Exercise 33- Human Cardiovascular Physiology- Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
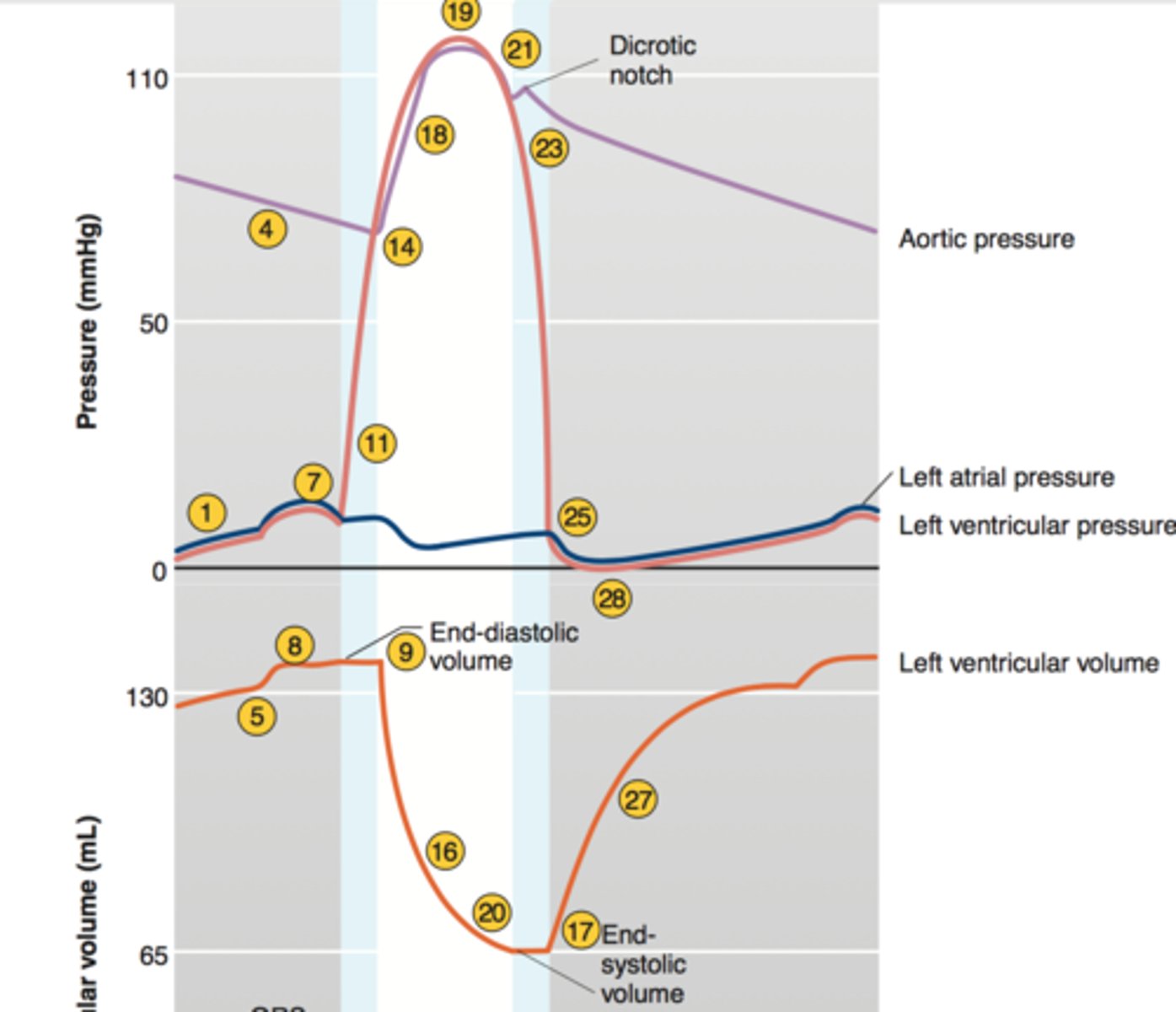
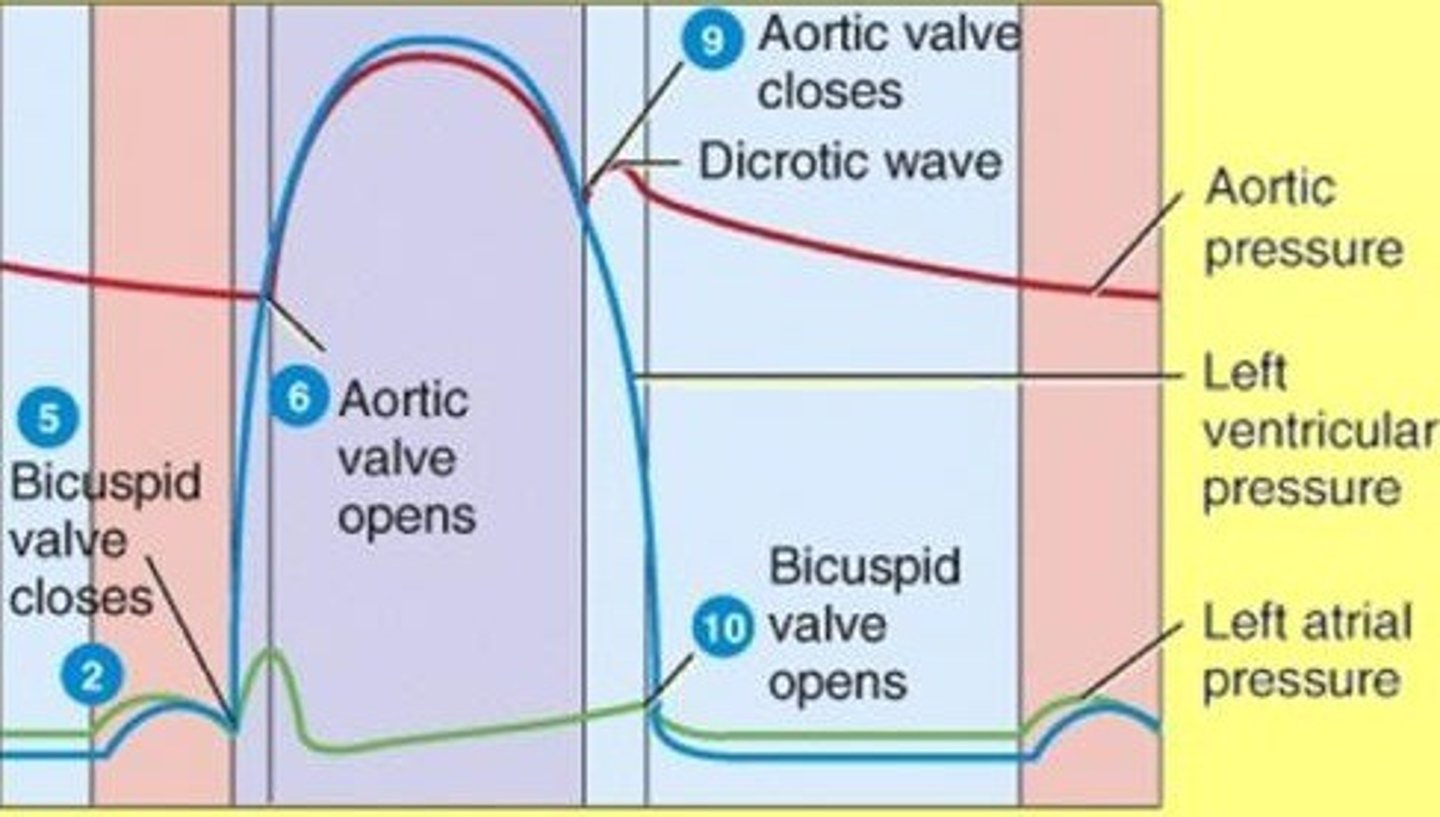
aortic pressure
second red line
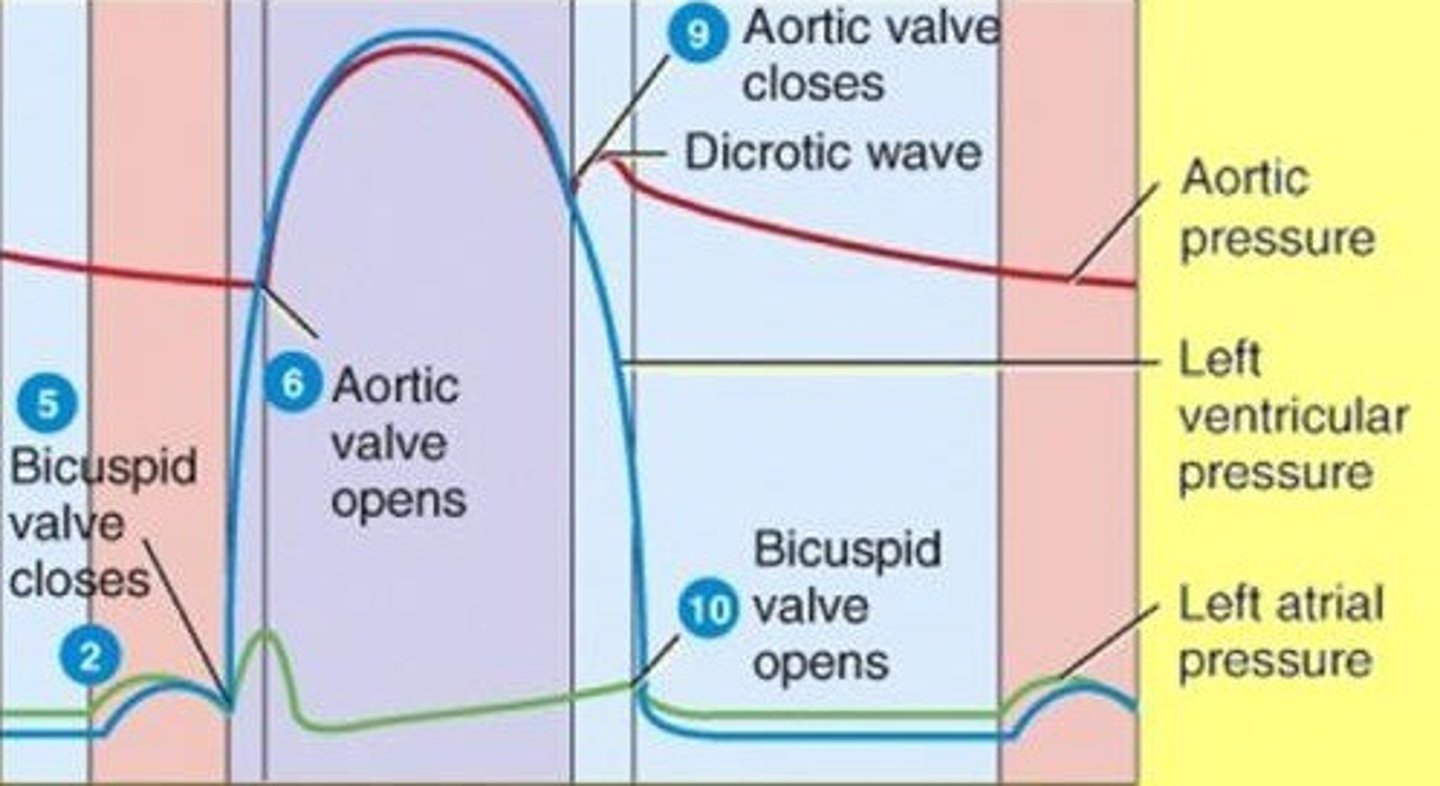
atrial pressure
dark blue line
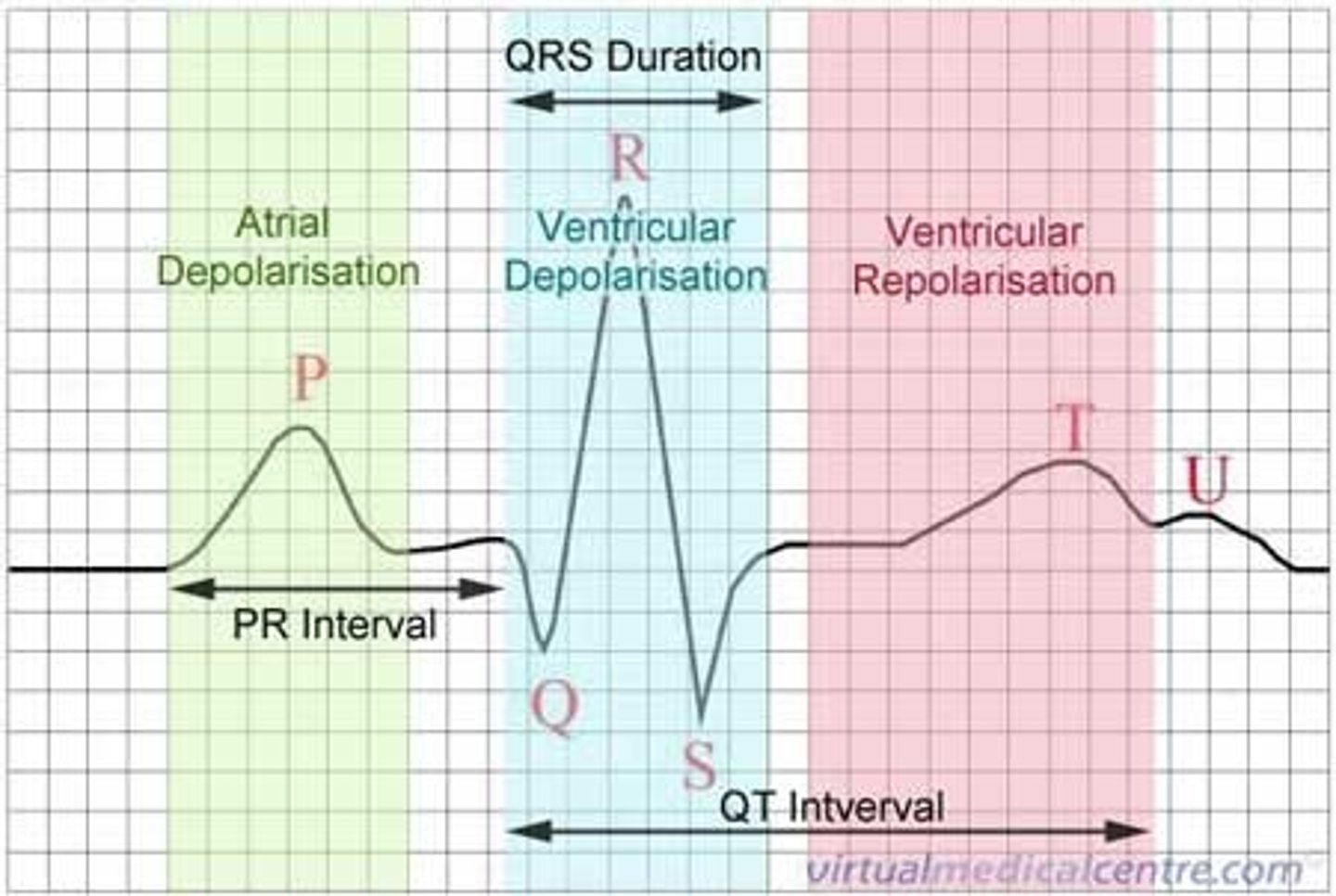
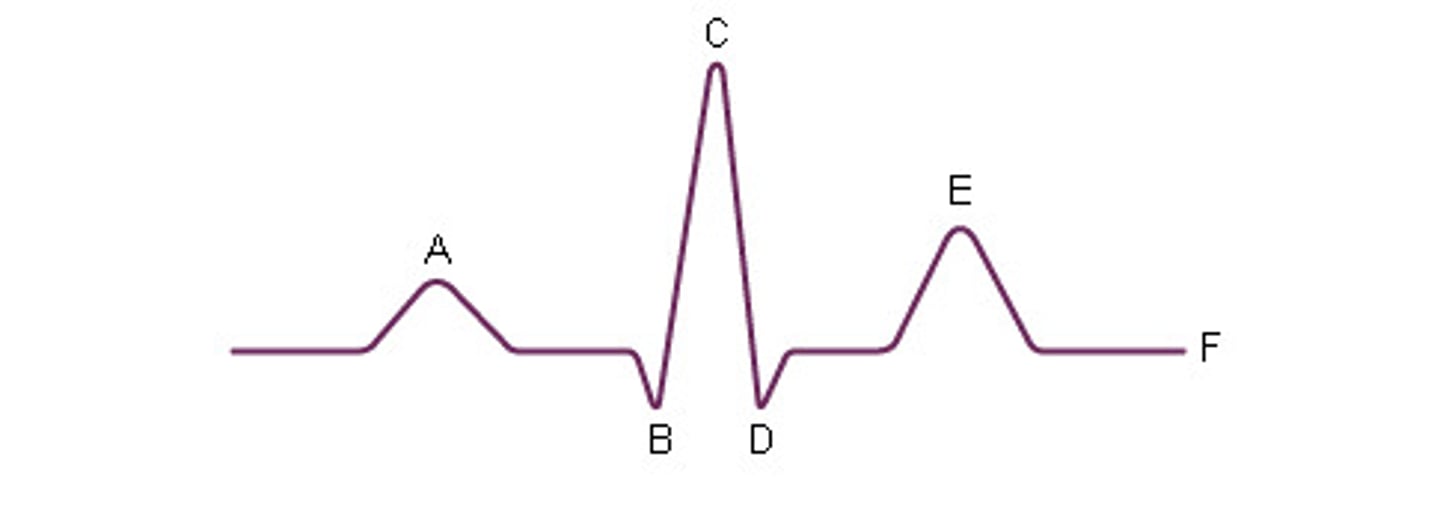
ECG
first heart sound
QRS
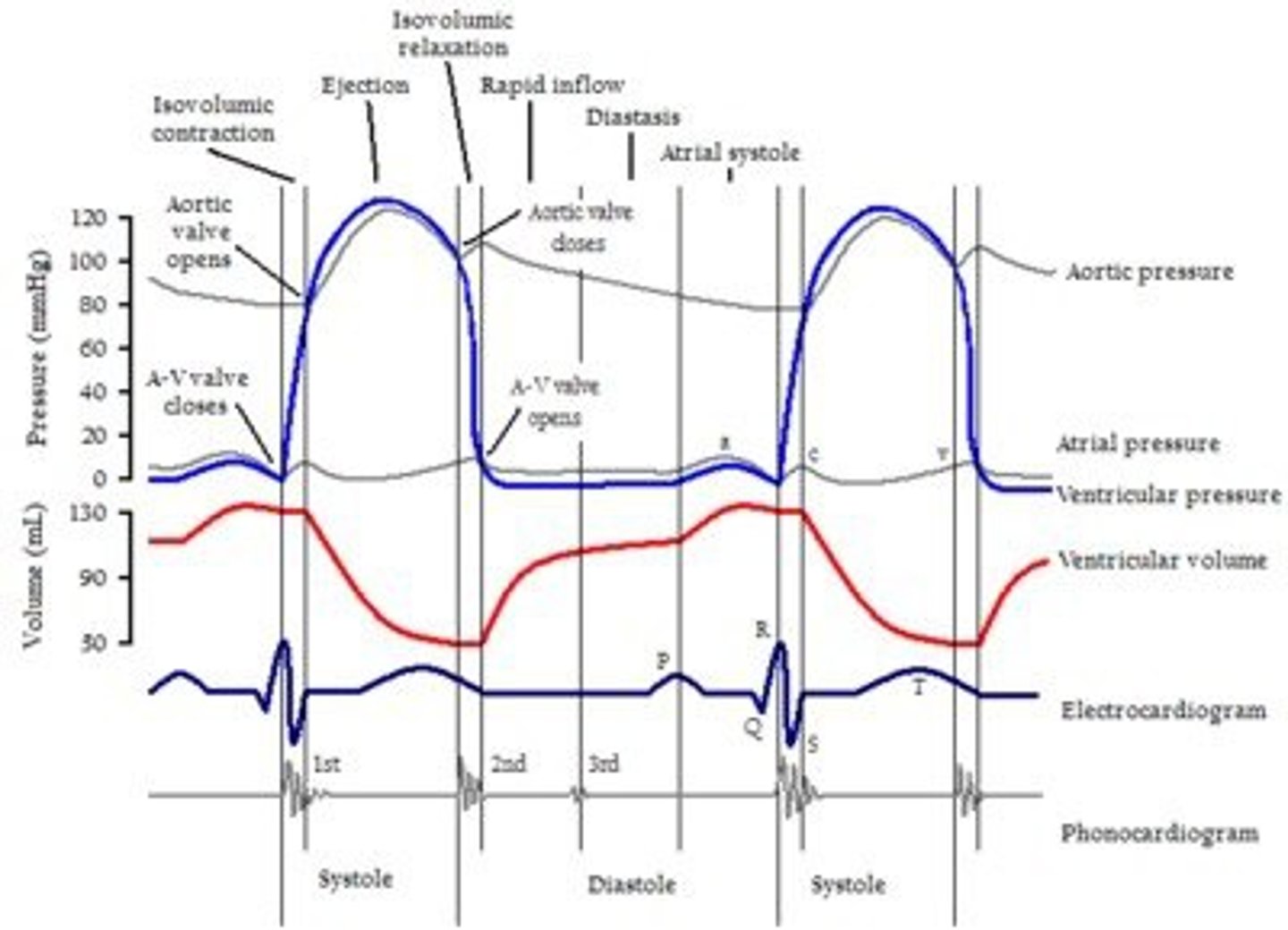
second heart sound
after T
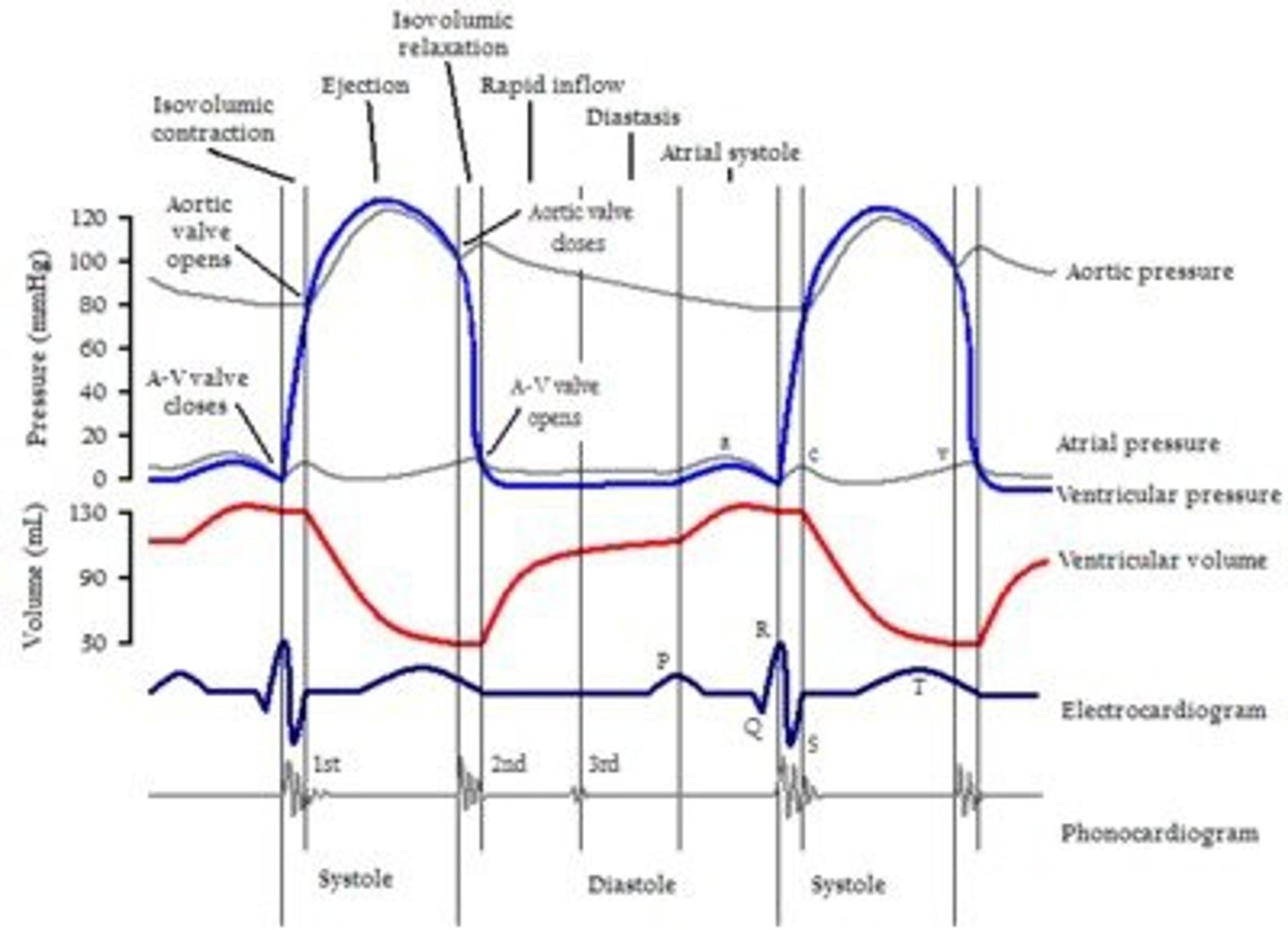
ventricular pressure (left)
(falling blue line)
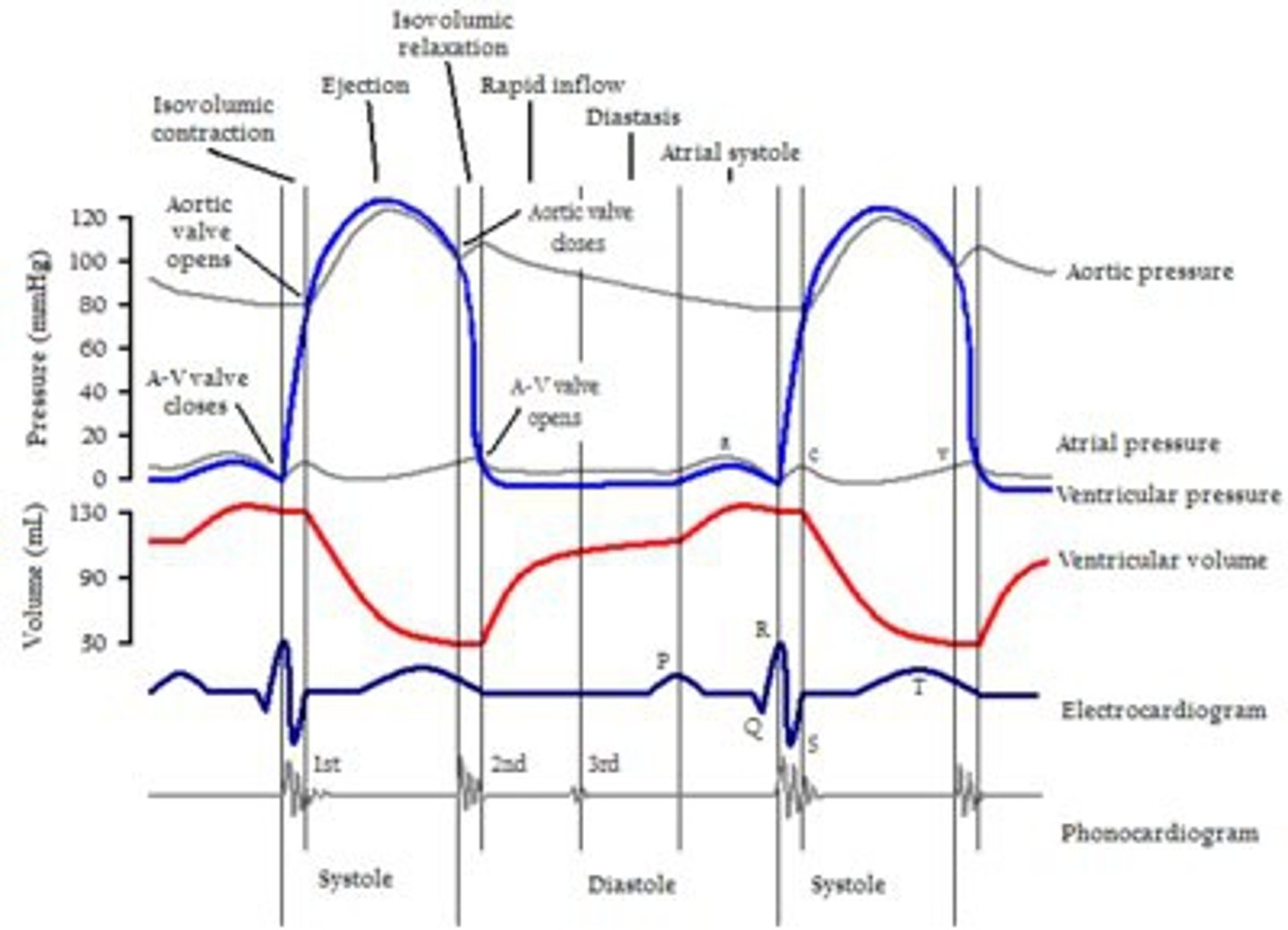
