SPI III- Hemodynamics and Doppler
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Viscosity
A measure of fluid’s resistance to flow
The thickness of a fluid
Unit: poise or kg/m-s
Density
Mass/Volume
Blood is higher than water
Hematocrit
the percentage of volume of red blood cells (most common type of cell)
Normal is 36-50
Intertia
A measure of the resistance to acceleration of an object
Pulmonary system is
to the lungs
Systemic system is to
the body
Cardiac output
the volume of blood that crosses part of the circulatory system per time
The cardiac cycle
controlled by the electrical system at the SA node
Systole, Diastole, EKG
Flow is the result of
pressure differences
Pressure is
omnidirectional
Direction of flow is from ______ to ______ pressure
high, low
If P1=P2 then
no flow/stationary
Pressure gradient equation
change in pressure/ length
Volumetric flow rate (Q)
Flow is quantified by the volume that passes by any given point per time
Volumetric flow rate equation
Q= Delta P/ Resistance (R)
Volumetric flow rate/ poiseullie’s law only applies to
straight rigid tubes
Resistance
the opposition to flow
is controlled by arteroiles
Resistance equation
R= 8L(visosity)/ Pie(r4)
Poiseuille equation
Delta P (pie) (r4)/ 8L*viscosity
The vascular system is a ______ system
closed loop
The total CSA increases toward the periphery thus
decreasing velocity in the distal vessels
Doppler provides information about
presence, direction, speed and character
Shift and velocity are directly
porportional
As the doppler angle increases, the % of error in speed _______ with each degree of angle degree error
increases
Flow
the movement of a fluid from one location to another
Classifications of flow
temporal and spatial
Steady flow
fluid that moves at a constant speed or velocity
blood through arterioles, peripheral veins
temporal
Pulsatile flow
non-steady flow with acceleration and deceleration over the cardiac cycle
moves with a variable velocity
blood through arteries, SVC, IVC
Acceleration
occurs during early systole when the ventricles are rapidly ejecting blood
deceleration
occurs during late systole
tends to uniformly slow down
Two major characteristics of pulsatile flow
flow reversal
windkessel effect
Compliance
expansion and contraction of the vessel
A compliant vessel….
expands with increase pressure which expands it volume
then it recoils when the pressure drops later in the cardiac cycle
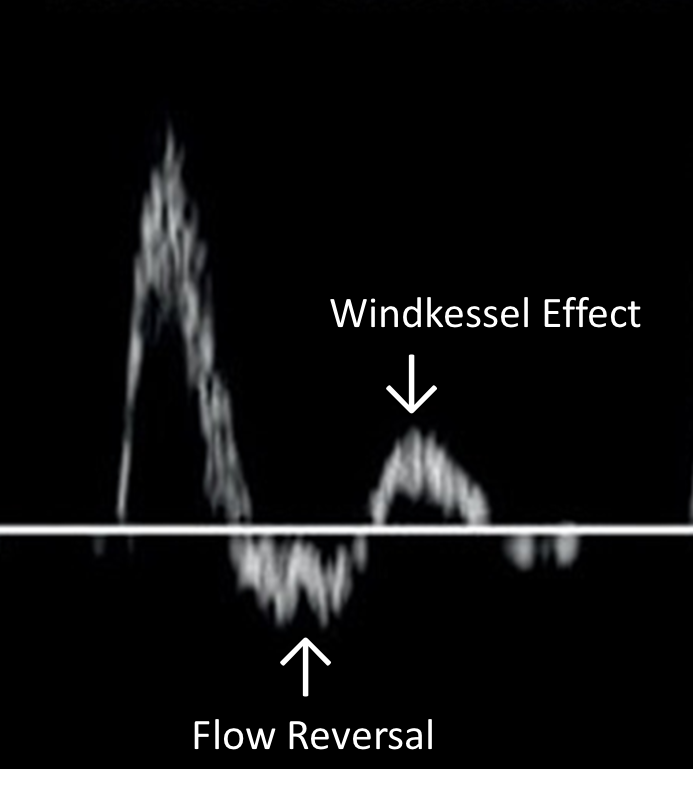
Windkessel effect
the contraction (recoiling) of the compliant vessel then increases the upstream pressure and adds forward flow later in the cycle
Flow reversal
the expansion of elastic vessels leads to this during diastole as the pressure distally overcomes the pressure upstream because of the heart relaxing
Laminar flow
made up of layers that travel at individual speeds
streamlines are aligned and parallel
plug flow
the majority of fluids travels at the same speed
occurs at the entrance to a vessel
similar to the motion of a solid object that moves as a unit
parabolic flow
average velocity = ½ max velocity in the center of the vessel
laminar flow close to vessel wall
low velocity
center of lumen for laminar flow
highest velocity
disturbed flow
