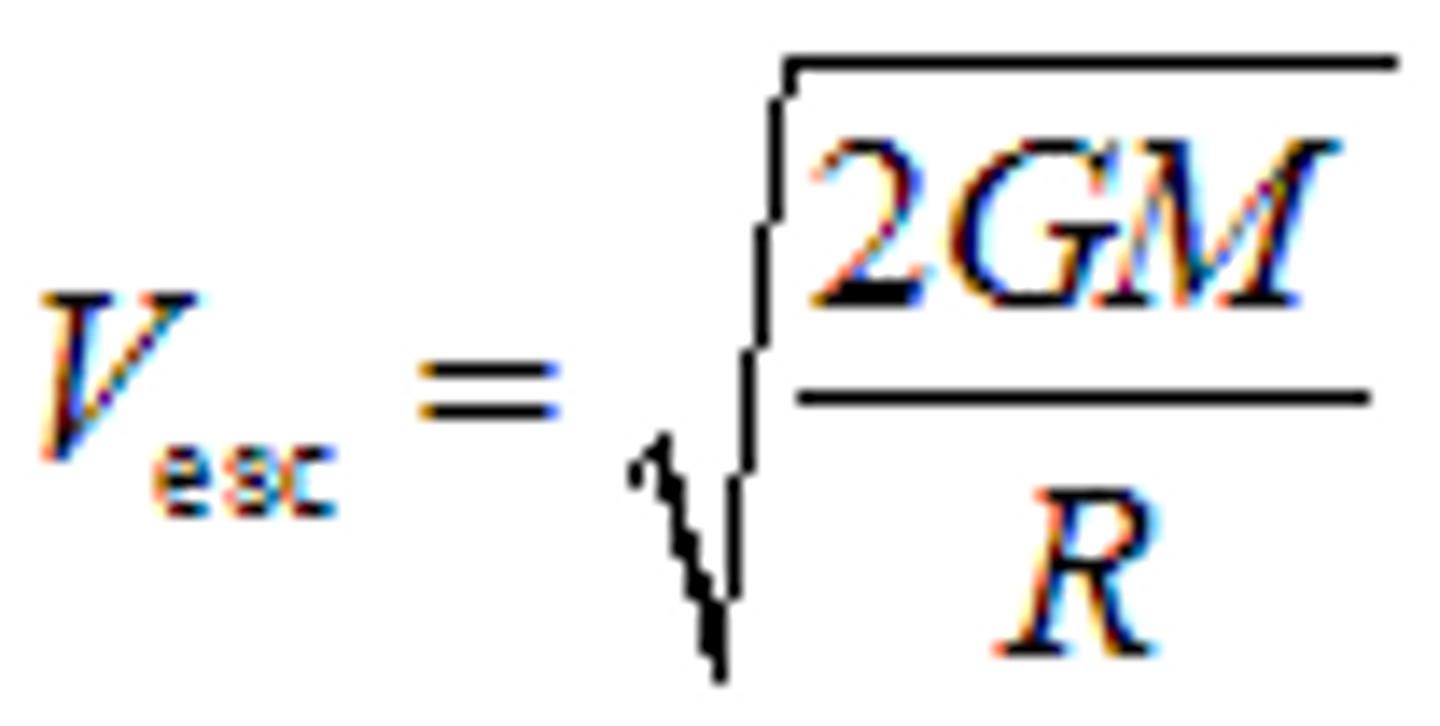
what is a point mass
a theoretical object that has mass but no dimensions, all mass acts at a single point
weightlessness
-astronaut in satellite in free fall, acceleration
towards the Earth is the same as that if the satellite, floor exerts no forces on her. She feels the same sensation of weightlessness as she would in 0 gravity, without actually being weightless
how to derive equation g=Gm/r^2
F=mg and F=Gm1m2/r^2
mg=Gm1m2/r^2
g=Gm/r^2
how do astronauts on the ISS experience weightlessness
-the ISS is in free fall towards the earth's surface
-there is no reaction force o=from the ground on the astronaut because they are falling at the same rate