ventricular volume
(blue line)
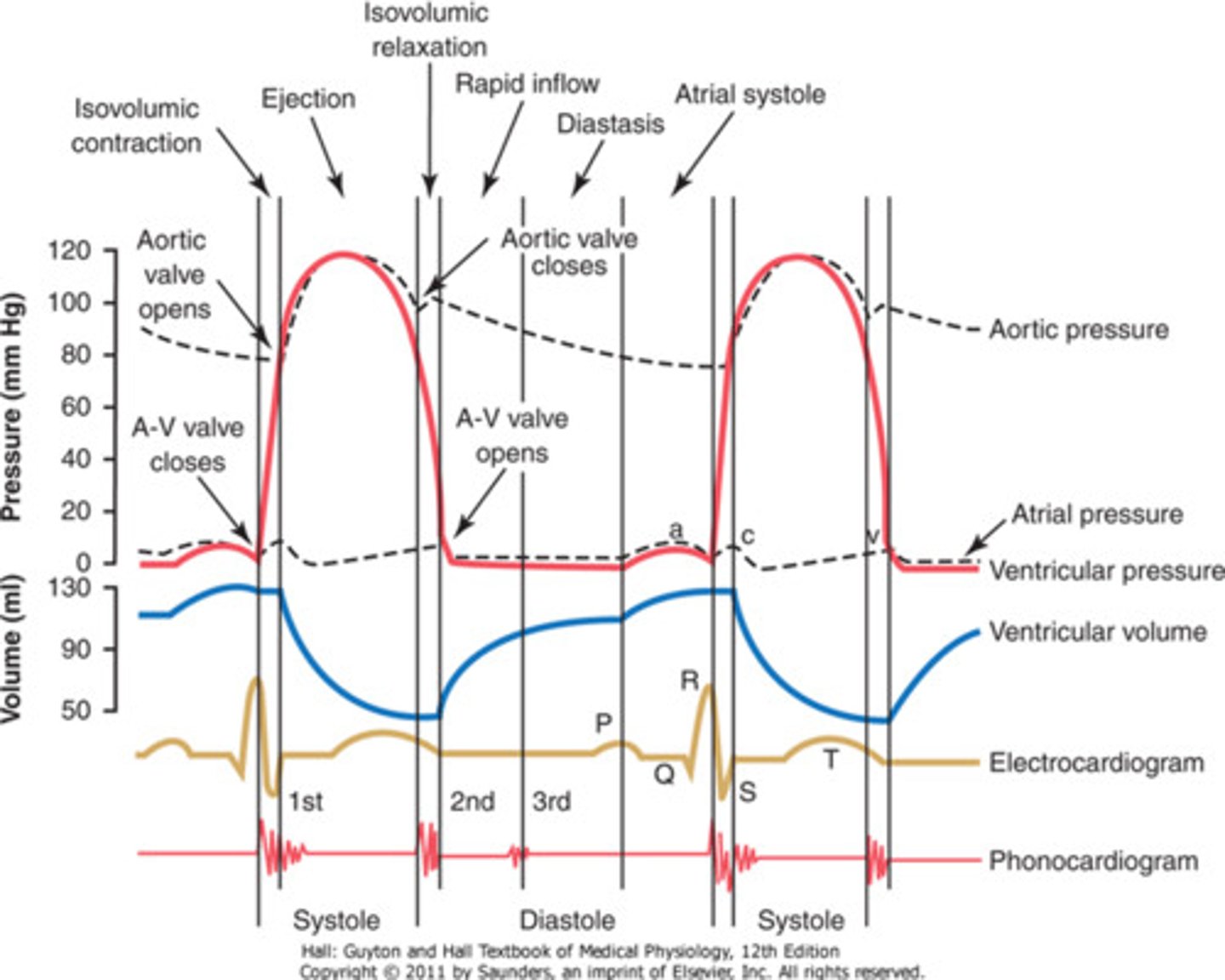
aortic semilunar valve closes
E
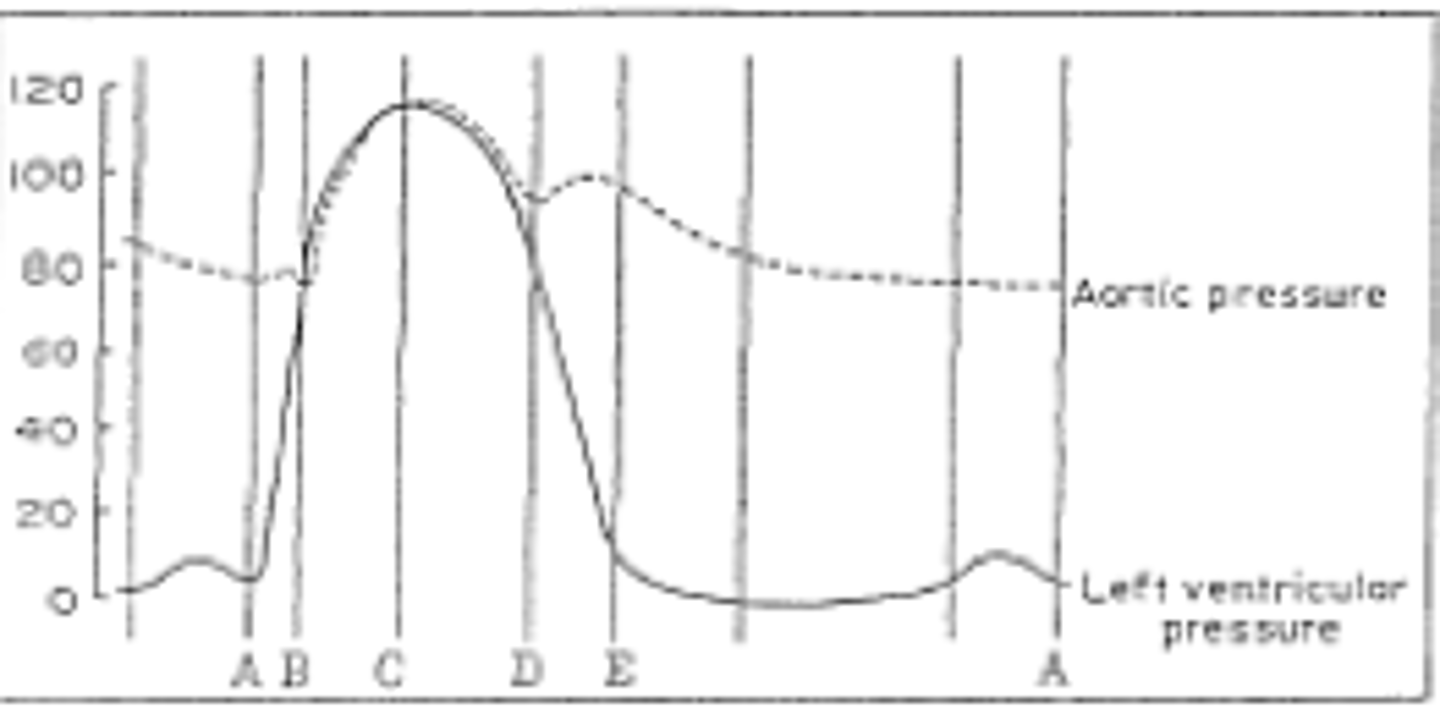
aortic semilunar valve opens
B
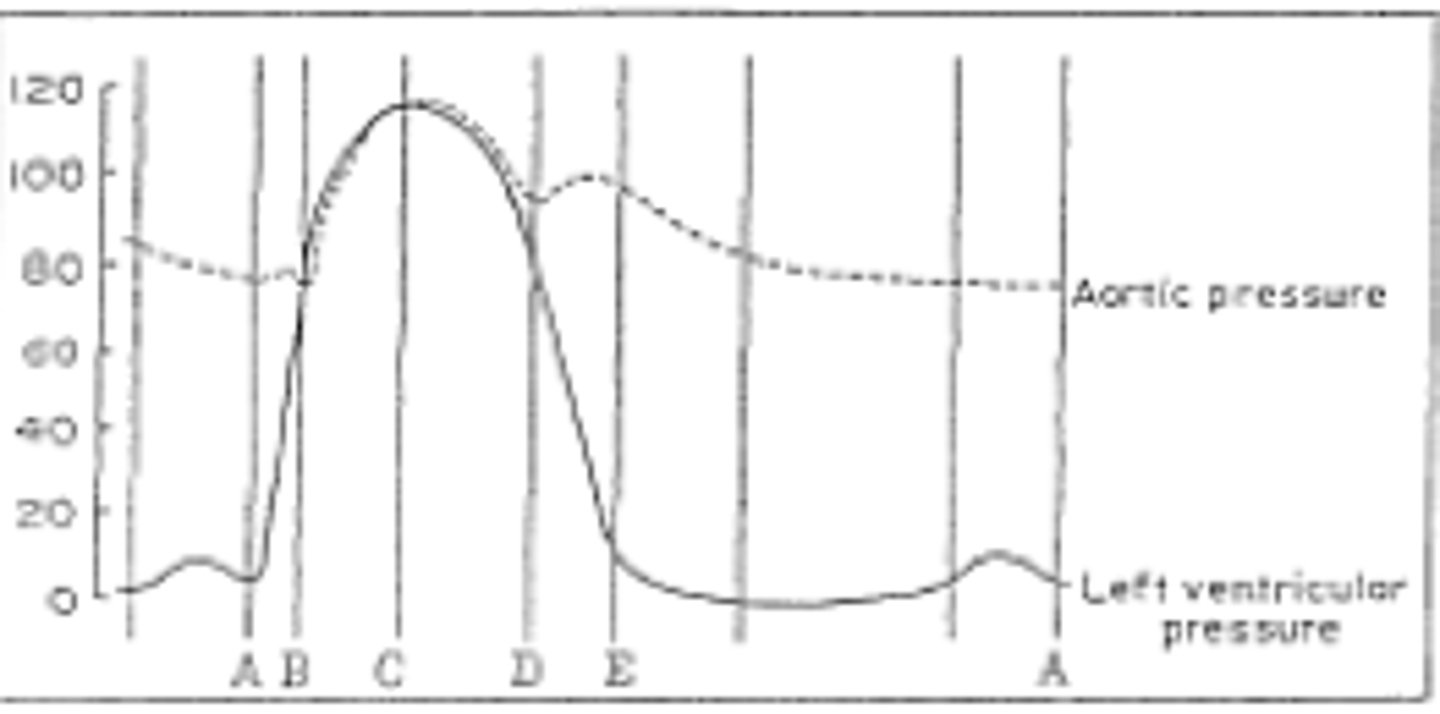
AV and semilunar valves are closed
(.8 seconds)
AV valve closes
(1)
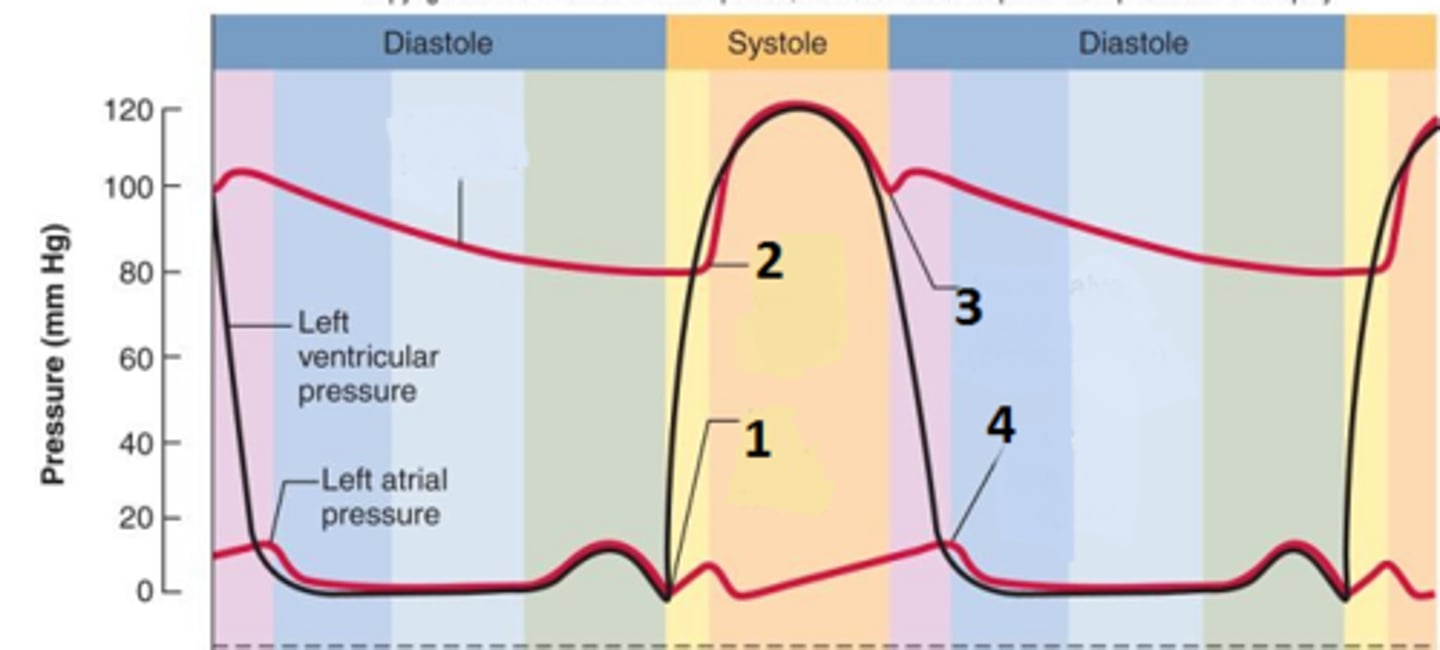
AV valve opens
(After E)
ventricular diastole
(G and H)
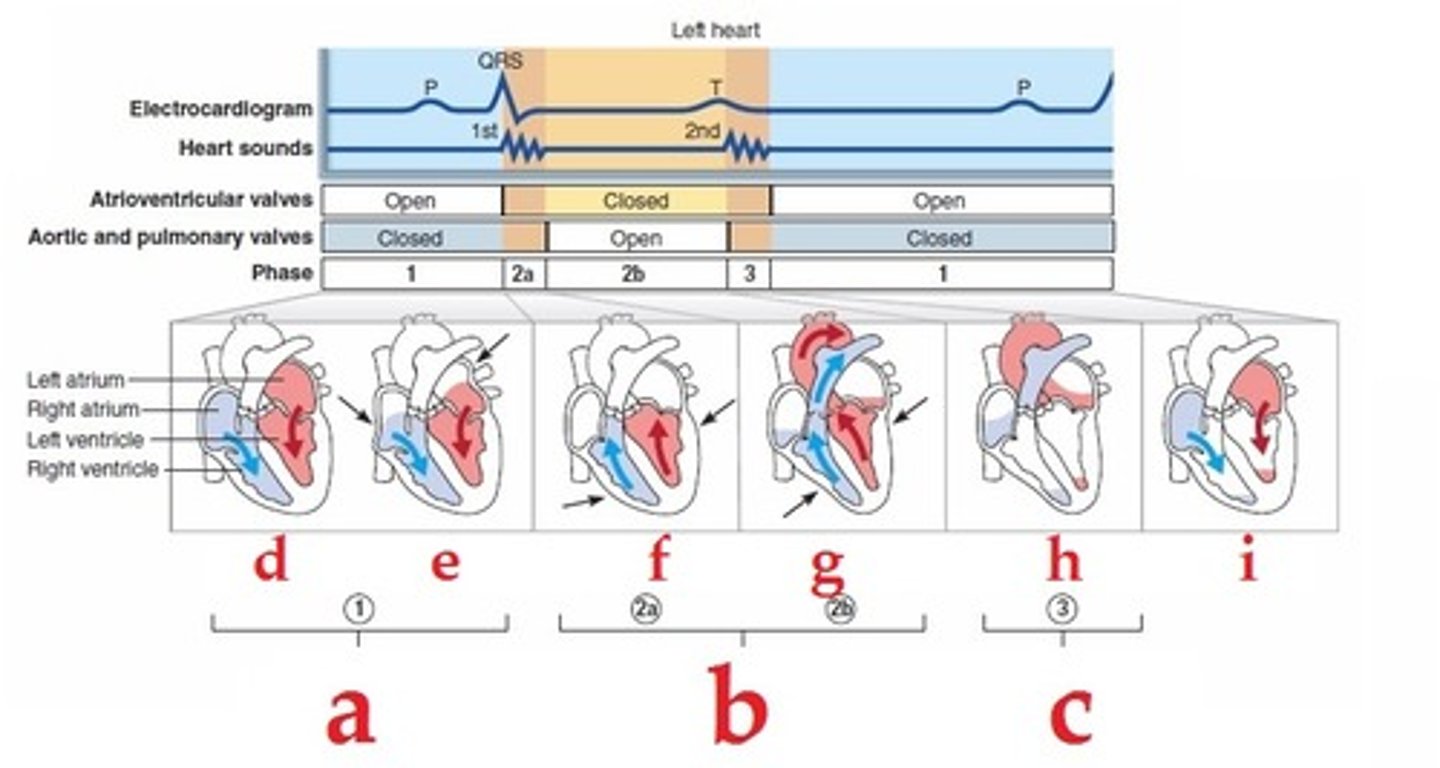
ventricular systole
purple
systole
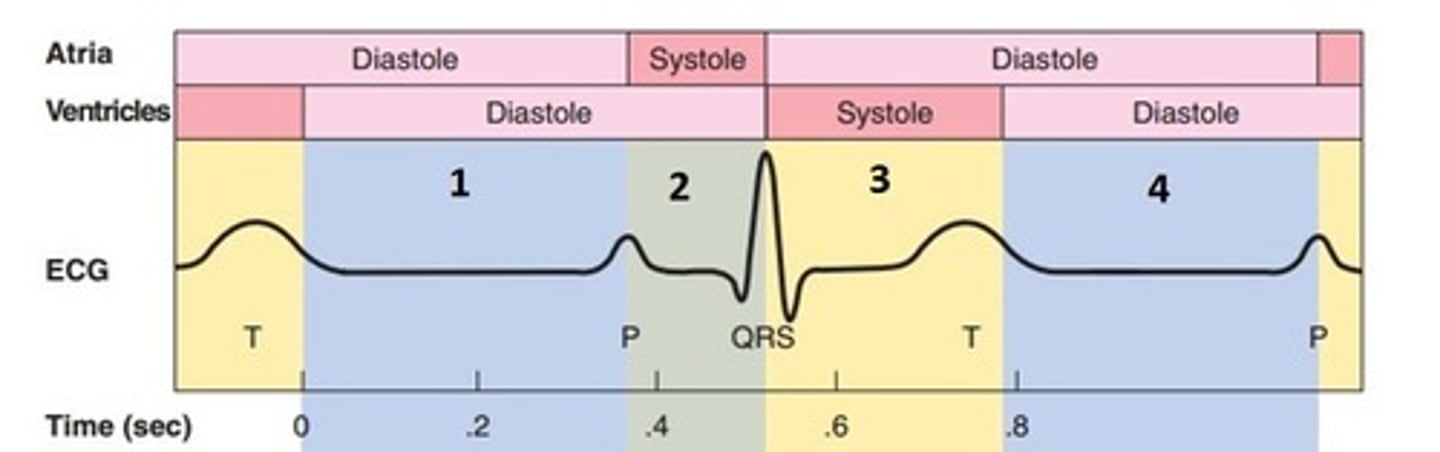
contraction of the heart
diastole
relaxation of the heart