streamlines persist, but waver and vary
irregular pattern which is oscillatory
causes of disturbed flow
increased velocity
altered vessel geometry
turbulent flow
chaotic flow in many directions and speeds, streamlines are obliterated
flow energy converted to sound (murmurs, bruits) or vibration (thrill)
Reynold’s number
The likelihood of turbulence
A Re above _____ indicates turbulent flow
2000
At the origin of a vessel,
plug flow appears
when a vessel suddenly widens, the fluid
falls toward the new vessel boundary
results in flow reversal in the small region at the vessel expansion
Eddy current
rotational motion from turbulent flow
referred to a mosaic color doppler pattern
commonly occurs distal from a stenosis
lower velocity than in stenosis
Tapering vessels
blunted or flattened flow
most of blood cells travel at the same velocity, regardless of their position within the vessel
Diverging vessels
elongated flow profile
lamina spread out
flow is likely to destabilize
results in disturbed or turbulent flow
What is the primary vessel of systemic circulation
aorta
Vessel compliance ensures
forward flow
the energy and pressure drop from the aorta to the distal end of the arteries is normally quite small. this indicates that the resistance to flow in these vessels is
low
A low change in pressure means
low resistance
Arterioles are considered
regulators of flow
Pulsatile flow patterns are abolished in the arterioles the pattern is converted to
steady flow
The highest pressure drop is at the level of
arterioles
Pressures at the same location on the right and left sides of the body should be
similar
severity of disease is not typically
symmetrical
During periods of increased flow, such as exercise, the pressure drop across the ____ diseased segnemtn can become
mildly, noticeable
Why ankle-brachial indices are often taken with and without exercise
Severe arterial disease
can typically be diagnosed at rest
because the obstruction offers a high resistance to flow the pulsatile nature of the pressure wave is diminished downstream from the obstruction
Peripheral resistance
in a rigid straight tube, the volume of liquid inserted into one end is immediately expelled at the other end
Flow patterns with high peripheral resistance
energy stored in the distended artery is unable to overcome the high resistance downstream
triphasic flow patterns may result
Flow patterns with low resistance
energy stored in the distended artery overcomes the low resistance downstream
forward flow occurs throughout cardiac cycle
Critcal stenosis
a partial obstruction that decreases both pressure and flow
90% reduction in large arteries
Occlusion
complete blockage of a vessel without any flow around it
Factors that determine the hemodynamic effects of arterial obstruction
length and diameter of narrowing
endothelial surface (rough or smooth)
gradual or abrupt narrowing
% area reduction of orifice
flow through the obstruction
arterial-venous pressure gradient
peripheral resistance distal to stenosis
Continuity rule
blood is neither created nor destroyed as it flows through a vessel
Volumetric flow rate must be constant proximal, within and distal to a stenosis
Turbulence can occur _____ to a stenosis
