BU3 - Lighting Intro, Definition of Terms, Physics of Light
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Luminous Flux
Measure of total perceived power of light
Lumen
SI Unit of Luminous Flux
Color Rendering Index
CRI stands for?
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
A quantitative measure of the ability of a light source to reveal the colors of various objects faithfully in comparison with an ideal or natural light source
100
CRI Range of Incandescent Light
Correlated Color Temperature
CCT Stands for?
A specification of the color apperance of the light emitted by a lamp, relating its color to the color of light from a reference source when heated to a particular temperature.
Correlated Color Temperature
Illuminance
Total amount of luminous flux on a surface, per unit area. It is a measure of how much the incident of light illuminates the surface.
Lux
SI Unit of Illuminance
Contrast
The difference in luminance or color that makes an object (or its representation in an image or display) distinguishable
True
True or False: Contrast is a fundamental element of interior design because it adds visual interest to a space that makes it striking and dynamic.
Glare
A phenomenon caused by extremely bright light sources or by strong brightness contrasts in the visual field.
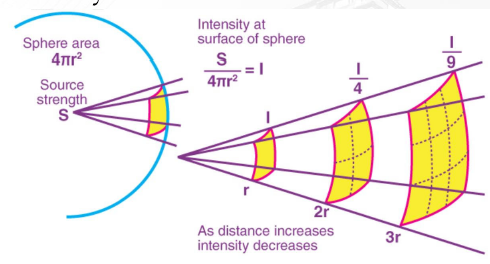
Inverse Square Law
Light loses its brightness or luminosity as it moves away from the source.
Luminescence
Emission of light by certain materials when they are relatively cool ; The practical value of luminescent materials lies in their capacity to transform invisible forms of energy into visible light.
Fluorescence
Producing light from gaseous discharge
Phosphorescence
Organic fluorescent material which retains the radiant energy
Electroluminescence
Conversion of electric energy to light
Absorption
When a light beam passes through a transparent or transluscent medium
Reflection
The phenomenon in which light travelling in one medium, incident on the surface of another returns to the first medium
Specular Reflection
When any type of material has a polished surface, the light will be reflected at an angle equal to the angle of incidence
Diffuse Reflection
When the material has an unpolished surface, the reflected light is spread in all directions by multiple reflections on the unpolished surface
Spread Reflection
When the reflecting surface is not smooth, it spreads parallel rays into a cone of reflected rays
Compound Reflection
Reflector material that exhibit all the three types of reflection components to varying degrees
Transmission
When light falls upon a transparent material it is transmitted through it refracted (bent) as it enters the material, but emerges at the same angle that it entered.
Diffusion
Breaking up beam of light and the spreading of its rays in many direction by irregular reflection and refraction
Refraction
Change in the speed of light as it travels from one medium to another and there is a bending of the ray of light
Interference
Modification in the intensity of light due to redistribution of light energy in the region of two or more light waves
Diffraction
Bending light around small obstacles and hence its encroachment into the region of geometrical shadow