cardiac cycle
the sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats
When are the AV valves closed?
during ventricular systole
What event within the heart causes the AV valves to open
atrial pressure > ventricular pressure
When are the semi lunar valves closed
during the period of relaxation of the heart as a whole during atrial contraction
What event causes the semi lunar valves to open
ventricular pressure > pressure in the arteries
At what point in the cardiac cycle is the pressure in the heart the highest
ventricular systole
At what point in the cardiac cycle is the pressure in the heart the lowest
ventricular diastole
What event results in dicrotic notch
momentary increase in aortic pressure that occurs when the semi lunar valves snap shut
The length of a normal cardiac cycle
0.8 sec
The time interval of atrial systole
0.1 sec
The ventricular contraction period
0.3 sec
The quiescent period, or pause
0.4 sec
Two factors that promote movement of blood through the heart
alternate contraction and relaxation of the myocardium and opening and closing of the heart valves
The monosyllables describing the heart sounds are
lub dub
The first heart sound is a result of the closure of the
AV valves
The second heart sound is a result of the closure of the
semi lunar valves
The heart chambers that have just been filled when you hear the first sound are the
ventricles
The chambers that have just been emptied are the
atria
Immediately after the second heart sound, the ___ and ___ fill with blood
atria and ventricles
As you listened to the heart sounds during the laboratory session, what differences in pitch, length, and amplitude (loudness) of the two sounds did you observe?
First heart sound is longer, louder, and lower in pitch than the second heart sound, which is short, sharp, and high-pitched.
In order to auscultate most accurately, indicate where you would place your stethoscope for the following sounds:
closure of the tricuspid valve:
Left or right sternal border of the 5th intercostal space.
In order to auscultate most accurately, indicate where you would place your stethoscope for the following sounds:
closure of the aortic semilunar valve:
Right sternal border of the 2nd intercostal space.
In order to auscultate most accurately, indicate where you would place your stethoscope for the following sounds:
apical heartbeat:
5th intercostal space in line with the middle of the left clavicle.
Which valve is heard most clearly when the apical heartbeat is auscultated?
Mitral
how might abnormal sounds be used to diagnose heart problems?
Abnormal sounds such as swishing sounds after valvular closure or high-pitched sounds arising when blood is forced through constricted (valve) openings might indicate valvular problems.
pulse
a rhythmical throbbing of the arteries as blood is propelled through them, typically as felt in the wrists or neck.