distal
continuity rule equation
Qp= Qs= Qd
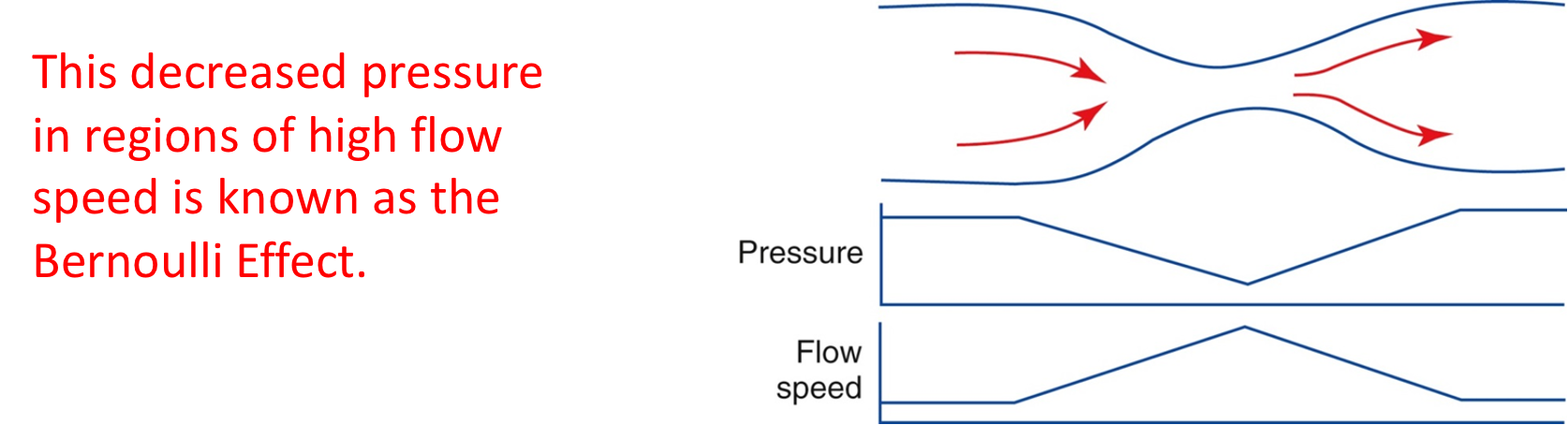
Bernoulli effect
to maintain flow continuity, flow speed must increase through a stenosis
to allow fluid to accelerate into the stenosis there is a
pressure drop
Pressure and velocity are _______ related
inversely
The decreased pressure in regions of high flow speed is known as the
bernoulli effect
Effects of stenosis: upstream
triphasic patter
plug flow
may demonstrate high resistance waveform
There may be some turbulence
Effects of stenosis: within lesion
elevated flow velocities
decrease in pressure
possibility of some turbulence
Effects of stenosis: downstream
dampened pattern
loos of pulsatility
delayed upstroke
loss of triphasic
spectral broadening
murmurs or thrills
turbulence with flow reversal or eddies
may demonstrate low resistance
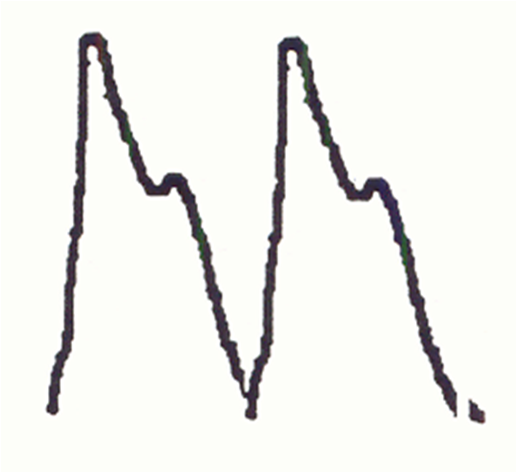
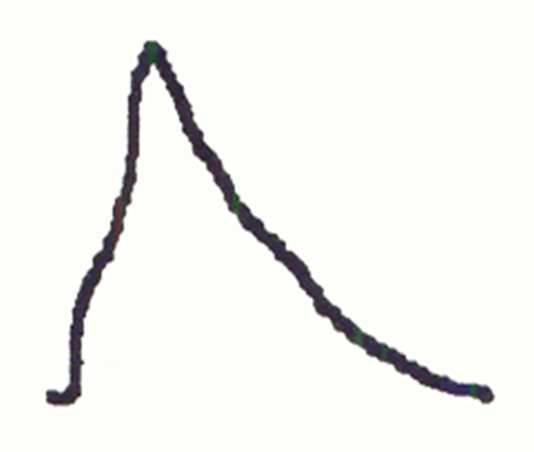
Normal tracing
rapid upstroke, sharp peak, prominent dicrotic notch

mildly abnormal waveform
rapid upstroke, sharp peak, absent dicrotic notch, bowed downslope.

Moderately abnormal waveform
flattened peak
upslope=downslope
absent dicrotic notch

Severely abnormal waveform
low amp
loss of pulsatility
venous circulation is normally affected by
respiration
flow direction is from
superficial to deep
venous pump
return of blood from legs to heart is facilitated by compression of the veins by leg muscles
flow in the arteries equal
flow in the veins
pressure drop from the aorta to the distal arteries is the same as that from the
veins to the right atrium
continuity rule
transmural pressure is the pressure
across the vessel wall
Hydrostatic pressure
the weight of blood pressure against the vessel walls
comes from gravity
same for adjacent arteries and veins
Hydrostatic pressure is equal to the weight of the column of blood from
the heart to the point of measurement
In a supine patient
hydrostatic pressure is 0
no column of blood
Pressure at the ankle equals
circulatory pressure plus the weight of blood pressing on ankle
Hydrostatic pressure below the heart
pressure positive
measured pressure will be higher than true circulatory pressure
Hydrostatic pressure above heart level
is negative
pressure is decreased counter-acting gravitational forces
measured pressure will be lower than the true circulatory pressure
During inspiration
diaphragm pressure into abdomen
pressure in abdominal cavity increases
pressure in thoracic cavity decreases
results in increased flow from abdomen to chest
during expiration
diaphragm presses into the thorax
pressure in the thorax increases
pressure in the abdomen decreases
results in decreased flow from the abdomen to the chest
Incompetent valves
allow blood flow backward from the heart woard the periphery
Deep vein thrombosis
venous stasis can cause the blood to clot resulting in partial or complete obstruction of the vein
Edema
accumulation of abnormally large volumes of fluid in the intracellular spaces of the body
Arteriovenous fistula
a direct connection between an artery and vein
low resistance pathway
Pesudoaneurysm
vessel wall ruptures resulting in extravascular blood collection
usually because of trauma
ying yang doppler appearance