Pulse taking procedure
Gently place 2 fingers of your other hand on this artery. Do not use your thumb, because it has its own pulse that you may feel. Count the beats for 30 seconds, and then double the result to get the number of beats per minute.
Identify the artery palpated at each of the pressure points listed: at the wrist
Radial
Identify the artery palpated at each of the pressure points listed: in front of the ear:
Temporal
Identify the artery palpated at each of the pressure points listed. on the dorsum of the foot:
Dorsalis pedis
Identify the artery palpated at each of the pressure points listed. at the side of the neck:
Carotid
When you were palpating the various pulse or pressure points, which appeared to have the greatest amplitude or tension? Why?
The carotid artery(ies) is the major artery delivering blood to the brain (against gravity) and it is closest to the heart.
Assume someone has been injured in an auto accident and is hemorrhaging badly. What pressure point would you compress on the thigh?
Femoral artery
Assume someone has been injured in an auto accident and is hemorrhaging badly. What pressure point would you compress on the calf?
Popliteal artery
Assume someone has been injured in an auto accident and is hemorrhaging badly. What pressure point would you compress
to help stop bleeding from each of the following areas?
the forearm:
Brachial artery
Assume someone has been injured in an auto accident and is hemorrhaging badly. What pressure point would you compress
to help stop bleeding from each of the following areas?
the calf:
tibial artery
How can you tell if the bleeding is arterious or venous by sight?
Color
What is the difference between an apical pulse and an arterial pulse called?
pulse deficit
blood pressure
the pressure that is exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels
Identify the phase of the cardiac cycle to which of the following apply? Systolic pressure
Systole (ventricular contraction)
Identify the phase of the cardiac cycle to which of the following apply? Diastolic pressure
Diastole (relaxation)
What is the name of the instrument used to compress the artery and record pressures in the auscultatory method of determining
blood pressure?
Sphygmomanometer
What are the sounds of Korotkoff?
Sounds that can be auscultated over a partially occluded artery.
What causes the systolic sound?
Sound of turbulent blood flow as it first begins to move through the constricted artery.
What causes the disappearance of the systolic sound?
Blood is flowing freely; the artery is no longer constricted.
Interpret 145/85
145 = systolic pressure; 85 = diastolic pressure reported as the point where the sound muffles
Pulse pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
Why is this measurement important?
It indicates the actual working pressure (actual amount of blood forced out of the heart during
systole).
Explain why pulse pressure is different from pulse rate?
Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure and the pulse rate is the pressure surges per minute.
How do venous pressures compare to arterial pressures? Why?
Venous pressures are lower; Veins are far removed (in the circuit) from the pumping action of the heart.
What maneuver to increase the thoracic pressure illustrates the effect of external factors on venous pressure?
Valsalva maneuver
How is Valsalva maneuver performed?
A person takes a deep breath, and mimics the motions of exhaling forcibly, but without actually exhaling. The
glottis will close and the intrathoracic pressure will increase.
What might an abnormal increase in venous pressure indicate?
Heart failure. With the heart unable to adequately pump blood, it pools in the lower extremities and increases venous pressure.
WHAT EFFECT DO THE FOLLOWING HAVE ON BLOOD PRESSURE? :INCREASED DIAMETER OF THE ARTERIOLES
DECREASES
WHAT EFFECT DO THE FOLLOWING HAVE ON BLOOD PRESSURE? :INCREASED BLOOD VISCOSITY
INCREASES
WHAT EFFECT DO THE FOLLOWING HAVE ON BLOOD PRESSURE? INCREASED CARDIAC OUTPUT
INCREASES
WHAT EFFECT DO THE FOLLOWING HAVE ON BLOOD PRESSURE? HEMORRHAGE
DECREASES
WHAT EFFECT DO THE FOLLOWING HAVE ON BLOOD PRESSURE? ARTERIOSCLEROSIS
INCREASES
WHAT EFFECT DO THE FOLLOWING HAVE ON BLOOD PRESSURE? INCREASED PULSE RATE
INCREASES
IN WHICH POSITION (SITTING, RECLINING, OR STANDING) IS THE BLOOD PRESSURE NORMALLY THE HIGHEST? THE LOWEST
HIGHEST: RECLINING LOWEST: STANDING
WHAT IMMEDIATE CHANGES IN BLOOD PRESSURE DID YOU OBSERVE WHEN THE SUBJECT STOOD UP AFTER BEING IN THE SITTING OR RECLINING POSITION?
Your blood pressure is higher when your heart is hard at work, pumping blood while your body is moving, keeping balance, etc. (when you're awake and standing.) And when you are reclining, your heart is at rest and doesn't need to work as hard to pump blood through out the bodY
WHAT CHANGES IN THE BLOOD VESSELS MIGHT ACCOUNT FOR THE CHANGE?
Blood vessels can feel the shear stress caused by blood flow. When shear stress increases the blood vessel responds and the diameter becomes larger. Thus in short, changes in blood flow might cause blood vessels to change diameter
AFTER THE SUBJECT STOOD FOR 3 MINUTES, WHAT CHANGES IN BLOOD PRESSURE WERE OBSERVED? HOW DO YOU ACCOUNT FOR THIS CHANGE?
The blood pressure evened out back to normal, took 3 minutes for blood to be distributed normally to and from the heart to body.
WHAT WAS THE EFFECT OF EXERCISE ON BLOOD PRESSURE?
During exercise systolic blood pressure (the upper reading) usually increases gradually. However, regular exercise normally causes routine resting systolic and diastolic blood pressure to decrease
WHAT WAS THE EFFECT OF EXERCISE ON PULSE RATE?
When you are working out, your body is using a lot of energy, therefore your heart has to pump faster in order to keep up with the rate of breathing. Sometimes if not enough oxygen is being delivered to each cell, lactic fermentation occurs where lactic acid is produced
DO YOU THINK THESE EFFECTS REFLECT CHANGES IN CARDIAC OUTPUT OR IN PERIPHERAL RESISTANCE?
CARDIAC OUTPUT
WHY ARE THERE NORMALLY NO SIGNIFICANT INCREASES IN DIASTOLIC PRESSURE AFTER EXERCISE?
Diastolic pressure is the pressure in the circulatory system in between heartbeats. The blood isn't at any pressure inbetween beats, whether you've just exercised or are sleeping
WHAT EFFECTS OF THE FOLLOWING DID YOU OBSERVE ON BLOOD PRESSURE IN THE LABORATORY? COLD TEMPERATURE:
INCREASES BLOOD PRESSURE
WHAT DO YOU THINK THE EFFECT OF HEAT WOULD BE? WHY?
HEAT WOULD DECREASE BLOOD PRESSURE, BECAUSE IT CAUSES YOUR BLOOD VESSELS TO DILATE (OPEN UP)
Differentiate between a hypo- and a hyperreactor relative to the cold pressor test
Hyperreactors exhibit a rise of 23 mm Hg or more in bp during the test. Hyporeactors exhibit a smaller increase or a decrease in bp
Describe normal skin skin color and appearance of veins
Skin pink; veins flat and difficult to raise
What is the importance of collateral blood supplies?
Can maintain the blood supply to an organ or body part in case the nutrient artery is occluded
Explain the mechanism by which mechanical stimulation of the skin produced a flare.
Local inflammatory response produced by the chemical mediators released by injured tissue cells
What changes occured when the subject emptied the forearm of blood (by raising the arm and making a fist) and the flow was occluded with the cuff?
Skin becomes pale and cool